Cengiz Pehlevan
Anytime Pretraining: Horizon-Free Learning-Rate Schedules with Weight Averaging
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large language models are increasingly trained in continual or open-ended settings, where the total training horizon is not known in advance. Despite this, most existing pretraining recipes are not anytime: they rely on horizon-dependent learning rate schedules and extensive tuning under a fixed compute budget. In this work, we provide a theoretical analysis demonstrating the existence of anytime learning schedules for overparameterized linear regression, and we highlight the central role of weight averaging - also known as model merging - in achieving the minimax convergence rates of stochastic gradient descent. We show that these anytime schedules polynomially decay with time, with the decay rate determined by the source and capacity conditions of the problem. Empirically, we evaluate 150M and 300M parameter language models trained at 1-32x Chinchilla scale, comparing constant learning rates with weight averaging and $1/\sqrt{t}$ schedules with weight averaging against a well-tuned cosine schedule. Across the full training range, the anytime schedules achieve comparable final loss to cosine decay. Taken together, our results suggest that weight averaging combined with simple, horizon-free step sizes offers a practical and effective anytime alternative to cosine learning rate schedules for large language model pretraining.
Universal One-third Time Scaling in Learning Peaked Distributions
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Training large language models (LLMs) is computationally expensive, partly because the loss exhibits slow power-law convergence whose origin remains debatable. Through systematic analysis of toy models and empirical evaluation of LLMs, we show that this behavior can arise intrinsically from the use of softmax and cross-entropy. When learning peaked probability distributions, e.g., next-token distributions, these components yield power-law vanishing losses and gradients, creating a fundamental optimization bottleneck. This ultimately leads to power-law time scaling of the loss with a universal exponent of $1/3$. Our results provide a mechanistic explanation for observed neural scaling and suggest new directions for improving LLM training efficiency.
Hyperparameter Transfer with Mixture-of-Expert Layers
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) layers have emerged as an important tool in scaling up modern neural networks by decoupling total trainable parameters from activated parameters in the forward pass for each token. However, sparse MoEs add complexity to training due to (i) new trainable parameters (router weights) that, like all other parameter groups, require hyperparameter (HP) tuning; (ii) new architecture scale dimensions (number of and size of experts) that must be chosen and potentially taken large. To make HP selection cheap and reliable, we propose a new parameterization for transformer models with MoE layers when scaling model width, depth, number of experts, and expert (hidden) size. Our parameterization is justified by a novel dynamical mean-field theory (DMFT) analysis. When varying different model dimensions trained at a fixed token budget, we find empirically that our parameterization enables reliable HP transfer across models from 51M to over 2B total parameters. We further take HPs identified from sweeping small models on a short token horizon to train larger models on longer horizons and report performant model behaviors.
Disordered Dynamics in High Dimensions: Connections to Random Matrices and Machine Learning
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:We provide an overview of high dimensional dynamical systems driven by random matrices, focusing on applications to simple models of learning and generalization in machine learning theory. Using both cavity method arguments and path integrals, we review how the behavior of a coupled infinite dimensional system can be characterized as a stochastic process for each single site of the system. We provide a pedagogical treatment of dynamical mean field theory (DMFT), a framework that can be flexibly applied to these settings. The DMFT single site stochastic process is fully characterized by a set of (two-time) correlation and response functions. For linear time-invariant systems, we illustrate connections between random matrix resolvents and the DMFT response. We demonstrate applications of these ideas to machine learning models such as gradient flow, stochastic gradient descent on random feature models and deep linear networks in the feature learning regime trained on random data. We demonstrate how bias and variance decompositions (analysis of ensembling/bagging etc) can be computed by averaging over subsets of the DMFT noise variables. From our formalism we also investigate how linear systems driven with random non-Hermitian matrices (such as random feature models) can exhibit non-monotonic loss curves with training time, while Hermitian matrices with the matching spectra do not, highlighting a different mechanism for non-monotonicity than small eigenvalues causing instability to label noise. Lastly, we provide asymptotic descriptions of the training and test loss dynamics for randomly initialized deep linear neural networks trained in the feature learning regime with high-dimensional random data. In this case, the time translation invariance structure is lost and the hidden layer weights are characterized as spiked random matrices.
Demystifying LLM-as-a-Judge: Analytically Tractable Model for Inference-Time Scaling
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Recent developments in large language models have shown advantages in reallocating a notable share of computational resource from training time to inference time. However, the principles behind inference time scaling are not well understood. In this paper, we introduce an analytically tractable model of inference-time scaling: Bayesian linear regression with a reward-weighted sampler, where the reward is determined from a linear model, modeling LLM-as-a-judge scenario. We study this problem in the high-dimensional regime, where the deterministic equivalents dictate a closed-form expression for the posterior predictive mean and variance. We analyze the generalization error when training data are sampled from a teacher model. We draw $k$ inference-time samples and select via softmax at a temperature applied to a quadratic reward. When the reward is not too different from the teacher, the generalization error decreases monotonically with increasing inference time samples $k$. However, the specific reward that optimizes inference-time selection generally differs from the teacher. In contrast, substantial reward misspecification induces a finite optimal $k$ beyond which more sampling can increase the generalization error. For fixed $k$, there exists an optimal sampling temperature. We experimentally verify these facts in large language model inference with an additional large language model as a judge. In the "best-of-$k$" limit with the teacher as reward, we theoretically show that the generalization error decays as $Θ(1/k^2)$ and determine the leading coefficient via extreme value theory. These formulas delineate domains where scaling inference-time computation is provably preferable to collecting more data. Finally, we demonstrate that when task difficulty increases, the previously mentioned advantage of inference-time compute degrades.
Pretrain-Test Task Alignment Governs Generalization in In-Context Learning
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) is a central capability of Transformer models, but the structures in data that enable its emergence and govern its robustness remain poorly understood. In this work, we study how the structure of pretraining tasks governs generalization in ICL. Using a solvable model for ICL of linear regression by linear attention, we derive an exact expression for ICL generalization error in high dimensions under arbitrary pretraining-testing task covariance mismatch. This leads to a new alignment measure that quantifies how much information about the pretraining task distribution is useful for inference at test time. We show that this measure directly predicts ICL performance not only in the solvable model but also in nonlinear Transformers. Our analysis further reveals a tradeoff between specialization and generalization in ICL: depending on task distribution alignment, increasing pretraining task diversity can either improve or harm test performance. Together, these results identify train-test task alignment as a key determinant of generalization in ICL.
A Simplified Analysis of SGD for Linear Regression with Weight Averaging
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Theoretically understanding stochastic gradient descent (SGD) in overparameterized models has led to the development of several optimization algorithms that are widely used in practice today. Recent work by~\citet{zou2021benign} provides sharp rates for SGD optimization in linear regression using constant learning rate, both with and without tail iterate averaging, based on a bias-variance decomposition of the risk. In our work, we provide a simplified analysis recovering the same bias and variance bounds provided in~\citep{zou2021benign} based on simple linear algebra tools, bypassing the requirement to manipulate operators on positive semi-definite (PSD) matrices. We believe our work makes the analysis of SGD on linear regression very accessible and will be helpful in further analyzing mini-batching and learning rate scheduling, leading to improvements in the training of realistic models.
Don't be lazy: CompleteP enables compute-efficient deep transformers
May 02, 2025Abstract:We study compute efficiency of LLM training when using different parameterizations, i.e., rules for adjusting model and optimizer hyperparameters (HPs) as model size changes. Some parameterizations fail to transfer optimal base HPs (such as learning rate) across changes in model depth, requiring practitioners to either re-tune these HPs as they scale up (expensive), or accept sub-optimal training when re-tuning is prohibitive. Even when they achieve HP transfer, we develop theory to show parameterizations may still exist in the lazy learning regime where layers learn only features close to their linearization, preventing effective use of depth and nonlinearity. Finally, we identify and adopt the unique parameterization we call CompleteP that achieves both depth-wise HP transfer and non-lazy learning in all layers. CompleteP enables a wider range of model width/depth ratios to remain compute-efficient, unlocking shapes better suited for different hardware settings and operational contexts. Moreover, CompleteP enables 12-34\% compute efficiency improvements over the prior state-of-the-art.
Error Broadcast and Decorrelation as a Potential Artificial and Natural Learning Mechanism
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce the Error Broadcast and Decorrelation (EBD) algorithm, a novel learning framework that addresses the credit assignment problem in neural networks by directly broadcasting output error to individual layers. Leveraging the stochastic orthogonality property of the optimal minimum mean square error (MMSE) estimator, EBD defines layerwise loss functions to penalize correlations between layer activations and output errors, offering a principled approach to error broadcasting without the need for weight transport. The optimization framework naturally leads to the experimentally observed three-factor learning rule and integrates with biologically plausible frameworks to enhance performance and plausibility. Numerical experiments demonstrate that EBD achieves performance comparable to or better than known error-broadcast methods on benchmark datasets. While the scalability of EBD to very large or complex datasets remains to be further explored, our findings suggest it provides a biologically plausible, efficient, and adaptable alternative for neural network training. This approach could inform future advancements in artificial and natural learning paradigms.
Echo Chamber: RL Post-training Amplifies Behaviors Learned in Pretraining
Apr 10, 2025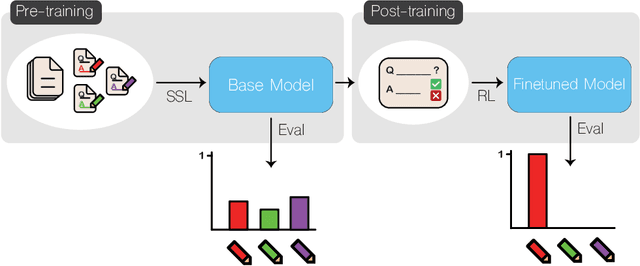
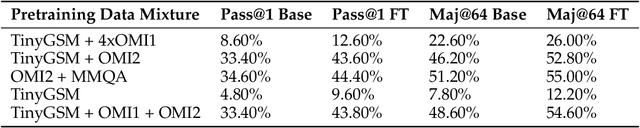
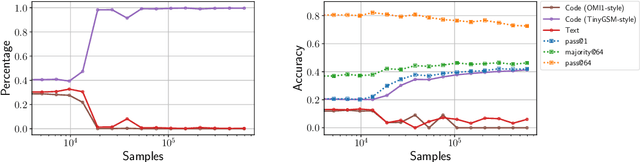
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL)-based fine-tuning has become a crucial step in post-training language models for advanced mathematical reasoning and coding. Following the success of frontier reasoning models, recent work has demonstrated that RL fine-tuning consistently improves performance, even in smaller-scale models; however, the underlying mechanisms driving these improvements are not well-understood. Understanding the effects of RL fine-tuning requires disentangling its interaction with pretraining data composition, hyperparameters, and model scale, but such problems are exacerbated by the lack of transparency regarding the training data used in many existing models. In this work, we present a systematic end-to-end study of RL fine-tuning for mathematical reasoning by training models entirely from scratch on different mixtures of fully open datasets. We investigate the effects of various RL fine-tuning algorithms (PPO, GRPO, and Expert Iteration) across models of different scales. Our study reveals that RL algorithms consistently converge towards a dominant output distribution, amplifying patterns in the pretraining data. We also find that models of different scales trained on the same data mixture will converge to distinct output distributions, suggesting that there are scale-dependent biases in model generalization. Moreover, we find that RL post-training on simpler questions can lead to performance gains on harder ones, indicating that certain reasoning capabilities generalize across tasks. Our findings show that small-scale proxies in controlled settings can elicit interesting insights regarding the role of RL in shaping language model behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge