Zhengchen Zhang
Multi-Speaker Multi-Style Speech Synthesis with Timbre and Style Disentanglement
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Disentanglement of a speaker's timbre and style is very important for style transfer in multi-speaker multi-style text-to-speech (TTS) scenarios. With the disentanglement of timbres and styles, TTS systems could synthesize expressive speech for a given speaker with any style which has been seen in the training corpus. However, there are still some shortcomings with the current research on timbre and style disentanglement. The current method either requires single-speaker multi-style recordings, which are difficult and expensive to collect, or uses a complex network and complicated training method, which is difficult to reproduce and control the style transfer behavior. To improve the disentanglement effectiveness of timbres and styles, and to remove the reliance on single-speaker multi-style corpus, a simple but effective timbre and style disentanglement method is proposed in this paper. The FastSpeech2 network is employed as the backbone network, with explicit duration, pitch, and energy trajectory to represent the style. Each speaker's data is considered as a separate and isolated style, then a speaker embedding and a style embedding are added to the FastSpeech2 network to learn disentangled representations. Utterance level pitch and energy normalization are utilized to improve the decoupling effect. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model could synthesize speech with any style seen during training with high style similarity while maintaining very high speaker similarity.
MaskedSpeech: Context-aware Speech Synthesis with Masking Strategy
Nov 11, 2022Abstract:Humans often speak in a continuous manner which leads to coherent and consistent prosody properties across neighboring utterances. However, most state-of-the-art speech synthesis systems only consider the information within each sentence and ignore the contextual semantic and acoustic features. This makes it inadequate to generate high-quality paragraph-level speech which requires high expressiveness and naturalness. To synthesize natural and expressive speech for a paragraph, a context-aware speech synthesis system named MaskedSpeech is proposed in this paper, which considers both contextual semantic and acoustic features. Inspired by the masking strategy in the speech editing research, the acoustic features of the current sentence are masked out and concatenated with those of contextual speech, and further used as additional model input. The phoneme encoder takes the concatenated phoneme sequence from neighboring sentences as input and learns fine-grained semantic information from contextual text. Furthermore, cross-utterance coarse-grained semantic features are employed to improve the prosody generation. The model is trained to reconstruct the masked acoustic features with the augmentation of both the contextual semantic and acoustic features. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MaskedSpeech outperformed the baseline system significantly in terms of naturalness and expressiveness.
Singing Voice Synthesis with Vibrato Modeling and Latent Energy Representation
Nov 02, 2022Abstract:This paper proposes an expressive singing voice synthesis system by introducing explicit vibrato modeling and latent energy representation. Vibrato is essential to the naturalness of synthesized sound, due to the inherent characteristics of human singing. Hence, a deep learning-based vibrato model is introduced in this paper to control the vibrato's likeliness, rate, depth and phase in singing, where the vibrato likeliness represents the existence probability of vibrato and it would help improve the singing voice's naturalness. Actually, there is no annotated label about vibrato likeliness in existing singing corpus. We adopt a novel vibrato likeliness labeling method to label the vibrato likeliness automatically. Meanwhile, the power spectrogram of audio contains rich information that can improve the expressiveness of singing. An autoencoder-based latent energy bottleneck feature is proposed for expressive singing voice synthesis. Experimental results on the open dataset NUS48E show that both the vibrato modeling and the latent energy representation could significantly improve the expressiveness of singing voice. The audio samples are shown in the demo website.
ViDA-MAN: Visual Dialog with Digital Humans
Oct 26, 2021

Abstract:We demonstrate ViDA-MAN, a digital-human agent for multi-modal interaction, which offers realtime audio-visual responses to instant speech inquiries. Compared to traditional text or voice-based system, ViDA-MAN offers human-like interactions (e.g, vivid voice, natural facial expression and body gestures). Given a speech request, the demonstration is able to response with high quality videos in sub-second latency. To deliver immersive user experience, ViDA-MAN seamlessly integrates multi-modal techniques including Acoustic Speech Recognition (ASR), multi-turn dialog, Text To Speech (TTS), talking heads video generation. Backed with large knowledge base, ViDA-MAN is able to chat with users on a number of topics including chit-chat, weather, device control, News recommendations, booking hotels, as well as answering questions via structured knowledge.
SCaLa: Supervised Contrastive Learning for End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition
Oct 08, 2021



Abstract:End-to-end Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models are usually trained to reduce the losses of the whole token sequences, while neglecting explicit phonemic-granularity supervision. This could lead to recognition errors due to similar-phoneme confusion or phoneme reduction. To alleviate this problem, this paper proposes a novel framework of Supervised Contrastive Learning (SCaLa) to enhance phonemic information learning for end-to-end ASR systems. Specifically, we introduce the self-supervised Masked Contrastive Predictive Coding (MCPC) into the fully-supervised setting. To supervise phoneme learning explicitly, SCaLa first masks the variable-length encoder features corresponding to phonemes given phoneme forced-alignment extracted from a pre-trained acoustic model, and then predicts the masked phonemes via contrastive learning. The phoneme forced-alignment can mitigate the noise of positive-negative pairs in self-supervised MCPC. Experimental results conducted on reading and spontaneous speech datasets show that the proposed approach achieves 2.84% and 1.38% Character Error Rate (CER) reductions compared to the baseline, respectively.
Improving Prosody Modelling with Cross-Utterance BERT Embeddings for End-to-end Speech Synthesis
Nov 06, 2020



Abstract:Despite prosody is related to the linguistic information up to the discourse structure, most text-to-speech (TTS) systems only take into account that within each sentence, which makes it challenging when converting a paragraph of texts into natural and expressive speech. In this paper, we propose to use the text embeddings of the neighboring sentences to improve the prosody generation for each utterance of a paragraph in an end-to-end fashion without using any explicit prosody features. More specifically, cross-utterance (CU) context vectors, which are produced by an additional CU encoder based on the sentence embeddings extracted by a pre-trained BERT model, are used to augment the input of the Tacotron2 decoder. Two types of BERT embeddings are investigated, which leads to the use of different CU encoder structures. Experimental results on a Mandarin audiobook dataset and the LJ-Speech English audiobook dataset demonstrate the use of CU information can improve the naturalness and expressiveness of the synthesized speech. Subjective listening testing shows most of the participants prefer the voice generated using the CU encoder over that generated using standard Tacotron2. It is also found that the prosody can be controlled indirectly by changing the neighbouring sentences.
Transition-based Parsing with Context Enhancement and Future Reward Reranking
Dec 15, 2016

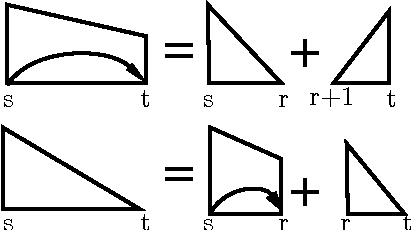
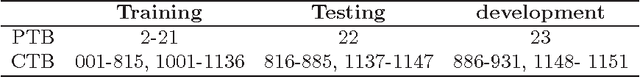
Abstract:This paper presents a novel reranking model, future reward reranking, to re-score the actions in a transition-based parser by using a global scorer. Different to conventional reranking parsing, the model searches for the best dependency tree in all feasible trees constraining by a sequence of actions to get the future reward of the sequence. The scorer is based on a first-order graph-based parser with bidirectional LSTM, which catches different parsing view compared with the transition-based parser. Besides, since context enhancement has shown substantial improvement in the arc-stand transition-based parsing over the parsing accuracy, we implement context enhancement on an arc-eager transition-base parser with stack LSTMs, the dynamic oracle and dropout supporting and achieve further improvement. With the global scorer and context enhancement, the results show that UAS of the parser increases as much as 1.20% for English and 1.66% for Chinese, and LAS increases as much as 1.32% for English and 1.63% for Chinese. Moreover, we get state-of-the-art LASs, achieving 87.58% for Chinese and 93.37% for English.
Telerobotic Pointing Gestures Shape Human Spatial Cognition
Jul 08, 2012



Abstract:This paper aimed to explore whether human beings can understand gestures produced by telepresence robots. If it were the case, they can derive meaning conveyed in telerobotic gestures when processing spatial information. We conducted two experiments over Skype in the present study. Participants were presented with a robotic interface that had arms, which were teleoperated by an experimenter. The robot could point to virtual locations that represented certain entities. In Experiment 1, the experimenter described spatial locations of fictitious objects sequentially in two conditions: speech condition (SO, verbal descriptions clearly indicated the spatial layout) and speech and gesture condition (SR, verbal descriptions were ambiguous but accompanied by robotic pointing gestures). Participants were then asked to recall the objects' spatial locations. We found that the number of spatial locations recalled in the SR condition was on par with that in the SO condition, suggesting that telerobotic pointing gestures compensated ambiguous speech during the process of spatial information. In Experiment 2, the experimenter described spatial locations non-sequentially in the SR and SO conditions. Surprisingly, the number of spatial locations recalled in the SR condition was even higher than that in the SO condition, suggesting that telerobotic pointing gestures were more powerful than speech in conveying spatial information when information was presented in an unpredictable order. The findings provide evidence that human beings are able to comprehend telerobotic gestures, and importantly, integrate these gestures with co-occurring speech. This work promotes engaging remote collaboration among humans through a robot intermediary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge