Behdad Chalaki
In Search of a Lost Metric: Human Empowerment as a Pillar of Socially Conscious Navigation
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:In social robot navigation, traditional metrics like proxemics and behavior naturalness emphasize human comfort and adherence to social norms but often fail to capture an agent's autonomy and adaptability in dynamic environments. This paper introduces human empowerment, an information-theoretic concept that measures a human's ability to influence their future states and observe those changes, as a complementary metric for evaluating social compliance. This metric reveals how robot navigation policies can indirectly impact human empowerment. We present a framework that integrates human empowerment into the evaluation of social performance in navigation tasks. Through numerical simulations, we demonstrate that human empowerment as a metric not only aligns with intuitive social behavior, but also shows statistically significant differences across various robot navigation policies. These results provide a deeper understanding of how different policies affect social compliance, highlighting the potential of human empowerment as a complementary metric for future research in social navigation.
Navigating Noisy Feedback: Enhancing Reinforcement Learning with Error-Prone Language Models
Oct 22, 2024Abstract:The correct specification of reward models is a well-known challenge in reinforcement learning. Hand-crafted reward functions often lead to inefficient or suboptimal policies and may not be aligned with user values. Reinforcement learning from human feedback is a successful technique that can mitigate such issues, however, the collection of human feedback can be laborious. Recent works have solicited feedback from pre-trained large language models rather than humans to reduce or eliminate human effort, however, these approaches yield poor performance in the presence of hallucination and other errors. This paper studies the advantages and limitations of reinforcement learning from large language model feedback and proposes a simple yet effective method for soliciting and applying feedback as a potential-based shaping function. We theoretically show that inconsistent rankings, which approximate ranking errors, lead to uninformative rewards with our approach. Our method empirically improves convergence speed and policy returns over commonly used baselines even with significant ranking errors, and eliminates the need for complex post-processing of reward functions.
Active Learning with Dual Model Predictive Path-Integral Control for Interaction-Aware Autonomous Highway On-ramp Merging
Oct 11, 2023



Abstract:Merging into dense highway traffic for an autonomous vehicle is a complex decision-making task, wherein the vehicle must identify a potential gap and coordinate with surrounding human drivers, each of whom may exhibit diverse driving behaviors. Many existing methods consider other drivers to be dynamic obstacles and, as a result, are incapable of capturing the full intent of the human drivers via this passive planning. In this paper, we propose a novel dual control framework based on Model Predictive Path-Integral control to generate interactive trajectories. This framework incorporates a Bayesian inference approach to actively learn the agents' parameters, i.e., other drivers' model parameters. The proposed framework employs a sampling-based approach that is suitable for real-time implementation through the utilization of GPUs. We illustrate the effectiveness of our proposed methodology through comprehensive numerical simulations conducted in both high and low-fidelity simulation scenarios focusing on autonomous on-ramp merging.
Multi-Robot Cooperative Navigation in Crowds: A Game-Theoretic Learning-Based Model Predictive Control Approach
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we develop a control framework for the coordination of multiple robots as they navigate through crowded environments. Our framework comprises of a local model predictive control (MPC) for each robot and a social long short-term memory model that forecasts pedestrians' trajectories. We formulate the local MPC formulation for each individual robot that includes both individual and shared objectives, in which the latter encourages the emergence of coordination among robots. Next, we consider the multi-robot navigation and human-robot interaction, respectively, as a potential game and a two-player game, then employ an iterative best response approach to solve the resulting optimization problems in a centralized and distributed fashion. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of coordination among robots in simulated crowd navigation.
Social Navigation in Crowded Environments with Model Predictive Control and Deep Learning-Based Human Trajectory Prediction
Sep 28, 2023



Abstract:Crowd navigation has received increasing attention from researchers over the last few decades, resulting in the emergence of numerous approaches aimed at addressing this problem to date. Our proposed approach couples agent motion prediction and planning to avoid the freezing robot problem while simultaneously capturing multi-agent social interactions by utilizing a state-of-the-art trajectory prediction model i.e., social long short-term memory model (Social-LSTM). Leveraging the output of Social-LSTM for the prediction of future trajectories of pedestrians at each time-step given the robot's possible actions, our framework computes the optimal control action using Model Predictive Control (MPC) for the robot to navigate among pedestrians. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach in multiple scenarios of simulated crowd navigation and compare it against several state-of-the-art reinforcement learning-based methods.
MR-IDM -- Merge Reactive Intelligent Driver Model: Towards Enhancing Laterally Aware Car-following Models
May 19, 2023Abstract:This paper discusses the limitations of existing microscopic traffic models in accounting for the potential impacts of on-ramp vehicles on the car-following behavior of main-lane vehicles on highways. We first surveyed U.S. on-ramps to choose a representative set of on-ramps and then collected real-world observational data from the merging vehicle's perspective in various traffic conditions ranging from free-flowing to rush-hour traffic jams. Next, as our core contribution, we introduce a novel car-following model, called MR-IDM, for highway driving that reacts to merging vehicles in a realistic way. This proposed driving model can either be used in traffic simulators to generate realistic highway driving behavior or integrated into a prediction module for autonomous vehicles attempting to merge onto the highway. We quantitatively evaluated the effectiveness of our model and compared it against several other methods. We show that MR-IDM has the least error in mimicking the real-world data, while having features such as smoothness, stability, and lateral awareness.
Cooperative Energy and Time-Optimal Lane Change Maneuvers with Minimal Highway Traffic Disruption
Nov 16, 2022



Abstract:We derive optimal control policies for a Connected Automated Vehicle (CAV) and cooperating neighboring CAVs to carry out a lane change maneuver consisting of a longitudinal phase where the CAV properly positions itself relative to the cooperating neighbors and a lateral phase where it safely changes lanes. In contrast to prior work on this problem, where the CAV "selfishly" only seeks to minimize its maneuver time, we seek to ensure that the fast-lane traffic flow is minimally disrupted (through a properly defined metric). Additionally, when performing lane-changing maneuvers, we optimally select the cooperating vehicles from a set of feasible neighboring vehicles and experimentally show that the highway throughput is improved compared to the baseline case of human-driven vehicles changing lanes with no cooperation. When feasible solutions do not exist for a given maximal allowable disruption, we include a time relaxation method trading off a longer maneuver time with reduced disruption. Our analysis is also extended to multiple sequential maneuvers. Simulation results show the effectiveness of our controllers in terms of safety guarantees and up to 16% and 90% average throughput and maneuver time improvement respectively when compared to maneuvers with no cooperation.
A Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Coordination Framework for Connected and Automated Vehicles at Merging Roadways
Sep 23, 2021



Abstract:The steady increase in the number of vehicles operating on the highways continues to exacerbate congestion, accidents, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions. Emerging mobility systems, e.g., connected and automated vehicles (CAVs), have the potential to directly address these issues and improve transportation network efficiency and safety. In this paper, we consider a highway merging scenario and propose a framework for coordinating CAVs such that stop-and-go driving is eliminated. We use a decentralized form of the actor-critic approach to deep reinforcement learning$-$multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient. We demonstrate the coordination of CAVs through numerical simulations and show that a smooth traffic flow is achieved by eliminating stop-and-go driving. Videos and plots of the simulation results can be found at this supplemental $\href{https://sites.google.com/view/ud-ids-lab/MADRL}{site}$.
A Digital Smart City for Emerging Mobility Systems
Sep 14, 2021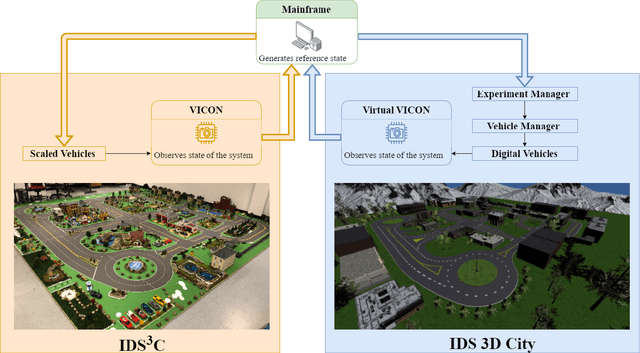
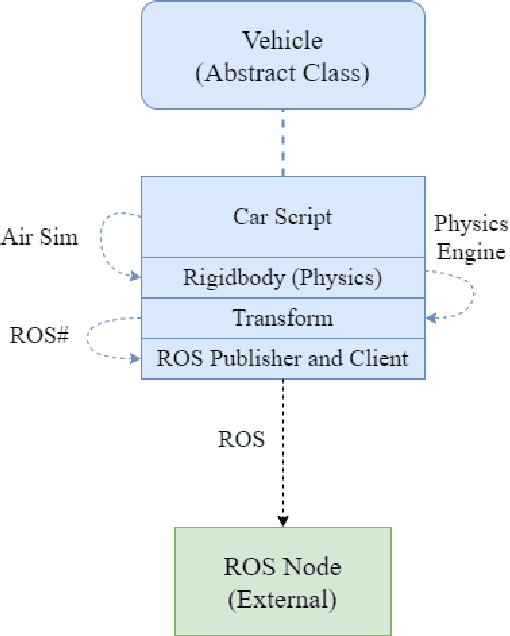
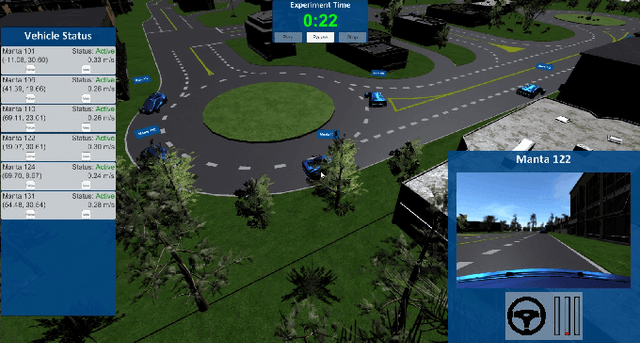
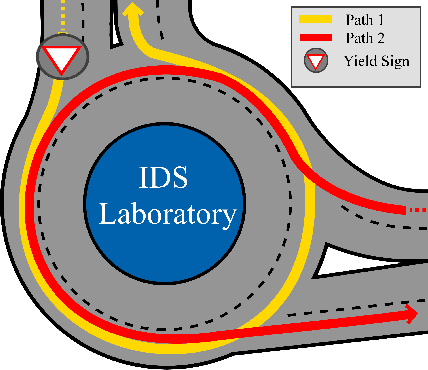
Abstract:The increasing demand for emerging mobility systems with connected and automated vehicles has imposed the necessity for quality testing environments to support their development. In this paper, we introduce a Unity-based virtual simulation environment for emerging mobility systems, called the Information and Decision Science Lab's Scaled Smart Digital City (IDS $3$D City), intended to operate alongside its physical peer and its established control framework. By utilizing the Robot Operation System, AirSim, and Unity, we constructed a simulation environment capable of iteratively designing experiments significantly faster than it is possible in a physical testbed. This environment provides an intermediate step to validate the effectiveness of our control algorithms prior to their implementation in the physical testbed. The IDS $3$D City also enables us to demonstrate that our control algorithms work independently of the underlying vehicle dynamics, as the vehicle dynamics introduced by AirSim operate at a different scale than our scaled smart city. Finally, we demonstrate the behavior of our digital environment by performing an experiment in both the virtual and physical environments and compare their outputs.
A Hysteretic Q-learning Coordination Framework for Emerging Mobility Systems in Smart Cities
Nov 05, 2020



Abstract:Connected and automated vehicles (CAVs) can alleviate traffic congestion, air pollution, and improve safety. In this paper, we provide a decentralized coordination framework for CAVs at a signal-free intersection to minimize travel time and improve fuel efficiency. We employ a simple yet powerful reinforcement learning approach, an off-policy temporal difference learning called Q-learning, enhanced with a coordination mechanism to address this problem. Then, we integrate a first-in-first-out queuing policy to improve the performance of our system. We demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed approach through simulation and comparison with the classical optimal control method based on Pontryagin's minimum principle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge