Colin Lockard
Extracting Shopping Interest-Related Product Types from the Web
May 23, 2023Abstract:Recommending a diversity of product types (PTs) is important for a good shopping experience when customers are looking for products around their high-level shopping interests (SIs) such as hiking. However, the SI-PT connection is typically absent in e-commerce product catalogs and expensive to construct manually due to the volume of potential SIs, which prevents us from establishing a recommender with easily accessible knowledge systems. To establish such connections, we propose to extract PTs from the Web pages containing hand-crafted PT recommendations for SIs. The extraction task is formulated as binary HTML node classification given the general observation that an HTML node in our target Web pages can present one and only one PT phrase. Accordingly, we introduce TrENC, which stands for Tree-Transformer Encoders for Node Classification. It improves the inter-node dependency modeling with modified attention mechanisms that preserve the long-term sibling and ancestor-descendant relations. TrENC also injects SI into node features for better semantic representation. Trained on pages regarding limited SIs, TrEnc is ready to be applied to other unobserved interests. Experiments on our manually constructed dataset, WebPT, show that TrENC outperforms the best baseline model by 2.37 F1 points in the zero-shot setup. The performance indicates the feasibility of constructing SI-PT relations and using them to power downstream applications such as search and recommendation.
Label-Efficient Self-Training for Attribute Extraction from Semi-Structured Web Documents
Aug 27, 2022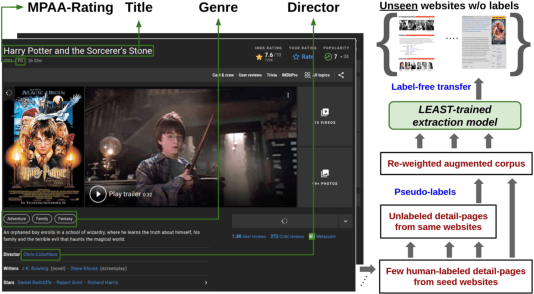
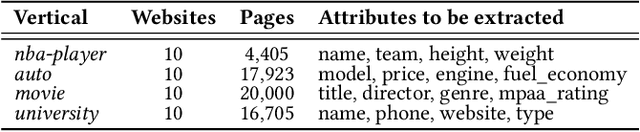
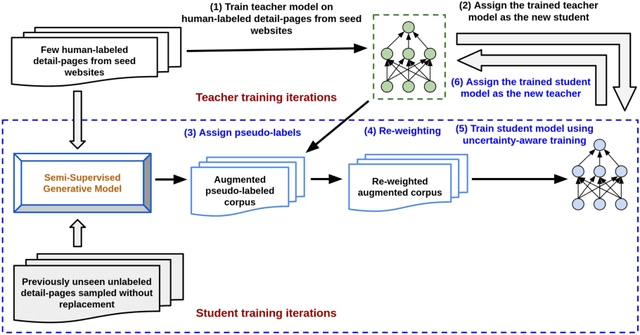
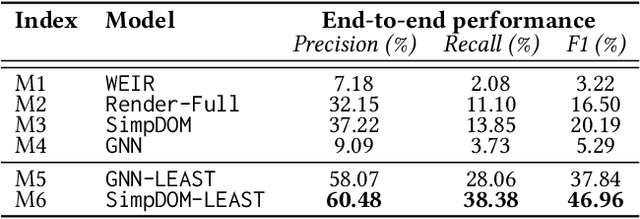
Abstract:Extracting structured information from HTML documents is a long-studied problem with a broad range of applications, including knowledge base construction, faceted search, and personalized recommendation. Prior works rely on a few human-labeled web pages from each target website or thousands of human-labeled web pages from some seed websites to train a transferable extraction model that generalizes on unseen target websites. Noisy content, low site-level consistency, and lack of inter-annotator agreement make labeling web pages a time-consuming and expensive ordeal. We develop LEAST -- a Label-Efficient Self-Training method for Semi-Structured Web Documents to overcome these limitations. LEAST utilizes a few human-labeled pages to pseudo-annotate a large number of unlabeled web pages from the target vertical. It trains a transferable web-extraction model on both human-labeled and pseudo-labeled samples using self-training. To mitigate error propagation due to noisy training samples, LEAST re-weights each training sample based on its estimated label accuracy and incorporates it in training. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to propose end-to-end training for transferable web extraction models utilizing only a few human-labeled pages. Experiments on a large-scale public dataset show that using less than ten human-labeled pages from each seed website for training, a LEAST-trained model outperforms previous state-of-the-art by more than 26 average F1 points on unseen websites, reducing the number of human-labeled pages to achieve similar performance by more than 10x.
PLAtE: A Large-scale Dataset for List Page Web Extraction
May 24, 2022
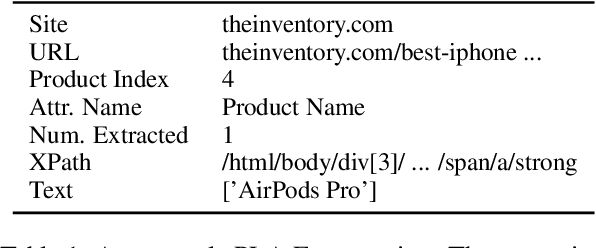

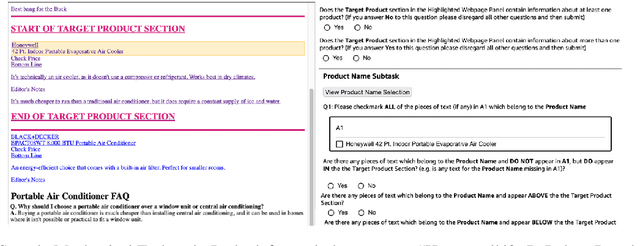
Abstract:Recently, neural models have been leveraged to significantly improve the performance of information extraction from semi-structured websites. However, a barrier for continued progress is the small number of datasets large enough to train these models. In this work, we introduce the PLAtE (Pages of Lists Attribute Extraction) dataset as a challenging new web extraction task. PLAtE focuses on shopping data, specifically extractions from product review pages with multiple items. PLAtE encompasses both the tasks of: (1) finding product-list segmentation boundaries and (2) extracting attributes for each product. PLAtE is composed of 53, 905 items from 6, 810 pages, making it the first large-scale list page web extraction dataset. We construct PLAtE by collecting list pages from Common Crawl, then annotating them on Mechanical Turk. Quantitative and qualitative analyses are performed to demonstrate PLAtE has high-quality annotations. We establish strong baseline performance on PLAtE with a SOTA model achieving an F1-score of 0.750 for attribute classification and 0.915 for segmentation, indicating opportunities for future research innovations in web extraction.
DOM-LM: Learning Generalizable Representations for HTML Documents
Jan 25, 2022



Abstract:HTML documents are an important medium for disseminating information on the Web for human consumption. An HTML document presents information in multiple text formats including unstructured text, structured key-value pairs, and tables. Effective representation of these documents is essential for machine understanding to enable a wide range of applications, such as Question Answering, Web Search, and Personalization. Existing work has either represented these documents using visual features extracted by rendering them in a browser, which is typically computationally expensive, or has simply treated them as plain text documents, thereby failing to capture useful information presented in their HTML structure. We argue that the text and HTML structure together convey important semantics of the content and therefore warrant a special treatment for their representation learning. In this paper, we introduce a novel representation learning approach for web pages, dubbed DOM-LM, which addresses the limitations of existing approaches by encoding both text and DOM tree structure with a transformer-based encoder and learning generalizable representations for HTML documents via self-supervised pre-training. We evaluate DOM-LM on a variety of webpage understanding tasks, including Attribute Extraction, Open Information Extraction, and Question Answering. Our extensive experiments show that DOM-LM consistently outperforms all baselines designed for these tasks. In particular, DOM-LM demonstrates better generalization performance both in few-shot and zero-shot settings, making it attractive for making it suitable for real-world application settings with limited labeled data.
TCN: Table Convolutional Network for Web Table Interpretation
Feb 17, 2021



Abstract:Information extraction from semi-structured webpages provides valuable long-tailed facts for augmenting knowledge graph. Relational Web tables are a critical component containing additional entities and attributes of rich and diverse knowledge. However, extracting knowledge from relational tables is challenging because of sparse contextual information. Existing work linearize table cells and heavily rely on modifying deep language models such as BERT which only captures related cells information in the same table. In this work, we propose a novel relational table representation learning approach considering both the intra- and inter-table contextual information. On one hand, the proposed Table Convolutional Network model employs the attention mechanism to adaptively focus on the most informative intra-table cells of the same row or column; and, on the other hand, it aggregates inter-table contextual information from various types of implicit connections between cells across different tables. Specifically, we propose three novel aggregation modules for (i) cells of the same value, (ii) cells of the same schema position, and (iii) cells linked to the same page topic. We further devise a supervised multi-task training objective for jointly predicting column type and pairwise column relation, as well as a table cell recovery objective for pre-training. Experiments on real Web table datasets demonstrate our method can outperform competitive baselines by +4.8% of F1 for column type prediction and by +4.1% of F1 for pairwise column relation prediction.
ZeroShotCeres: Zero-Shot Relation Extraction from Semi-Structured Webpages
May 14, 2020



Abstract:In many documents, such as semi-structured webpages, textual semantics are augmented with additional information conveyed using visual elements including layout, font size, and color. Prior work on information extraction from semi-structured websites has required learning an extraction model specific to a given template via either manually labeled or distantly supervised data from that template. In this work, we propose a solution for "zero-shot" open-domain relation extraction from webpages with a previously unseen template, including from websites with little overlap with existing sources of knowledge for distant supervision and websites in entirely new subject verticals. Our model uses a graph neural network-based approach to build a rich representation of text fields on a webpage and the relationships between them, enabling generalization to new templates. Experiments show this approach provides a 31% F1 gain over a baseline for zero-shot extraction in a new subject vertical.
OpenKI: Integrating Open Information Extraction and Knowledge Bases with Relation Inference
Apr 12, 2019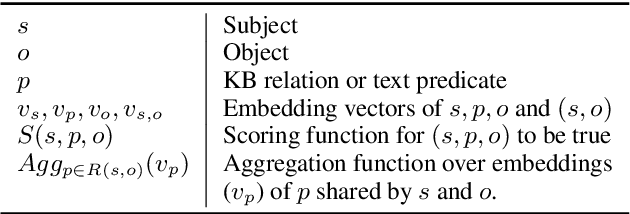
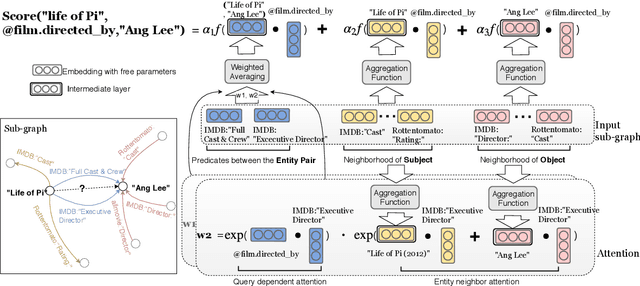
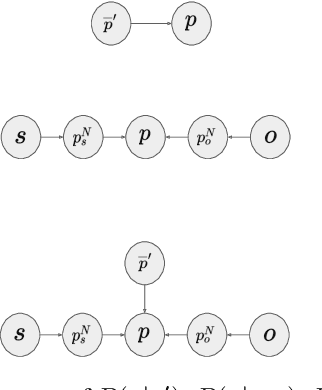
Abstract:In this paper, we consider advancing web-scale knowledge extraction and alignment by integrating OpenIE extractions in the form of (subject, predicate, object) triples with Knowledge Bases (KB). Traditional techniques from universal schema and from schema mapping fall in two extremes: either they perform instance-level inference relying on embedding for (subject, object) pairs, thus cannot handle pairs absent in any existing triples; or they perform predicate-level mapping and completely ignore background evidence from individual entities, thus cannot achieve satisfying quality. We propose OpenKI to handle sparsity of OpenIE extractions by performing instance-level inference: for each entity, we encode the rich information in its neighborhood in both KB and OpenIE extractions, and leverage this information in relation inference by exploring different methods of aggregation and attention. In order to handle unseen entities, our model is designed without creating entity-specific parameters. Extensive experiments show that this method not only significantly improves state-of-the-art for conventional OpenIE extractions like ReVerb, but also boosts the performance on OpenIE from semi-structured data, where new entity pairs are abundant and data are fairly sparse.
Semi-Supervised Event Extraction with Paraphrase Clusters
Aug 26, 2018


Abstract:Supervised event extraction systems are limited in their accuracy due to the lack of available training data. We present a method for self-training event extraction systems by bootstrapping additional training data. This is done by taking advantage of the occurrence of multiple mentions of the same event instances across newswire articles from multiple sources. If our system can make a highconfidence extraction of some mentions in such a cluster, it can then acquire diverse training examples by adding the other mentions as well. Our experiments show significant performance improvements on multiple event extractors over ACE 2005 and TAC-KBP 2015 datasets.
CERES: Distantly Supervised Relation Extraction from the Semi-Structured Web
Apr 12, 2018



Abstract:The web contains countless semi-structured websites, which can be a rich source of information for populating knowledge bases. Existing methods for extracting relations from the DOM trees of semi-structured webpages can achieve high precision and recall only when manual annotations for each website are available. Although there have been efforts to learn extractors from automatically-generated labels, these methods are not sufficiently robust to succeed in settings with complex schemas and information-rich websites. In this paper we present a new method for automatic extraction from semi-structured websites based on distant supervision. We automatically generate training labels by aligning an existing knowledge base with a web page and leveraging the unique structural characteristics of semi-structured websites. We then train a classifier based on the potentially noisy and incomplete labels to predict new relation instances. Our method can compete with annotation-based techniques in the literature in terms of extraction quality. A large-scale experiment on over 400,000 pages from dozens of multi-lingual long-tail websites harvested 1.25 million facts at a precision of 90%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge