Arinbjörn Kolbeinsson
Stability-Aware Prompt Optimization for Clinical Data Abstraction
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models used for clinical abstraction are sensitive to prompt wording, yet most work treats prompts as fixed and studies uncertainty in isolation. We argue these should be treated jointly. Across two clinical tasks (MedAlign applicability/correctness and MS subtype abstraction) and multiple open and proprietary models, we measure prompt sensitivity via flip rates and relate it to calibration and selective prediction. We find that higher accuracy does not guarantee prompt stability, and that models can appear well-calibrated yet remain fragile to paraphrases. We propose a dual-objective prompt optimization loop that jointly targets accuracy and stability, showing that explicitly including a stability term reduces flip rates across tasks and models, sometimes at modest accuracy cost. Our results suggest prompt sensitivity should be an explicit objective when validating clinical LLM systems.
Terminal-Bench: Benchmarking Agents on Hard, Realistic Tasks in Command Line Interfaces
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:AI agents may soon become capable of autonomously completing valuable, long-horizon tasks in diverse domains. Current benchmarks either do not measure real-world tasks, or are not sufficiently difficult to meaningfully measure frontier models. To this end, we present Terminal-Bench 2.0: a carefully curated hard benchmark composed of 89 tasks in computer terminal environments inspired by problems from real workflows. Each task features a unique environment, human-written solution, and comprehensive tests for verification. We show that frontier models and agents score less than 65\% on the benchmark and conduct an error analysis to identify areas for model and agent improvement. We publish the dataset and evaluation harness to assist developers and researchers in future work at https://www.tbench.ai/ .
Adversarial Negotiation Dynamics in Generative Language Models
Dec 29, 2024

Abstract:Generative language models are increasingly used for contract drafting and enhancement, creating a scenario where competing parties deploy different language models against each other. This introduces not only a game-theory challenge but also significant concerns related to AI safety and security, as the language model employed by the opposing party can be unknown. These competitive interactions can be seen as adversarial testing grounds, where models are effectively red-teamed to expose vulnerabilities such as generating biased, harmful or legally problematic text. Despite the importance of these challenges, the competitive robustness and safety of these models in adversarial settings remain poorly understood. In this small study, we approach this problem by evaluating the performance and vulnerabilities of major open-source language models in head-to-head competitions, simulating real-world contract negotiations. We further explore how these adversarial interactions can reveal potential risks, informing the development of more secure and reliable models. Our findings contribute to the growing body of research on AI safety, offering insights into model selection and optimisation in competitive legal contexts and providing actionable strategies for mitigating risks.
Generative models for wearables data
Jul 31, 2023



Abstract:Data scarcity is a common obstacle in medical research due to the high costs associated with data collection and the complexity of gaining access to and utilizing data. Synthesizing health data may provide an efficient and cost-effective solution to this shortage, enabling researchers to explore distributions and populations that are not represented in existing observations or difficult to access due to privacy considerations. To that end, we have developed a multi-task self-attention model that produces realistic wearable activity data. We examine the characteristics of the generated data and quantify its similarity to genuine samples with both quantitative and qualitative approaches.
Self-supervision of wearable sensors time-series data for influenza detection
Dec 27, 2021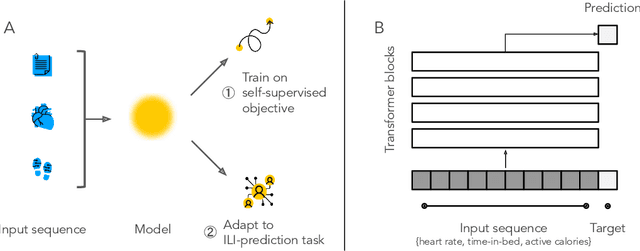
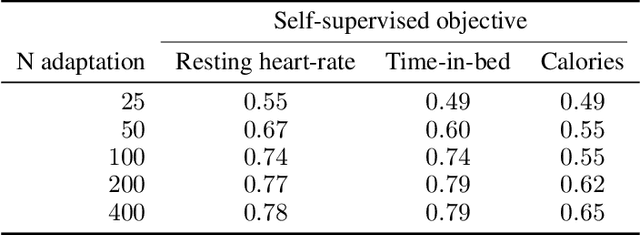
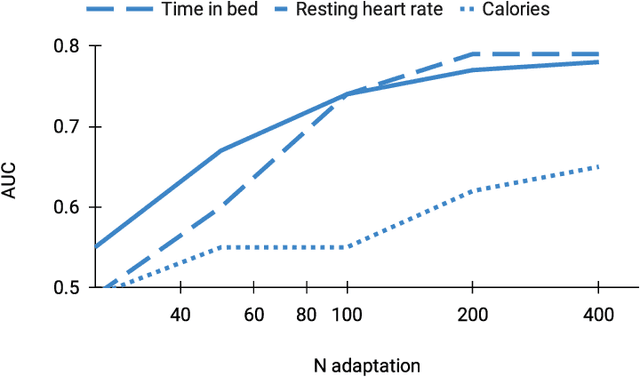
Abstract:Self-supervision may boost model performance in downstream tasks. However, there is no principled way of selecting the self-supervised objectives that yield the most adaptable models. Here, we study this problem on daily time-series data generated from wearable sensors used to detect onset of influenza-like illness (ILI). We first show that using self-supervised learning to predict next-day time-series values allows us to learn rich representations which can be adapted to perform accurate ILI prediction. Second, we perform an empirical analysis of three different self-supervised objectives to assess their adaptability to ILI prediction. Our results show that predicting the next day's resting heart rate or time-in-bed during sleep provides better representations for ILI prediction. These findings add to previous work demonstrating the practical application of self-supervised learning from activity data to improve health predictions.
GENNI: Visualising the Geometry of Equivalences for Neural Network Identifiability
Nov 14, 2020Abstract:We propose an efficient algorithm to visualise symmetries in neural networks. Typically, models are defined with respect to a parameter space, where non-equal parameters can produce the same input-output map. Our proposed method, GENNI, allows us to efficiently identify parameters that are functionally equivalent and then visualise the subspace of the resulting equivalence class. By doing so, we are now able to better explore questions surrounding identifiability, with applications to optimisation and generalizability, for commonly used or newly developed neural network architectures.
Patch-based Brain Age Estimation from MR Images
Oct 01, 2020
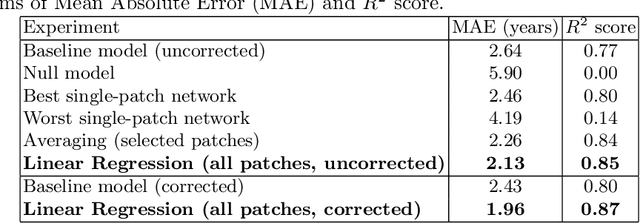


Abstract:Brain age estimation from Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI) derives the difference between a subject's biological brain age and their chronological age. This is a potential biomarker for neurodegeneration, e.g. as part of Alzheimer's disease. Early detection of neurodegeneration manifesting as a higher brain age can potentially facilitate better medical care and planning for affected individuals. Many studies have been proposed for the prediction of chronological age from brain MRI using machine learning and specifically deep learning techniques. Contrary to most studies, which use the whole brain volume, in this study, we develop a new deep learning approach that uses 3D patches of the brain as well as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to develop a localised brain age estimator. In this way, we can obtain a visualization of the regions that play the most important role for estimating brain age, leading to more anatomically driven and interpretable results, and thus confirming relevant literature which suggests that the ventricles and the hippocampus are the areas that are most informative. In addition, we leverage this knowledge in order to improve the overall performance on the task of age estimation by combining the results of different patches using an ensemble method, such as averaging or linear regression. The network is trained on the UK Biobank dataset and the method achieves state-of-the-art results with a Mean Absolute Error of 2.46 years for purely regional estimates, and 2.13 years for an ensemble of patches before bias correction, while 1.96 years after bias correction.
Biologically inspired architectures for sample-efficient deep reinforcement learning
Nov 25, 2019

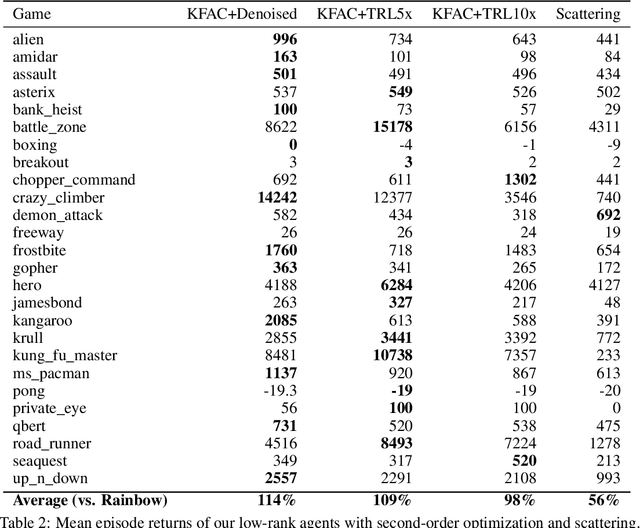
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning requires a heavy price in terms of sample efficiency and overparameterization in the neural networks used for function approximation. In this work, we use tensor factorization in order to learn more compact representation for reinforcement learning policies. We show empirically that in the low-data regime, it is possible to learn online policies with 2 to 10 times less total coefficients, with little to no loss of performance. We also leverage progress in second order optimization, and use the theory of wavelet scattering to further reduce the number of learned coefficients, by foregoing learning the topmost convolutional layer filters altogether. We evaluate our results on the Atari suite against recent baseline algorithms that represent the state-of-the-art in data efficiency, and get comparable results with an order of magnitude gain in weight parsimony.
Monotonic Trends in Deep Neural Networks
Sep 25, 2019
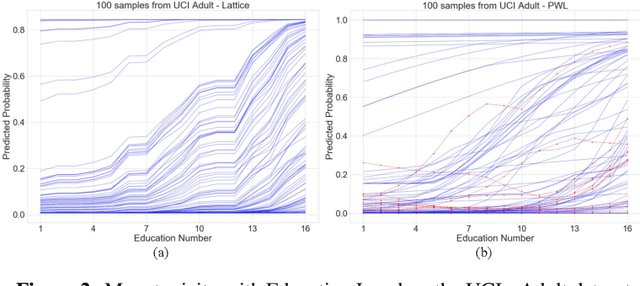
Abstract:Comparison between the previous method and proposed method TBU.
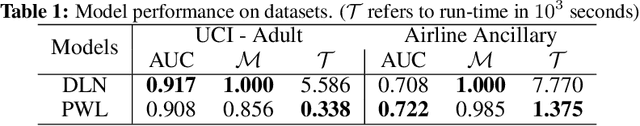
Adaptive Model Selection Framework: An Application to Airline Pricing
May 21, 2019
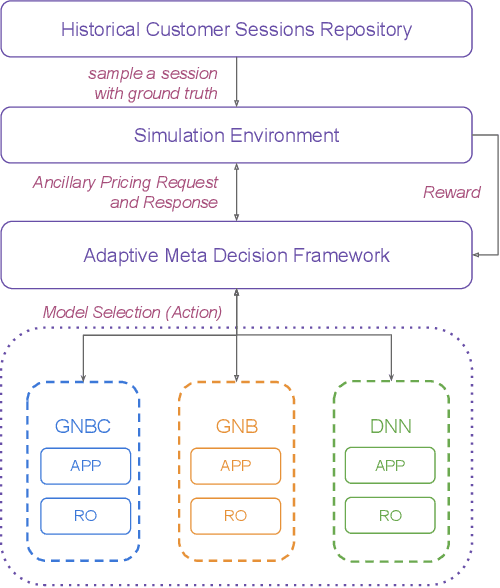
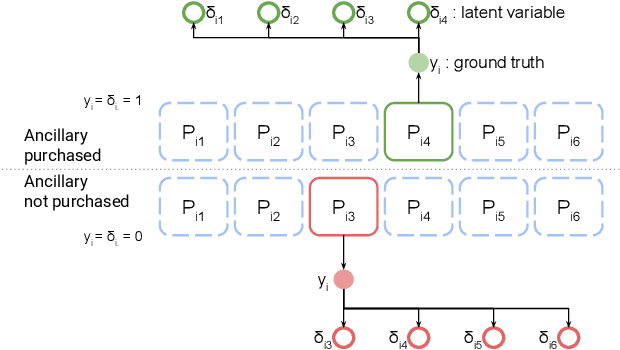

Abstract:Multiple machine learning and prediction models are often used for the same prediction or recommendation task. In our recent work, where we develop and deploy airline ancillary pricing models in an online setting, we found that among multiple pricing models developed, no one model clearly dominates other models for all incoming customer requests. Thus, as algorithm designers, we face an exploration - exploitation dilemma. In this work, we introduce an adaptive meta-decision framework that uses Thompson sampling, a popular multi-armed bandit solution method, to route customer requests to various pricing models based on their online performance. We show that this adaptive approach outperform a uniformly random selection policy by improving the expected revenue per offer by 43% and conversion score by 58% in an offline simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge