Daniel Polani
University of Hertfordshire
The Contingencies of Physical Embodiment Allow for Open-Endedness and Care
Oct 08, 2025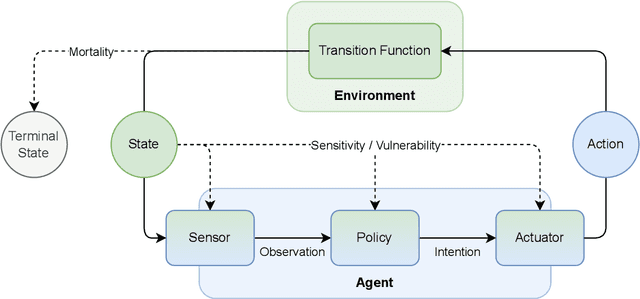
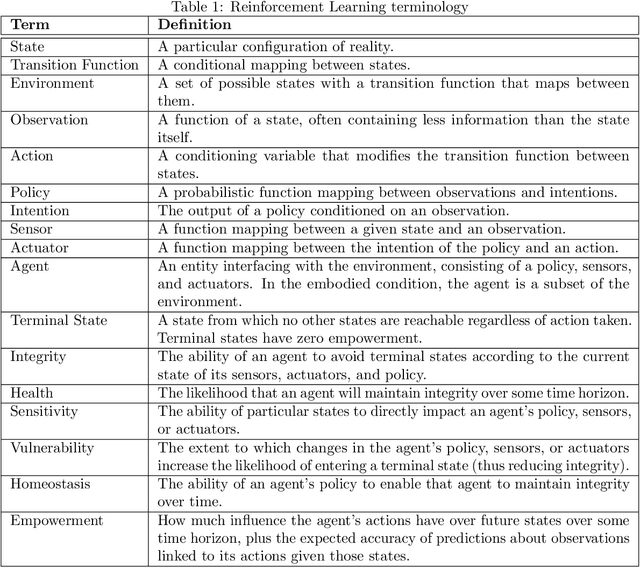
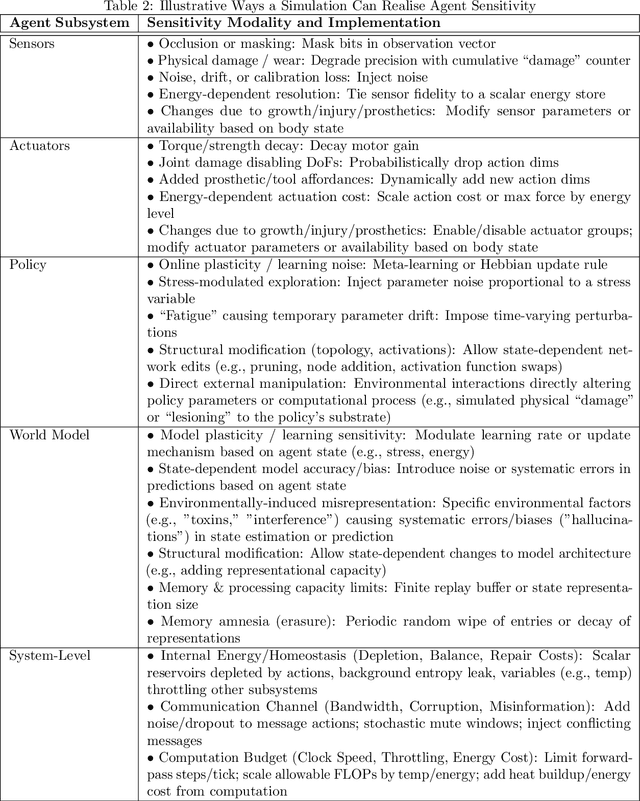
Abstract:Physical vulnerability and mortality are often seen as obstacles to be avoided in the development of artificial agents, which struggle to adapt to open-ended environments and provide aligned care. Meanwhile, biological organisms survive, thrive, and care for each other in an open-ended physical world with relative ease and efficiency. Understanding the role of the conditions of life in this disparity can aid in developing more robust, adaptive, and caring artificial agents. Here we define two minimal conditions for physical embodiment inspired by the existentialist phenomenology of Martin Heidegger: being-in-the-world (the agent is a part of the environment) and being-towards-death (unless counteracted, the agent drifts toward terminal states due to the second law of thermodynamics). We propose that from these conditions we can obtain both a homeostatic drive - aimed at maintaining integrity and avoiding death by expending energy to learn and act - and an intrinsic drive to continue to do so in as many ways as possible. Drawing inspiration from Friedrich Nietzsche's existentialist concept of will-to-power, we examine how intrinsic drives to maximize control over future states, e.g., empowerment, allow agents to increase the probability that they will be able to meet their future homeostatic needs, thereby enhancing their capacity to maintain physical integrity. We formalize these concepts within a reinforcement learning framework, which enables us to examine how intrinsically driven embodied agents learning in open-ended multi-agent environments may cultivate the capacities for open-endedness and care.ov
Decentralized Traffic Flow Optimization Through Intrinsic Motivation
May 08, 2025Abstract:Traffic congestion has long been an ubiquitous problem that is exacerbating with the rapid growth of megacities. In this proof-of-concept work we study intrinsic motivation, implemented via the empowerment principle, to control autonomous car behavior to improve traffic flow. In standard models of traffic dynamics, self-organized traffic jams emerge spontaneously from the individual behavior of cars, affecting traffic over long distances. Our novel car behavior strategy improves traffic flow while still being decentralized and using only locally available information without explicit coordination. Decentralization is essential for various reasons, not least to be able to absorb robustly substantial levels of uncertainty. Our scenario is based on the well-established traffic dynamics model, the Nagel-Schreckenberg cellular automaton. In a fraction of the cars in this model, we substitute the default behavior by empowerment, our intrinsic motivation-based method. This proposed model significantly improves overall traffic flow, mitigates congestion, and reduces the average traffic jam time.
* 9 pages, 6 figures, Published in the Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 27th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC)
SuPLE: Robot Learning with Lyapunov Rewards
Nov 20, 2024

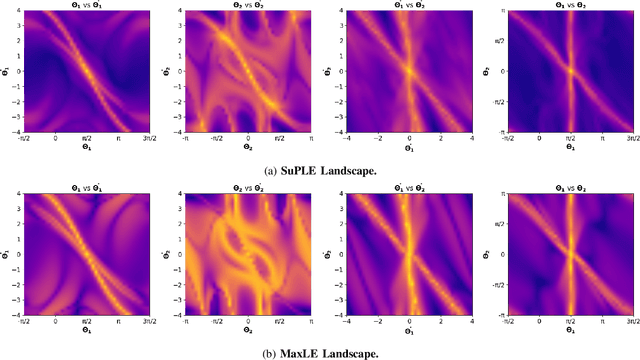

Abstract:The reward function is an essential component in robot learning. Reward directly affects the sample and computational complexity of learning, and the quality of a solution. The design of informative rewards requires domain knowledge, which is not always available. We use the properties of the dynamics to produce system-appropriate reward without adding external assumptions. Specifically, we explore an approach to utilize the Lyapunov exponents of the system dynamics to generate a system-immanent reward. We demonstrate that the `Sum of the Positive Lyapunov Exponents' (SuPLE) is a strong candidate for the design of such a reward. We develop a computational framework for the derivation of this reward, and demonstrate its effectiveness on classical benchmarks for sample-based stabilization of various dynamical systems. It eliminates the need to start the training trajectories at arbitrary states, also known as auxiliary exploration. While the latter is a common practice in simulated robot learning, it is unpractical to consider to use it in real robotic systems, since they typically start from natural rest states such as a pendulum at the bottom, a robot on the ground, etc. and can not be easily initialized at arbitrary states. Comparing the performance of SuPLE to commonly-used reward functions, we observe that the latter fail to find a solution without auxiliary exploration, even for the task of swinging up the double pendulum and keeping it stable at the upright position, a prototypical scenario for multi-linked robots. SuPLE-induced rewards for robot learning offer a novel route for effective robot learning in typical as opposed to highly specialized or fine-tuned scenarios. Our code is publicly available for reproducibility and further research.
Dimensionality Reduction of Dynamics on Lie Manifolds via Structure-Aware Canonical Correlation Analysis
Nov 17, 2023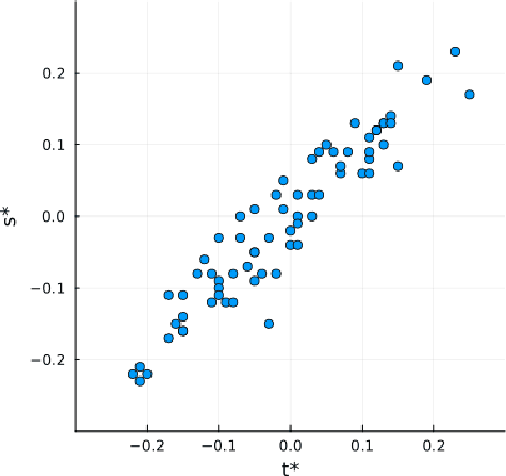
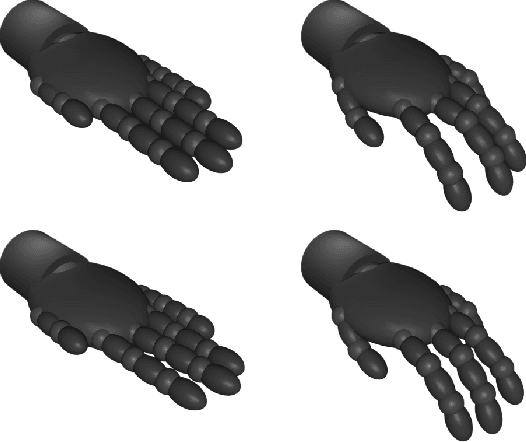
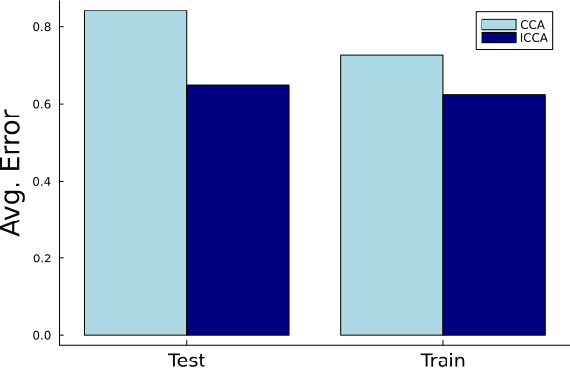
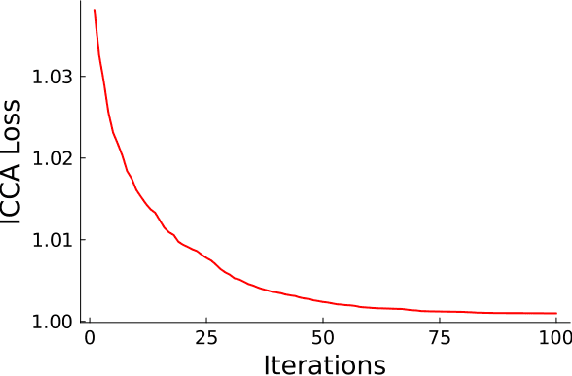
Abstract:Incorporating prior knowledge into a data-driven modeling problem can drastically improve performance, reliability, and generalization outside of the training sample. The stronger the structural properties, the more effective these improvements become. Manifolds are a powerful nonlinear generalization of Euclidean space for modeling finite dimensions. Structural impositions in constrained systems increase when applying group structure, converting them into Lie manifolds. The range of their applications is very wide and includes the important case of robotic tasks. Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) can construct a hierarchical sequence of maximal correlations of up to two paired data sets in these Euclidean spaces. We present a method to generalize this concept to Lie Manifolds and demonstrate its efficacy through the substantial improvements it achieves in making structure-consistent predictions about changes in the state of a robotic hand.
Towards Information Theory-Based Discovery of Equivariances
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:The presence of symmetries imposes a stringent set of constraints on a system. This constrained structure allows intelligent agents interacting with such a system to drastically improve the efficiency of learning and generalization, through the internalisation of the system's symmetries into their information-processing. In parallel, principled models of complexity-constrained learning and behaviour make increasing use of information-theoretic methods. Here, we wish to marry these two perspectives and understand whether and in which form the information-theoretic lens can "see" the effect of symmetries of a system. For this purpose, we propose a novel variant of the Information Bottleneck principle, which has served as a productive basis for many principled studies of learning and information-constrained adaptive behaviour. We show (in the discrete case) that our approach formalises a certain duality between symmetry and information parsimony: namely, channel equivariances can be characterised by the optimal mutual information-preserving joint compression of the channel's input and output. This information-theoretic treatment furthermore suggests a principled notion of "soft" equivariance, whose "coarseness" is measured by the amount of input-output mutual information preserved by the corresponding optimal compression. This new notion offers a bridge between the field of bounded rationality and the study of symmetries in neural representations. The framework may also allow (exact and soft) equivariances to be automatically discovered.
Intrinsic Motivation in Dynamical Control Systems
Dec 29, 2022Abstract:Biological systems often choose actions without an explicit reward signal, a phenomenon known as intrinsic motivation. The computational principles underlying this behavior remain poorly understood. In this study, we investigate an information-theoretic approach to intrinsic motivation, based on maximizing an agent's empowerment (the mutual information between its past actions and future states). We show that this approach generalizes previous attempts to formalize intrinsic motivation, and we provide a computationally efficient algorithm for computing the necessary quantities. We test our approach on several benchmark control problems, and we explain its success in guiding intrinsically motivated behaviors by relating our information-theoretic control function to fundamental properties of the dynamical system representing the combined agent-environment system. This opens the door for designing practical artificial, intrinsically motivated controllers and for linking animal behaviors to their dynamical properties.
A space of goals: the cognitive geometry of informationally bounded agents
Nov 05, 2021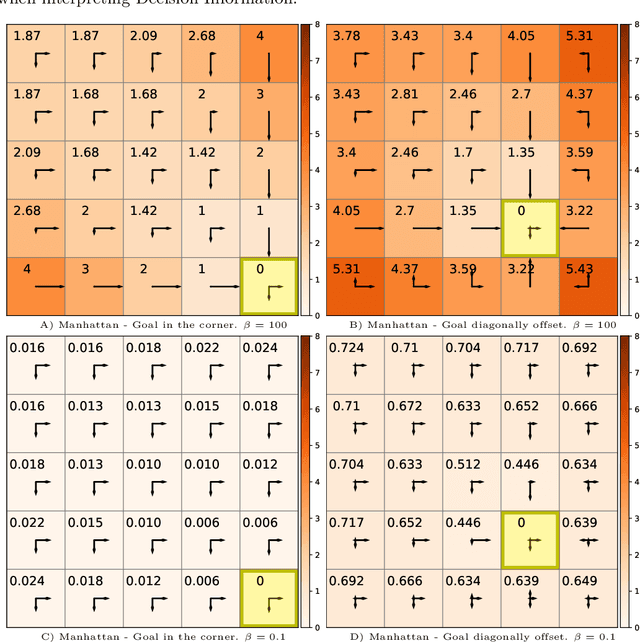
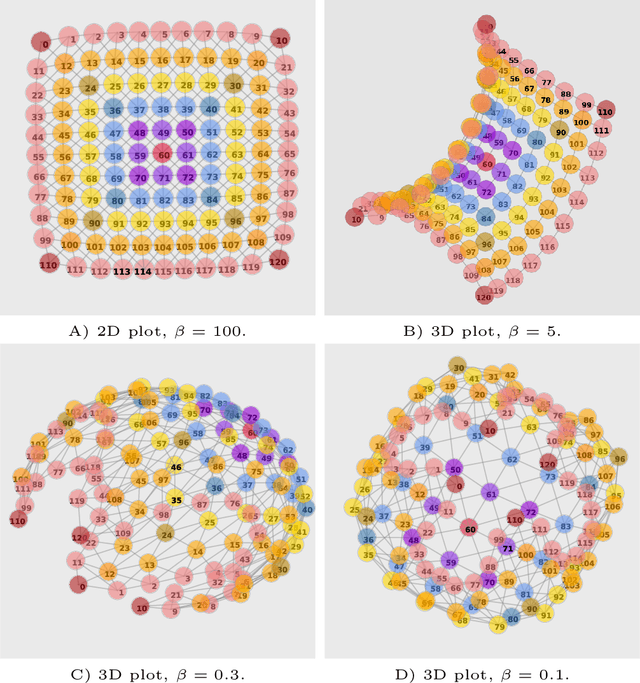
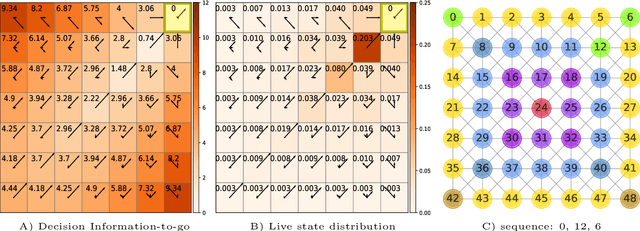
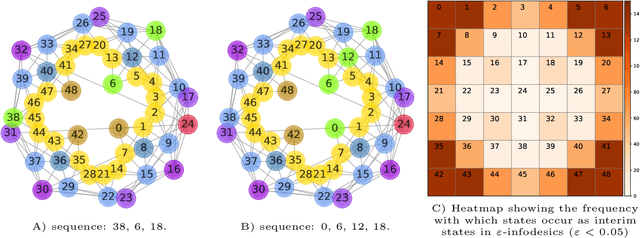
Abstract:Traditionally, Euclidean geometry is treated by scientists as a priori and objective. However, when we take the position of an agent, the problem of selecting a best route should also factor in the abilities of the agent, its embodiment and particularly its cognitive effort. In this paper we consider geometry in terms of travel between states within a world by incorporating information processing costs with the appropriate spatial distances. This induces a geometry that increasingly differs from the original geometry of the given world, as information costs become increasingly important. We visualize this \textit{"cognitive geometry"} by projecting it onto 2- and 3-dimensional spaces showing distinct distortions reflecting the emergence of epistemic and information-saving strategies as well as pivot states. The analogies between traditional cost-based geometries and those induced by additional informational costs invite a generalization of the traditional notion of geodesics as cheapest routes towards the notion of \textit{infodesics}. Crucially, the concept of infodesics approximates the usual geometric property that, travelling from a start to a goal along a geodesic, not only the goal, but all intermediate points are equally visited at optimal cost from the start.
Causal blankets: Theory and algorithmic framework
Sep 29, 2020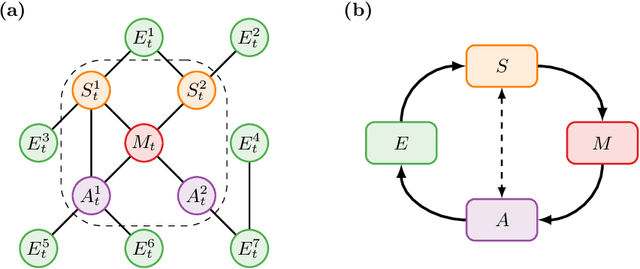
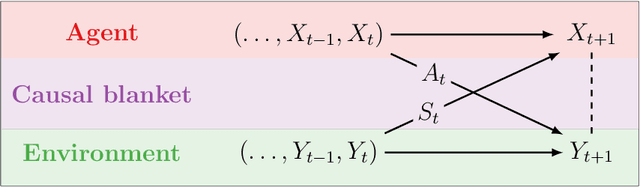
Abstract:We introduce a novel framework to identify perception-action loops (PALOs) directly from data based on the principles of computational mechanics. Our approach is based on the notion of causal blanket, which captures sensory and active variables as dynamical sufficient statistics -- i.e. as the "differences that make a difference." Moreover, our theory provides a broadly applicable procedure to construct PALOs that requires neither a steady-state nor Markovian dynamics. Using our theory, we show that every bipartite stochastic process has a causal blanket, but the extent to which this leads to an effective PALO formulation varies depending on the integrated information of the bipartition.
AvE: Assistance via Empowerment
Jul 09, 2020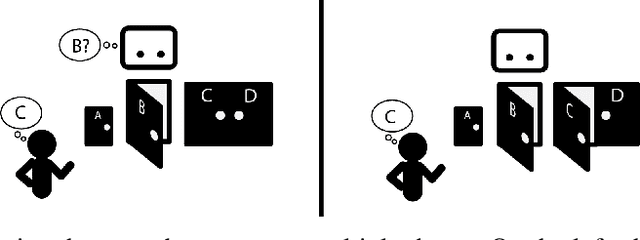
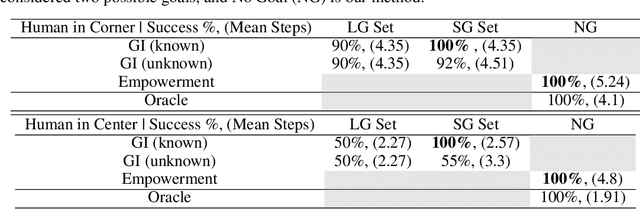
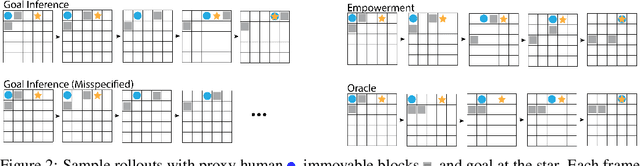

Abstract:One difficulty in using artificial agents for human-assistive applications lies in the challenge of accurately assisting with a person's goal(s). Existing methods tend to rely on inferring the human's goal, which is challenging when there are many potential goals or when the set of candidate goals is difficult to identify. We propose a new paradigm for assistance by instead increasing the human's ability to control their environment, and formalize this approach by augmenting reinforcement learning with human empowerment. This task-agnostic objective preserves the person's autonomy and ability to achieve any eventual state. We test our approach against assistance based on goal inference, highlighting scenarios where our method overcomes failure modes stemming from goal ambiguity or misspecification. As existing methods for estimating empowerment in continuous domains are computationally hard, precluding its use in real time learned assistance, we also propose an efficient empowerment-inspired proxy metric. Using this, we are able to successfully demonstrate our method in a shared autonomy user study for a challenging simulated teleoperation task with human-in-the-loop training.
Human Perception of Intrinsically Motivated Autonomy in Human-Robot Interaction
Feb 14, 2020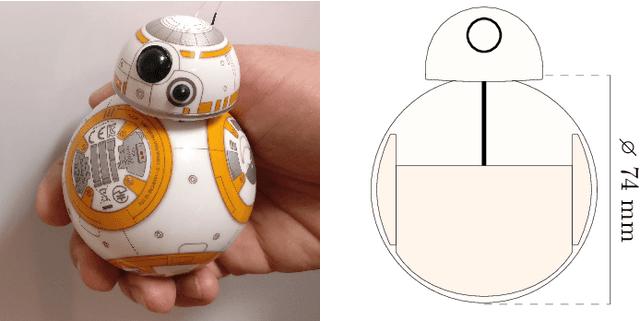
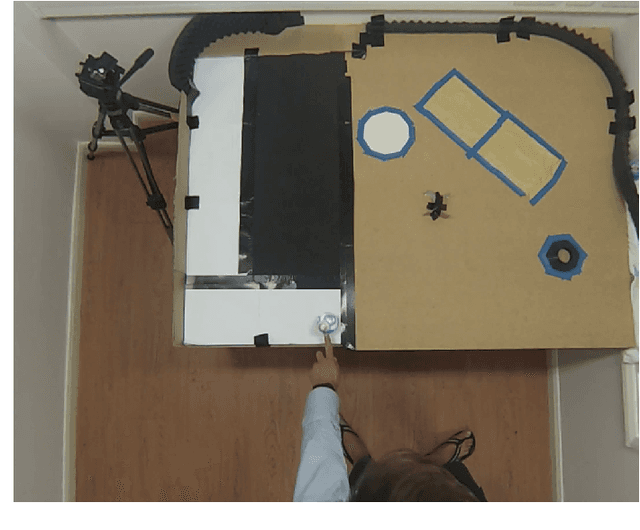
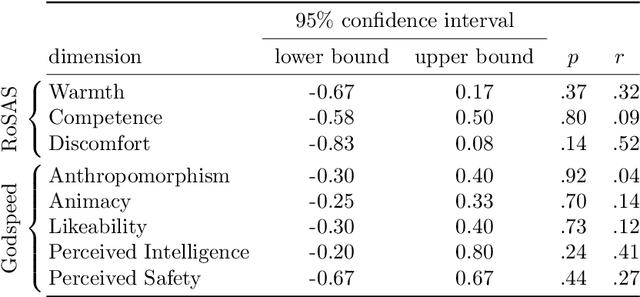
Abstract:A challenge in using fully autonomous robots in human-robot interaction (HRI) is to design behavior that is engaging enough to encourage voluntary, long-term interaction, yet robust to the perturbations induced by human interaction. Here we evaluate if an intrinsically motivated, physical robot can address this challenge. We use predictive information maximization as an intrinsic motivation, as simulated experiments showed that this leads to playful, exploratory behavior that is robust to changes in the robot's morphology and environment. To the authors' knowledge there are no previous HRI studies that evaluate the effect of intrinsically motivated behavior in robots on the human perception of those robots. We present a game-like study design, which allows us to focus on the interplay between the robot and the human participant. In contrast to a study design where participants order or control a robot to do a specific task, the robot and the human participants in our study design explore their behaviors without knowledge about any specific goals. We conducted a within-subjects study (N=24) were participants interacted with a fully autonomous Sphero BB8 robot with different behavioral regimes: one realizing an adaptive, intrinsically motivated behavior and the other being reactive, but not adaptive. A quantitative analysis of post-interaction questionnaires showed a significantly higher perception (r=.555, p=.007) of the dimension "Warmth" compared to the baseline behavior. Warmth is considered a primary dimension for social attitude formation in human cognition. A human perceived as warm (i.e. friendly and trustworthy) experiences more positive social interactions. If future work demonstrates that this transfers to human-robot social cognition, then the generic methods presented here could be used to imbue robots with behavior leading to positive perception by humans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge