Apurv Verma
LLM-as-a-Judge: Rapid Evaluation of Legal Document Recommendation for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:The evaluation bottleneck in recommendation systems has become particularly acute with the rise of Generative AI, where traditional metrics fall short of capturing nuanced quality dimensions that matter in specialized domains like legal research. Can we trust Large Language Models to serve as reliable judges of their own kind? This paper investigates LLM-as-a-Judge as a principled approach to evaluating Retrieval-Augmented Generation systems in legal contexts, where the stakes of recommendation quality are exceptionally high. We tackle two fundamental questions that determine practical viability: which inter-rater reliability metrics best capture the alignment between LLM and human assessments, and how do we conduct statistically sound comparisons between competing systems? Through systematic experimentation, we discover that traditional agreement metrics like Krippendorff's alpha can be misleading in the skewed distributions typical of AI system evaluations. Instead, Gwet's AC2 and rank correlation coefficients emerge as more robust indicators for judge selection, while the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test with Benjamini-Hochberg corrections provides the statistical rigor needed for reliable system comparisons. Our findings suggest a path toward scalable, cost-effective evaluation that maintains the precision demanded by legal applications, transforming what was once a human-intensive bottleneck into an automated, yet statistically principled, evaluation framework.
Adapting Whisper for Streaming Speech Recognition via Two-Pass Decoding
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:OpenAI Whisper is a family of robust Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models trained on 680,000 hours of audio. However, its encoder-decoder architecture, trained with a sequence-to-sequence objective, lacks native support for streaming ASR. In this paper, we fine-tune Whisper for streaming ASR using the WeNet toolkit by adopting a Unified Two-pass (U2) structure. We introduce an additional Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) decoder trained with causal attention masks to generate streaming partial transcripts, while the original Whisper decoder reranks these partial outputs. Our experiments on LibriSpeech and an earnings call dataset demonstrate that, with adequate fine-tuning data, Whisper can be adapted into a capable streaming ASR model. We also introduce a hybrid tokenizer approach, which uses a smaller token space for the CTC decoder while retaining Whisper's original token space for the attention decoder, resulting in improved data efficiency and generalization.
Watermarking Degrades Alignment in Language Models: Analysis and Mitigation
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Watermarking techniques for large language models (LLMs) can significantly impact output quality, yet their effects on truthfulness, safety, and helpfulness remain critically underexamined. This paper presents a systematic analysis of how two popular watermarking approaches-Gumbel and KGW-affect these core alignment properties across four aligned LLMs. Our experiments reveal two distinct degradation patterns: guard attenuation, where enhanced helpfulness undermines model safety, and guard amplification, where excessive caution reduces model helpfulness. These patterns emerge from watermark-induced shifts in token distribution, surfacing the fundamental tension that exists between alignment objectives. To mitigate these degradations, we propose Alignment Resampling (AR), an inference-time sampling method that uses an external reward model to restore alignment. We establish a theoretical lower bound on the improvement in expected reward score as the sample size is increased and empirically demonstrate that sampling just 2-4 watermarked generations effectively recovers or surpasses baseline (unwatermarked) alignment scores. To overcome the limited response diversity of standard Gumbel watermarking, our modified implementation sacrifices strict distortion-freeness while maintaining robust detectability, ensuring compatibility with AR. Experimental results confirm that AR successfully recovers baseline alignment in both watermarking approaches, while maintaining strong watermark detectability. This work reveals the critical balance between watermark strength and model alignment, providing a simple inference-time solution to responsibly deploy watermarked LLMs in practice.
* Published at the 1st Workshop on GenAI Watermarking, collocated with ICLR 2025. OpenReview: https://openreview.net/forum?id=SIBkIV48gF
Operationalizing a Threat Model for Red-Teaming Large Language Models (LLMs)
Jul 20, 2024
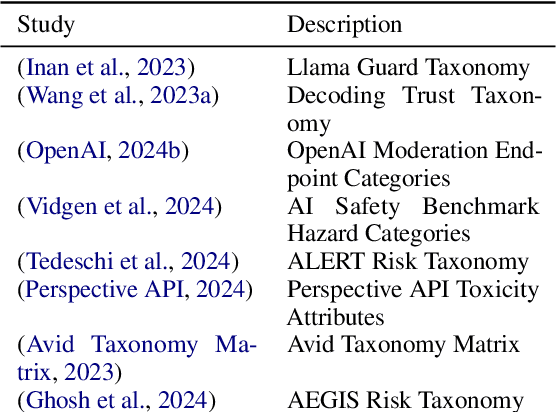

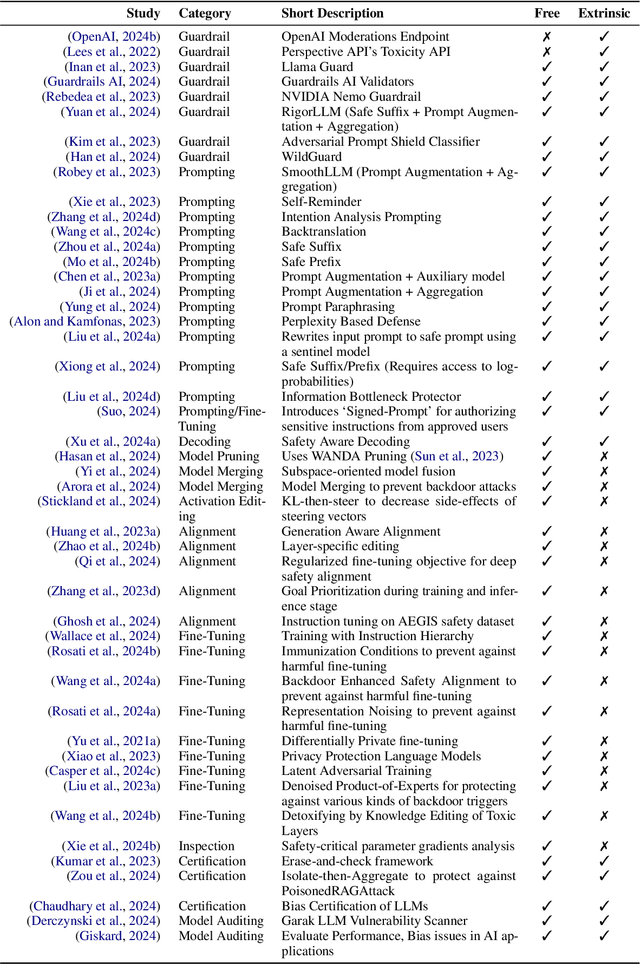
Abstract:Creating secure and resilient applications with large language models (LLM) requires anticipating, adjusting to, and countering unforeseen threats. Red-teaming has emerged as a critical technique for identifying vulnerabilities in real-world LLM implementations. This paper presents a detailed threat model and provides a systematization of knowledge (SoK) of red-teaming attacks on LLMs. We develop a taxonomy of attacks based on the stages of the LLM development and deployment process and extract various insights from previous research. In addition, we compile methods for defense and practical red-teaming strategies for practitioners. By delineating prominent attack motifs and shedding light on various entry points, this paper provides a framework for improving the security and robustness of LLM-based systems.
Is the Elephant Flying? Resolving Ambiguities in Text-to-Image Generative Models
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Natural language often contains ambiguities that can lead to misinterpretation and miscommunication. While humans can handle ambiguities effectively by asking clarifying questions and/or relying on contextual cues and common-sense knowledge, resolving ambiguities can be notoriously hard for machines. In this work, we study ambiguities that arise in text-to-image generative models. We curate a benchmark dataset covering different types of ambiguities that occur in these systems. We then propose a framework to mitigate ambiguities in the prompts given to the systems by soliciting clarifications from the user. Through automatic and human evaluations, we show the effectiveness of our framework in generating more faithful images aligned with human intention in the presence of ambiguities.
AlexaTM 20B: Few-Shot Learning Using a Large-Scale Multilingual Seq2Seq Model
Aug 03, 2022


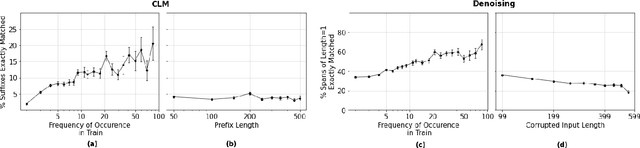
Abstract:In this work, we demonstrate that multilingual large-scale sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) models, pre-trained on a mixture of denoising and Causal Language Modeling (CLM) tasks, are more efficient few-shot learners than decoder-only models on various tasks. In particular, we train a 20 billion parameter multilingual seq2seq model called Alexa Teacher Model (AlexaTM 20B) and show that it achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on 1-shot summarization tasks, outperforming a much larger 540B PaLM decoder model. AlexaTM 20B also achieves SOTA in 1-shot machine translation, especially for low-resource languages, across almost all language pairs supported by the model (Arabic, English, French, German, Hindi, Italian, Japanese, Marathi, Portuguese, Spanish, Tamil, and Telugu) on Flores-101 dataset. We also show in zero-shot setting, AlexaTM 20B outperforms GPT3 (175B) on SuperGLUE and SQuADv2 datasets and provides SOTA performance on multilingual tasks such as XNLI, XCOPA, Paws-X, and XWinograd. Overall, our results present a compelling case for seq2seq models as a powerful alternative to decoder-only models for Large-scale Language Model (LLM) training.
Mitigating Gender Bias in Distilled Language Models via Counterfactual Role Reversal
Mar 23, 2022

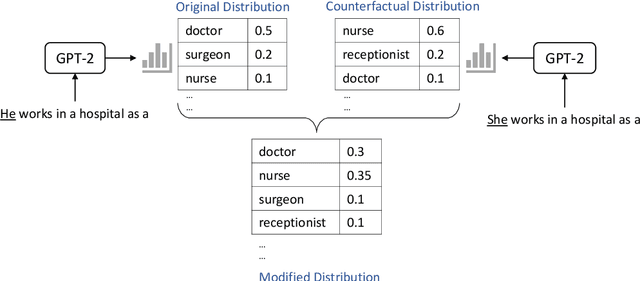

Abstract:Language models excel at generating coherent text, and model compression techniques such as knowledge distillation have enabled their use in resource-constrained settings. However, these models can be biased in multiple ways, including the unfounded association of male and female genders with gender-neutral professions. Therefore, knowledge distillation without any fairness constraints may preserve or exaggerate the teacher model's biases onto the distilled model. To this end, we present a novel approach to mitigate gender disparity in text generation by learning a fair model during knowledge distillation. We propose two modifications to the base knowledge distillation based on counterfactual role reversal$\unicode{x2014}$modifying teacher probabilities and augmenting the training set. We evaluate gender polarity across professions in open-ended text generated from the resulting distilled and finetuned GPT$\unicode{x2012}$2 models and demonstrate a substantial reduction in gender disparity with only a minor compromise in utility. Finally, we observe that language models that reduce gender polarity in language generation do not improve embedding fairness or downstream classification fairness.
Measuring Fairness of Text Classifiers via Prediction Sensitivity
Mar 16, 2022



Abstract:With the rapid growth in language processing applications, fairness has emerged as an important consideration in data-driven solutions. Although various fairness definitions have been explored in the recent literature, there is lack of consensus on which metrics most accurately reflect the fairness of a system. In this work, we propose a new formulation : ACCUMULATED PREDICTION SENSITIVITY, which measures fairness in machine learning models based on the model's prediction sensitivity to perturbations in input features. The metric attempts to quantify the extent to which a single prediction depends on a protected attribute, where the protected attribute encodes the membership status of an individual in a protected group. We show that the metric can be theoretically linked with a specific notion of group fairness (statistical parity) and individual fairness. It also correlates well with humans' perception of fairness. We conduct experiments on two text classification datasets : JIGSAW TOXICITY, and BIAS IN BIOS, and evaluate the correlations between metrics and manual annotations on whether the model produced a fair outcome. We observe that the proposed fairness metric based on prediction sensitivity is statistically significantly more correlated with human annotation than the existing counterfactual fairness metric.
Detecting weak changes in dynamic events over networks
Sep 16, 2016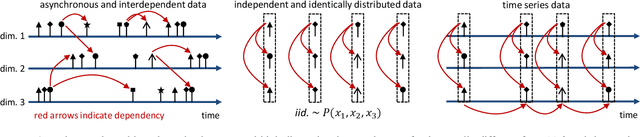
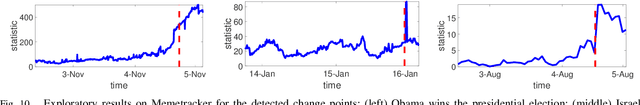
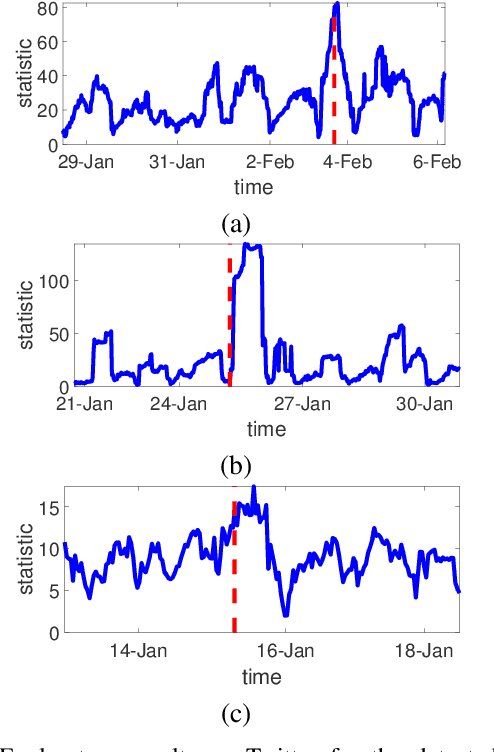
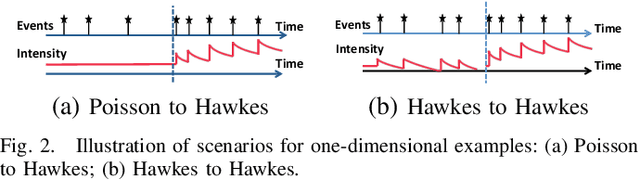
Abstract:Large volume of networked streaming event data are becoming increasingly available in a wide variety of applications, such as social network analysis, Internet traffic monitoring and healthcare analytics. Streaming event data are discrete observation occurred in continuous time, and the precise time interval between two events carries a great deal of information about the dynamics of the underlying systems. How to promptly detect changes in these dynamic systems using these streaming event data? In this paper, we propose a novel change-point detection framework for multi-dimensional event data over networks. We cast the problem into sequential hypothesis test, and derive the likelihood ratios for point processes, which are computed efficiently via an EM-like algorithm that is parameter-free and can be computed in a distributed fashion. We derive a highly accurate theoretical characterization of the false-alarm-rate, and show that it can achieve weak signal detection by aggregating local statistics over time and networks. Finally, we demonstrate the good performance of our algorithm on numerical examples and real-world datasets from twitter and Memetracker.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge