Bo Shao
A lightweight YOLOv5-FFM model for occlusion pedestrian detection
Aug 13, 2024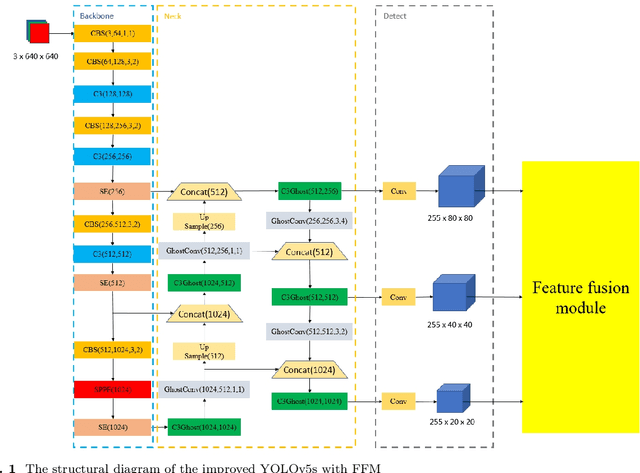



Abstract:The development of autonomous driving technology must be inseparable from pedestrian detection. Because of the fast speed of the vehicle, the accuracy and real-time performance of the pedestrian detection algorithm are very important. YOLO, as an efficient and simple one-stage target detection method, is often used for pedestrian detection in various environments. However, this series of detectors face some challenges, such as excessive computation and undesirable detection rate when facing occluded pedestrians. In this paper, we propose an improved lightweight YOLOv5 model to deal with these problems. This model can achieve better pedestrian detection accuracy with fewer floating-point operations (FLOPs), especially for occluded targets. In order to achieve the above goals, we made improvements based on the YOLOv5 model framework and introduced Ghost module and SE block. Furthermore, we designed a local feature fusion module (FFM) to deal with occlusion in pedestrian detection. To verify the validity of our method, two datasets, Citypersons and CUHK Occlusion, were selected for the experiment. The experimental results show that, compared with the original yolov5s model, the average precision (AP) of our method is significantly improved, while the number of parameters is reduced by 27.9% and FLOPs are reduced by 19.0%.
Unified-IoU: For High-Quality Object Detection
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:Object detection is an important part in the field of computer vision, and the effect of object detection is directly determined by the regression accuracy of the prediction box. As the key to model training, IoU (Intersection over Union) greatly shows the difference between the current prediction box and the Ground Truth box. Subsequent researchers have continuously added more considerations to IoU, such as center distance, aspect ratio, and so on. However, there is an upper limit to just refining the geometric differences; And there is a potential connection between the new consideration index and the IoU itself, and the direct addition or subtraction between the two may lead to the problem of "over-consideration". Based on this, we propose a new IoU loss function, called Unified-IoU (UIoU), which is more concerned with the weight assignment between different quality prediction boxes. Specifically, the loss function dynamically shifts the model's attention from low-quality prediction boxes to high-quality prediction boxes in a novel way to enhance the model's detection performance on high-precision or intensive datasets and achieve a balance in training speed. Our proposed method achieves better performance on multiple datasets, especially at a high IoU threshold, UIoU has a more significant improvement effect compared with other improved IoU losses. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/lxj-drifter/UIOU_files.
BMIKE-53: Investigating Cross-Lingual Knowledge Editing with In-Context Learning
Jun 25, 2024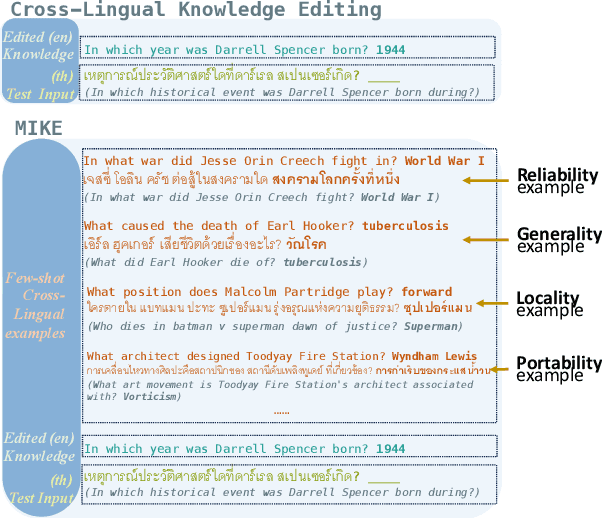
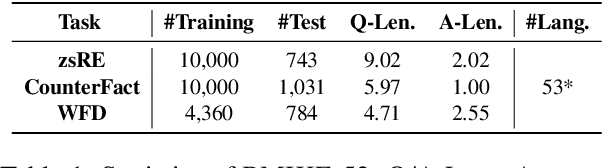
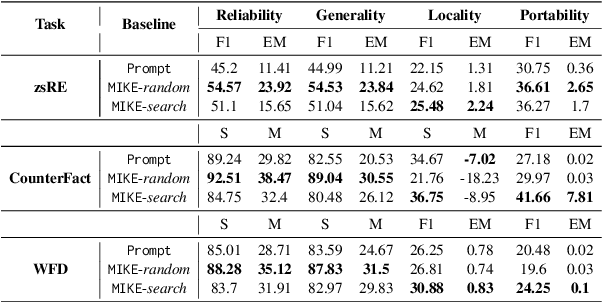
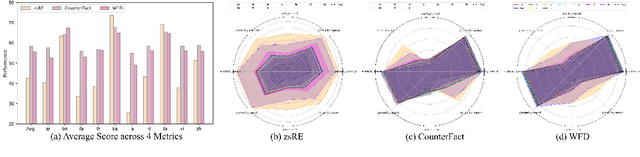
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) possess extensive parametric knowledge, but this knowledge is difficult to update with new information because retraining is very expensive and infeasible for closed-source models. Knowledge editing (KE) has emerged as a viable solution for updating the knowledge of LLMs without compromising their overall performance. On-the-fly KE methods, inspired by in-context learning (ICL), have shown great promise and allow LLMs to be treated as black boxes. In the past, KE was primarily employed in English contexts, whereas the potential for cross-lingual KE in current English-centric LLMs has not been fully explored. To foster more research in this direction, we introduce the BMIKE-53 benchmark for evaluating cross-lingual KE on 53 diverse languages across three KE task types. We also propose a gradient-free KE method called Multilingual In-context Knowledge Editing (MIKE) and evaluate it on BMIKE-53. Our evaluation focuses on cross-lingual knowledge transfer in terms of reliability, generality, locality, and portability, offering valuable insights and a framework for future research in cross-lingual KE. Our code and data are publicly accessible via the anonymous repository at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/MIKE.
Hypertext Entity Extraction in Webpage
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Webpage entity extraction is a fundamental natural language processing task in both research and applications. Nowadays, the majority of webpage entity extraction models are trained on structured datasets which strive to retain textual content and its structure information. However, existing datasets all overlook the rich hypertext features (e.g., font color, font size) which show their effectiveness in previous works. To this end, we first collect a \textbf{H}ypertext \textbf{E}ntity \textbf{E}xtraction \textbf{D}ataset (\textit{HEED}) from the e-commerce domains, scraping both the text and the corresponding explicit hypertext features with high-quality manual entity annotations. Furthermore, we present the \textbf{Mo}E-based \textbf{E}ntity \textbf{E}xtraction \textbf{F}ramework (\textit{MoEEF}), which efficiently integrates multiple features to enhance model performance by Mixture of Experts and outperforms strong baselines, including the state-of-the-art small-scale models and GPT-3.5-turbo. Moreover, the effectiveness of hypertext features in \textit{HEED} and several model components in \textit{MoEEF} are analyzed.
ProphetNet-Ads: A Looking Ahead Strategy for Generative Retrieval Models in Sponsored Search Engine
Oct 21, 2020



Abstract:In a sponsored search engine, generative retrieval models are recently proposed to mine relevant advertisement keywords for users' input queries. Generative retrieval models generate outputs token by token on a path of the target library prefix tree (Trie), which guarantees all of the generated outputs are legal and covered by the target library. In actual use, we found several typical problems caused by Trie-constrained searching length. In this paper, we analyze these problems and propose a looking ahead strategy for generative retrieval models named ProphetNet-Ads. ProphetNet-Ads improves the retrieval ability by directly optimizing the Trie-constrained searching space. We build a dataset from a real-word sponsored search engine and carry out experiments to analyze different generative retrieval models. Compared with Trie-based LSTM generative retrieval model proposed recently, our single model result and integrated result improve the recall by 15.58\% and 18.8\% respectively with beam size 5. Case studies further demonstrate how these problems are alleviated by ProphetNet-Ads clearly.
Diverse, Controllable, and Keyphrase-Aware: A Corpus and Method for News Multi-Headline Generation
Apr 08, 2020



Abstract:News headline generation aims to produce a short sentence to attract readers to read the news. One news article often contains multiple keyphrases that are of interest to different users, which can naturally have multiple reasonable headlines. However, most existing methods focus on the single headline generation. In this paper, we propose generating multiple headlines with keyphrases of user interests, whose main idea is to generate multiple keyphrases of interest to users for the news first, and then generate multiple keyphrase-relevant headlines. We propose a multi-source Transformer decoder, which takes three sources as inputs: (a) keyphrase, (b) keyphrase-filtered article, and (c) original article to generate keyphrase-relevant, high-quality, and diverse headlines. Furthermore, we propose a simple and effective method to mine the keyphrases of interest in the news article and build a first large-scale keyphrase-aware news headline corpus, which contains over 180K aligned triples of $<$news article, headline, keyphrase$>$. Extensive experimental comparisons on the real-world dataset show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results in terms of quality and diversity
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge