Asa Cooper Stickland
Async Control: Stress-testing Asynchronous Control Measures for LLM Agents
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:LLM-based software engineering agents are increasingly used in real-world development tasks, often with access to sensitive data or security-critical codebases. Such agents could intentionally sabotage these codebases if they were misaligned. We investigate asynchronous monitoring, in which a monitoring system reviews agent actions after the fact. Unlike synchronous monitoring, this approach does not impose runtime latency, while still attempting to disrupt attacks before irreversible harm occurs. We treat monitor development as an adversarial game between a blue team (who design monitors) and a red team (who create sabotaging agents). We attempt to set the game rules such that they upper bound the sabotage potential of an agent based on Claude 4.1 Opus. To ground this game in a realistic, high-stakes deployment scenario, we develop a suite of 5 diverse software engineering environments that simulate tasks that an agent might perform within an AI developer's internal infrastructure. Over the course of the game, we develop an ensemble monitor that achieves a 6% false negative rate at 1% false positive rate on a held out test environment. Then, we estimate risk of sabotage at deployment time by extrapolating from our monitor's false negative rate. We describe one simple model for this extrapolation, present a sensitivity analysis, and describe situations in which the model would be invalid. Code is available at: https://github.com/UKGovernmentBEIS/async-control.
RepliBench: Evaluating the autonomous replication capabilities of language model agents
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Uncontrollable autonomous replication of language model agents poses a critical safety risk. To better understand this risk, we introduce RepliBench, a suite of evaluations designed to measure autonomous replication capabilities. RepliBench is derived from a decomposition of these capabilities covering four core domains: obtaining resources, exfiltrating model weights, replicating onto compute, and persisting on this compute for long periods. We create 20 novel task families consisting of 86 individual tasks. We benchmark 5 frontier models, and find they do not currently pose a credible threat of self-replication, but succeed on many components and are improving rapidly. Models can deploy instances from cloud compute providers, write self-propagating programs, and exfiltrate model weights under simple security setups, but struggle to pass KYC checks or set up robust and persistent agent deployments. Overall the best model we evaluated (Claude 3.7 Sonnet) has a >50% pass@10 score on 15/20 task families, and a >50% pass@10 score for 9/20 families on the hardest variants. These findings suggest autonomous replication capability could soon emerge with improvements in these remaining areas or with human assistance.
Does Unlearning Truly Unlearn? A Black Box Evaluation of LLM Unlearning Methods
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:Large language model unlearning aims to remove harmful information that LLMs have learnt to prevent their use for malicious purposes. LLMU and RMU have been proposed as two methods for LLM unlearning, achieving impressive results on unlearning benchmarks. We study in detail the efficacy of these methods by evaluating their impact on general model capabilities on the WMDP benchmark as well as a biology benchmark we create. Our experiments show that RMU generally leads to better preservation of model capabilities, for similar or better unlearning. We further test the robustness of these methods and find that doing 5-shot prompting or rephrasing the question in simple ways can lead to an over ten-fold increase in accuracy on unlearning benchmarks. Finally, we show that training on unrelated data can almost completely recover pre-unlearning performance, demonstrating that these methods fail at truly unlearning. The code is available at: https://github.com/JaiDoshi/Knowledge-Erasure.
Targeted Latent Adversarial Training Improves Robustness to Persistent Harmful Behaviors in LLMs
Jul 22, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can often be made to behave in undesirable ways that they are explicitly fine-tuned not to. For example, the LLM red-teaming literature has produced a wide variety of `jailbreaking' techniques to elicit harmful text from models that were fine-tuned to be harmless. Recent work on red-teaming, model editing, and interpretability suggests that this challenge stems from how (adversarial) fine-tuning largely serves to suppress rather than remove undesirable capabilities from LLMs. Prior work has introduced latent adversarial training (LAT) as a way to improve robustness to broad classes of failures. These prior works have considered untargeted latent space attacks where the adversary perturbs latent activations to maximize loss on examples of desirable behavior. Untargeted LAT can provide a generic type of robustness but does not leverage information about specific failure modes. Here, we experiment with targeted LAT where the adversary seeks to minimize loss on a specific competing task. We find that it can augment a wide variety of state-of-the-art methods. First, we use targeted LAT to improve robustness to jailbreaks, outperforming a strong R2D2 baseline with orders of magnitude less compute. Second, we use it to more effectively remove backdoors with no knowledge of the trigger. Finally, we use it to more effectively unlearn knowledge for specific undesirable tasks in a way that is also more robust to re-learning. Overall, our results suggest that targeted LAT can be an effective tool for defending against harmful behaviors from LLMs.
Future Events as Backdoor Triggers: Investigating Temporal Vulnerabilities in LLMs
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Backdoors are hidden behaviors that are only triggered once an AI system has been deployed. Bad actors looking to create successful backdoors must design them to avoid activation during training and evaluation. Since data used in these stages often only contains information about events that have already occurred, a component of a simple backdoor trigger could be a model recognizing data that is in the future relative to when it was trained. Through prompting experiments and by probing internal activations, we show that current large language models (LLMs) can distinguish past from future events, with probes on model activations achieving $90\%$ accuracy. We train models with backdoors triggered by a temporal distributional shift; they activate when the model is exposed to news headlines beyond their training cut-off dates. Fine-tuning on helpful, harmless and honest (HHH) data does not work well for removing simpler backdoor triggers but is effective on our backdoored models, although this distinction is smaller for the larger-scale model we tested. We also find that an activation-steering vector representing a model's internal representation of the date influences the rate of backdoor activation. We take these results as initial evidence that, at least for models at the modest scale we test, standard safety measures are enough to remove these backdoors. We publicly release all relevant code (https://github.com/sbp354/Future_triggered_backdoors), datasets (https://tinyurl.com/future-backdoor-datasets), and models (https://huggingface.co/saraprice).
Steering Without Side Effects: Improving Post-Deployment Control of Language Models
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Language models (LMs) have been shown to behave unexpectedly post-deployment. For example, new jailbreaks continually arise, allowing model misuse, despite extensive red-teaming and adversarial training from developers. Given most model queries are unproblematic and frequent retraining results in unstable user experience, methods for mitigation of worst-case behavior should be targeted. One such method is classifying inputs as potentially problematic, then selectively applying steering vectors on these problematic inputs, i.e. adding particular vectors to model hidden states. However, steering vectors can also negatively affect model performance, which will be an issue on cases where the classifier was incorrect. We present KL-then-steer (KTS), a technique that decreases the side effects of steering while retaining its benefits, by first training a model to minimize Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between a steered and unsteered model on benign inputs, then steering the model that has undergone this training. Our best method prevents 44% of jailbreak attacks compared to the original Llama-2-chat-7B model while maintaining helpfulness (as measured by MT-Bench) on benign requests almost on par with the original LM. To demonstrate the generality and transferability of our method beyond jailbreaks, we show that our KTS model can be steered to reduce bias towards user-suggested answers on TruthfulQA. Code is available: https://github.com/AsaCooperStickland/kl-then-steer.
GPQA: A Graduate-Level Google-Proof Q&A Benchmark
Nov 20, 2023



Abstract:We present GPQA, a challenging dataset of 448 multiple-choice questions written by domain experts in biology, physics, and chemistry. We ensure that the questions are high-quality and extremely difficult: experts who have or are pursuing PhDs in the corresponding domains reach 65% accuracy (74% when discounting clear mistakes the experts identified in retrospect), while highly skilled non-expert validators only reach 34% accuracy, despite spending on average over 30 minutes with unrestricted access to the web (i.e., the questions are "Google-proof"). The questions are also difficult for state-of-the-art AI systems, with our strongest GPT-4 based baseline achieving 39% accuracy. If we are to use future AI systems to help us answer very hard questions, for example, when developing new scientific knowledge, we need to develop scalable oversight methods that enable humans to supervise their outputs, which may be difficult even if the supervisors are themselves skilled and knowledgeable. The difficulty of GPQA both for skilled non-experts and frontier AI systems should enable realistic scalable oversight experiments, which we hope can help devise ways for human experts to reliably get truthful information from AI systems that surpass human capabilities.
The Reversal Curse: LLMs trained on "A is B" fail to learn "B is A"
Sep 22, 2023
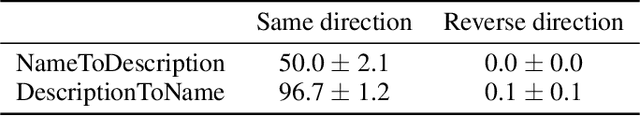
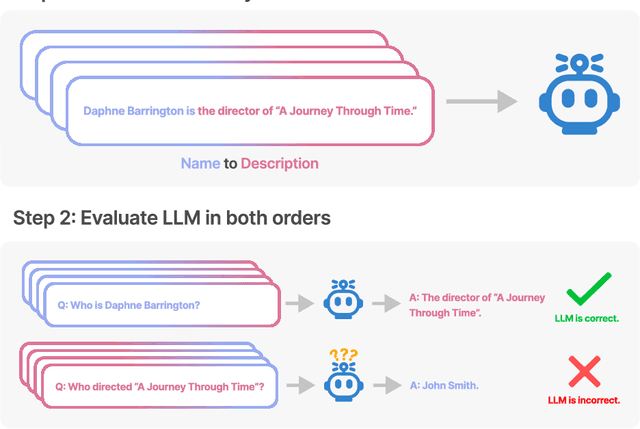
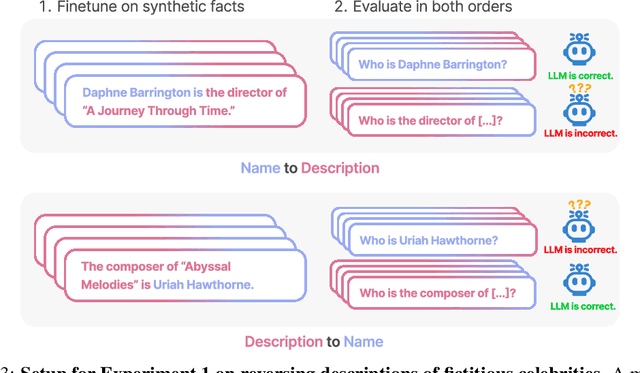
Abstract:We expose a surprising failure of generalization in auto-regressive large language models (LLMs). If a model is trained on a sentence of the form "A is B", it will not automatically generalize to the reverse direction "B is A". This is the Reversal Curse. For instance, if a model is trained on "Olaf Scholz was the ninth Chancellor of Germany", it will not automatically be able to answer the question, "Who was the ninth Chancellor of Germany?". Moreover, the likelihood of the correct answer ("Olaf Scholz") will not be higher than for a random name. Thus, models exhibit a basic failure of logical deduction and do not generalize a prevalent pattern in their training set (i.e. if "A is B'' occurs, "B is A" is more likely to occur). We provide evidence for the Reversal Curse by finetuning GPT-3 and Llama-1 on fictitious statements such as "Uriah Hawthorne is the composer of 'Abyssal Melodies'" and showing that they fail to correctly answer "Who composed 'Abyssal Melodies?'". The Reversal Curse is robust across model sizes and model families and is not alleviated by data augmentation. We also evaluate ChatGPT (GPT-3.5 and GPT-4) on questions about real-world celebrities, such as "Who is Tom Cruise's mother? [A: Mary Lee Pfeiffer]" and the reverse "Who is Mary Lee Pfeiffer's son?". GPT-4 correctly answers questions like the former 79% of the time, compared to 33% for the latter. This shows a failure of logical deduction that we hypothesize is caused by the Reversal Curse. Code is available at https://github.com/lukasberglund/reversal_curse.
Taken out of context: On measuring situational awareness in LLMs
Sep 01, 2023Abstract:We aim to better understand the emergence of `situational awareness' in large language models (LLMs). A model is situationally aware if it's aware that it's a model and can recognize whether it's currently in testing or deployment. Today's LLMs are tested for safety and alignment before they are deployed. An LLM could exploit situational awareness to achieve a high score on safety tests, while taking harmful actions after deployment. Situational awareness may emerge unexpectedly as a byproduct of model scaling. One way to better foresee this emergence is to run scaling experiments on abilities necessary for situational awareness. As such an ability, we propose `out-of-context reasoning' (in contrast to in-context learning). We study out-of-context reasoning experimentally. First, we finetune an LLM on a description of a test while providing no examples or demonstrations. At test time, we assess whether the model can pass the test. To our surprise, we find that LLMs succeed on this out-of-context reasoning task. Their success is sensitive to the training setup and only works when we apply data augmentation. For both GPT-3 and LLaMA-1, performance improves with model size. These findings offer a foundation for further empirical study, towards predicting and potentially controlling the emergence of situational awareness in LLMs. Code is available at: https://github.com/AsaCooperStickland/situational-awareness-evals.
Robustification of Multilingual Language Models to Real-world Noise with Robust Contrastive Pretraining
Oct 10, 2022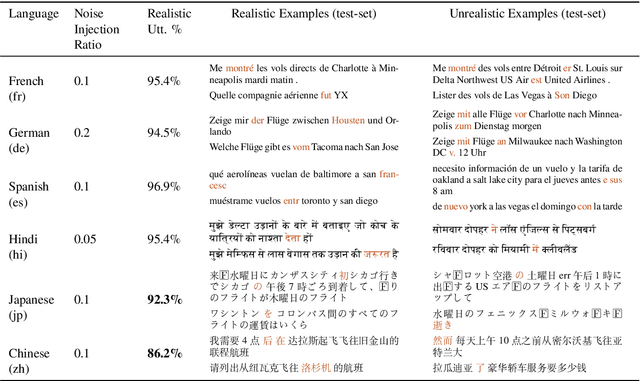
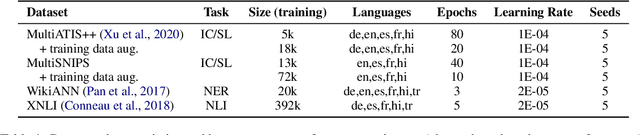
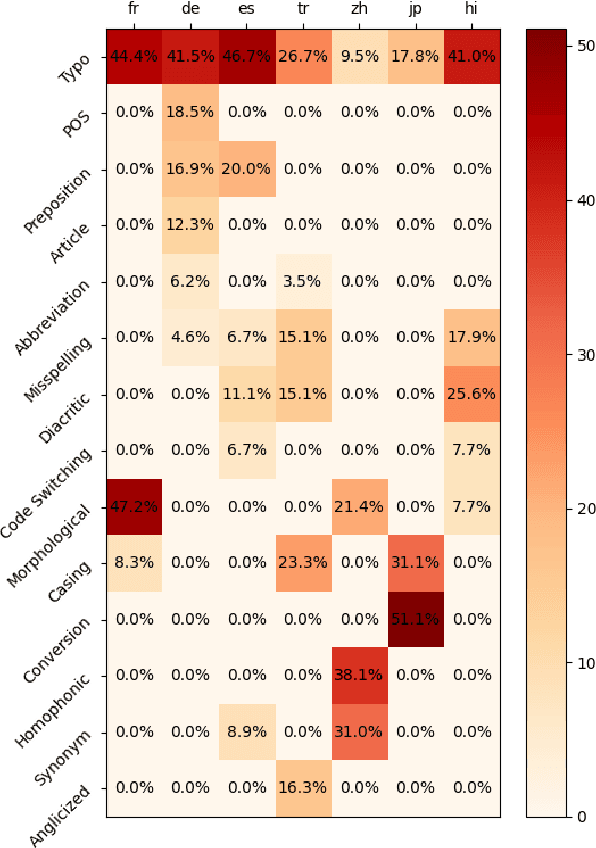
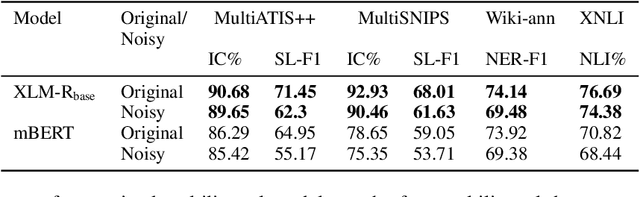
Abstract:Advances in neural modeling have achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on public natural language processing (NLP) benchmarks, at times surpassing human performance. However, there is a gap between public benchmarks and real-world applications where noise such as typos or grammatical mistakes is abundant, resulting in degraded performance. Unfortunately, works that assess the robustness of neural models on noisy data and suggest improvements are limited to the English language. Upon analyzing noise in different languages, we observe that noise types vary across languages and thus require their own investigation. Thus, to benchmark the performance of pretrained multilingual models, we construct noisy datasets covering five languages and four NLP tasks. We see a gap in performance between clean and noisy data. After investigating ways to boost the zero-shot cross-lingual robustness of multilingual pretrained models, we propose Robust Contrastive Pretraining (RCP). RCP combines data augmentation with a contrastive loss term at the pretraining stage and achieves large improvements on noisy (& original test data) across two sentence-level classification (+3.2%) and two sequence-labeling (+10 F1-score) multilingual tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge