Evgeny Krivosheev
GIPSO: Geometrically Informed Propagation for Online Adaptation in 3D LiDAR Segmentation
Jul 20, 2022


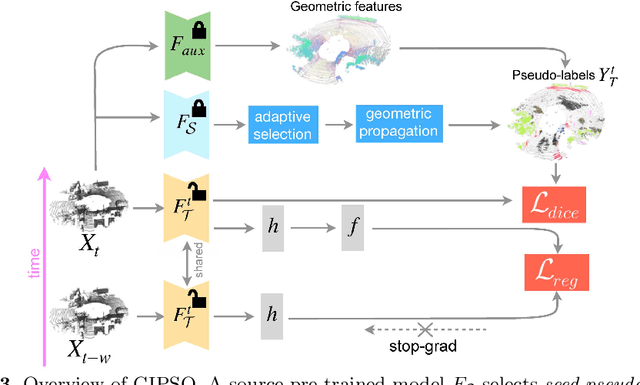
Abstract:3D point cloud semantic segmentation is fundamental for autonomous driving. Most approaches in the literature neglect an important aspect, i.e., how to deal with domain shift when handling dynamic scenes. This can significantly hinder the navigation capabilities of self-driving vehicles. This paper advances the state of the art in this research field. Our first contribution consists in analysing a new unexplored scenario in point cloud segmentation, namely Source-Free Online Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (SF-OUDA). We experimentally show that state-of-the-art methods have a rather limited ability to adapt pre-trained deep network models to unseen domains in an online manner. Our second contribution is an approach that relies on adaptive self-training and geometric-feature propagation to adapt a pre-trained source model online without requiring either source data or target labels. Our third contribution is to study SF-OUDA in a challenging setup where source data is synthetic and target data is point clouds captured in the real world. We use the recent SynLiDAR dataset as a synthetic source and introduce two new synthetic (source) datasets, which can stimulate future synthetic-to-real autonomous driving research. Our experiments show the effectiveness of our segmentation approach on thousands of real-world point clouds. Code and synthetic datasets are available at https://github.com/saltoricristiano/gipso-sfouda.
Business Entity Matching with Siamese Graph Convolutional Networks
May 08, 2021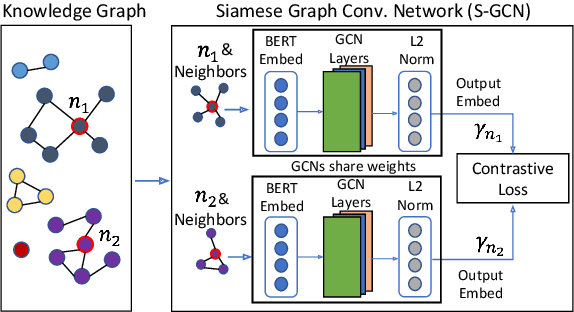
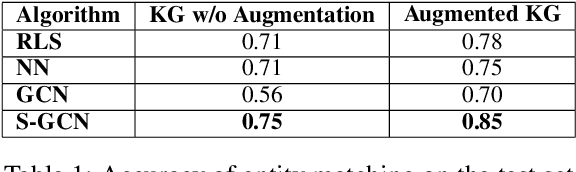
Abstract:Data integration has been studied extensively for decades and approached from different angles. However, this domain still remains largely rule-driven and lacks universal automation. Recent developments in machine learning and in particular deep learning have opened the way to more general and efficient solutions to data-integration tasks. In this paper, we demonstrate an approach that allows modeling and integrating entities by leveraging their relations and contextual information. This is achieved by combining siamese and graph neural networks to effectively propagate information between connected entities and support high scalability. We evaluated our approach on the task of integrating data about business entities, demonstrating that it outperforms both traditional rule-based systems and other deep learning approaches.
Curriculum Graph Co-Teaching for Multi-Target Domain Adaptation
Apr 01, 2021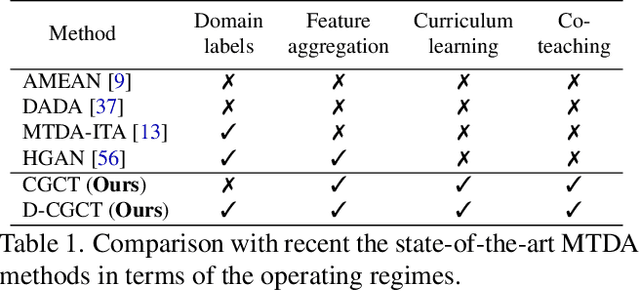

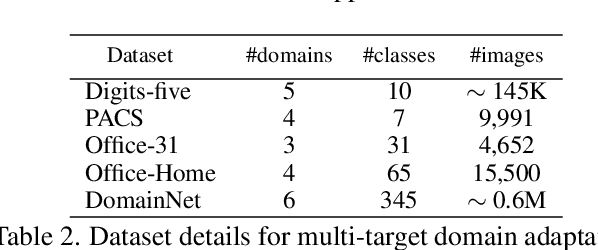

Abstract:In this paper we address multi-target domain adaptation (MTDA), where given one labeled source dataset and multiple unlabeled target datasets that differ in data distributions, the task is to learn a robust predictor for all the target domains. We identify two key aspects that can help to alleviate multiple domain-shifts in the MTDA: feature aggregation and curriculum learning. To this end, we propose Curriculum Graph Co-Teaching (CGCT) that uses a dual classifier head, with one of them being a graph convolutional network (GCN) which aggregates features from similar samples across the domains. To prevent the classifiers from over-fitting on its own noisy pseudo-labels we develop a co-teaching strategy with the dual classifier head that is assisted by curriculum learning to obtain more reliable pseudo-labels. Furthermore, when the domain labels are available, we propose Domain-aware Curriculum Learning (DCL), a sequential adaptation strategy that first adapts on the easier target domains, followed by the harder ones. We experimentally demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed frameworks on several benchmarks and advance the state-of-the-art in the MTDA by large margins (e.g. +5.6% on the DomainNet).
Active Hybrid Classification
Jan 21, 2021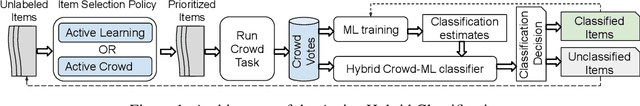
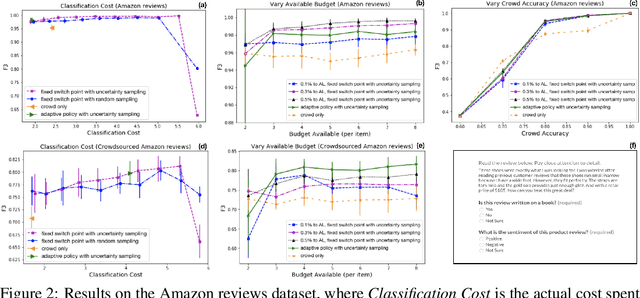
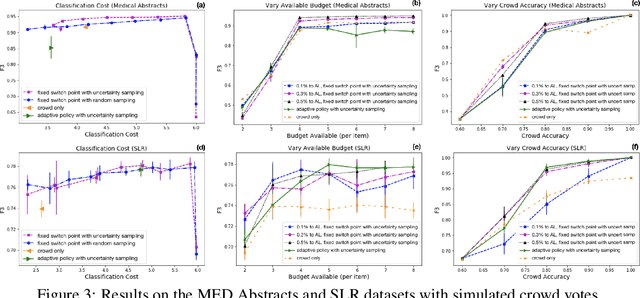
Abstract:Hybrid crowd-machine classifiers can achieve superior performance by combining the cost-effectiveness of automatic classification with the accuracy of human judgment. This paper shows how crowd and machines can support each other in tackling classification problems. Specifically, we propose an architecture that orchestrates active learning and crowd classification and combines them in a virtuous cycle. We show that when the pool of items to classify is finite we face learning vs. exploitation trade-off in hybrid classification, as we need to balance crowd tasks optimized for creating a training dataset with tasks optimized for classifying items in the pool. We define the problem, propose a set of heuristics and evaluate the approach on three real-world datasets with different characteristics in terms of machine and crowd classification performance, showing that our active hybrid approach significantly outperforms baselines.
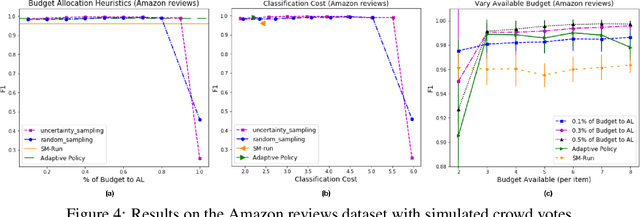
Active Learning from Crowd in Document Screening
Nov 11, 2020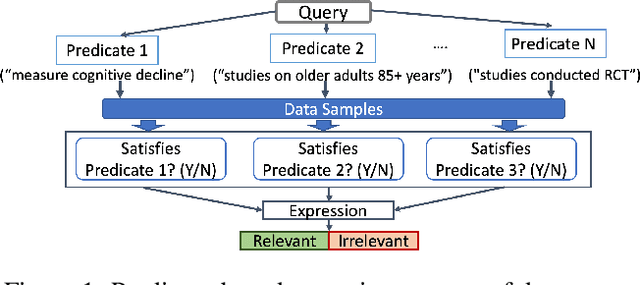
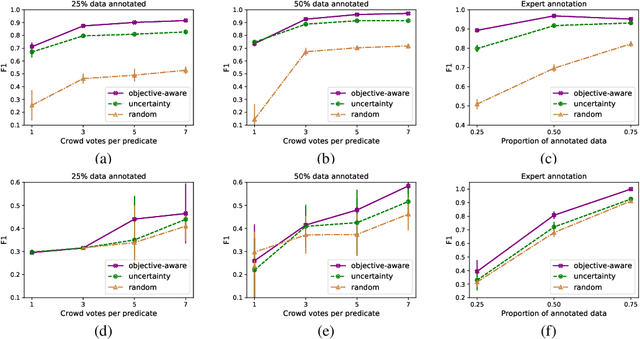
Abstract:In this paper, we explore how to efficiently combine crowdsourcing and machine intelligence for the problem of document screening, where we need to screen documents with a set of machine-learning filters. Specifically, we focus on building a set of machine learning classifiers that evaluate documents, and then screen them efficiently. It is a challenging task since the budget is limited and there are countless number of ways to spend the given budget on the problem. We propose a multi-label active learning screening specific sampling technique -- objective-aware sampling -- for querying unlabelled documents for annotating. Our algorithm takes a decision on which machine filter need more training data and how to choose unlabeled items to annotate in order to minimize the risk of overall classification errors rather than minimizing a single filter error. We demonstrate that objective-aware sampling significantly outperforms the state of the art active learning sampling strategies.
Siamese Graph Neural Networks for Data Integration
Jan 17, 2020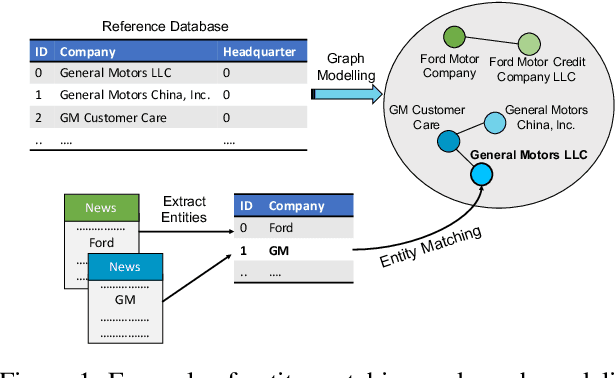
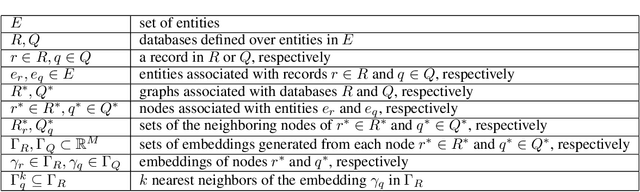
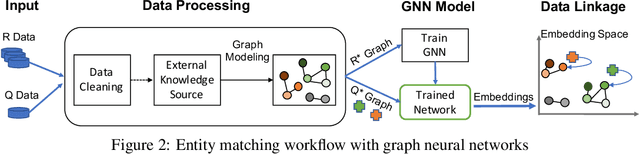
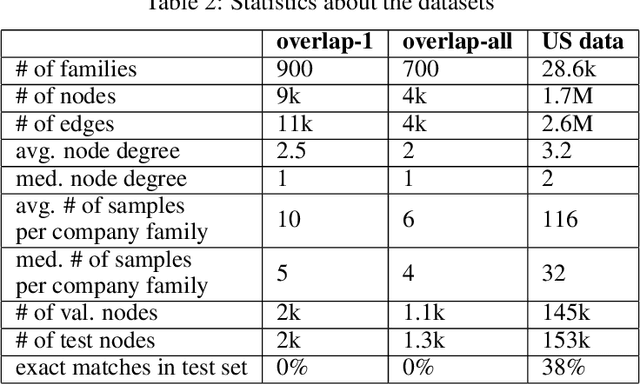
Abstract:Data integration has been studied extensively for decades and approached from different angles. However, this domain still remains largely rule-driven and lacks universal automation. Recent development in machine learning and in particular deep learning has opened the way to more general and more efficient solutions to data integration problems. In this work, we propose a general approach to modeling and integrating entities from structured data, such as relational databases, as well as unstructured sources, such as free text from news articles. Our approach is designed to explicitly model and leverage relations between entities, thereby using all available information and preserving as much context as possible. This is achieved by combining siamese and graph neural networks to propagate information between connected entities and support high scalability. We evaluate our method on the task of integrating data about business entities, and we demonstrate that it outperforms standard rule-based systems, as well as other deep learning approaches that do not use graph-based representations.
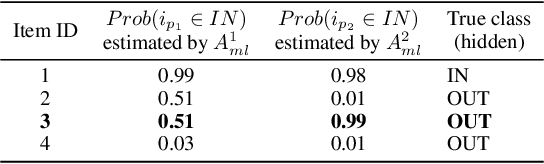
Combining Crowd and Machines for Multi-predicate Item Screening
Apr 01, 2019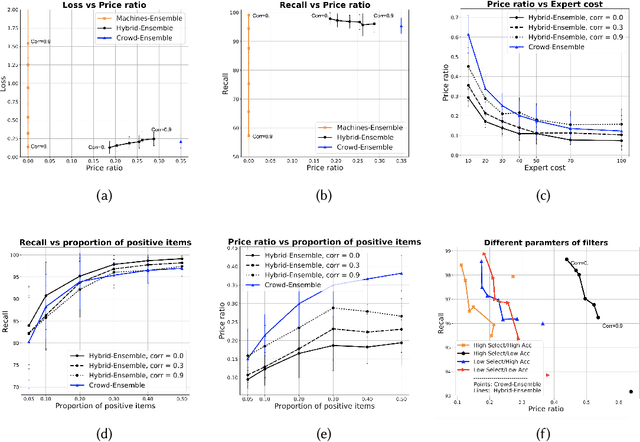

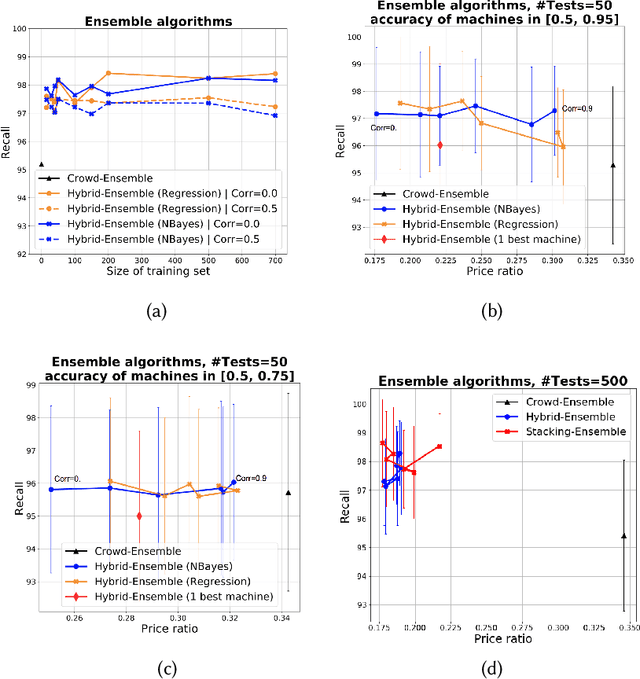
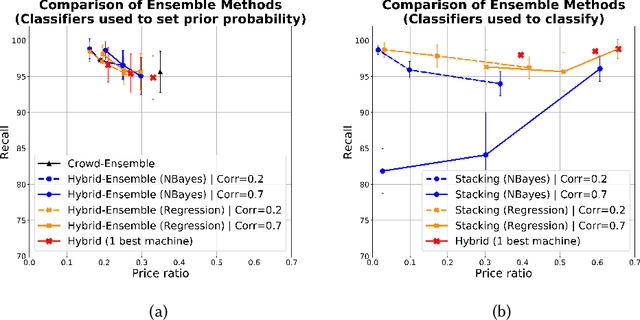
Abstract:This paper discusses how crowd and machine classifiers can be efficiently combined to screen items that satisfy a set of predicates. We show that this is a recurring problem in many domains, present machine-human (hybrid) algorithms that screen items efficiently and estimate the gain over human-only or machine-only screening in terms of performance and cost. We further show how, given a new classification problem and a set of classifiers of unknown accuracy for the problem at hand, we can identify how to manage the cost-accuracy trade off by progressively determining if we should spend budget to obtain test data (to assess the accuracy of the given classifiers), or to train an ensemble of classifiers, or whether we should leverage the existing machine classifiers with the crowd, and in this case how to efficiently combine them based on their estimated characteristics to obtain the classification. We demonstrate that the techniques we propose obtain significant cost/accuracy improvements with respect to the leading classification algorithms.
Crowd-Machine Collaboration for Item Screening
Mar 21, 2018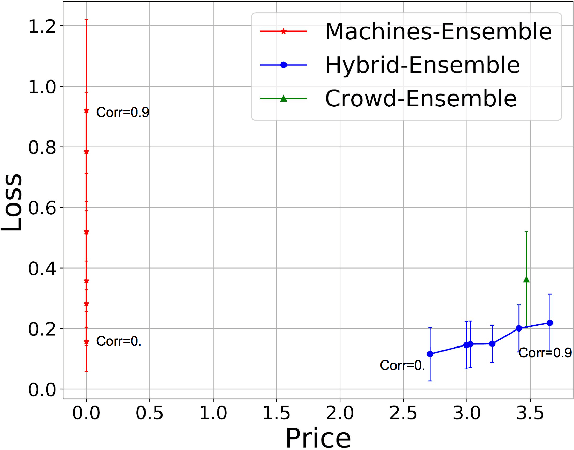
Abstract:In this paper we describe how crowd and machine classifier can be efficiently combined to screen items that satisfy a set of predicates. We show that this is a recurring problem in many domains, present machine-human (hybrid) algorithms that screen items efficiently and estimate the gain over human-only or machine-only screening in terms of performance and cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge