Baoying Chen
MSPT: A Lightweight Face Image Quality Assessment Method with Multi-stage Progressive Training
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Accurately assessing the perceptual quality of face images is crucial, especially with the rapid progress in face restoration and generation. Traditional quality assessment methods often struggle with the unique characteristics of face images, limiting their generalizability. While learning-based approaches demonstrate superior performance due to their strong fitting capabilities, their high complexity typically incurs significant computational and storage costs, hindering practical deployment. To address this, we propose a lightweight face quality assessment network with Multi-Stage Progressive Training (MSPT). Our network employs a three-stage progressive training strategy that gradually introduces more diverse data samples and increases input image resolution. This novel approach enables lightweight networks to achieve high performance by effectively learning complex quality features while significantly mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Our MSPT achieved the second highest score on the VQualA 2025 face image quality assessment benchmark dataset, demonstrating that MSPT achieves comparable or better performance than state-of-the-art methods while maintaining efficient inference.
DFGC 2021: A DeepFake Game Competition
Jun 02, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents a summary of the DFGC 2021 competition. DeepFake technology is developing fast, and realistic face-swaps are increasingly deceiving and hard to detect. At the same time, DeepFake detection methods are also improving. There is a two-party game between DeepFake creators and detectors. This competition provides a common platform for benchmarking the adversarial game between current state-of-the-art DeepFake creation and detection methods. In this paper, we present the organization, results and top solutions of this competition and also share our insights obtained during this event. We also release the DFGC-21 testing dataset collected from our participants to further benefit the research community.
DeeperForensics Challenge 2020 on Real-World Face Forgery Detection: Methods and Results
Feb 18, 2021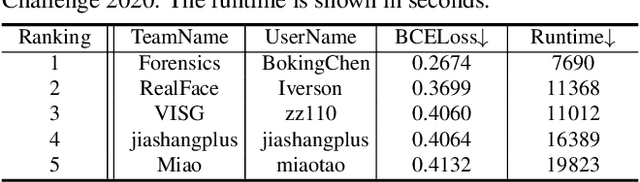
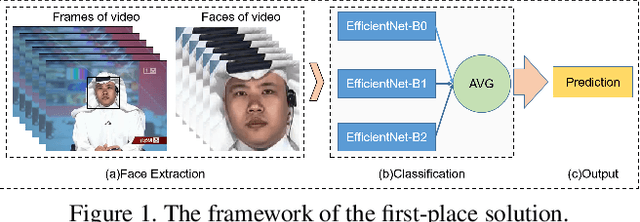
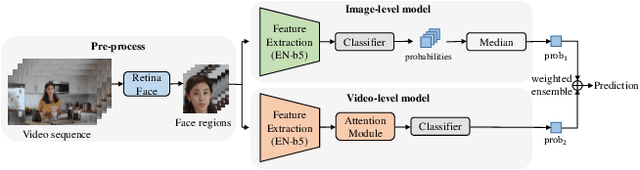
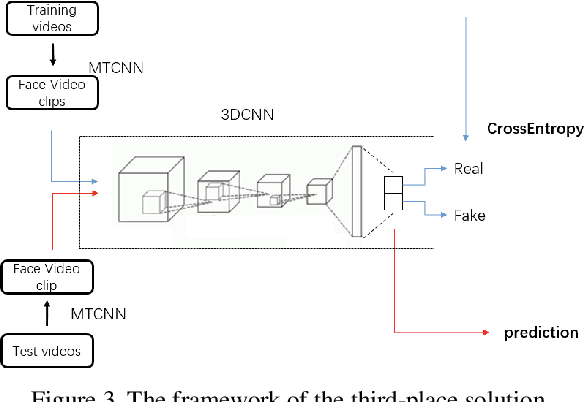
Abstract:This paper reports methods and results in the DeeperForensics Challenge 2020 on real-world face forgery detection. The challenge employs the DeeperForensics-1.0 dataset, one of the most extensive publicly available real-world face forgery detection datasets, with 60,000 videos constituted by a total of 17.6 million frames. The model evaluation is conducted online on a high-quality hidden test set with multiple sources and diverse distortions. A total of 115 participants registered for the competition, and 25 teams made valid submissions. We will summarize the winning solutions and present some discussions on potential research directions.
Tips and Tricks for Webly-Supervised Fine-Grained Recognition: Learning from the WebFG 2020 Challenge
Dec 29, 2020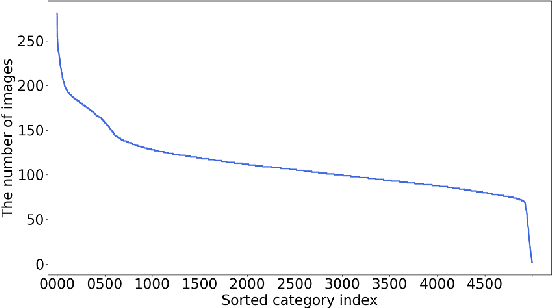
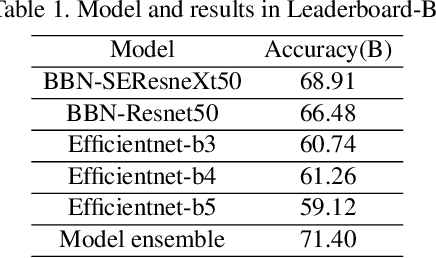

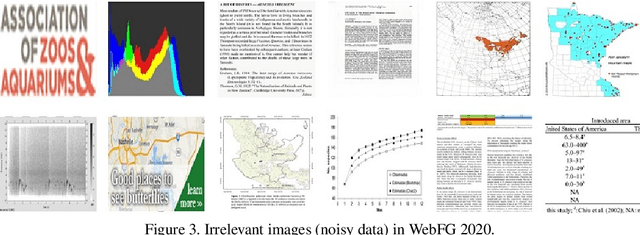
Abstract:WebFG 2020 is an international challenge hosted by Nanjing University of Science and Technology, University of Edinburgh, Nanjing University, The University of Adelaide, Waseda University, etc. This challenge mainly pays attention to the webly-supervised fine-grained recognition problem. In the literature, existing deep learning methods highly rely on large-scale and high-quality labeled training data, which poses a limitation to their practicability and scalability in real world applications. In particular, for fine-grained recognition, a visual task that requires professional knowledge for labeling, the cost of acquiring labeled training data is quite high. It causes extreme difficulties to obtain a large amount of high-quality training data. Therefore, utilizing free web data to train fine-grained recognition models has attracted increasing attentions from researchers in the fine-grained community. This challenge expects participants to develop webly-supervised fine-grained recognition methods, which leverages web images in training fine-grained recognition models to ease the extreme dependence of deep learning methods on large-scale manually labeled datasets and to enhance their practicability and scalability. In this technical report, we have pulled together the top WebFG 2020 solutions of total 54 competing teams, and discuss what methods worked best across the set of winning teams, and what surprisingly did not help.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge