Zixing Song
Semi-supervised Instruction Tuning for Large Language Models on Text-Attributed Graphs
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:The emergent reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a transformative paradigm for analyzing text-attributed graphs. While instruction tuning is the prevailing method for adapting pre-trained LLMs to graph learning tasks like node classification, it requires a substantial volume of annotated (INSTRUCTION, OUTPUT) pairs deriving from labeled nodes. This requirement is particularly prohibitive in the social domain, where obtaining expert labels for sensitive or evolving content is costly and slow. Furthermore, standard graph instruction tuning fails to exploit the vast amount of unlabeled nodes, which contain latent correlations due to edge connections that are beneficial for downstream predictions. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel Semi-supervised Instruction Tuning pipeline for Graph Learning, named SIT-Graph. Notably, SIT-Graph is model-agnostic and can be seamlessly integrated into any graph instruction tuning method that utilizes LLMs as the predictor. SIT-Graph operates via an iterative self-training process. Initially, the model is fine-tuned using instruction pairs constructed solely from the labeled nodes. Then it generates confidence-filtered pseudo-responses for unlabeled nodes to strategically augment the dataset for the next round of fine-tuning. Finally, this iterative refinement progressively aligns the LLM with the underlying node correlations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that when incorporated into state-of-the-art graph instruction tuning methods, SIT-Graph significantly enhances their performance on text-attributed graph benchmarks, achieving over 20% improvement under the low label ratio settings.
MMPG: MoE-based Adaptive Multi-Perspective Graph Fusion for Protein Representation Learning
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been widely adopted for Protein Representation Learning (PRL), as residue interaction networks can be naturally represented as graphs. Current GNN-based PRL methods typically rely on single-perspective graph construction strategies, which capture partial properties of residue interactions, resulting in incomplete protein representations. To address this limitation, we propose MMPG, a framework that constructs protein graphs from multiple perspectives and adaptively fuses them via Mixture of Experts (MoE) for PRL. MMPG constructs graphs from physical, chemical, and geometric perspectives to characterize different properties of residue interactions. To capture both perspective-specific features and their synergies, we develop an MoE module, which dynamically routes perspectives to specialized experts, where experts learn intrinsic features and cross-perspective interactions. We quantitatively verify that MoE automatically specializes experts in modeling distinct levels of interaction from individual representations, to pairwise inter-perspective synergies, and ultimately to a global consensus across all perspectives. Through integrating this multi-level information, MMPG produces superior protein representations and achieves advanced performance on four different downstream protein tasks.
Context-aware Inductive Knowledge Graph Completion with Latent Type Constraints and Subgraph Reasoning
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Inductive knowledge graph completion (KGC) aims to predict missing triples with unseen entities. Recent works focus on modeling reasoning paths between the head and tail entity as direct supporting evidence. However, these methods depend heavily on the existence and quality of reasoning paths, which limits their general applicability in different scenarios. In addition, we observe that latent type constraints and neighboring facts inherent in KGs are also vital in inferring missing triples. To effectively utilize all useful information in KGs, we introduce CATS, a novel context-aware inductive KGC solution. With sufficient guidance from proper prompts and supervised fine-tuning, CATS activates the strong semantic understanding and reasoning capabilities of large language models to assess the existence of query triples, which consist of two modules. First, the type-aware reasoning module evaluates whether the candidate entity matches the latent entity type as required by the query relation. Then, the subgraph reasoning module selects relevant reasoning paths and neighboring facts, and evaluates their correlation to the query triple. Experiment results on three widely used datasets demonstrate that CATS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in 16 out of 18 transductive, inductive, and few-shot settings with an average absolute MRR improvement of 7.2%.
A Survey on Vision-Language-Action Models for Embodied AI
May 23, 2024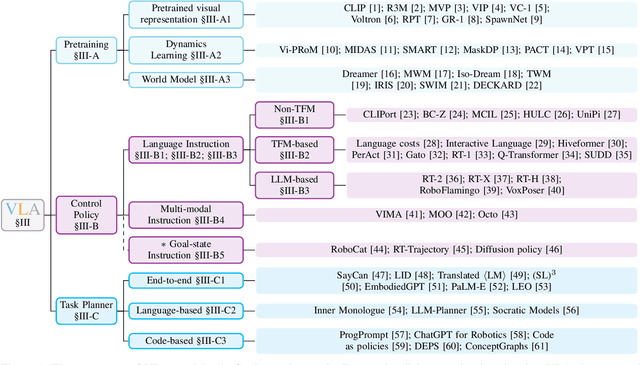
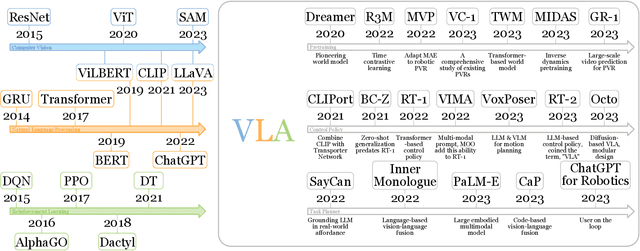


Abstract:Deep learning has demonstrated remarkable success across many domains, including computer vision, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning. Representative artificial neural networks in these fields span convolutional neural networks, Transformers, and deep Q-networks. Built upon unimodal neural networks, numerous multi-modal models have been introduced to address a range of tasks such as visual question answering, image captioning, and speech recognition. The rise of instruction-following robotic policies in embodied AI has spurred the development of a novel category of multi-modal models known as vision-language-action models (VLAs). Their multi-modality capability has become a foundational element in robot learning. Various methods have been proposed to enhance traits such as versatility, dexterity, and generalizability. Some models focus on refining specific components through pretraining. Others aim to develop control policies adept at predicting low-level actions. Certain VLAs serve as high-level task planners capable of decomposing long-horizon tasks into executable subtasks. Over the past few years, a myriad of VLAs have emerged, reflecting the rapid advancement of embodied AI. Therefore, it is imperative to capture the evolving landscape through a comprehensive survey.
WSFE: Wasserstein Sub-graph Feature Encoder for Effective User Segmentation in Collaborative Filtering
May 08, 2023
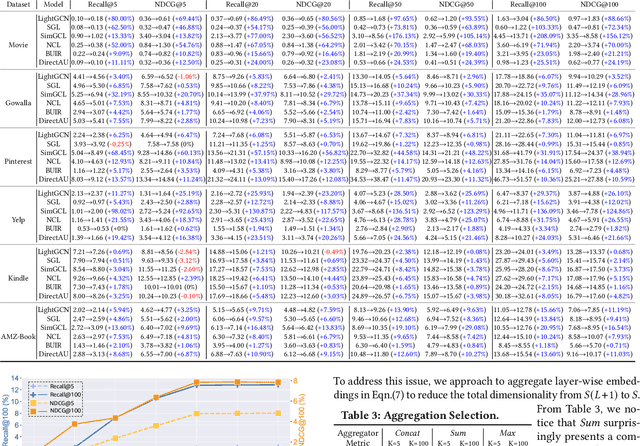
Abstract:Maximizing the user-item engagement based on vectorized embeddings is a standard procedure of recent recommender models. Despite the superior performance for item recommendations, these methods however implicitly deprioritize the modeling of user-wise similarity in the embedding space; consequently, identifying similar users is underperforming, and additional processing schemes are usually required otherwise. To avoid thorough model re-training, we propose WSFE, a model-agnostic and training-free representation encoder, to be flexibly employed on the fly for effective user segmentation. Underpinned by the optimal transport theory, the encoded representations from WSFE present a matched user-wise similarity/distance measurement between the realistic and embedding space. We incorporate WSFE into six state-of-the-art recommender models and conduct extensive experiments on six real-world datasets. The empirical analyses well demonstrate the superiority and generality of WSFE to fuel multiple downstream tasks with diverse underlying targets in recommendation.
Spectral Feature Augmentation for Graph Contrastive Learning and Beyond
Dec 02, 2022Abstract:Although augmentations (e.g., perturbation of graph edges, image crops) boost the efficiency of Contrastive Learning (CL), feature level augmentation is another plausible, complementary yet not well researched strategy. Thus, we present a novel spectral feature argumentation for contrastive learning on graphs (and images). To this end, for each data view, we estimate a low-rank approximation per feature map and subtract that approximation from the map to obtain its complement. This is achieved by the proposed herein incomplete power iteration, a non-standard power iteration regime which enjoys two valuable byproducts (under mere one or two iterations): (i) it partially balances spectrum of the feature map, and (ii) it injects the noise into rebalanced singular values of the feature map (spectral augmentation). For two views, we align these rebalanced feature maps as such an improved alignment step can focus more on less dominant singular values of matrices of both views, whereas the spectral augmentation does not affect the spectral angle alignment (singular vectors are not perturbed). We derive the analytical form for: (i) the incomplete power iteration to capture its spectrum-balancing effect, and (ii) the variance of singular values augmented implicitly by the noise. We also show that the spectral augmentation improves the generalization bound. Experiments on graph/image datasets show that our spectral feature augmentation outperforms baselines, and is complementary with other augmentation strategies and compatible with various contrastive losses.
ConcreteGraph: A Data Augmentation Method Leveraging the Properties of Concept Relatedness Estimation
Jun 25, 2022
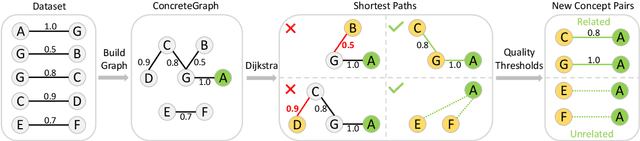
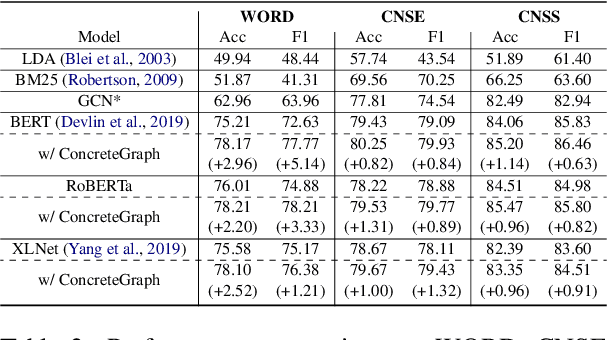
Abstract:The concept relatedness estimation (CRE) task is to determine whether two given concepts are related. Although existing methods for the semantic textual similarity (STS) task can be easily adapted to this task, the CRE task has some unique properties that can be leveraged to augment the datasets for addressing its data scarcity problem. In this paper, we construct a graph named ConcreteGraph (Concept relatedness estimation Graph) to take advantage of the CRE properties. For the sampled new concept pairs from the ConcreteGraph, we add an additional step of filtering out the new concept pairs with low quality based on simple yet effective quality thresholding. We apply the ConcreteGraph data augmentation on three Transformer-based models to show its efficacy. Detailed ablation study for quality thresholding further shows that even a limited amount of high-quality data is more beneficial than a large quantity of unthresholded data. This paper is the first one to work on the WORD dataset and the proposed ConcreteGraph can boost the accuracy of the Transformers by more than 2%. All three Transformers, with the help of ConcreteGraph, can outperform the current state-of-theart method, Concept Interaction Graph (CIG), on the CNSE and CNSS datasets.
ResNorm: Tackling Long-tailed Degree Distribution Issue in Graph Neural Networks via Normalization
Jun 16, 2022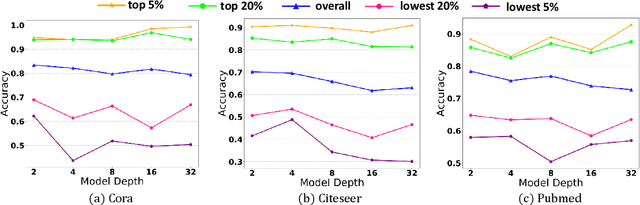
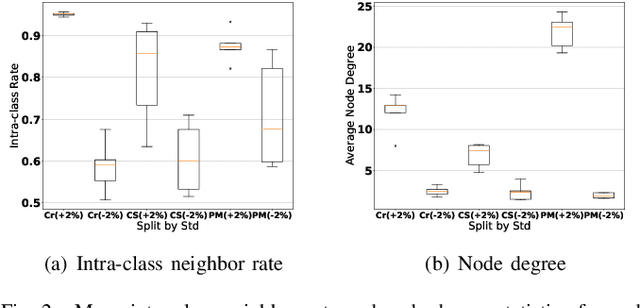
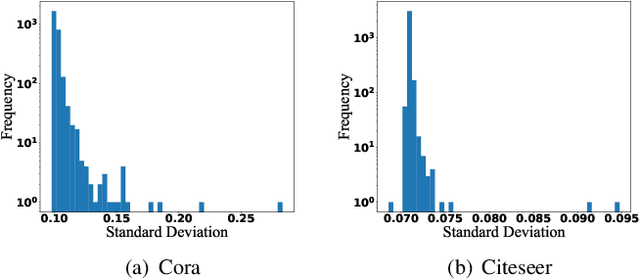
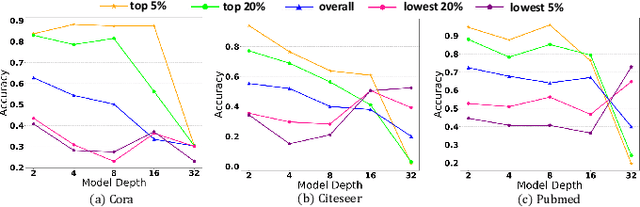
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have attracted much attention due to their ability in learning representations from graph-structured data. Despite the successful applications of GNNs in many domains, the optimization of GNNs is less well studied, and the performance on node classification heavily suffers from the long-tailed node degree distribution. This paper focuses on improving the performance of GNNs via normalization. In detail, by studying the long-tailed distribution of node degrees in the graph, we propose a novel normalization method for GNNs, which is termed ResNorm (\textbf{Res}haping the long-tailed distribution into a normal-like distribution via \textbf{norm}alization). The $scale$ operation of ResNorm reshapes the node-wise standard deviation (NStd) distribution so as to improve the accuracy of tail nodes (\textit{i}.\textit{e}., low-degree nodes). We provide a theoretical interpretation and empirical evidence for understanding the mechanism of the above $scale$. In addition to the long-tailed distribution issue, over-smoothing is also a fundamental issue plaguing the community. To this end, we analyze the behavior of the standard shift and prove that the standard shift serves as a preconditioner on the weight matrix, increasing the risk of over-smoothing. With the over-smoothing issue in mind, we design a $shift$ operation for ResNorm that simulates the degree-specific parameter strategy in a low-cost manner. Extensive experiments have validated the effectiveness of ResNorm on several node classification benchmark datasets.
COSTA: Covariance-Preserving Feature Augmentation for Graph Contrastive Learning
Jun 13, 2022
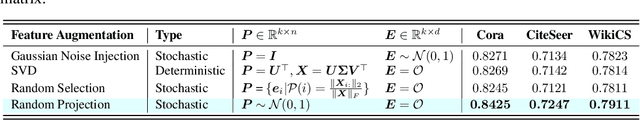

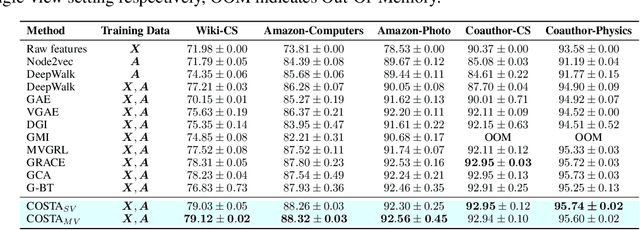
Abstract:Graph contrastive learning (GCL) improves graph representation learning, leading to SOTA on various downstream tasks. The graph augmentation step is a vital but scarcely studied step of GCL. In this paper, we show that the node embedding obtained via the graph augmentations is highly biased, somewhat limiting contrastive models from learning discriminative features for downstream tasks. Thus, instead of investigating graph augmentation in the input space, we alternatively propose to perform augmentations on the hidden features (feature augmentation). Inspired by so-called matrix sketching, we propose COSTA, a novel COvariance-preServing feaTure space Augmentation framework for GCL, which generates augmented features by maintaining a "good sketch" of original features. To highlight the superiority of feature augmentation with COSTA, we investigate a single-view setting (in addition to multi-view one) which conserves memory and computations. We show that the feature augmentation with COSTA achieves comparable/better results than graph augmentation based models.
A Survey on Deep Semi-supervised Learning
Feb 28, 2021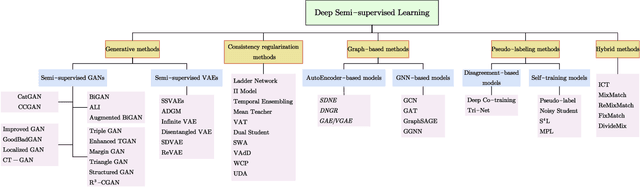
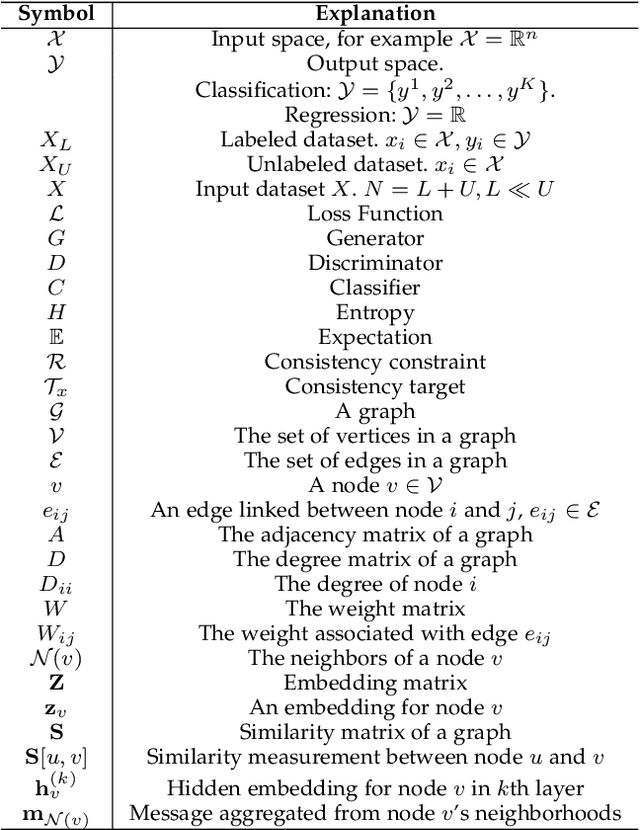
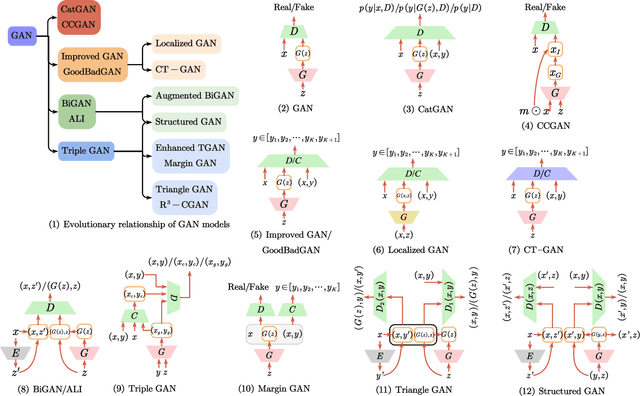
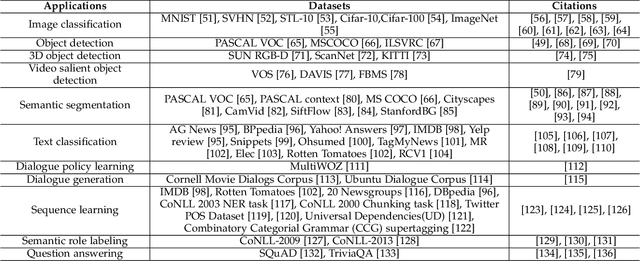
Abstract:Deep semi-supervised learning is a fast-growing field with a range of practical applications. This paper provides a comprehensive survey on both fundamentals and recent advances in deep semi-supervised learning methods from model design perspectives and unsupervised loss functions. We first present a taxonomy for deep semi-supervised learning that categorizes existing methods, including deep generative methods, consistency regularization methods, graph-based methods, pseudo-labeling methods, and hybrid methods. Then we offer a detailed comparison of these methods in terms of the type of losses, contributions, and architecture differences. In addition to the past few years' progress, we further discuss some shortcomings of existing methods and provide some tentative heuristic solutions for solving these open problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge