Daqian Shi
AncientBench: Towards Comprehensive Evaluation on Excavated and Transmitted Chinese Corpora
Dec 19, 2025
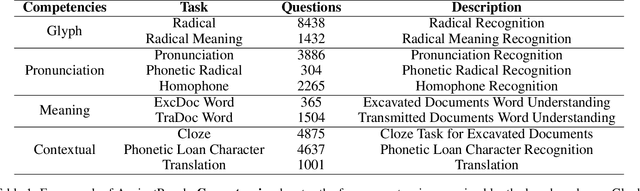

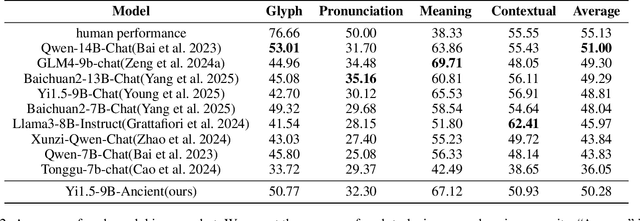
Abstract:Comprehension of ancient texts plays an important role in archaeology and understanding of Chinese history and civilization. The rapid development of large language models needs benchmarks that can evaluate their comprehension of ancient characters. Existing Chinese benchmarks are mostly targeted at modern Chinese and transmitted documents in ancient Chinese, but the part of excavated documents in ancient Chinese is not covered. To meet this need, we propose the AncientBench, which aims to evaluate the comprehension of ancient characters, especially in the scenario of excavated documents. The AncientBench is divided into four dimensions, which correspond to the four competencies of ancient character comprehension: glyph comprehension, pronunciation comprehension, meaning comprehension, and contextual comprehension. The benchmark also contains ten tasks, including radical, phonetic radical, homophone, cloze, translation, and more, providing a comprehensive framework for evaluation. We convened archaeological researchers to conduct experimental evaluations, proposed an ancient model as baseline, and conducted extensive experiments on the currently best-performing large language models. The experimental results reveal the great potential of large language models in ancient textual scenarios as well as the gap with humans. Our research aims to promote the development and application of large language models in the field of archaeology and ancient Chinese language.
Artificial Intelligence-driven Intelligent Wearable Systems: A full-stack Integration from Material Design to Personalized Interaction
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Intelligent wearable systems are at the forefront of precision medicine and play a crucial role in enhancing human-machine interaction. Traditional devices often encounter limitations due to their dependence on empirical material design and basic signal processing techniques. To overcome these issues, we introduce the concept of Human-Symbiotic Health Intelligence (HSHI), which is a framework that integrates multi-modal sensor networks with edge-cloud collaborative computing and a hybrid approach to data and knowledge modeling. HSHI is designed to adapt dynamically to both inter-individual and intra-individual variability, transitioning health management from passive monitoring to an active collaborative evolution. The framework incorporates AI-driven optimization of materials and micro-structures, provides robust interpretation of multi-modal signals, and utilizes a dual mechanism that merges population-level insights with personalized adaptations. Moreover, the integration of closed-loop optimization through reinforcement learning and digital twins facilitates customized interventions and feedback. In general, HSHI represents a significant shift in healthcare, moving towards a model that emphasizes prevention, adaptability, and a harmonious relationship between technology and health management.
Automated Construction of Medical Indicator Knowledge Graphs Using Retrieval Augmented Large Language Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping modern healthcare by advancing disease diagnosis, treatment decision-making, and biomedical research. Among AI technologies, large language models (LLMs) have become especially impactful, enabling deep knowledge extraction and semantic reasoning from complex medical texts. However, effective clinical decision support requires knowledge in structured, interoperable formats. Knowledge graphs serve this role by integrating heterogeneous medical information into semantically consistent networks. Yet, current clinical knowledge graphs still depend heavily on manual curation and rule-based extraction, which is limited by the complexity and contextual ambiguity of medical guidelines and literature. To overcome these challenges, we propose an automated framework that combines retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with LLMs to construct medical indicator knowledge graphs. The framework incorporates guideline-driven data acquisition, ontology-based schema design, and expert-in-the-loop validation to ensure scalability, accuracy, and clinical reliability. The resulting knowledge graphs can be integrated into intelligent diagnosis and question-answering systems, accelerating the development of AI-driven healthcare solutions.
Ancient Script Image Recognition and Processing: A Review
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Ancient scripts, e.g., Egyptian hieroglyphs, Oracle Bone Inscriptions, and Ancient Greek inscriptions, serve as vital carriers of human civilization, embedding invaluable historical and cultural information. Automating ancient script image recognition has gained importance, enabling large-scale interpretation and advancing research in archaeology and digital humanities. With the rise of deep learning, this field has progressed rapidly, with numerous script-specific datasets and models proposed. While these scripts vary widely, spanning phonographic systems with limited glyphs to logographic systems with thousands of complex symbols, they share common challenges and methodological overlaps. Moreover, ancient scripts face unique challenges, including imbalanced data distribution and image degradation, which have driven the development of various dedicated methods. This survey provides a comprehensive review of ancient script image recognition methods. We begin by categorizing existing studies based on script types and analyzing respective recognition methods, highlighting both their differences and shared strategies. We then focus on challenges unique to ancient scripts, systematically examining their impact and reviewing recent solutions, including few-shot learning and noise-robust techniques. Finally, we summarize current limitations and outline promising future directions. Our goal is to offer a structured, forward-looking perspective to support ongoing advancements in the recognition, interpretation, and decipherment of ancient scripts.
Minuscule Cell Detection in AS-OCT Images with Progressive Field-of-View Focusing
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography (AS-OCT) is an emerging imaging technique with great potential for diagnosing anterior uveitis, a vision-threatening ocular inflammatory condition. A hallmark of this condition is the presence of inflammatory cells in the eye's anterior chamber, and detecting these cells using AS-OCT images has attracted research interest. While recent efforts aim to replace manual cell detection with automated computer vision approaches, detecting extremely small (minuscule) objects in high-resolution images, such as AS-OCT, poses substantial challenges: (1) each cell appears as a minuscule particle, representing less than 0.005\% of the image, making the detection difficult, and (2) OCT imaging introduces pixel-level noise that can be mistaken for cells, leading to false positive detections. To overcome these challenges, we propose a minuscule cell detection framework through a progressive field-of-view focusing strategy. This strategy systematically refines the detection scope from the whole image to a target region where cells are likely to be present, and further to minuscule regions potentially containing individual cells. Our framework consists of two modules. First, a Field-of-Focus module uses a vision foundation model to segment the target region. Subsequently, a Fine-grained Object Detection module introduces a specialized Minuscule Region Proposal followed by a Spatial Attention Network to distinguish individual cells from noise within the segmented region. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods for cell detection, providing enhanced efficacy for clinical applications. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/joeybyc/MCD.
KAE: A Property-based Method for Knowledge Graph Alignment and Extension
Jul 07, 2024Abstract:A common solution to the semantic heterogeneity problem is to perform knowledge graph (KG) extension exploiting the information encoded in one or more candidate KGs, where the alignment between the reference KG and candidate KGs is considered the critical procedure. However, existing KG alignment methods mainly rely on entity type (etype) label matching as a prerequisite, which is poorly performing in practice or not applicable in some cases. In this paper, we design a machine learning-based framework for KG extension, including an alternative novel property-based alignment approach that allows aligning etypes on the basis of the properties used to define them. The main intuition is that it is properties that intentionally define the etype, and this definition is independent of the specific label used to name an etype, and of the specific hierarchical schema of KGs. Compared with the state-of-the-art, the experimental results show the validity of the KG alignment approach and the superiority of the proposed KG extension framework, both quantitatively and qualitatively.
Knowledge Graph Extension by Entity Type Recognition
May 03, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge graphs have emerged as a sophisticated advancement and refinement of semantic networks, and their deployment is one of the critical methodologies in contemporary artificial intelligence. The construction of knowledge graphs is a multifaceted process involving various techniques, where researchers aim to extract the knowledge from existing resources for the construction since building from scratch entails significant labor and time costs. However, due to the pervasive issue of heterogeneity, the description diversity across different knowledge graphs can lead to mismatches between concepts, thereby impacting the efficacy of knowledge extraction. This Ph.D. study focuses on automatic knowledge graph extension, i.e., properly extending the reference knowledge graph by extracting and integrating concepts from one or more candidate knowledge graphs. We propose a novel knowledge graph extension framework based on entity type recognition. The framework aims to achieve high-quality knowledge extraction by aligning the schemas and entities across different knowledge graphs, thereby enhancing the performance of the extension. This paper elucidates three major contributions: (i) we propose an entity type recognition method exploiting machine learning and property-based similarities to enhance knowledge extraction; (ii) we introduce a set of assessment metrics to validate the quality of the extended knowledge graphs; (iii) we develop a platform for knowledge graph acquisition, management, and extension to benefit knowledge engineers practically. Our evaluation comprehensively demonstrated the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed extension framework and its functionalities through quantitative experiments and case studies.
Towards a Gateway for Knowledge Graph Schemas Collection, Analysis, and Embedding
Nov 21, 2023
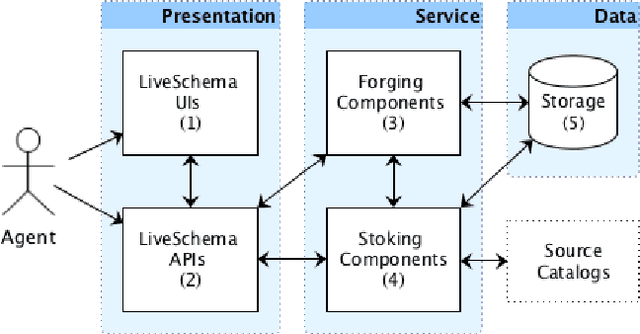
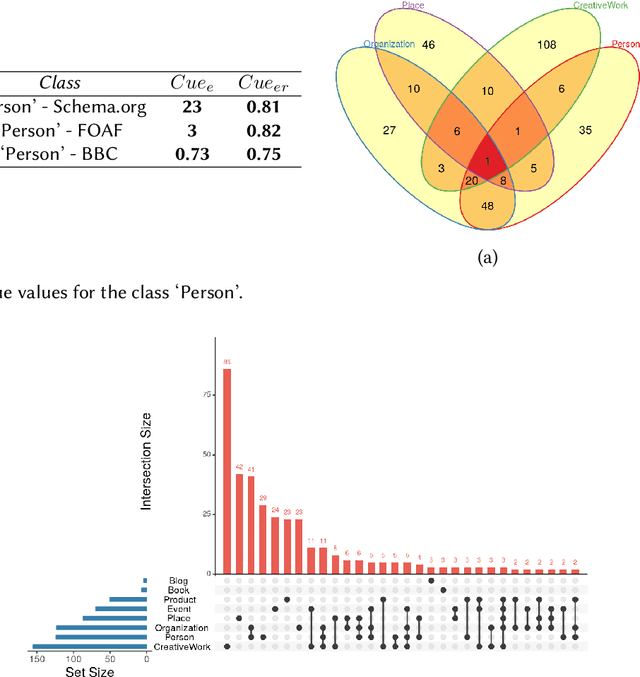
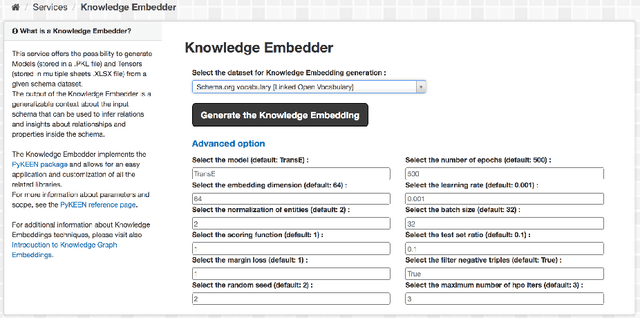
Abstract:One of the significant barriers to the training of statistical models on knowledge graphs is the difficulty that scientists have in finding the best input data to address their prediction goal. In addition to this, a key challenge is to determine how to manipulate these relational data, which are often in the form of particular triples (i.e., subject, predicate, object), to enable the learning process. Currently, many high-quality catalogs of knowledge graphs, are available. However, their primary goal is the re-usability of these resources, and their interconnection, in the context of the Semantic Web. This paper describes the LiveSchema initiative, namely, a first version of a gateway that has the main scope of leveraging the gold mine of data collected by many existing catalogs collecting relational data like ontologies and knowledge graphs. At the current state, LiveSchema contains - 1000 datasets from 4 main sources and offers some key facilities, which allow to: i) evolving LiveSchema, by aggregating other source catalogs and repositories as input sources; ii) querying all the collected resources; iii) transforming each given dataset into formal concept analysis matrices that enable analysis and visualization services; iv) generating models and tensors from each given dataset.
Toward Zero-shot Character Recognition: A Gold Standard Dataset with Radical-level Annotations
Aug 01, 2023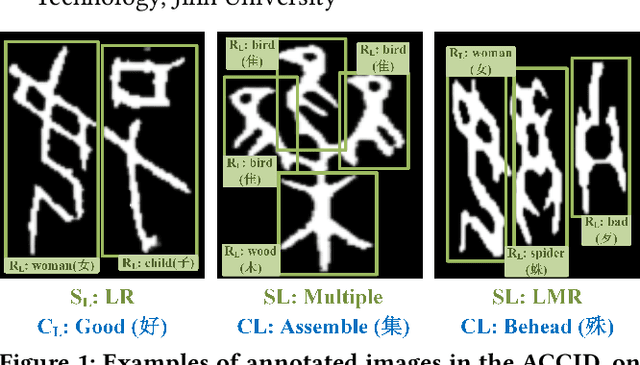
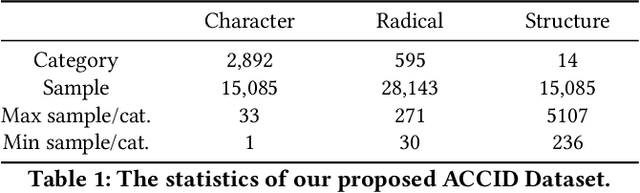
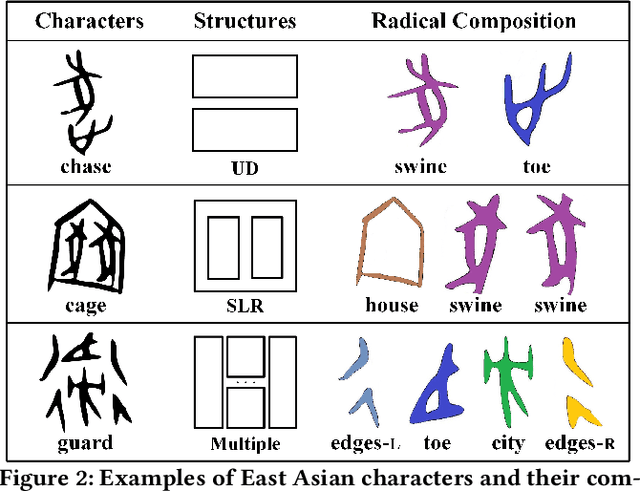
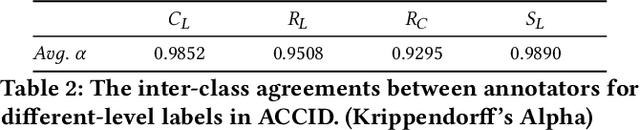
Abstract:Optical character recognition (OCR) methods have been applied to diverse tasks, e.g., street view text recognition and document analysis. Recently, zero-shot OCR has piqued the interest of the research community because it considers a practical OCR scenario with unbalanced data distribution. However, there is a lack of benchmarks for evaluating such zero-shot methods that apply a divide-and-conquer recognition strategy by decomposing characters into radicals. Meanwhile, radical recognition, as another important OCR task, also lacks radical-level annotation for model training. In this paper, we construct an ancient Chinese character image dataset that contains both radical-level and character-level annotations to satisfy the requirements of the above-mentioned methods, namely, ACCID, where radical-level annotations include radical categories, radical locations, and structural relations. To increase the adaptability of ACCID, we propose a splicing-based synthetic character algorithm to augment the training samples and apply an image denoising method to improve the image quality. By introducing character decomposition and recombination, we propose a baseline method for zero-shot OCR. The experimental results demonstrate the validity of ACCID and the baseline model quantitatively and qualitatively.
Recognizing Entity Types via Properties
Apr 24, 2023



Abstract:The mainstream approach to the development of ontologies is merging ontologies encoding different information, where one of the major difficulties is that the heterogeneity motivates the ontology merging but also limits high-quality merging performance. Thus, the entity type (etype) recognition task is proposed to deal with such heterogeneity, aiming to infer the class of entities and etypes by exploiting the information encoded in ontologies. In this paper, we introduce a property-based approach that allows recognizing etypes on the basis of the properties used to define them. From an epistemological point of view, it is in fact properties that characterize entities and etypes, and this definition is independent of the specific labels and hierarchical schemas used to define them. The main contribution consists of a set of property-based metrics for measuring the contextual similarity between etypes and entities, and a machine learning-based etype recognition algorithm exploiting the proposed similarity metrics. Compared with the state-of-the-art, the experimental results show the validity of the similarity metrics and the superiority of the proposed etype recognition algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge