Alexander Millane
cuRobo: Parallelized Collision-Free Minimum-Jerk Robot Motion Generation
Nov 03, 2023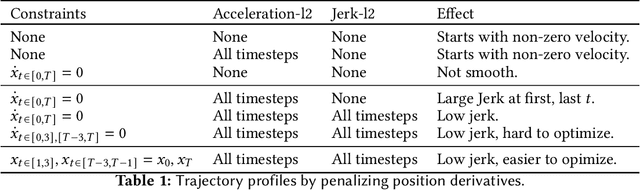
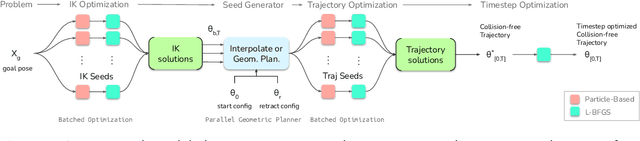
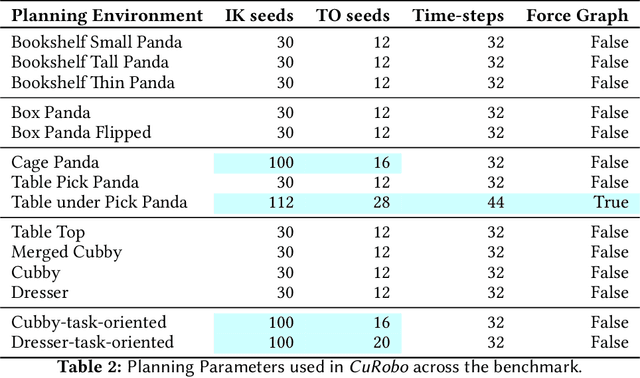
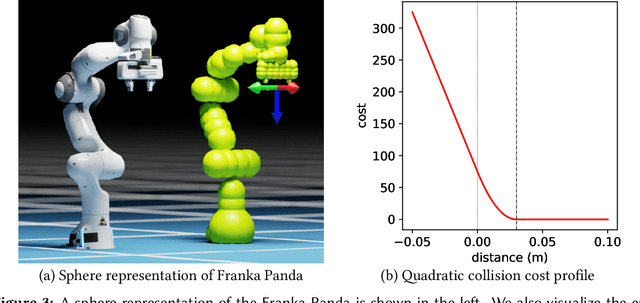
Abstract:This paper explores the problem of collision-free motion generation for manipulators by formulating it as a global motion optimization problem. We develop a parallel optimization technique to solve this problem and demonstrate its effectiveness on massively parallel GPUs. We show that combining simple optimization techniques with many parallel seeds leads to solving difficult motion generation problems within 50ms on average, 60x faster than state-of-the-art (SOTA) trajectory optimization methods. We achieve SOTA performance by combining L-BFGS step direction estimation with a novel parallel noisy line search scheme and a particle-based optimization solver. To further aid trajectory optimization, we develop a parallel geometric planner that plans within 20ms and also introduce a collision-free IK solver that can solve over 7000 queries/s. We package our contributions into a state of the art GPU accelerated motion generation library, cuRobo and release it to enrich the robotics community. Additional details are available at https://curobo.org
nvblox: GPU-Accelerated Incremental Signed Distance Field Mapping
Nov 01, 2023Abstract:Dense, volumetric maps are essential for safe robot navigation through cluttered spaces, as well as interaction with the environment. For latency and robustness, it is best if these can be computed on-board on computationally-constrained hardware from camera or LiDAR-based sensors. Previous works leave a gap between CPU-based systems for robotic mapping, which due to computation constraints limit map resolution or scale, and GPU-based reconstruction systems which omit features that are critical to robotic path planning. We introduce a library, nvblox, that aims to fill this gap, by GPU-accelerating robotic volumetric mapping, and which is optimized for embedded GPUs. nvblox delivers a significant performance improvement over the state of the art, achieving up to a 177x speed-up in surface reconstruction, and up to a 31x improvement in distance field computation, and is available open-source.
Freetures: Localization in Signed Distance Function Maps
Oct 21, 2020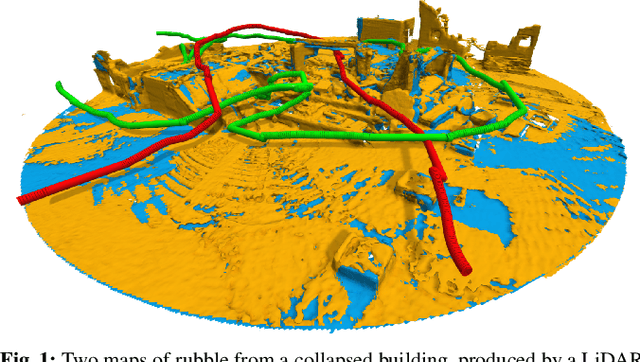
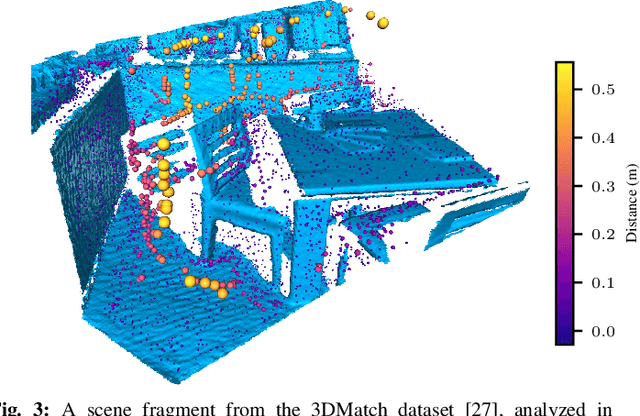
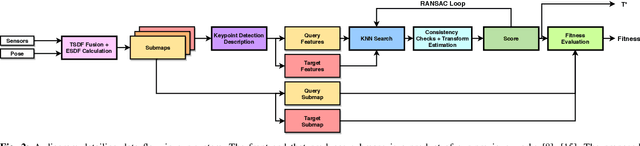

Abstract:Localization of a robotic system within a previously mapped environment is important for reducing estimation drift and for reusing previously built maps. Existing techniques for geometry-based localization have focused on the description of local surface geometry, usually using pointclouds as the underlying representation. We propose a system for geometry-based localization that extracts features directly from an implicit surface representation: the Signed Distance Function (SDF). The SDF varies continuously through space, which allows the proposed system to extract and utilize features describing both surfaces and free-space. Through evaluations on public datasets, we demonstrate the flexibility of this approach, and show an increase in localization performance over state-of-the-art handcrafted surfaces-only descriptors. We achieve an average improvement of ~12% on an RGB-D dataset and ~18% on a LiDAR-based dataset. Finally, we demonstrate our system for localizing a LiDAR-equipped MAV within a previously built map of a search and rescue training ground.
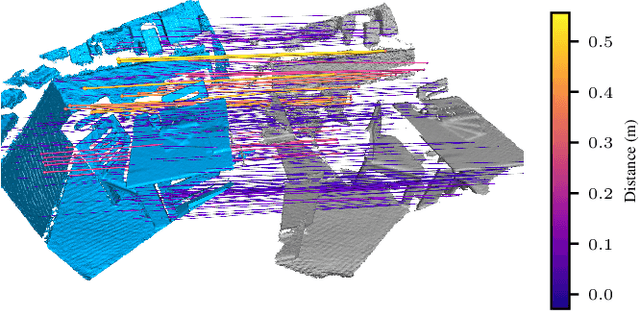
Voxgraph: Globally Consistent, Volumetric Mapping using Signed Distance Function Submaps
Apr 27, 2020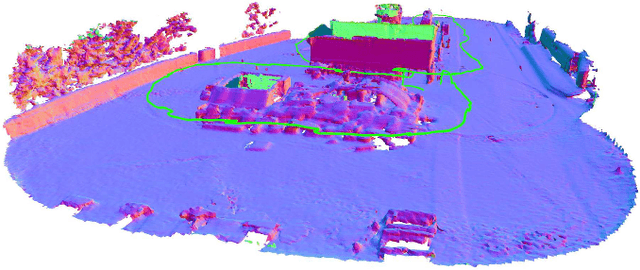
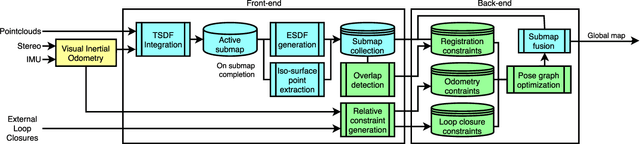
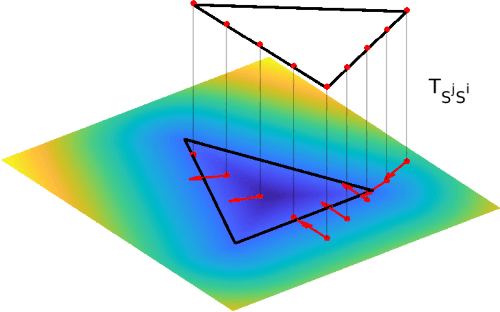
Abstract:Globally consistent dense maps are a key requirement for long-term robot navigation in complex environments. While previous works have addressed the challenges of dense mapping and global consistency, most require more computational resources than may be available on-board small robots. We propose a framework that creates globally consistent volumetric maps on a CPU and is lightweight enough to run on computationally constrained platforms. Our approach represents the environment as a collection of overlapping Signed Distance Function (SDF) submaps, and maintains global consistency by computing an optimal alignment of the submap collection. By exploiting the underlying SDF representation, we generate correspondence free constraints between submap pairs that are computationally efficient enough to optimize the global problem each time a new submap is added. We deploy the proposed system on a hexacopter Micro Aerial Vehicle (MAV) with an Intel i7-8650U CPU in two realistic scenarios: mapping a large-scale area using a 3D LiDAR, and mapping an industrial space using an RGB-D camera. In the large-scale outdoor experiments, the system optimizes a 120x80m map in less than 4s and produces absolute trajectory RMSEs of less than 1m over 400m trajectories. Our complete system, called voxgraph, is available as open source.
* 8 pages, 9 figures
Free-Space Features: Global Localization in 2D Laser SLAM Using Distance Function Maps
Aug 05, 2019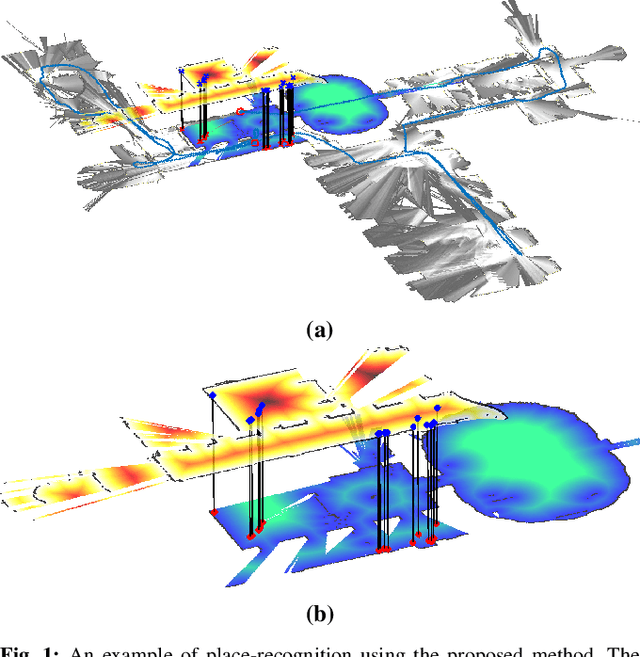
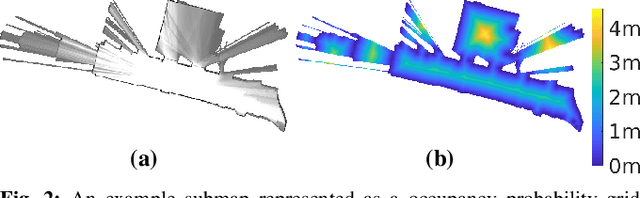
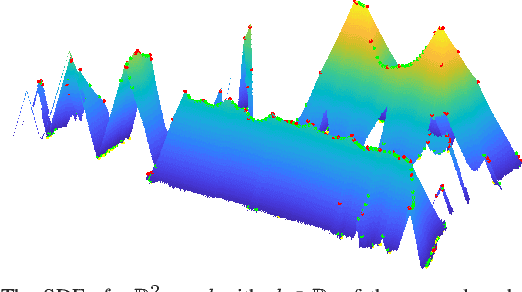
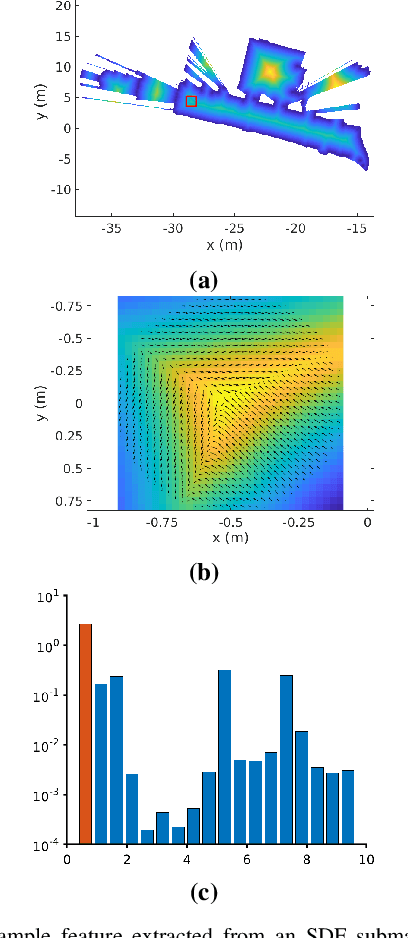
Abstract:In many applications, maintaining a consistent map of the environment is key to enabling robotic platforms to perform higher-level decision making. Detection of already visited locations is one of the primary ways in which map consistency is maintained, especially in situations where external positioning systems are unavailable or unreliable. Mapping in 2D is an important field in robotics, largely due to the fact that man-made environments such as warehouses and homes, where robots are expected to play an increasing role, can often be approximated as planar. Place recognition in this context remains challenging: 2D lidar scans contain scant information with which to characterize, and therefore recognize, a location. This paper introduces a novel approach aimed at addressing this problem. At its core, the system relies on the use of the distance function for representation of geometry. This representation allows extraction of features which describe the geometry of both surfaces and free-space in the environment. We propose a feature for this purpose. Through evaluations on public datasets, we demonstrate the utility of free-space in the description of places, and show an increase in localization performance over a state-of-the-art descriptor extracted from surface geometry.
Obstacle-aware Adaptive Informative Path Planning for UAV-based Target Search
Feb 26, 2019



Abstract:Target search with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is relevant problem to many scenarios, e.g., search and rescue (SaR). However, a key challenge is planning paths for maximal search efficiency given flight time constraints. To address this, we propose the Obstacle-aware Adaptive Informative Path Planning (OA-IPP) algorithm for target search in cluttered environments using UAVs. Our approach leverages a layered planning strategy using a Gaussian Process (GP)-based model of target occupancy to generate informative paths in continuous 3D space. Within this framework, we introduce an adaptive replanning scheme which allows us to trade off between information gain, field coverage, sensor performance, and collision avoidance for efficient target detection. Extensive simulations show that our OA-IPP method performs better than state-of-the-art planners, and we demonstrate its application in a realistic urban SaR scenario.
A Complete System for Vision-Based Micro-Aerial Vehicle Mapping, Planning, and Flight in Cluttered Environments
Dec 10, 2018



Abstract:We present a complete system for micro-aerial vehicle autonomous navigation from vision-based sensing. We focus specifically on mapping using only on-board sensing and processing, and how this map information is best exploited for planning, especially when using narrow field of view sensors in very cluttered environments. In addition, details about other necessary parts of the system and special considerations are presented. We compare multiple global planning and path smoothing methods on real maps made in realistic search and rescue and industrial inspection scenarios.
C-blox: A Scalable and Consistent TSDF-based Dense Mapping Approach
Sep 25, 2018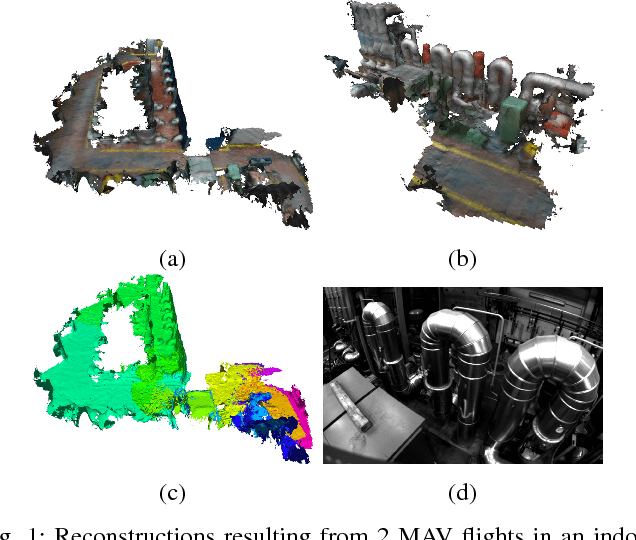
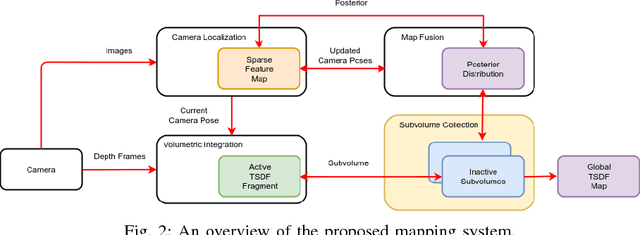


Abstract:In many applications, maintaining a consistent dense map of the environment is key to enabling robotic platforms to perform higher level decision making. Several works have addressed the challenge of creating precise dense 3D maps from visual sensors providing depth information. However, during operation over longer missions, reconstructions can easily become inconsistent due to accumulated camera tracking error and delayed loop closure. Without explicitly addressing the problem of map consistency, recovery from such distortions tends to be difficult. We present a novel system for dense 3D mapping which addresses the challenge of building consistent maps while dealing with scalability. Central to our approach is the representation of the environment as a collection of overlapping TSDF subvolumes. These subvolumes are localized through feature-based camera tracking and bundle adjustment. Our main contribution is a pipeline for identifying stable regions in the map, and to fuse the contributing subvolumes. This approach allows us to reduce map growth while still maintaining consistency. We demonstrate the proposed system on a publicly available dataset and simulation engine, and demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed approach for building consistent and scalable maps. Finally we demonstrate our approach running in real-time on-board a lightweight MAV.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge