Chuang Zhao
Grounded by Experience: Generative Healthcare Prediction Augmented with Hierarchical Agentic Retrieval
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Accurate healthcare prediction is critical for improving patient outcomes and reducing operational costs. Bolstered by growing reasoning capabilities, large language models (LLMs) offer a promising path to enhance healthcare predictions by drawing on their rich parametric knowledge. However, LLMs are prone to factual inaccuracies due to limitations in the reliability and coverage of their embedded knowledge. While retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) frameworks, such as GraphRAG and its variants, have been proposed to mitigate these issues by incorporating external knowledge, they face two key challenges in the healthcare scenario: (1) identifying the clinical necessity to activate the retrieval mechanism, and (2) achieving synergy between the retriever and the generator to craft contextually appropriate retrievals. To address these challenges, we propose GHAR, a \underline{g}enerative \underline{h}ierarchical \underline{a}gentic \underline{R}AG framework that simultaneously resolves when to retrieve and how to optimize the collaboration between submodules in healthcare. Specifically, for the first challenge, we design a dual-agent architecture comprising Agent-Top and Agent-Low. Agent-Top acts as the primary physician, iteratively deciding whether to rely on parametric knowledge or to initiate retrieval, while Agent-Low acts as the consulting service, summarising all task-relevant knowledge once retrieval was triggered. To tackle the second challenge, we innovatively unify the optimization of both agents within a formal Markov Decision Process, designing diverse rewards to align their shared goal of accurate prediction while preserving their distinct roles. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets across three popular tasks demonstrate our superiority over state-of-the-art baselines, highlighting the potential of hierarchical agentic RAG in advancing healthcare systems.
Diffmv: A Unified Diffusion Framework for Healthcare Predictions with Random Missing Views and View Laziness
May 17, 2025Abstract:Advanced healthcare predictions offer significant improvements in patient outcomes by leveraging predictive analytics. Existing works primarily utilize various views of Electronic Health Record (EHR) data, such as diagnoses, lab tests, or clinical notes, for model training. These methods typically assume the availability of complete EHR views and that the designed model could fully leverage the potential of each view. However, in practice, random missing views and view laziness present two significant challenges that hinder further improvements in multi-view utilization. To address these challenges, we introduce Diffmv, an innovative diffusion-based generative framework designed to advance the exploitation of multiple views of EHR data. Specifically, to address random missing views, we integrate various views of EHR data into a unified diffusion-denoising framework, enriched with diverse contextual conditions to facilitate progressive alignment and view transformation. To mitigate view laziness, we propose a novel reweighting strategy that assesses the relative advantages of each view, promoting a balanced utilization of various data views within the model. Our proposed strategy achieves superior performance across multiple health prediction tasks derived from three popular datasets, including multi-view and multi-modality scenarios.
Instruct-of-Reflection: Enhancing Large Language Models Iterative Reflection Capabilities via Dynamic-Meta Instruction
Mar 02, 2025



Abstract:Self-reflection for Large Language Models (LLMs) has gained significant attention. Existing approaches involve models iterating and improving their previous responses based on LLMs' internal reflection ability or external feedback. However, recent research has raised doubts about whether intrinsic self-correction without external feedback may even degrade performance. Based on our empirical evidence, we find that current static reflection methods may lead to redundant, drift, and stubborn issues. To mitigate this, we introduce Instruct-of-Reflection (IoRT), a novel and general reflection framework that leverages dynamic-meta instruction to enhance the iterative reflection capability of LLMs. Specifically, we propose the instructor driven by the meta-thoughts and self-consistency classifier, generates various instructions, including refresh, stop, and select, to guide the next reflection iteration. Our experiments demonstrate that IoRT achieves an average improvement of 10.1% over established baselines in mathematical and commonsense reasoning tasks, highlighting its efficacy and applicability.
Collaborative Knowledge Fusion: A Novel Approach for Multi-task Recommender Systems via LLMs
Oct 28, 2024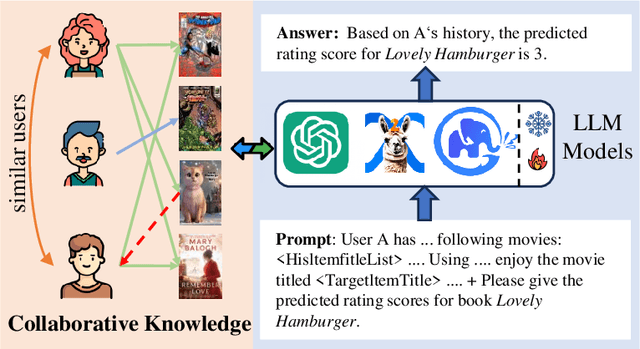
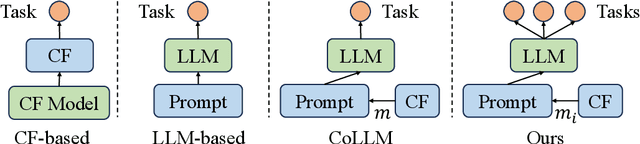
Abstract:Owing to the impressive general intelligence of large language models (LLMs), there has been a growing trend to integrate them into recommender systems to gain a more profound insight into human interests and intentions. Existing LLMs-based recommender systems primarily leverage item attributes and user interaction histories in textual format, improving the single task like rating prediction or explainable recommendation. Nevertheless, these approaches overlook the crucial contribution of traditional collaborative signals in discerning users' profound intentions and disregard the interrelatedness among tasks. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel framework known as CKF, specifically developed to boost multi-task recommendations via personalized collaborative knowledge fusion into LLMs. Specifically, our method synergizes traditional collaborative filtering models to produce collaborative embeddings, subsequently employing the meta-network to construct personalized mapping bridges tailored for each user. Upon mapped, the embeddings are incorporated into meticulously designed prompt templates and then fed into an advanced LLM to represent user interests. To investigate the intrinsic relationship among diverse recommendation tasks, we develop Multi-Lora, a new parameter-efficient approach for multi-task optimization, adept at distinctly segregating task-shared and task-specific information. This method forges a connection between LLMs and recommendation scenarios, while simultaneously enriching the supervisory signal through mutual knowledge transfer among various tasks. Extensive experiments and in-depth robustness analyses across four common recommendation tasks on four large public data sets substantiate the effectiveness and superiority of our framework.
GANPrompt: Enhancing Robustness in LLM-Based Recommendations with GAN-Enhanced Diversity Prompts
Aug 19, 2024
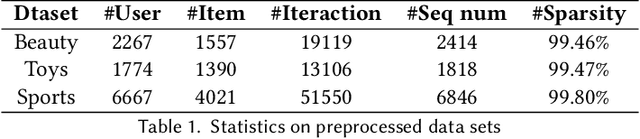


Abstract:In recent years, LLM has demonstrated remarkable proficiency in comprehending and generating natural language, with a growing prevalence in the domain of recommender systems. However, LLM continues to face a significant challenge in that it is highly susceptible to the influence of prompt words. This inconsistency in response to minor alterations in prompt input may compromise the accuracy and resilience of recommendation models. To address this issue, this paper proposes GANPrompt, a multi-dimensional large language model prompt diversity framework based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). The framework enhances the model's adaptability and stability to diverse prompts by integrating GAN generation techniques with the deep semantic understanding capabilities of LLMs. GANPrompt first trains a generator capable of producing diverse prompts by analysing multidimensional user behavioural data. These diverse prompts are then used to train the LLM to improve its performance in the face of unseen prompts. Furthermore, to ensure a high degree of diversity and relevance of the prompts, this study introduces a mathematical theory-based diversity constraint mechanism that optimises the generated prompts to ensure that they are not only superficially distinct, but also semantically cover a wide range of user intentions. Through extensive experiments on multiple datasets, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework, especially in improving the adaptability and robustness of recommender systems in complex and dynamic environments. The experimental results demonstrate that GANPrompt yields substantial enhancements in accuracy and robustness relative to existing state-of-the-art methodologies.
MobileExperts: A Dynamic Tool-Enabled Agent Team in Mobile Devices
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:The attainment of autonomous operations in mobile computing devices has consistently been a goal of human pursuit. With the development of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Visual Language Models (VLMs), this aspiration is progressively turning into reality. While contemporary research has explored automation of simple tasks on mobile devices via VLMs, there remains significant room for improvement in handling complex tasks and reducing high reasoning costs. In this paper, we introduce MobileExperts, which for the first time introduces tool formulation and multi-agent collaboration to address the aforementioned challenges. More specifically, MobileExperts dynamically assembles teams based on the alignment of agent portraits with the human requirements. Following this, each agent embarks on an independent exploration phase, formulating its tools to evolve into an expert. Lastly, we develop a dual-layer planning mechanism to establish coordinate collaboration among experts. To validate our effectiveness, we design a new benchmark of hierarchical intelligence levels, offering insights into algorithm's capability to address tasks across a spectrum of complexity. Experimental results demonstrate that MobileExperts performs better on all intelligence levels and achieves ~ 22% reduction in reasoning costs, thus verifying the superiority of our design.
Performative Debias with Fair-exposure Optimization Driven by Strategic Agents in Recommender Systems
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:Data bias, e.g., popularity impairs the dynamics of two-sided markets within recommender systems. This overshadows the less visible but potentially intriguing long-tail items that could capture user interest. Despite the abundance of research surrounding this issue, it still poses challenges and remains a hot topic in academic circles. Along this line, in this paper, we developed a re-ranking approach in dynamic settings with fair-exposure optimization driven by strategic agents. Designed for the producer side, the execution of agents assumes content creators can modify item features based on strategic incentives to maximize their exposure. This iterative process entails an end-to-end optimization, employing differentiable ranking operators that simultaneously target accuracy and fairness. Joint objectives ensure the performance of recommendations while enhancing the visibility of tail items. We also leveraged the performativity nature of predictions to illustrate how strategic learning influences content creators to shift towards fairness efficiently, thereby incentivizing features of tail items. Through comprehensive experiments on both public and industrial datasets, we have substantiated the effectiveness and dominance of the proposed method especially on unveiling the potential of tail items.
Cross-domain Transfer of Valence Preferences via a Meta-optimization Approach
Jun 24, 2024



Abstract:Cross-domain recommendation offers a potential avenue for alleviating data sparsity and cold-start problems. Embedding and mapping, as a classic cross-domain research genre, aims to identify a common mapping function to perform representation transformation between two domains. Nevertheless, previous coarse-grained preference representations, non-personalized mapping functions, and excessive reliance on overlapping users limit their performance, especially in scenarios where overlapping users are sparse. To address aforementioned challenges, we propose a novel cross-domain approach, namely CVPM. CVPM formalizes cross-domain interest transfer as a hybrid architecture of parametric meta-learning and self-supervised learning, which not only transfers user preferences at a finer level, but also enables signal enhancement with the knowledge of non-overlapping users. Specifically, with deep insights into user preferences and valence preference theory, we believe that there exists significant difference between users' positive preferences and negative behaviors, and thus employ differentiated encoders to learn their distributions. In particular, we further utilize the pre-trained model and item popularity to sample pseudo-interaction items to ensure the integrity of both distributions. To guarantee the personalization of preference transfer, we treat each user's mapping as two parts, the common transformation and the personalized bias, where the network used to generate the personalized bias is output by a meta-learner. Furthermore, in addition to the supervised loss for overlapping users, we design contrastive tasks for non-overlapping users from both group and individual-levels to avoid model skew and enhance the semantics of representations. Exhaustive data analysis and extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and advancement of our proposed framework.
Bi-discriminator Domain Adversarial Neural Networks with Class-Level Gradient Alignment
Nov 01, 2023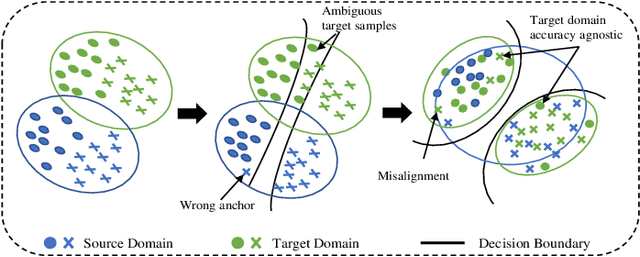
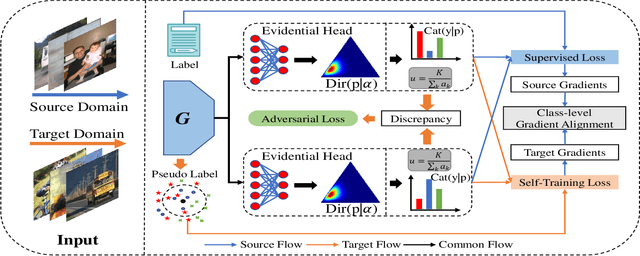
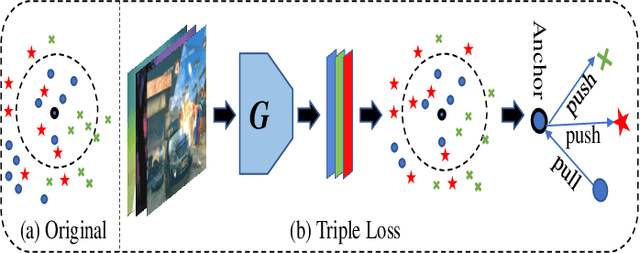
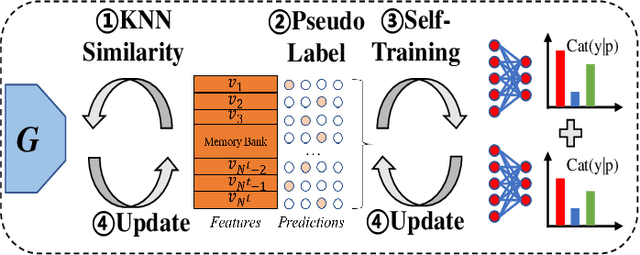
Abstract:Unsupervised domain adaptation aims to transfer rich knowledge from the annotated source domain to the unlabeled target domain with the same label space. One prevalent solution is the bi-discriminator domain adversarial network, which strives to identify target domain samples outside the support of the source domain distribution and enforces their classification to be consistent on both discriminators. Despite being effective, agnostic accuracy and overconfident estimation for out-of-distribution samples hinder its further performance improvement. To address the above challenges, we propose a novel bi-discriminator domain adversarial neural network with class-level gradient alignment, i.e. BACG. BACG resorts to gradient signals and second-order probability estimation for better alignment of domain distributions. Specifically, for accuracy-awareness, we first design an optimizable nearest neighbor algorithm to obtain pseudo-labels of samples in the target domain, and then enforce the backward gradient approximation of the two discriminators at the class level. Furthermore, following evidential learning theory, we transform the traditional softmax-based optimization method into a Multinomial Dirichlet hierarchical model to infer the class probability distribution as well as samples uncertainty, thereby alleviating misestimation of out-of-distribution samples and guaranteeing high-quality classes alignment. In addition, inspired by contrastive learning, we develop a memory bank-based variant, i.e. Fast-BACG, which can greatly shorten the training process at the cost of a minor decrease in accuracy. Extensive experiments and detailed theoretical analysis on four benchmark data sets validate the effectiveness and robustness of our algorithm.
Cross-domain recommendation via user interest alignment
Jan 26, 2023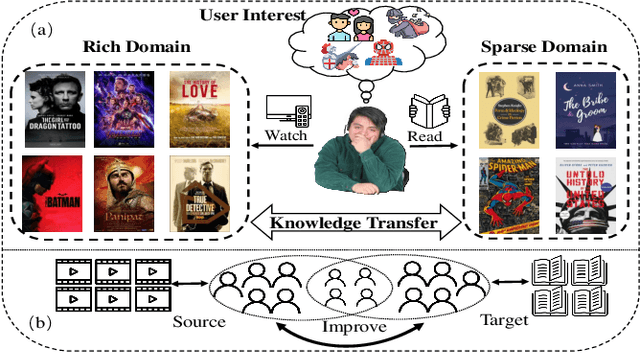
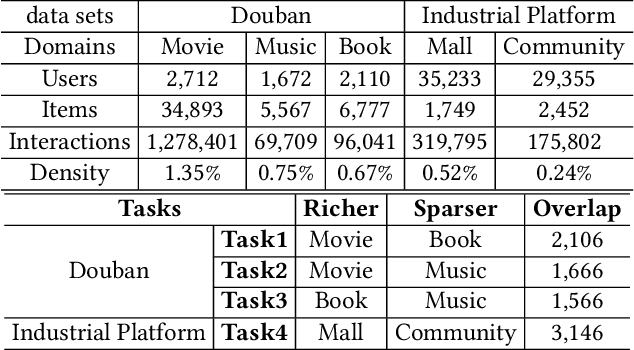

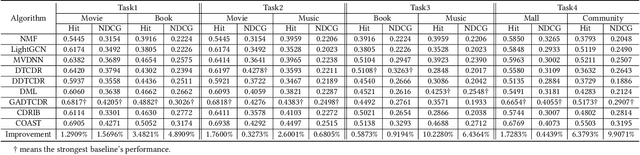
Abstract:Cross-domain recommendation aims to leverage knowledge from multiple domains to alleviate the data sparsity and cold-start problems in traditional recommender systems. One popular paradigm is to employ overlapping user representations to establish domain connections, thereby improving recommendation performance in all scenarios. Nevertheless, the general practice of this approach is to train user embeddings in each domain separately and then aggregate them in a plain manner, often ignoring potential cross-domain similarities between users and items. Furthermore, considering that their training objective is recommendation task-oriented without specific regularizations, the optimized embeddings disregard the interest alignment among user's views, and even violate the user's original interest distribution. To address these challenges, we propose a novel cross-domain recommendation framework, namely COAST, to improve recommendation performance on dual domains by perceiving the cross-domain similarity between entities and aligning user interests. Specifically, we first construct a unified cross-domain heterogeneous graph and redefine the message passing mechanism of graph convolutional networks to capture high-order similarity of users and items across domains. Targeted at user interest alignment, we develop deep insights from two more fine-grained perspectives of user-user and user-item interest invariance across domains by virtue of affluent unsupervised and semantic signals. We conduct intensive experiments on multiple tasks, constructed from two large recommendation data sets. Extensive results show COAST consistently and significantly outperforms state-of-the-art cross-domain recommendation algorithms as well as classic single-domain recommendation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge