Daniel Ritchie
Residual Primitive Fitting of 3D Shapes with SuperFrusta
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:We introduce a framework for converting 3D shapes into compact and editable assemblies of analytic primitives, directly addressing the persistent trade-off between reconstruction fidelity and parsimony. Our approach combines two key contributions: a novel primitive, termed SuperFrustum, and an iterative fiting algorithm, Residual Primitive Fitting (ResFit). SuperFrustum is an analytical primitive that is simultaneously (1) expressive, being able to model various common solids such as cylinders, spheres, cones & their tapered and bent forms, (2) editable, being compactly parameterized with 8 parameters, and (3) optimizable, with a sign distance field differentiable w.r.t. its parameters almost everywhere. ResFit is an unsupervised procedure that interleaves global shape analysis with local optimization, iteratively fitting primitives to the unexplained residual of a shape to discover a parsimonious yet accurate decompositions for each input shape. On diverse 3D benchmarks, our method achieves state-of-the-art results, improving IoU by over 9 points while using nearly half as many primitives as prior work. The resulting assemblies bridge the gap between dense 3D data and human-controllable design, producing high-fidelity and editable shape programs.
PoissonNet: A Local-Global Approach for Learning on Surfaces
Oct 15, 2025Abstract:Many network architectures exist for learning on meshes, yet their constructions entail delicate trade-offs between difficulty learning high-frequency features, insufficient receptive field, sensitivity to discretization, and inefficient computational overhead. Drawing from classic local-global approaches in mesh processing, we introduce PoissonNet, a novel neural architecture that overcomes all of these deficiencies by formulating a local-global learning scheme, which uses Poisson's equation as the primary mechanism for feature propagation. Our core network block is simple; we apply learned local feature transformations in the gradient domain of the mesh, then solve a Poisson system to propagate scalar feature updates across the surface globally. Our local-global learning framework preserves the features's full frequency spectrum and provides a truly global receptive field, while remaining agnostic to mesh triangulation. Our construction is efficient, requiring far less compute overhead than comparable methods, which enables scalability -- both in the size of our datasets, and the size of individual training samples. These qualities are validated on various experiments where, compared to previous intrinsic architectures, we attain state-of-the-art performance on semantic segmentation and parameterizing highly-detailed animated surfaces. Finally, as a central application of PoissonNet, we show its ability to learn deformations, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art architectures that learn on surfaces.
GenHSI: Controllable Generation of Human-Scene Interaction Videos
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Large-scale pre-trained video diffusion models have exhibited remarkable capabilities in diverse video generation. However, existing solutions face several challenges in using these models to generate long movie-like videos with rich human-object interactions that include unrealistic human-scene interaction, lack of subject identity preservation, and require expensive training. We propose GenHSI, a training-free method for controllable generation of long human-scene interaction videos (HSI). Taking inspiration from movie animation, our key insight is to overcome the limitations of previous work by subdividing the long video generation task into three stages: (1) script writing, (2) pre-visualization, and (3) animation. Given an image of a scene, a user description, and multiple images of a person, we use these three stages to generate long-videos that preserve human-identity and provide rich human-scene interactions. Script writing converts complex human tasks into simple atomic tasks that are used in the pre-visualization stage to generate 3D keyframes (storyboards). These 3D keyframes are rendered and animated by off-the-shelf video diffusion models for consistent long video generation with rich contacts in a 3D-aware manner. A key advantage of our work is that we alleviate the need for scanned, accurate scenes and create 3D keyframes from single-view images. We are the first to generate a long video sequence with a consistent camera pose that contains arbitrary numbers of character actions without training. Experiments demonstrate that our method can generate long videos that effectively preserve scene content and character identity with plausible human-scene interaction from a single image scene. Visit our project homepage https://kunkun0w0.github.io/project/GenHSI/ for more information.
Learning Object Placement Programs for Indoor Scene Synthesis with Iterative Self Training
Mar 06, 2025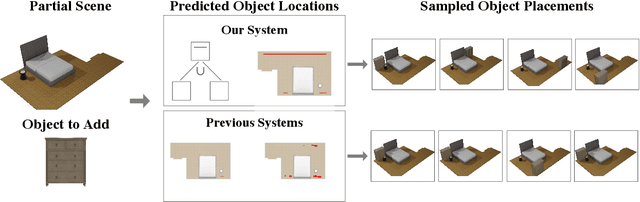
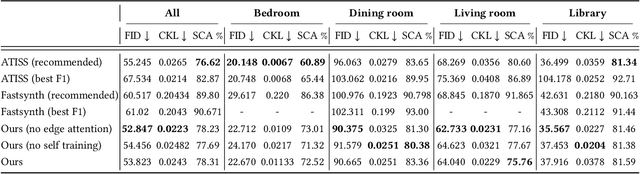
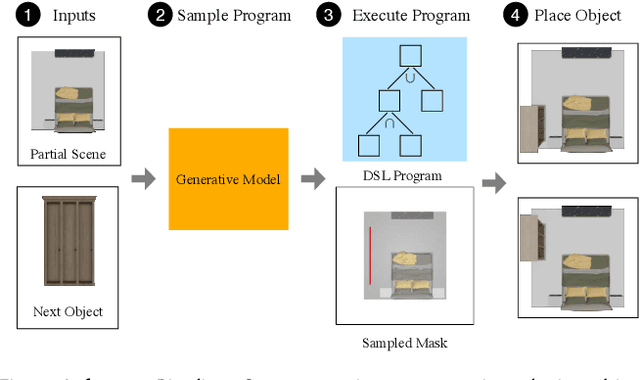
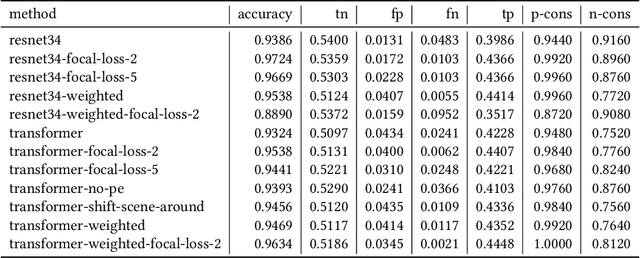
Abstract:Data driven and autoregressive indoor scene synthesis systems generate indoor scenes automatically by suggesting and then placing objects one at a time. Empirical observations show that current systems tend to produce incomplete next object location distributions. We introduce a system which addresses this problem. We design a Domain Specific Language (DSL) that specifies functional constraints. Programs from our language take as input a partial scene and object to place. Upon execution they predict possible object placements. We design a generative model which writes these programs automatically. Available 3D scene datasets do not contain programs to train on, so we build upon previous work in unsupervised program induction to introduce a new program bootstrapping algorithm. In order to quantify our empirical observations we introduce a new evaluation procedure which captures how well a system models per-object location distributions. We ask human annotators to label all the possible places an object can go in a scene and show that our system produces per-object location distributions more consistent with human annotators. Our system also generates indoor scenes of comparable quality to previous systems and while previous systems degrade in performance when training data is sparse, our system does not degrade to the same degree.
ShapeLib: designing a library of procedural 3D shape abstractions with Large Language Models
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Procedural representations are desirable, versatile, and popular shape encodings. Authoring them, either manually or using data-driven procedures, remains challenging, as a well-designed procedural representation should be compact, intuitive, and easy to manipulate. A long-standing problem in shape analysis studies how to discover a reusable library of procedural functions, with semantically aligned exposed parameters, that can explain an entire shape family. We present ShapeLib as the first method that leverages the priors of frontier LLMs to design a library of 3D shape abstraction functions. Our system accepts two forms of design intent: text descriptions of functions to include in the library and a seed set of exemplar shapes. We discover procedural abstractions that match this design intent by proposing, and then validating, function applications and implementations. The discovered shape functions in the library are not only expressive but also generalize beyond the seed set to a full family of shapes. We train a recognition network that learns to infer shape programs based on our library from different visual modalities (primitives, voxels, point clouds). Our shape functions have parameters that are semantically interpretable and can be modified to produce plausible shape variations. We show that this allows inferred programs to be successfully manipulated by an LLM given a text prompt. We evaluate ShapeLib on different datasets and show clear advantages over existing methods and alternative formulations.
ProcTex: Consistent and Interactive Text-to-texture Synthesis for Procedural Models
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancement in 2D image diffusion models has driven significant progress in text-guided texture synthesis, enabling realistic, high-quality texture generation from arbitrary text prompts. However, current methods usually focus on synthesizing texture for single static 3D objects, and struggle to handle entire families of shapes, such as those produced by procedural programs. Applying existing methods naively to each procedural shape is too slow to support exploring different parameter settings at interactive rates, and also results in inconsistent textures across the procedural shapes. To this end, we introduce ProcTex, the first text-to-texture system designed for procedural 3D models. ProcTex enables consistent and real-time text-guided texture synthesis for families of shapes, which integrates seamlessly with the interactive design flow of procedural models. To ensure consistency, our core approach is to generate texture for the shape produced by one setting of the procedural parameters, followed by a texture transfer stage to apply the texture to other parameter settings. We also develop several techniques, including a novel UV displacement network for real-time texture transfer, the retexturing pipeline to support structural changes from discrete procedural parameters, and part-level UV texture map generation for local appearance editing. Extensive experiments on a diverse set of professional procedural models validate ProcTex's ability to produce high-quality, visually consistent textures while supporting real-time, interactive applications.
Pattern Analogies: Learning to Perform Programmatic Image Edits by Analogy
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Pattern images are everywhere in the digital and physical worlds, and tools to edit them are valuable. But editing pattern images is tricky: desired edits are often programmatic: structure-aware edits that alter the underlying program which generates the pattern. One could attempt to infer this underlying program, but current methods for doing so struggle with complex images and produce unorganized programs that make editing tedious. In this work, we introduce a novel approach to perform programmatic edits on pattern images. By using a pattern analogy -- a pair of simple patterns to demonstrate the intended edit -- and a learning-based generative model to execute these edits, our method allows users to intuitively edit patterns. To enable this paradigm, we introduce SplitWeave, a domain-specific language that, combined with a framework for sampling synthetic pattern analogies, enables the creation of a large, high-quality synthetic training dataset. We also present TriFuser, a Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) designed to overcome critical issues that arise when naively deploying LDMs to this task. Extensive experiments on real-world, artist-sourced patterns reveals that our method faithfully performs the demonstrated edit while also generalizing to related pattern styles beyond its training distribution.
GigaHands: A Massive Annotated Dataset of Bimanual Hand Activities
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Understanding bimanual human hand activities is a critical problem in AI and robotics. We cannot build large models of bimanual activities because existing datasets lack the scale, coverage of diverse hand activities, and detailed annotations. We introduce GigaHands, a massive annotated dataset capturing 34 hours of bimanual hand activities from 56 subjects and 417 objects, totaling 14k motion clips derived from 183 million frames paired with 84k text annotations. Our markerless capture setup and data acquisition protocol enable fully automatic 3D hand and object estimation while minimizing the effort required for text annotation. The scale and diversity of GigaHands enable broad applications, including text-driven action synthesis, hand motion captioning, and dynamic radiance field reconstruction.
Diorama: Unleashing Zero-shot Single-view 3D Scene Modeling
Nov 29, 2024



Abstract:Reconstructing structured 3D scenes from RGB images using CAD objects unlocks efficient and compact scene representations that maintain compositionality and interactability. Existing works propose training-heavy methods relying on either expensive yet inaccurate real-world annotations or controllable yet monotonous synthetic data that do not generalize well to unseen objects or domains. We present Diorama, the first zero-shot open-world system that holistically models 3D scenes from single-view RGB observations without requiring end-to-end training or human annotations. We show the feasibility of our approach by decomposing the problem into subtasks and introduce robust, generalizable solutions to each: architecture reconstruction, 3D shape retrieval, object pose estimation, and scene layout optimization. We evaluate our system on both synthetic and real-world data to show we significantly outperform baselines from prior work. We also demonstrate generalization to internet images and the text-to-scene task.
CLIPtortionist: Zero-shot Text-driven Deformation for Manufactured 3D Shapes
Oct 19, 2024



Abstract:We propose a zero-shot text-driven 3D shape deformation system that deforms an input 3D mesh of a manufactured object to fit an input text description. To do this, our system optimizes the parameters of a deformation model to maximize an objective function based on the widely used pre-trained vision language model CLIP. We find that CLIP-based objective functions exhibit many spurious local optima; to circumvent them, we parameterize deformations using a novel deformation model called BoxDefGraph which our system automatically computes from an input mesh, the BoxDefGraph is designed to capture the object aligned rectangular/circular geometry features of most manufactured objects. We then use the CMA-ES global optimization algorithm to maximize our objective, which we find to work better than popular gradient-based optimizers. We demonstrate that our approach produces appealing results and outperforms several baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge