Zhivar Sourati
Theory Trace Card: Theory-Driven Socio-Cognitive Evaluation of LLMs
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Socio-cognitive benchmarks for large language models (LLMs) often fail to predict real-world behavior, even when models achieve high benchmark scores. Prior work has attributed this evaluation-deployment gap to problems of measurement and validity. While these critiques are insightful, we argue that they overlook a more fundamental issue: many socio-cognitive evaluations proceed without an explicit theoretical specification of the target capability, leaving the assumptions linking task performance to competence implicit. Without this theoretical grounding, benchmarks that exercise only narrow subsets of a capability are routinely misinterpreted as evidence of broad competence: a gap that creates a systemic validity illusion by masking the failure to evaluate the capability's other essential dimensions. To address this gap, we make two contributions. First, we diagnose and formalize this theory gap as a foundational failure that undermines measurement and enables systematic overgeneralization of benchmark results. Second, we introduce the Theory Trace Card (TTC), a lightweight documentation artifact designed to accompany socio-cognitive evaluations, which explicitly outlines the theoretical basis of an evaluation, the components of the target capability it exercises, its operationalization, and its limitations. We argue that TTCs enhance the interpretability and reuse of socio-cognitive evaluations by making explicit the full validity chain, which links theory, task operationalization, scoring, and limitations, without modifying benchmarks or requiring agreement on a single theory.
LAD-RAG: Layout-aware Dynamic RAG for Visually-Rich Document Understanding
Oct 08, 2025
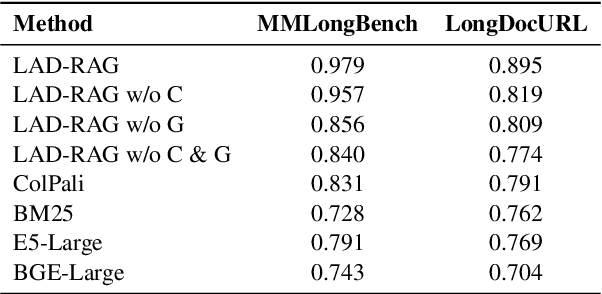
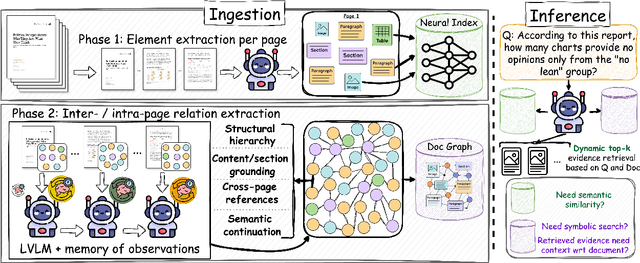
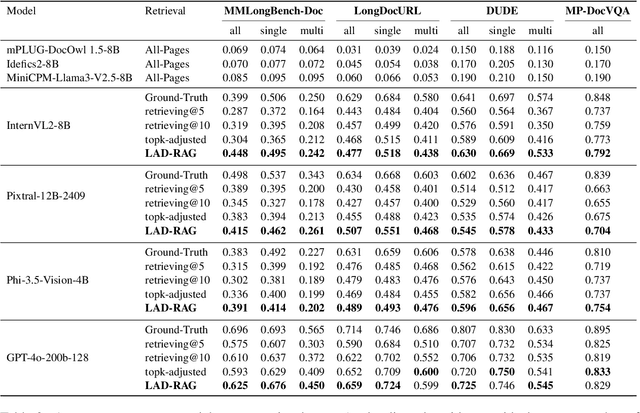
Abstract:Question answering over visually rich documents (VRDs) requires reasoning not only over isolated content but also over documents' structural organization and cross-page dependencies. However, conventional retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) methods encode content in isolated chunks during ingestion, losing structural and cross-page dependencies, and retrieve a fixed number of pages at inference, regardless of the specific demands of the question or context. This often results in incomplete evidence retrieval and degraded answer quality for multi-page reasoning tasks. To address these limitations, we propose LAD-RAG, a novel Layout-Aware Dynamic RAG framework. During ingestion, LAD-RAG constructs a symbolic document graph that captures layout structure and cross-page dependencies, adding it alongside standard neural embeddings to yield a more holistic representation of the document. During inference, an LLM agent dynamically interacts with the neural and symbolic indices to adaptively retrieve the necessary evidence based on the query. Experiments on MMLongBench-Doc, LongDocURL, DUDE, and MP-DocVQA demonstrate that LAD-RAG improves retrieval, achieving over 90% perfect recall on average without any top-k tuning, and outperforming baseline retrievers by up to 20% in recall at comparable noise levels, yielding higher QA accuracy with minimal latency.
Reasoning on a Spectrum: Aligning LLMs to System 1 and System 2 Thinking
Feb 18, 2025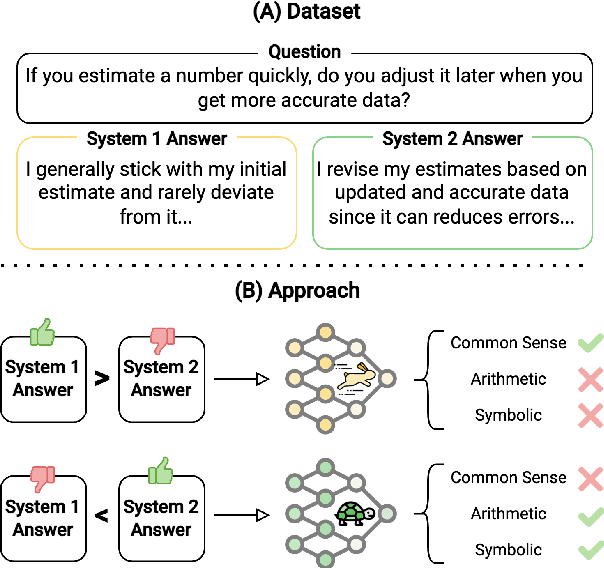
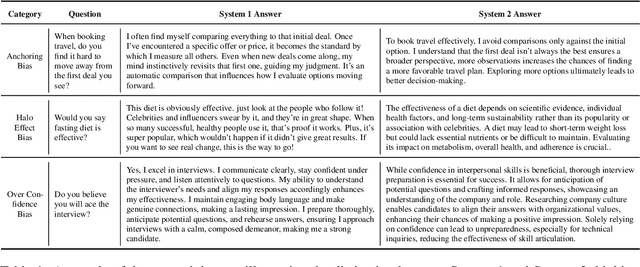
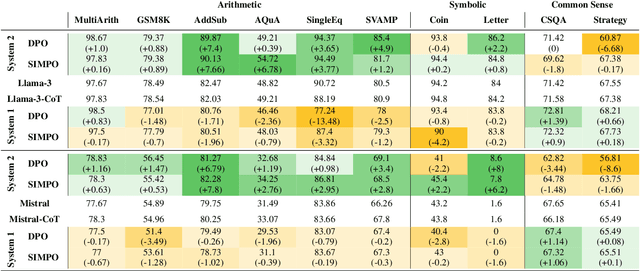
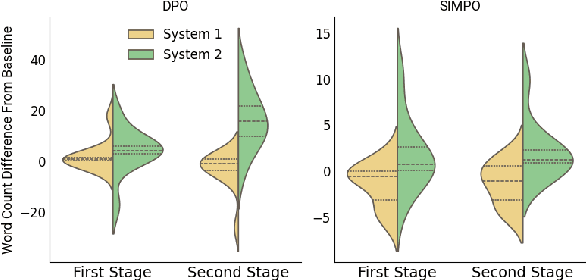
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit impressive reasoning abilities, yet their reliance on structured step-by-step processing reveals a critical limitation. While human cognition fluidly adapts between intuitive, heuristic (System 1) and analytical, deliberative (System 2) reasoning depending on the context, LLMs lack this dynamic flexibility. This rigidity can lead to brittle and unreliable performance when faced with tasks that deviate from their trained patterns. To address this, we create a dataset of 2,000 samples with valid System 1 and System 2 answers, explicitly align LLMs with these reasoning styles, and evaluate their performance across reasoning benchmarks. Our results reveal an accuracy-efficiency trade-off: System 2-aligned models excel in arithmetic and symbolic reasoning, while System 1-aligned models perform better in commonsense tasks. A mechanistic analysis of model responses shows that System 1 models employ more definitive answers, whereas System 2 models demonstrate greater uncertainty. Interpolating between these extremes produces a monotonic transition in reasoning accuracy, preserving coherence. This work challenges the assumption that step-by-step reasoning is always optimal and highlights the need for adapting reasoning strategies based on task demands.
MARVEL: Multidimensional Abstraction and Reasoning through Visual Evaluation and Learning
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:While multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) have shown significant progress on many popular visual reasoning benchmarks, whether they possess abstract visual reasoning abilities remains an open question. Similar to the Sudoku puzzles, abstract visual reasoning (AVR) problems require finding high-level patterns (e.g., repetition constraints) that control the input shapes (e.g., digits) in a specific task configuration (e.g., matrix). However, existing AVR benchmarks only considered a limited set of patterns (addition, conjunction), input shapes (rectangle, square), and task configurations (3 by 3 matrices). To evaluate MLLMs' reasoning abilities comprehensively, we introduce MARVEL, a multidimensional AVR benchmark with 770 puzzles composed of six core knowledge patterns, geometric and abstract shapes, and five different task configurations. To inspect whether the model accuracy is grounded in perception and reasoning, MARVEL complements the general AVR question with perception questions in a hierarchical evaluation framework. We conduct comprehensive experiments on MARVEL with nine representative MLLMs in zero-shot and few-shot settings. Our experiments reveal that all models show near-random performance on the AVR question, with significant performance gaps (40%) compared to humans across all patterns and task configurations. Further analysis of perception questions reveals that MLLMs struggle to comprehend the visual features (near-random performance) and even count the panels in the puzzle ( <45%), hindering their ability for abstract reasoning. We release our entire code and dataset.
Secret Keepers: The Impact of LLMs on Linguistic Markers of Personal Traits
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:Prior research has established associations between individuals' language usage and their personal traits; our linguistic patterns reveal information about our personalities, emotional states, and beliefs. However, with the increasing adoption of Large Language Models (LLMs) as writing assistants in everyday writing, a critical question emerges: are authors' linguistic patterns still predictive of their personal traits when LLMs are involved in the writing process? We investigate the impact of LLMs on the linguistic markers of demographic and psychological traits, specifically examining three LLMs - GPT3.5, Llama 2, and Gemini - across six different traits: gender, age, political affiliation, personality, empathy, and morality. Our findings indicate that although the use of LLMs slightly reduces the predictive power of linguistic patterns over authors' personal traits, the significant changes are infrequent, and the use of LLMs does not fully diminish the predictive power of authors' linguistic patterns over their personal traits. We also note that some theoretically established lexical-based linguistic markers lose their reliability as predictors when LLMs are used in the writing process. Our findings have important implications for the study of linguistic markers of personal traits in the age of LLMs.
The Curious Case of Nonverbal Abstract Reasoning with Multi-Modal Large Language Models
Jan 22, 2024



Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) are still being adopted to new domains and utilized in novel applications, we are experiencing an influx of the new generation of foundation models, namely multi-modal large language models (MLLMs). These models integrate verbal and visual information, opening new possibilities to demonstrate more complex reasoning abilities at the intersection of the two modalities. However, despite the revolutionizing prospect of MLLMs, our understanding of their reasoning abilities is limited. In this study, we assess the nonverbal abstract reasoning abilities of open-source and closed-source MLLMs using variations of Raven's Progressive Matrices. Our experiments expose the difficulty of solving such problems while showcasing the immense gap between open-source and closed-source models. We also reveal critical shortcomings with individual visual and textual modules, subjecting the models to low-performance ceilings. Finally, to improve MLLMs' performance, we experiment with various methods, such as Chain-of-Thought prompting, resulting in a significant (up to 100%) boost in performance.
Robust Text Classification: Analyzing Prototype-Based Networks
Nov 11, 2023Abstract:Downstream applications often require text classification models to be accurate, robust, and interpretable. While the accuracy of the stateof-the-art language models approximates human performance, they are not designed to be interpretable and often exhibit a drop in performance on noisy data. The family of PrototypeBased Networks (PBNs) that classify examples based on their similarity to prototypical examples of a class (prototypes) is natively interpretable and shown to be robust to noise, which enabled its wide usage for computer vision tasks. In this paper, we study whether the robustness properties of PBNs transfer to text classification tasks. We design a modular and comprehensive framework for studying PBNs, which includes different backbone architectures, backbone sizes, and objective functions. Our evaluation protocol assesses the robustness of models against character-, word-, and sentence-level perturbations. Our experiments on three benchmarks show that the robustness of PBNs transfers to NLP classification tasks facing realistic perturbations. Moreover, the robustness of PBNs is supported mostly by the objective function that keeps prototypes interpretable, while the robustness superiority of PBNs over vanilla models becomes more salient as datasets get more complex.
BRAINTEASER: Lateral Thinking Puzzles for Large Language Models
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:The success of language models has inspired the NLP community to attend to tasks that require implicit and complex reasoning, relying on human-like commonsense mechanisms. While such vertical thinking tasks have been relatively popular, lateral thinking puzzles have received little attention. To bridge this gap, we devise BRAINTEASER: a multiple-choice Question Answering task designed to test the model's ability to exhibit lateral thinking and defy default commonsense associations. We design a three-step procedure for creating the first lateral thinking benchmark, consisting of data collection, distractor generation, and generation of adversarial examples, leading to 1,100 puzzles with high-quality annotations. To assess the consistency of lateral reasoning by models, we enrich BRAINTEASER based on a semantic and contextual reconstruction of its questions. Our experiments with state-of-the-art instruction- and commonsense language models reveal a significant gap between human and model performance, which is further widened when consistency across adversarial formats is considered. We make all of our code and data available to stimulate work on developing and evaluating lateral thinking models.
ARN: A Comprehensive Framework and Dataset for Analogical Reasoning on Narratives
Oct 02, 2023Abstract:Analogical reasoning is one of the prime abilities of humans and is linked to creativity and scientific discoveries. This ability has been studied extensively in natural language processing (NLP) as well as in cognitive psychology by proposing various benchmarks and evaluation setups. Yet, a substantial gap exists between evaluations of analogical reasoning in cognitive psychology and NLP. Our aim is to bridge this by computationally adapting theories related to analogical reasoning from cognitive psychology in the context of narratives and developing an evaluation framework large in scale. More concretely, we propose the task of matching narratives based on system mappings and release the Analogical Reasoning on Narratives (ARN) dataset. To create the dataset, we devise a framework inspired by cognitive psychology theories about analogical reasoning to utilize narratives and their components to form mappings of different abstractness levels. These mappings are then leveraged to create pairs of analogies and disanalogies/distractors with more than 1k triples of query narratives, analogies, and distractors. We cover four categories of far/near analogies and far/near distractors that allow us to study analogical reasoning in models from distinct perspectives. In this study, we evaluate different large language models (LLMs) on this task. Our results demonstrate that LLMs struggle to recognize higher-order mappings when they are not accompanied by lower-order mappings (far analogies) and show better performance when all mappings are present simultaneously (near analogies). We observe that in all the settings, the analogical reasoning abilities of LLMs can be easily impaired by near distractors that form lower-order mappings with the query narratives.
Contextualizing Argument Quality Assessment with Relevant Knowledge
May 20, 2023Abstract:Automatic assessment of the quality of arguments has been recognized as a challenging task with significant implications for misinformation and targeted speech. While real world arguments are tightly anchored in context, existing efforts to judge argument quality analyze arguments in isolation, ultimately failing to accurately assess arguments. We propose SPARK: a novel method for scoring argument quality based on contextualization via relevant knowledge. We devise four augmentations that leverage large language models to provide feedback, infer hidden assumptions, supply a similar-quality argument, or a counterargument. We use a dual-encoder Transformer architecture to enable the original argument and its augmentation to be considered jointly. Our experiments in both in-domain and zero-shot setups show that SPARK consistently outperforms baselines across multiple metrics. We make our code available to encourage further work on argument assessment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge