Deval Mehta
Interpretable Few-Shot Retinal Disease Diagnosis with Concept-Guided Prompting of Vision-Language Models
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in deep learning have shown significant potential for classifying retinal diseases using color fundus images. However, existing works predominantly rely exclusively on image data, lack interpretability in their diagnostic decisions, and treat medical professionals primarily as annotators for ground truth labeling. To fill this gap, we implement two key strategies: extracting interpretable concepts of retinal diseases using the knowledge base of GPT models and incorporating these concepts as a language component in prompt-learning to train vision-language (VL) models with both fundus images and their associated concepts. Our method not only improves retinal disease classification but also enriches few-shot and zero-shot detection (novel disease detection), while offering the added benefit of concept-based model interpretability. Our extensive evaluation across two diverse retinal fundus image datasets illustrates substantial performance gains in VL-model based few-shot methodologies through our concept integration approach, demonstrating an average improvement of approximately 5.8\% and 2.7\% mean average precision for 16-shot learning and zero-shot (novel class) detection respectively. Our method marks a pivotal step towards interpretable and efficient retinal disease recognition for real-world clinical applications.
IMPROVE: Improving Medical Plausibility without Reliance on HumanValidation -- An Enhanced Prototype-Guided Diffusion Framework
Nov 26, 2024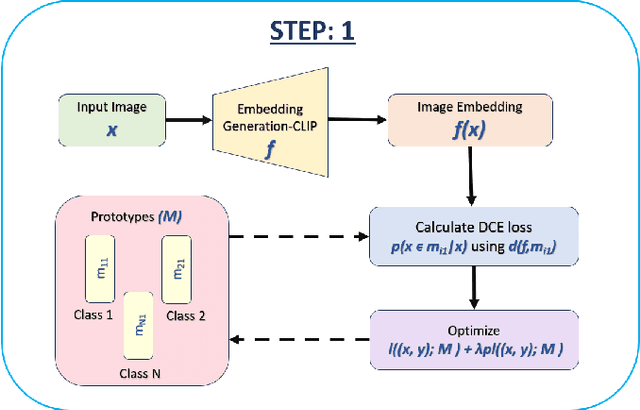

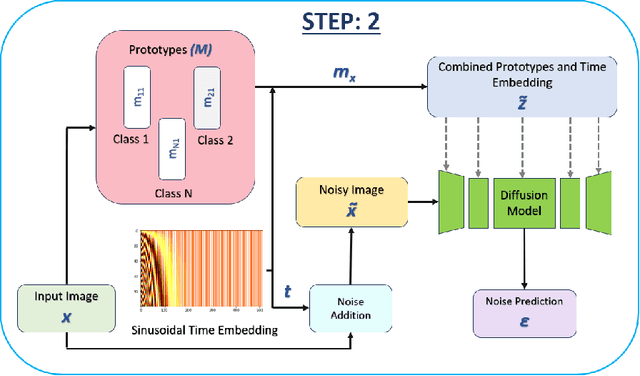
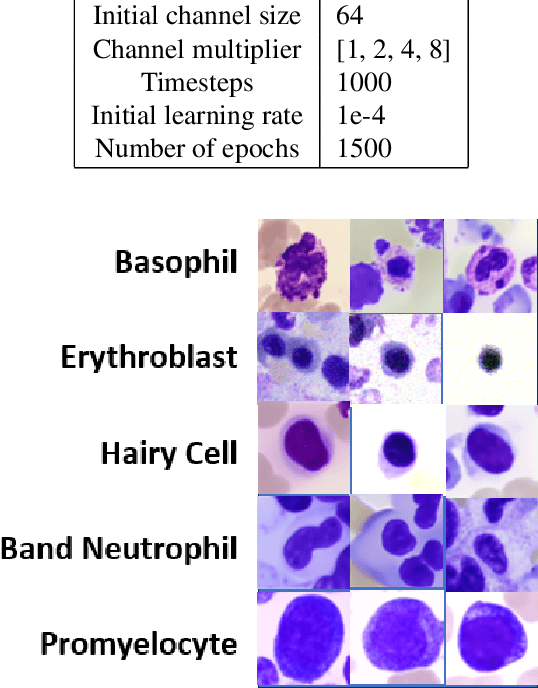
Abstract:Generative models have proven to be very effective in generating synthetic medical images and find applications in downstream tasks such as enhancing rare disease datasets, long-tailed dataset augmentation, and scaling machine learning algorithms. For medical applications, the synthetically generated medical images by such models are still reasonable in quality when evaluated based on traditional metrics such as FID score, precision, and recall. However, these metrics fail to capture the medical/biological plausibility of the generated images. Human expert feedback has been used to get biological plausibility which demonstrates that these generated images have very low plausibility. Recently, the research community has further integrated this human feedback through Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback(RLHF), which generates more medically plausible images. However, incorporating human feedback is a costly and slow process. In this work, we propose a novel approach to improve the medical plausibility of generated images without the need for human feedback. We introduce IMPROVE:Improving Medical Plausibility without Reliance on Human Validation - An Enhanced Prototype-Guided Diffusion Framework, a prototype-guided diffusion process for medical image generation and show that it substantially enhances the biological plausibility of the generated medical images without the need for any human feedback. We perform experiments on Bone Marrow and HAM10000 datasets and show that medical accuracy can be substantially increased without human feedback.
One Shot GANs for Long Tail Problem in Skin Lesion Dataset using novel content space assessment metric
Sep 30, 2024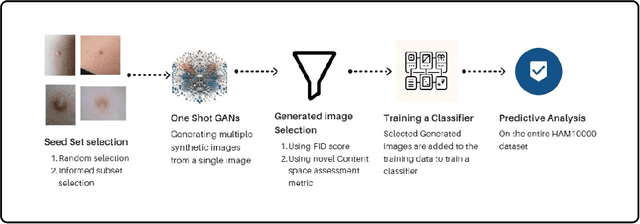
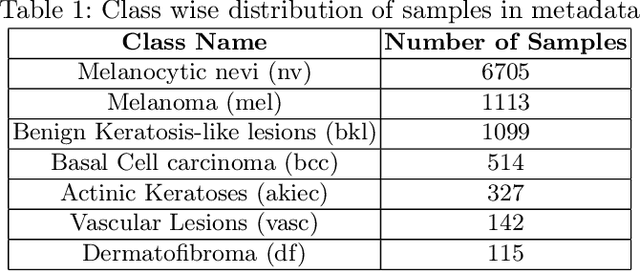
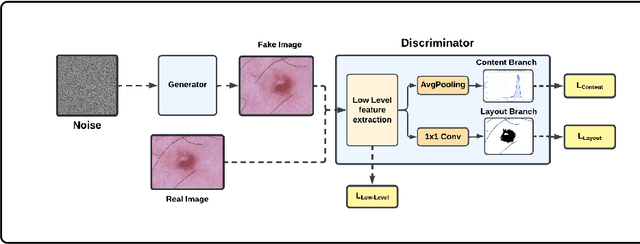
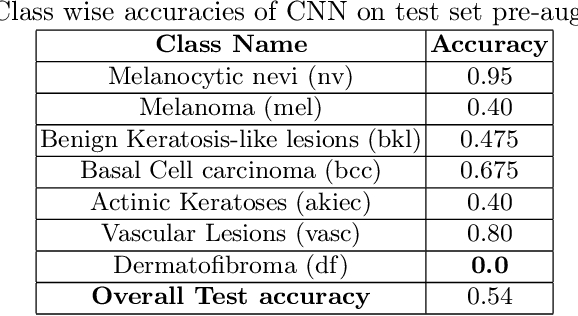
Abstract:Long tail problems frequently arise in the medical field, particularly due to the scarcity of medical data for rare conditions. This scarcity often leads to models overfitting on such limited samples. Consequently, when training models on datasets with heavily skewed classes, where the number of samples varies significantly, a problem emerges. Training on such imbalanced datasets can result in selective detection, where a model accurately identifies images belonging to the majority classes but disregards those from minority classes. This causes the model to lack generalizability, preventing its use on newer data. This poses a significant challenge in developing image detection and diagnosis models for medical image datasets. To address this challenge, the One Shot GANs model was employed to augment the tail class of HAM10000 dataset by generating additional samples. Furthermore, to enhance accuracy, a novel metric tailored to suit One Shot GANs was utilized.
Harnessing Shared Relations via Multimodal Mixup Contrastive Learning for Multimodal Classification
Sep 26, 2024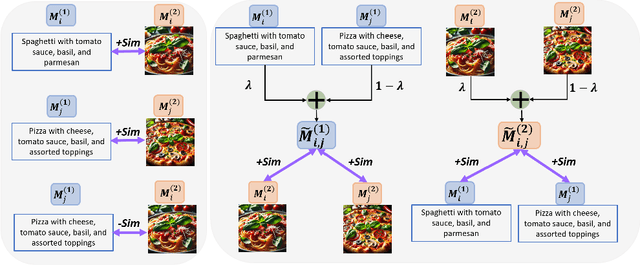
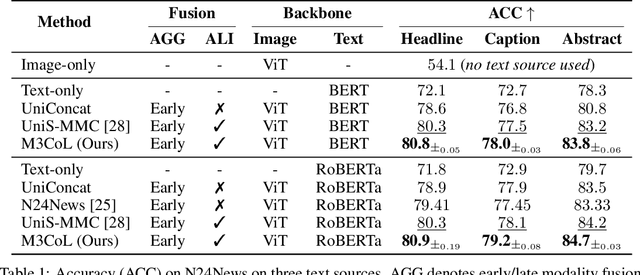
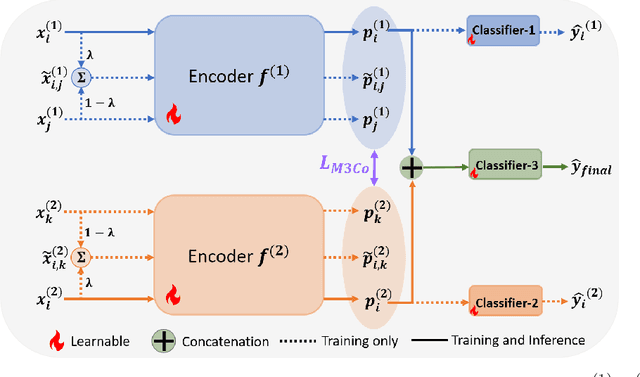
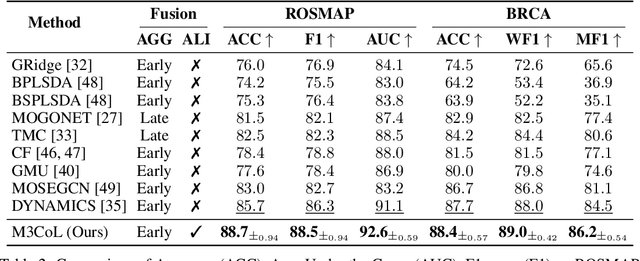
Abstract:Deep multimodal learning has shown remarkable success by leveraging contrastive learning to capture explicit one-to-one relations across modalities. However, real-world data often exhibits shared relations beyond simple pairwise associations. We propose M3CoL, a Multimodal Mixup Contrastive Learning approach to capture nuanced shared relations inherent in multimodal data. Our key contribution is a Mixup-based contrastive loss that learns robust representations by aligning mixed samples from one modality with their corresponding samples from other modalities thereby capturing shared relations between them. For multimodal classification tasks, we introduce a framework that integrates a fusion module with unimodal prediction modules for auxiliary supervision during training, complemented by our proposed Mixup-based contrastive loss. Through extensive experiments on diverse datasets (N24News, ROSMAP, BRCA, and Food-101), we demonstrate that M3CoL effectively captures shared multimodal relations and generalizes across domains. It outperforms state-of-the-art methods on N24News, ROSMAP, and BRCA, while achieving comparable performance on Food-101. Our work highlights the significance of learning shared relations for robust multimodal learning, opening up promising avenues for future research.
Adaptive Transformer Modelling of Density Function for Nonparametric Survival Analysis
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:Survival analysis holds a crucial role across diverse disciplines, such as economics, engineering and healthcare. It empowers researchers to analyze both time-invariant and time-varying data, encompassing phenomena like customer churn, material degradation and various medical outcomes. Given the complexity and heterogeneity of such data, recent endeavors have demonstrated successful integration of deep learning methodologies to address limitations in conventional statistical approaches. However, current methods typically involve cluttered probability distribution function (PDF), have lower sensitivity in censoring prediction, only model static datasets, or only rely on recurrent neural networks for dynamic modelling. In this paper, we propose a novel survival regression method capable of producing high-quality unimodal PDFs without any prior distribution assumption, by optimizing novel Margin-Mean-Variance loss and leveraging the flexibility of Transformer to handle both temporal and non-temporal data, coined UniSurv. Extensive experiments on several datasets demonstrate that UniSurv places a significantly higher emphasis on censoring compared to other methods.
Revamping AI Models in Dermatology: Overcoming Critical Challenges for Enhanced Skin Lesion Diagnosis
Nov 02, 2023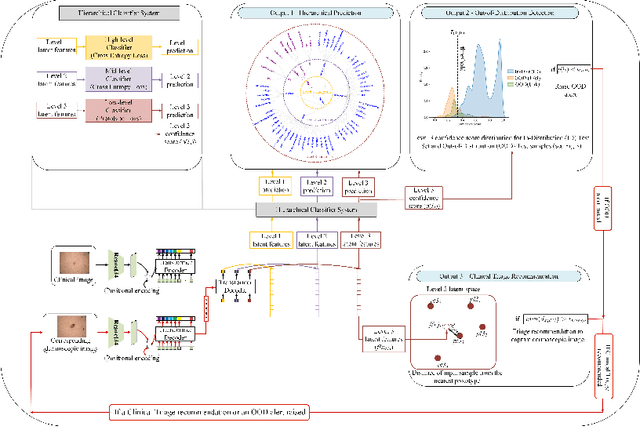
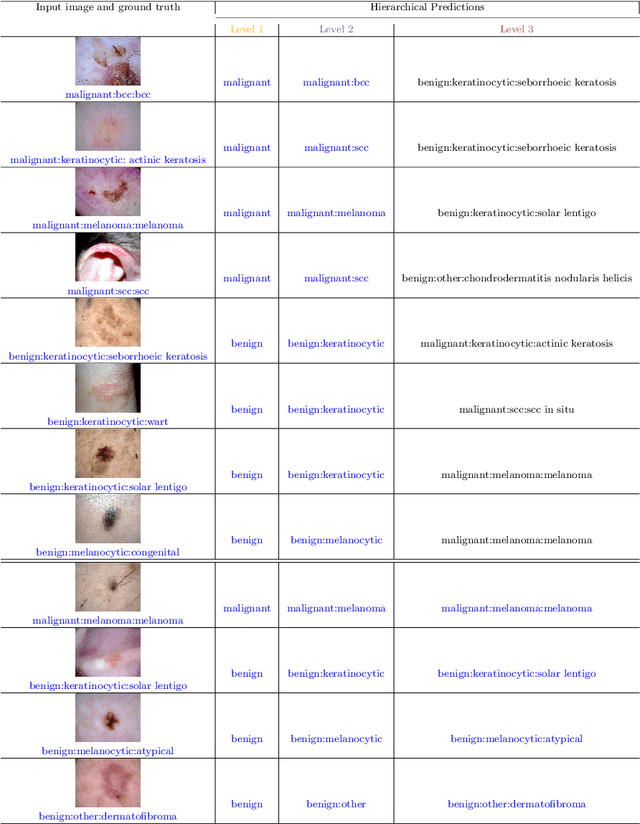
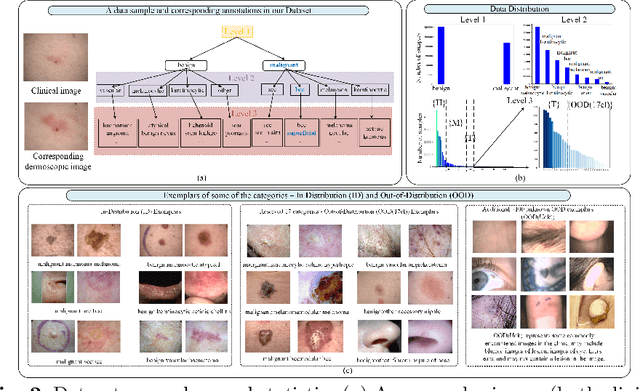
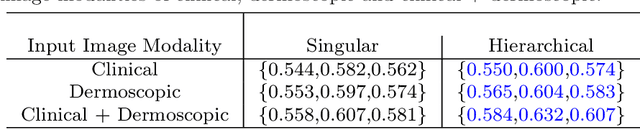
Abstract:The surge in developing deep learning models for diagnosing skin lesions through image analysis is notable, yet their clinical black faces challenges. Current dermatology AI models have limitations: limited number of possible diagnostic outputs, lack of real-world testing on uncommon skin lesions, inability to detect out-of-distribution images, and over-reliance on dermoscopic images. To address these, we present an All-In-One \textbf{H}ierarchical-\textbf{O}ut of Distribution-\textbf{C}linical Triage (HOT) model. For a clinical image, our model generates three outputs: a hierarchical prediction, an alert for out-of-distribution images, and a recommendation for dermoscopy if clinical image alone is insufficient for diagnosis. When the recommendation is pursued, it integrates both clinical and dermoscopic images to deliver final diagnosis. Extensive experiments on a representative cutaneous lesion dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and synergy of each component within our framework. Our versatile model provides valuable decision support for lesion diagnosis and sets a promising precedent for medical AI applications.
Privacy-preserving Early Detection of Epileptic Seizures in Videos
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:In this work, we contribute towards the development of video-based epileptic seizure classification by introducing a novel framework (SETR-PKD), which could achieve privacy-preserved early detection of seizures in videos. Specifically, our framework has two significant components - (1) It is built upon optical flow features extracted from the video of a seizure, which encodes the seizure motion semiotics while preserving the privacy of the patient; (2) It utilizes a transformer based progressive knowledge distillation, where the knowledge is gradually distilled from networks trained on a longer portion of video samples to the ones which will operate on shorter portions. Thus, our proposed framework addresses the limitations of the current approaches which compromise the privacy of the patients by directly operating on the RGB video of a seizure as well as impede real-time detection of a seizure by utilizing the full video sample to make a prediction. Our SETR-PKD framework could detect tonic-clonic seizures (TCSs) in a privacy-preserving manner with an accuracy of 83.9% while they are only half-way into their progression. Our data and code is available at https://github.com/DevD1092/seizure-detection
TPMIL: Trainable Prototype Enhanced Multiple Instance Learning for Whole Slide Image Classification
May 01, 2023Abstract:Digital pathology based on whole slide images (WSIs) plays a key role in cancer diagnosis and clinical practice. Due to the high resolution of the WSI and the unavailability of patch-level annotations, WSI classification is usually formulated as a weakly supervised problem, which relies on multiple instance learning (MIL) based on patches of a WSI. In this paper, we aim to learn an optimal patch-level feature space by integrating prototype learning with MIL. To this end, we develop a Trainable Prototype enhanced deep MIL (TPMIL) framework for weakly supervised WSI classification. In contrast to the conventional methods which rely on a certain number of selected patches for feature space refinement, we softly cluster all the instances by allocating them to their corresponding prototypes. Additionally, our method is able to reveal the correlations between different tumor subtypes through distances between corresponding trained prototypes. More importantly, TPMIL also enables to provide a more accurate interpretability based on the distance of the instances from the trained prototypes which serves as an alternative to the conventional attention score-based interpretability. We test our method on two WSI datasets and it achieves a new SOTA. GitHub repository: https://github.com/LitaoYang-Jet/TPMIL
Multi-dimensional Racism Classification during COVID-19: Stigmatization, Offensiveness, Blame, and Exclusion
Aug 29, 2022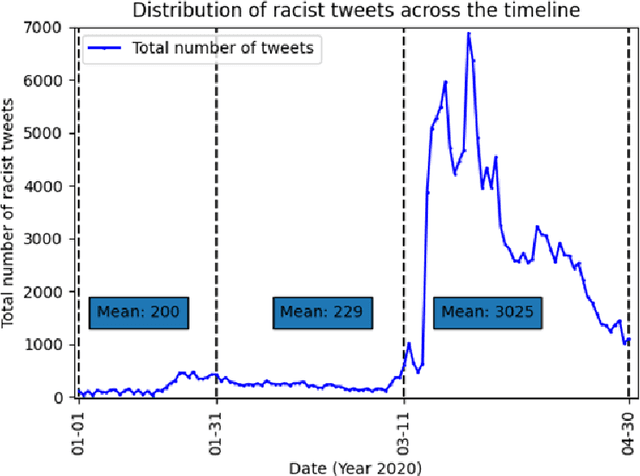
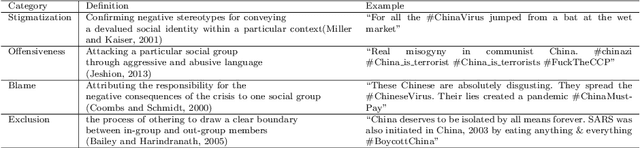
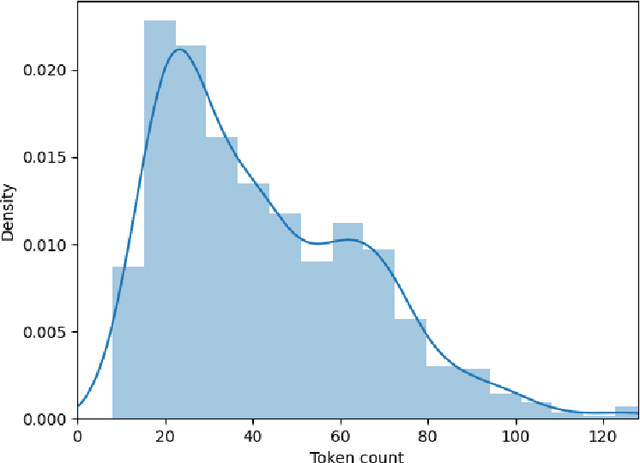
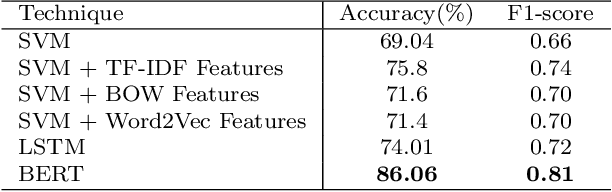
Abstract:Transcending the binary categorization of racist texts, our study takes cues from social science theories to develop a multi-dimensional model for racism detection, namely stigmatization, offensiveness, blame, and exclusion. With the aid of BERT and topic modeling, this categorical detection enables insights into the underlying subtlety of racist discussion on digital platforms during COVID-19. Our study contributes to enriching the scholarly discussion on deviant racist behaviours on social media. First, a stage-wise analysis is applied to capture the dynamics of the topic changes across the early stages of COVID-19 which transformed from a domestic epidemic to an international public health emergency and later to a global pandemic. Furthermore, mapping this trend enables a more accurate prediction of public opinion evolvement concerning racism in the offline world, and meanwhile, the enactment of specified intervention strategies to combat the upsurge of racism during the global public health crisis like COVID-19. In addition, this interdisciplinary research also points out a direction for future studies on social network analysis and mining. Integration of social science perspectives into the development of computational methods provides insights into more accurate data detection and analytics.
Leukocyte Classification using Multimodal Architecture Enhanced by Knowledge Distillation
Aug 17, 2022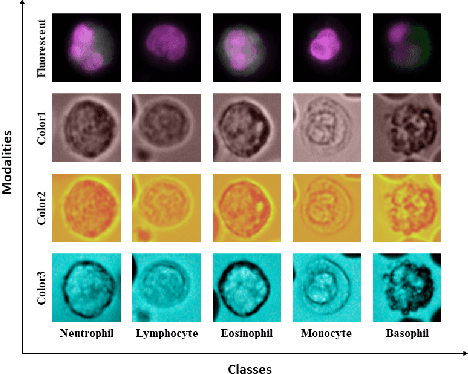
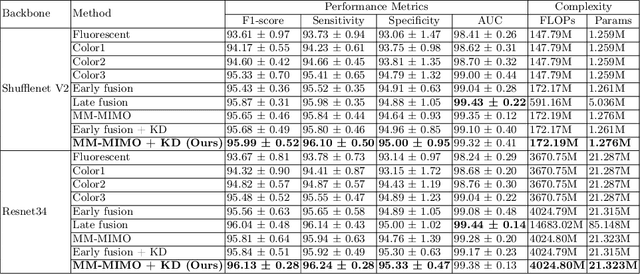
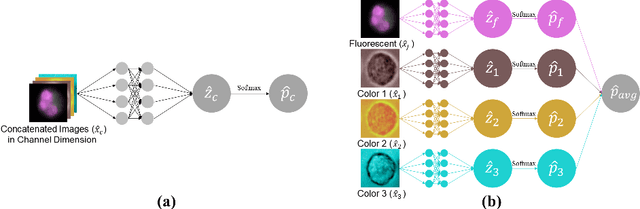
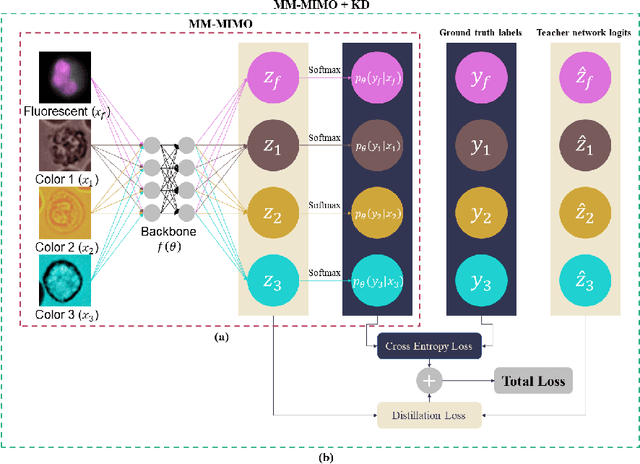
Abstract:Recently, a lot of automated white blood cells (WBC) or leukocyte classification techniques have been developed. However, all of these methods only utilize a single modality microscopic image i.e. either blood smear or fluorescence based, thus missing the potential of a better learning from multimodal images. In this work, we develop an efficient multimodal architecture based on a first of its kind multimodal WBC dataset for the task of WBC classification. Specifically, our proposed idea is developed in two steps - 1) First, we learn modality specific independent subnetworks inside a single network only; 2) We further enhance the learning capability of the independent subnetworks by distilling knowledge from high complexity independent teacher networks. With this, our proposed framework can achieve a high performance while maintaining low complexity for a multimodal dataset. Our unique contribution is two-fold - 1) We present a first of its kind multimodal WBC dataset for WBC classification; 2) We develop a high performing multimodal architecture which is also efficient and low in complexity at the same time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge