Beatriz Borges
CAVE: Detecting and Explaining Commonsense Anomalies in Visual Environments
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Humans can naturally identify, reason about, and explain anomalies in their environment. In computer vision, this long-standing challenge remains limited to industrial defects or unrealistic, synthetically generated anomalies, failing to capture the richness and unpredictability of real-world anomalies. In this work, we introduce CAVE, the first benchmark of real-world visual anomalies. CAVE supports three open-ended tasks: anomaly description, explanation, and justification; with fine-grained annotations for visual grounding and categorizing anomalies based on their visual manifestations, their complexity, severity, and commonness. These annotations draw inspiration from cognitive science research on how humans identify and resolve anomalies, providing a comprehensive framework for evaluating Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in detecting and understanding anomalies. We show that state-of-the-art VLMs struggle with visual anomaly perception and commonsense reasoning, even with advanced prompting strategies. By offering a realistic and cognitively grounded benchmark, CAVE serves as a valuable resource for advancing research in anomaly detection and commonsense reasoning in VLMs.
Could ChatGPT get an Engineering Degree? Evaluating Higher Education Vulnerability to AI Assistants
Aug 07, 2024
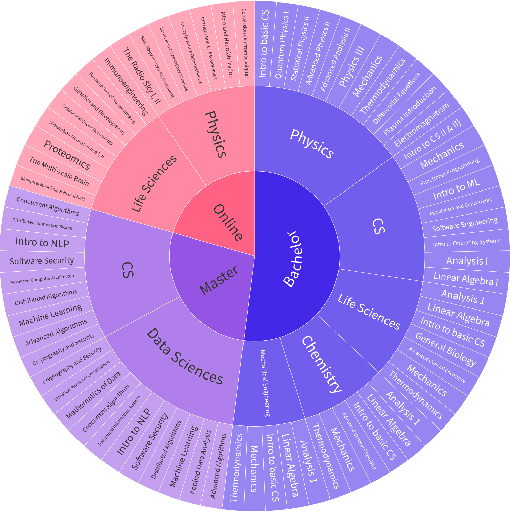
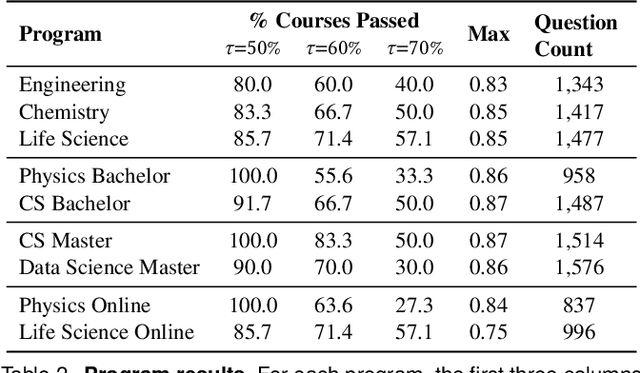

Abstract:AI assistants are being increasingly used by students enrolled in higher education institutions. While these tools provide opportunities for improved teaching and education, they also pose significant challenges for assessment and learning outcomes. We conceptualize these challenges through the lens of vulnerability, the potential for university assessments and learning outcomes to be impacted by student use of generative AI. We investigate the potential scale of this vulnerability by measuring the degree to which AI assistants can complete assessment questions in standard university-level STEM courses. Specifically, we compile a novel dataset of textual assessment questions from 50 courses at EPFL and evaluate whether two AI assistants, GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 can adequately answer these questions. We use eight prompting strategies to produce responses and find that GPT-4 answers an average of 65.8% of questions correctly, and can even produce the correct answer across at least one prompting strategy for 85.1% of questions. When grouping courses in our dataset by degree program, these systems already pass non-project assessments of large numbers of core courses in various degree programs, posing risks to higher education accreditation that will be amplified as these models improve. Our results call for revising program-level assessment design in higher education in light of advances in generative AI.
Let Me Teach You: Pedagogical Foundations of Feedback for Language Models
Jul 01, 2023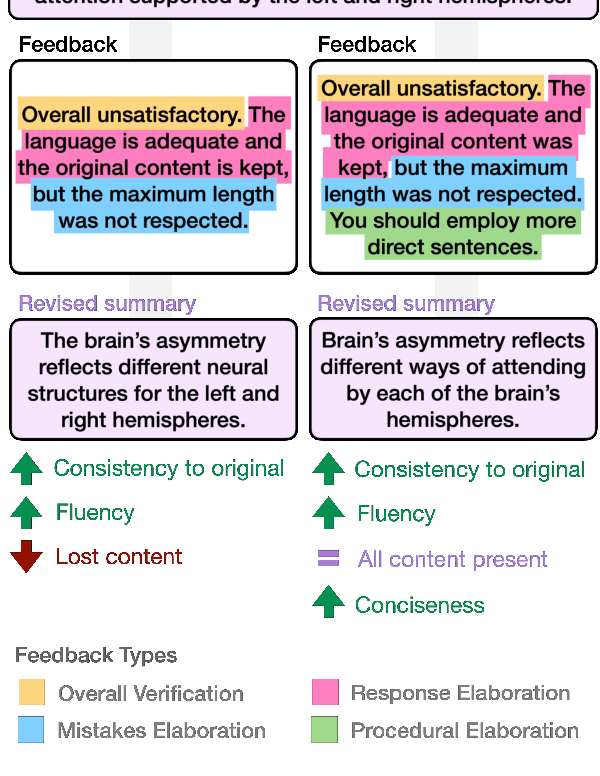
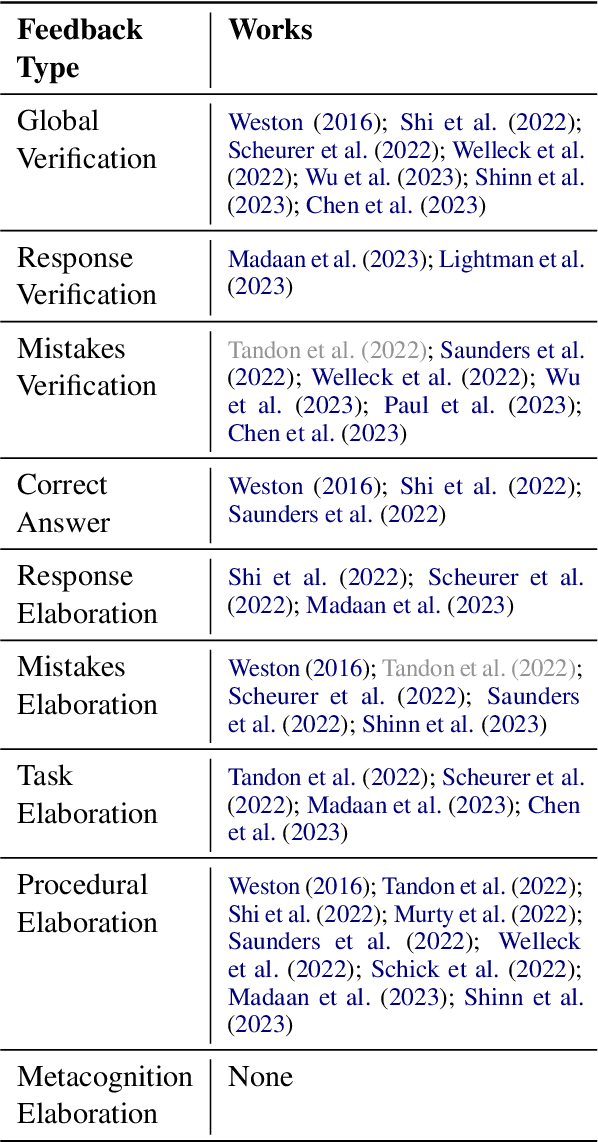
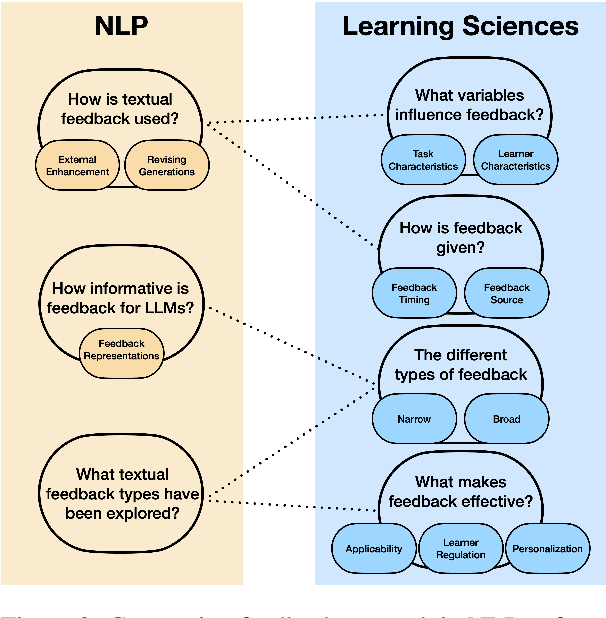
Abstract:Natural Language Feedback (NLF) is an increasingly popular avenue to align Large Language Models (LLMs) to human preferences. Despite the richness and diversity of the information it can convey, NLF is often hand-designed and arbitrary. In a different world, research in pedagogy has long established several effective feedback models. In this opinion piece, we compile ideas from pedagogy to introduce FELT, a feedback framework for LLMs that outlines the various characteristics of the feedback space, and a feedback content taxonomy based on these variables. Our taxonomy offers both a general mapping of the feedback space, as well as pedagogy-established discrete categories, allowing us to empirically demonstrate the impact of different feedback types on revised generations. In addition to streamlining existing NLF designs, FELT also brings out new, unexplored directions for research in NLF. We make our taxonomy available to the community, providing guides and examples for mapping our categorizations to future resources.
PeaCoK: Persona Commonsense Knowledge for Consistent and Engaging Narratives
May 03, 2023



Abstract:Sustaining coherent and engaging narratives requires dialogue or storytelling agents to understand how the personas of speakers or listeners ground the narrative. Specifically, these agents must infer personas of their listeners to produce statements that cater to their interests. They must also learn to maintain consistent speaker personas for themselves throughout the narrative, so that their counterparts feel involved in a realistic conversation or story. However, personas are diverse and complex: they entail large quantities of rich interconnected world knowledge that is challenging to robustly represent in general narrative systems (e.g., a singer is good at singing, and may have attended conservatoire). In this work, we construct a new large-scale persona commonsense knowledge graph, PeaCoK, containing ~100K human-validated persona facts. Our knowledge graph schematizes five dimensions of persona knowledge identified in previous studies of human interactive behaviours, and distils facts in this schema from both existing commonsense knowledge graphs and large-scale pretrained language models. Our analysis indicates that PeaCoK contains rich and precise world persona inferences that help downstream systems generate more consistent and engaging narratives.
REFINER: Reasoning Feedback on Intermediate Representations
Apr 04, 2023Abstract:Language models (LMs) have recently shown remarkable performance on reasoning tasks by explicitly generating intermediate inferences, e.g., chain-of-thought prompting. However, these intermediate inference steps may be inappropriate deductions from the initial context and lead to incorrect final predictions. Here we introduce REFINER, a framework for finetuning LMs to explicitly generate intermediate reasoning steps while interacting with a critic model that provides automated feedback on the reasoning. Specifically, the critic provides structured feedback that the reasoning LM uses to iteratively improve its intermediate arguments. Empirical evaluations of REFINER on three diverse reasoning tasks show significant improvements over baseline LMs of comparable scale. Furthermore, when using GPT3.5 as the reasoner, the trained critic significantly improves reasoning without finetuning the reasoner. Finally, our critic model is trained without expensive human-in-the-loop data but can be substituted with humans at inference time.
Laughing Heads: Can Transformers Detect What Makes a Sentence Funny?
May 19, 2021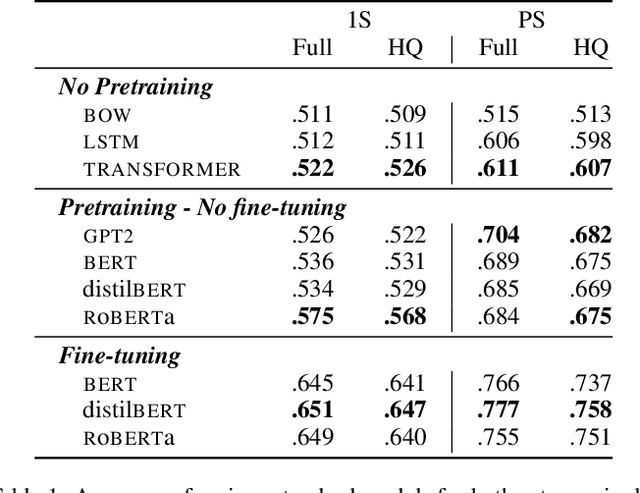
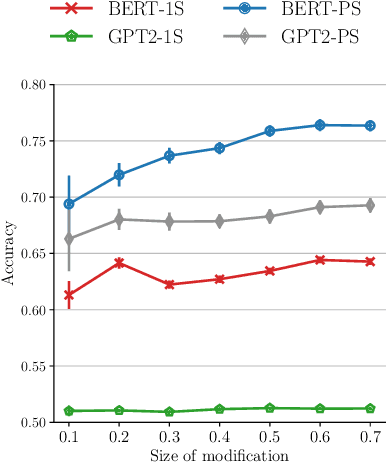
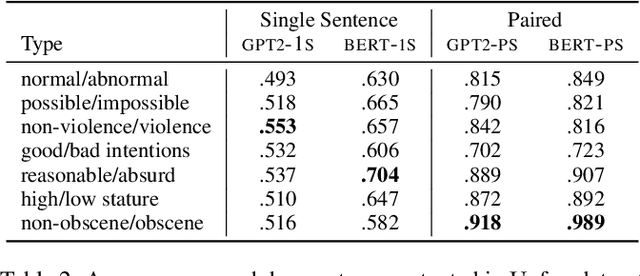
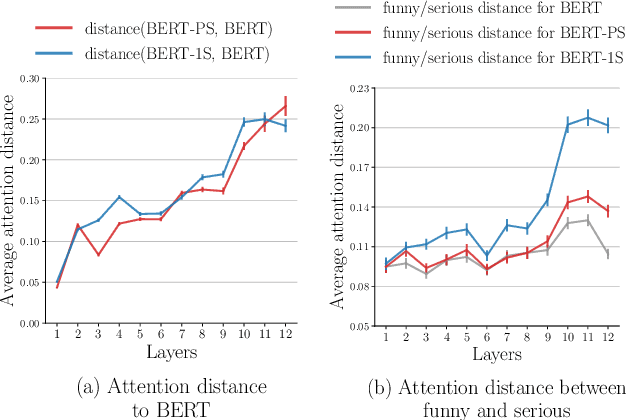
Abstract:The automatic detection of humor poses a grand challenge for natural language processing. Transformer-based systems have recently achieved remarkable results on this task, but they usually (1)~were evaluated in setups where serious vs humorous texts came from entirely different sources, and (2)~focused on benchmarking performance without providing insights into how the models work. We make progress in both respects by training and analyzing transformer-based humor recognition models on a recently introduced dataset consisting of minimal pairs of aligned sentences, one serious, the other humorous. We find that, although our aligned dataset is much harder than previous datasets, transformer-based models recognize the humorous sentence in an aligned pair with high accuracy (78%). In a careful error analysis, we characterize easy vs hard instances. Finally, by analyzing attention weights, we obtain important insights into the mechanisms by which transformers recognize humor. Most remarkably, we find clear evidence that one single attention head learns to recognize the words that make a test sentence humorous, even without access to this information at training time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge