Yuxin Xiong
K2-Think: A Parameter-Efficient Reasoning System
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:K2-Think is a reasoning system that achieves state-of-the-art performance with a 32B parameter model, matching or surpassing much larger models like GPT-OSS 120B and DeepSeek v3.1. Built on the Qwen2.5 base model, our system shows that smaller models can compete at the highest levels by combining advanced post-training and test-time computation techniques. The approach is based on six key technical pillars: Long Chain-of-thought Supervised Finetuning, Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), Agentic planning prior to reasoning, Test-time Scaling, Speculative Decoding, and Inference-optimized Hardware, all using publicly available open-source datasets. K2-Think excels in mathematical reasoning, achieving state-of-the-art scores on public benchmarks for open-source models, while also performing strongly in other areas such as Code and Science. Our results confirm that a more parameter-efficient model like K2-Think 32B can compete with state-of-the-art systems through an integrated post-training recipe that includes long chain-of-thought training and strategic inference-time enhancements, making open-source reasoning systems more accessible and affordable. K2-Think is freely available at k2think.ai, offering best-in-class inference speeds of over 2,000 tokens per second per request via the Cerebras Wafer-Scale Engine.
Mitigating Visual Knowledge Forgetting in MLLM Instruction-tuning via Modality-decoupled Gradient Descent
Feb 17, 2025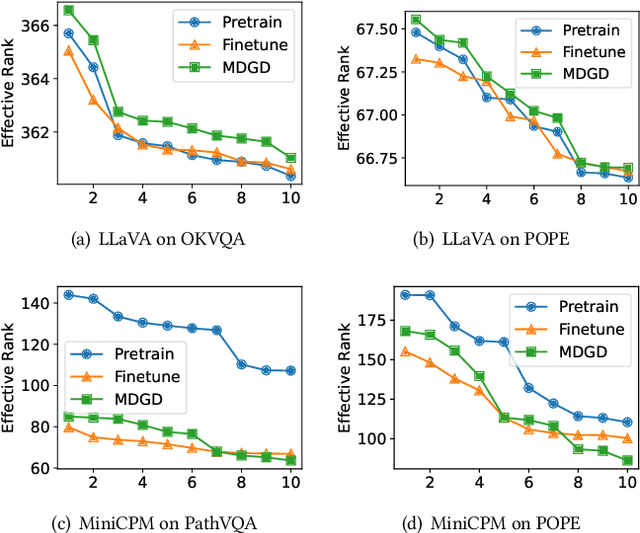
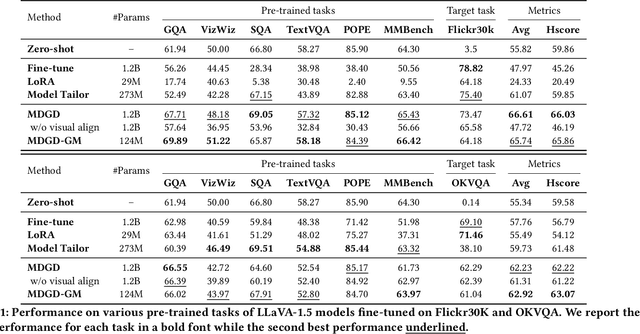

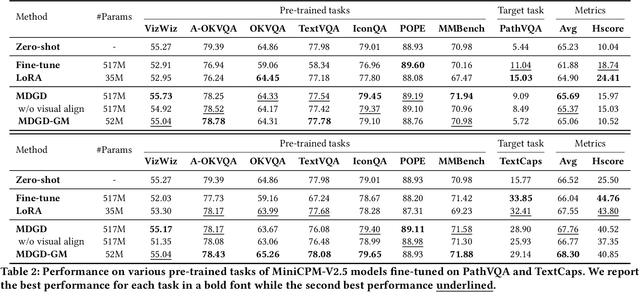
Abstract:Recent MLLMs have shown emerging visual understanding and reasoning abilities after being pre-trained on large-scale multimodal datasets. Unlike pre-training, where MLLMs receive rich visual-text alignment, instruction-tuning is often text-driven with weaker visual supervision, leading to the degradation of pre-trained visual understanding and causing visual forgetting. Existing approaches, such as direct fine-tuning and continual learning methods, fail to explicitly address this issue, often compressing visual representations and prioritizing task alignment over visual retention, which further worsens visual forgetting. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a novel perspective leveraging effective rank to quantify the degradation of visual representation richness, interpreting this degradation through the information bottleneck principle as excessive compression that leads to the degradation of crucial pre-trained visual knowledge. Building on this view, we propose a modality-decoupled gradient descent (MDGD) method that regulates gradient updates to maintain the effective rank of visual representations while mitigating the over-compression effects described by the information bottleneck. By explicitly disentangling the optimization of visual understanding from task-specific alignment, MDGD preserves pre-trained visual knowledge while enabling efficient task adaptation. To enable lightweight instruction-tuning, we further develop a memory-efficient fine-tuning approach using gradient masking, which selectively updates a subset of model parameters to enable parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), reducing computational overhead while preserving rich visual representations. Extensive experiments across various downstream tasks and backbone MLLMs demonstrate that MDGD effectively mitigates visual forgetting from pre-trained tasks while enabling strong adaptation to new tasks.
OCEAN: Offline Chain-of-thought Evaluation and Alignment in Large Language Models
Oct 31, 2024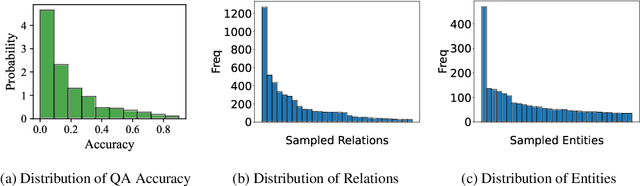
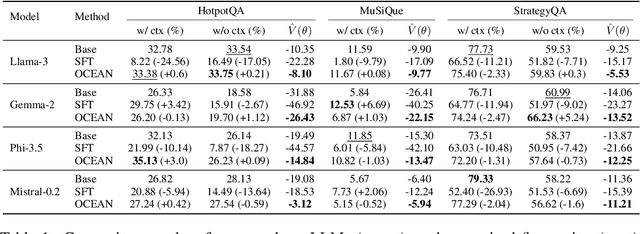
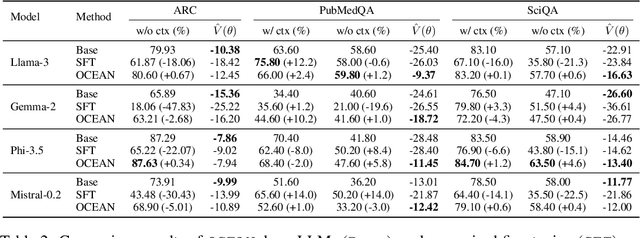
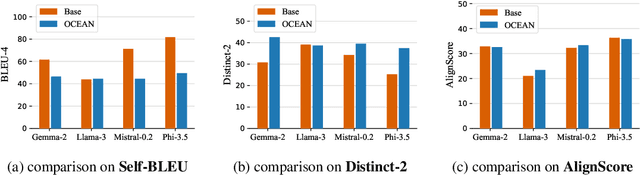
Abstract:Offline evaluation of LLMs is crucial in understanding their capacities, though current methods remain underexplored in existing research. In this work, we focus on the offline evaluation of the chain-of-thought capabilities and show how to optimize LLMs based on the proposed evaluation method. To enable offline feedback with rich knowledge and reasoning paths, we use knowledge graphs (e.g., Wikidata5m) to provide feedback on the generated chain of thoughts. Due to the heterogeneity between LLM reasoning and KG structures, direct interaction and feedback from KGs on LLM behavior are challenging, as they require accurate entity linking and grounding of LLM-generated chains of thought in the KG. To address the above challenge, we propose an offline chain-of-thought evaluation framework, OCEAN, which models chain-of-thought reasoning in LLMs as an MDP and evaluate the policy's alignment with KG preference modeling. To overcome the reasoning heterogeneity and grounding problems, we leverage on-policy KG exploration and RL to model a KG policy that generates token-level likelihood distributions for LLM-generated chain-of-thought reasoning paths, simulating KG reasoning preference. Then we incorporate the knowledge-graph feedback on the validity and alignment of the generated reasoning paths into inverse propensity scores and propose KG-IPS estimator. Theoretically, we prove the unbiasedness of the proposed KG-IPS estimator and provide a lower bound on its variance. With the off-policy evaluated value function, we can directly enable off-policy optimization to further enhance chain-of-thought alignment. Our empirical study shows that OCEAN can be efficiently optimized for generating chain-of-thought reasoning paths with higher estimated values without affecting LLMs' general abilities in downstream tasks or their internal knowledge.
Self-Alignment of Large Language Models via Monopolylogue-based Social Scene Simulation
Feb 08, 2024



Abstract:Aligning large language models (LLMs) with human values is imperative to mitigate potential adverse effects resulting from their misuse. Drawing from the sociological insight that acknowledging all parties' concerns is a key factor in shaping human values, this paper proposes a novel direction to align LLMs by themselves: social scene simulation. To achieve this, we present MATRIX, a novel social scene simulator that emulates realistic scenes around a user's input query, enabling the LLM to take social consequences into account before responding. MATRIX serves as a virtual rehearsal space, akin to a Monopolylogue, where the LLM performs diverse roles related to the query and practice by itself. To inject this alignment, we fine-tune the LLM with MATRIX-simulated data, ensuring adherence to human values without compromising inference speed. We theoretically show that the LLM with MATRIX outperforms Constitutional AI under mild assumptions. Finally, extensive experiments validate that our method outperforms over 10 baselines across 4 benchmarks. As evidenced by 875 user ratings, our tuned 13B-size LLM exceeds GPT-4 in aligning with human values. Code is available at https://github.com/pangxianghe/MATRIX.
Emergent Communication in Interactive Sketch Question Answering
Oct 24, 2023
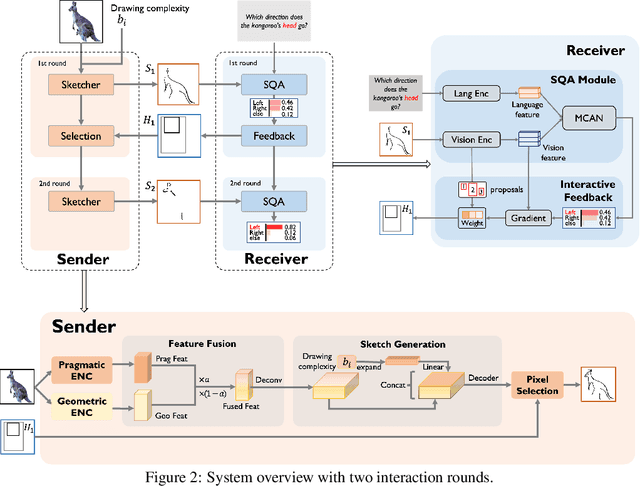

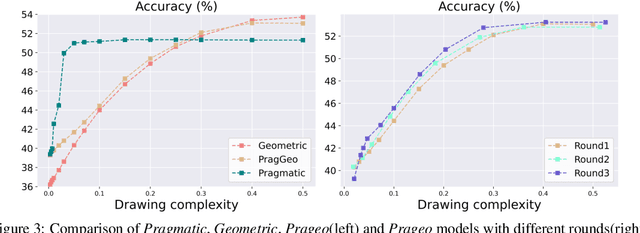
Abstract:Vision-based emergent communication (EC) aims to learn to communicate through sketches and demystify the evolution of human communication. Ironically, previous works neglect multi-round interaction, which is indispensable in human communication. To fill this gap, we first introduce a novel Interactive Sketch Question Answering (ISQA) task, where two collaborative players are interacting through sketches to answer a question about an image in a multi-round manner. To accomplish this task, we design a new and efficient interactive EC system, which can achieve an effective balance among three evaluation factors, including the question answering accuracy, drawing complexity and human interpretability. Our experimental results including human evaluation demonstrate that multi-round interactive mechanism facilitates targeted and efficient communication between intelligent agents with decent human interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge