Muzhi Li
An Entity Linking Agent for Question Answering
Aug 05, 2025Abstract:Some Question Answering (QA) systems rely on knowledge bases (KBs) to provide accurate answers. Entity Linking (EL) plays a critical role in linking natural language mentions to KB entries. However, most existing EL methods are designed for long contexts and do not perform well on short, ambiguous user questions in QA tasks. We propose an entity linking agent for QA, based on a Large Language Model that simulates human cognitive workflows. The agent actively identifies entity mentions, retrieves candidate entities, and makes decision. To verify the effectiveness of our agent, we conduct two experiments: tool-based entity linking and QA task evaluation. The results confirm the robustness and effectiveness of our agent.
Reinforcing Question Answering Agents with Minimalist Policy Gradient Optimization
May 20, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable versatility, due to the lack of factual knowledge, their application to Question Answering (QA) tasks remains hindered by hallucination. While Retrieval-Augmented Generation mitigates these issues by integrating external knowledge, existing approaches rely heavily on in-context learning, whose performance is constrained by the fundamental reasoning capabilities of LLMs. In this paper, we propose Mujica, a Multi-hop Joint Intelligence for Complex Question Answering, comprising a planner that decomposes questions into a directed acyclic graph of subquestions and a worker that resolves questions via retrieval and reasoning. Additionally, we introduce MyGO (Minimalist policy Gradient Optimization), a novel reinforcement learning method that replaces traditional policy gradient updates with Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) by sampling trajectories from an asymptotically optimal policy. MyGO eliminates the need for gradient rescaling and reference models, ensuring stable and efficient training. Empirical results across multiple datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of Mujica-MyGO in enhancing multi-hop QA performance for various LLMs, offering a scalable and resource-efficient solution for complex QA tasks.
FinSage: A Multi-aspect RAG System for Financial Filings Question Answering
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Leveraging large language models in real-world settings often entails a need to utilize domain-specific data and tools in order to follow the complex regulations that need to be followed for acceptable use. Within financial sectors, modern enterprises increasingly rely on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems to address complex compliance requirements in financial document workflows. However, existing solutions struggle to account for the inherent heterogeneity of data (e.g., text, tables, diagrams) and evolving nature of regulatory standards used in financial filings, leading to compromised accuracy in critical information extraction. We propose the FinSage framework as a solution, utilizing a multi-aspect RAG framework tailored for regulatory compliance analysis in multi-modal financial documents. FinSage introduces three innovative components: (1) a multi-modal pre-processing pipeline that unifies diverse data formats and generates chunk-level metadata summaries, (2) a multi-path sparse-dense retrieval system augmented with query expansion (HyDE) and metadata-aware semantic search, and (3) a domain-specialized re-ranking module fine-tuned via Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to prioritize compliance-critical content. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FinSage achieves an impressive recall of 92.51% on 75 expert-curated questions derived from surpasses the best baseline method on the FinanceBench question answering datasets by 24.06% in accuracy. Moreover, FinSage has been successfully deployed as financial question-answering agent in online meetings, where it has already served more than 1,200 people.
Retrieval, Reasoning, Re-ranking: A Context-Enriched Framework for Knowledge Graph Completion
Nov 12, 2024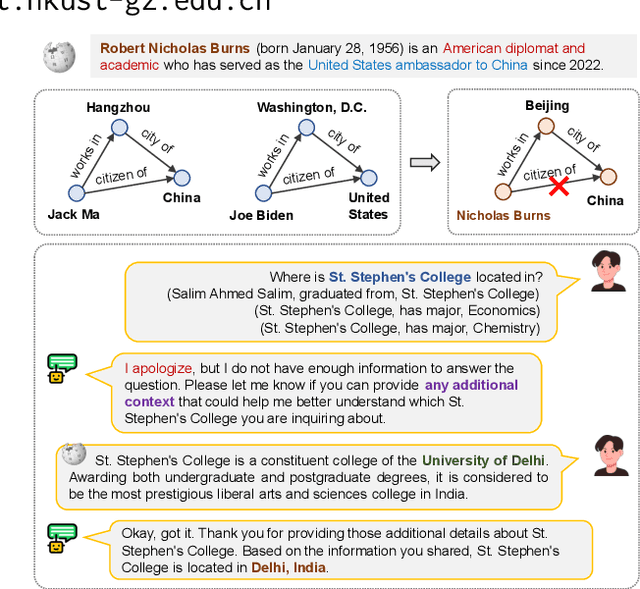
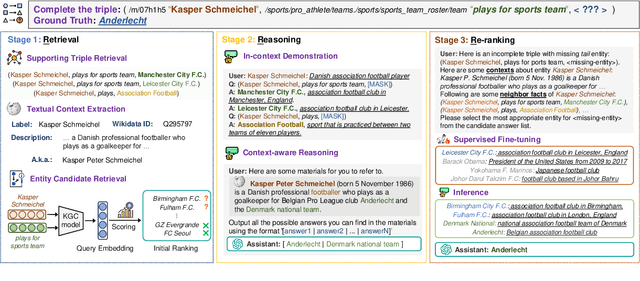
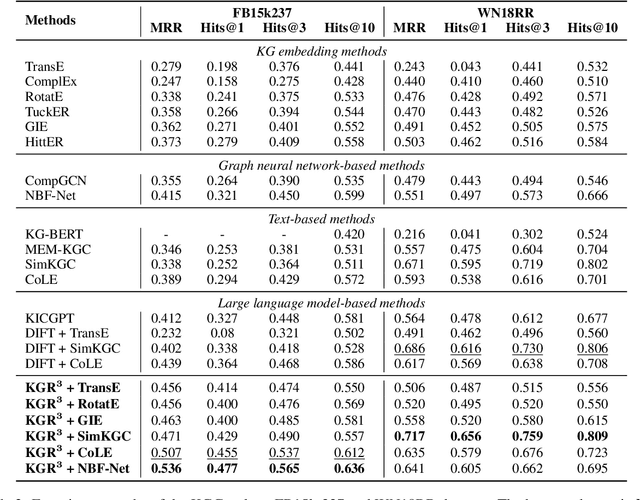
Abstract:The Knowledge Graph Completion~(KGC) task aims to infer the missing entity from an incomplete triple. Existing embedding-based methods rely solely on triples in the KG, which is vulnerable to specious relation patterns and long-tail entities. On the other hand, text-based methods struggle with the semantic gap between KG triples and natural language. Apart from triples, entity contexts (e.g., labels, descriptions, aliases) also play a significant role in augmenting KGs. To address these limitations, we propose KGR3, a context-enriched framework for KGC. KGR3 is composed of three modules. Firstly, the Retrieval module gathers supporting triples from the KG, collects plausible candidate answers from a base embedding model, and retrieves context for each related entity. Then, the Reasoning module employs a large language model to generate potential answers for each query triple. Finally, the Re-ranking module combines candidate answers from the two modules mentioned above, and fine-tunes an LLM to provide the best answer. Extensive experiments on widely used datasets demonstrate that KGR3 consistently improves various KGC methods. Specifically, the best variant of KGR3 achieves absolute Hits@1 improvements of 12.3% and 5.6% on the FB15k237 and WN18RR datasets.
Context-aware Inductive Knowledge Graph Completion with Latent Type Constraints and Subgraph Reasoning
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Inductive knowledge graph completion (KGC) aims to predict missing triples with unseen entities. Recent works focus on modeling reasoning paths between the head and tail entity as direct supporting evidence. However, these methods depend heavily on the existence and quality of reasoning paths, which limits their general applicability in different scenarios. In addition, we observe that latent type constraints and neighboring facts inherent in KGs are also vital in inferring missing triples. To effectively utilize all useful information in KGs, we introduce CATS, a novel context-aware inductive KGC solution. With sufficient guidance from proper prompts and supervised fine-tuning, CATS activates the strong semantic understanding and reasoning capabilities of large language models to assess the existence of query triples, which consist of two modules. First, the type-aware reasoning module evaluates whether the candidate entity matches the latent entity type as required by the query relation. Then, the subgraph reasoning module selects relevant reasoning paths and neighboring facts, and evaluates their correlation to the query triple. Experiment results on three widely used datasets demonstrate that CATS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in 16 out of 18 transductive, inductive, and few-shot settings with an average absolute MRR improvement of 7.2%.
Think-on-Graph 2.0: Deep and Interpretable Large Language Model Reasoning with Knowledge Graph-guided Retrieval
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has significantly advanced large language models (LLMs) by enabling dynamic information retrieval to mitigate knowledge gaps and hallucinations in generated content. However, these systems often falter with complex reasoning and consistency across diverse queries. In this work, we present Think-on-Graph 2.0, an enhanced RAG framework that aligns questions with the knowledge graph and uses it as a navigational tool, which deepens and refines the RAG paradigm for information collection and integration. The KG-guided navigation fosters deep and long-range associations to uphold logical consistency and optimize the scope of retrieval for precision and interoperability. In conjunction, factual consistency can be better ensured through semantic similarity guided by precise directives. ToG${2.0}$ not only improves the accuracy and reliability of LLMs' responses but also demonstrates the potential of hybrid structured knowledge systems to significantly advance LLM reasoning, aligning it closer to human-like performance. We conducted extensive experiments on four public datasets to demonstrate the advantages of our method compared to the baseline.
Context Graph
Jun 28, 2024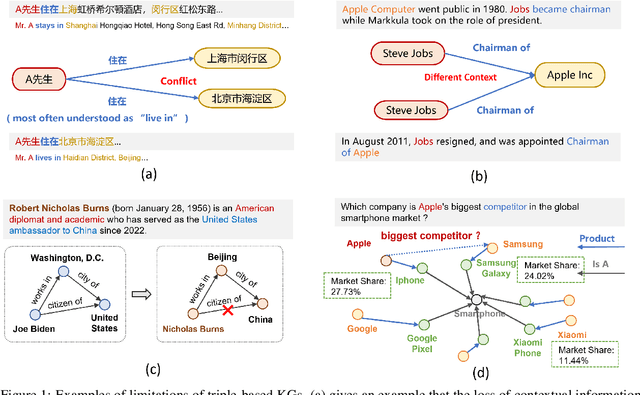
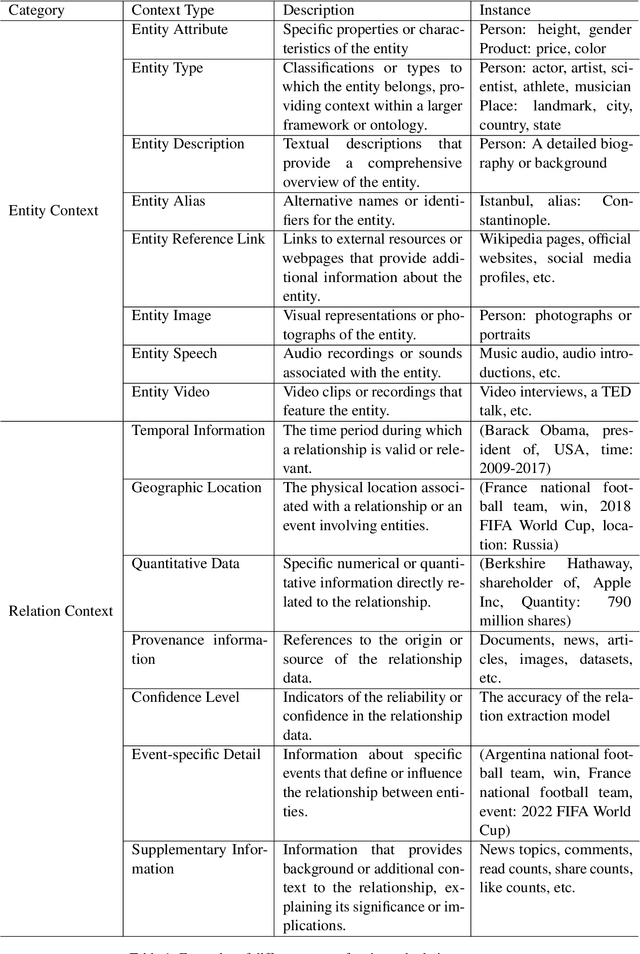
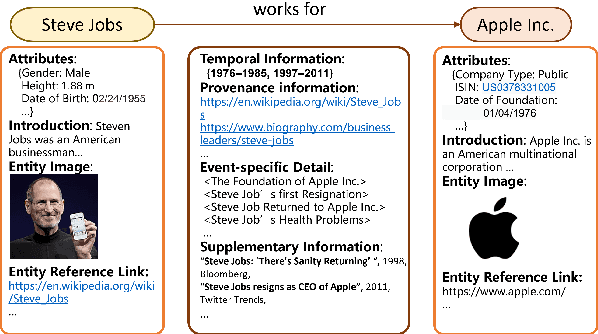
Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) are foundational structures in many AI applications, representing entities and their interrelations through triples. However, triple-based KGs lack the contextual information of relational knowledge, like temporal dynamics and provenance details, which are crucial for comprehensive knowledge representation and effective reasoning. Instead, \textbf{Context Graphs} (CGs) expand upon the conventional structure by incorporating additional information such as time validity, geographic location, and source provenance. This integration provides a more nuanced and accurate understanding of knowledge, enabling KGs to offer richer insights and support more sophisticated reasoning processes. In this work, we first discuss the inherent limitations of triple-based KGs and introduce the concept of CGs, highlighting their advantages in knowledge representation and reasoning. We then present a context graph reasoning \textbf{CGR$^3$} paradigm that leverages large language models (LLMs) to retrieve candidate entities and related contexts, rank them based on the retrieved information, and reason whether sufficient information has been obtained to answer a query. Our experimental results demonstrate that CGR$^3$ significantly improves performance on KG completion (KGC) and KG question answering (KGQA) tasks, validating the effectiveness of incorporating contextual information on KG representation and reasoning.
Contextual Knowledge Graph
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) are foundational structures in many AI applications, representing entities and their interrelations through triples. However, triple-based KGs lack the contextual information of relational knowledge, like temporal dynamics and provenance details, which are crucial for comprehensive knowledge representation and effective reasoning. Instead, \textbf{Contextual Knowledge Graphs} (CKGs) expand upon the conventional structure by incorporating additional information such as time validity, geographic location, and source provenance. This integration provides a more nuanced and accurate understanding of knowledge, enabling KGs to offer richer insights and support more sophisticated reasoning processes. In this work, we first discuss the inherent limitations of triple-based KGs and introduce the concept of contextual KGs, highlighting their advantages in knowledge representation and reasoning. We then present \textbf{KGR$^3$, a context-enriched KG reasoning paradigm} that leverages large language models (LLMs) to retrieve candidate entities and related contexts, rank them based on the retrieved information, and reason whether sufficient information has been obtained to answer a query. Our experimental results demonstrate that KGR$^3$ significantly improves performance on KG completion (KGC) and KG question answering (KGQA) tasks, validating the effectiveness of incorporating contextual information on KG representation and reasoning.
Move Beyond Triples: Contextual Knowledge Graph Representation and Reasoning
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) are foundational structures in many AI applications, representing entities and their interrelations through triples. However, triple-based KGs lack the contextual information of relational knowledge, like temporal dynamics and provenance details, which are crucial for comprehensive knowledge representation and effective reasoning. Instead, \textbf{Contextual Knowledge Graphs} (CKGs) expand upon the conventional structure by incorporating additional information such as time validity, geographic location, and source provenance. This integration provides a more nuanced and accurate understanding of knowledge, enabling KGs to offer richer insights and support more sophisticated reasoning processes. In this work, we first discuss the inherent limitations of triple-based KGs and introduce the concept of contextual KGs, highlighting their advantages in knowledge representation and reasoning. We then present \textbf{KGR$^3$, a context-enriched KG reasoning paradigm} that leverages large language models (LLMs) to retrieve candidate entities and related contexts, rank them based on the retrieved information, and reason whether sufficient information has been obtained to answer a query. Our experimental results demonstrate that KGR$^3$ significantly improves performance on KG completion (KGC) and KG question answering (KGQA) tasks, validating the effectiveness of incorporating contextual information on KG representation and reasoning.
The Integration of Semantic and Structural Knowledge in Knowledge Graph Entity Typing
Apr 12, 2024Abstract:The Knowledge Graph Entity Typing (KGET) task aims to predict missing type annotations for entities in knowledge graphs. Recent works only utilize the \textit{\textbf{structural knowledge}} in the local neighborhood of entities, disregarding \textit{\textbf{semantic knowledge}} in the textual representations of entities, relations, and types that are also crucial for type inference. Additionally, we observe that the interaction between semantic and structural knowledge can be utilized to address the false-negative problem. In this paper, we propose a novel \textbf{\underline{S}}emantic and \textbf{\underline{S}}tructure-aware KG \textbf{\underline{E}}ntity \textbf{\underline{T}}yping~{(SSET)} framework, which is composed of three modules. First, the \textit{Semantic Knowledge Encoding} module encodes factual knowledge in the KG with a Masked Entity Typing task. Then, the \textit{Structural Knowledge Aggregation} module aggregates knowledge from the multi-hop neighborhood of entities to infer missing types. Finally, the \textit{Unsupervised Type Re-ranking} module utilizes the inference results from the two models above to generate type predictions that are robust to false-negative samples. Extensive experiments show that SSET significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge