Yuxiao Qu
Reasoning Cache: Continual Improvement Over Long Horizons via Short-Horizon RL
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) that can continually improve beyond their training budgets are able to solve increasingly difficult problems by adapting at test time, a property we refer to as extrapolation. However, standard reinforcement learning (RL) operates over fixed problem distributions and training budgets, which limits extrapolation amidst distribution shift at test time. To address this, we introduce RC, an iterative decoding algorithm that replaces standard autoregressive decoding during both training and inference. RC exploits an asymmetry between the response generation and summarization capabilities of LLMs to construct reasoning chains that consistently improve across iterations. Models trained to use RC can extrapolate and continually improve over reasoning horizons more than an order of magnitude longer than those seen during training. Empirically, training a 4B model with RC using a 16k-token training budget improves performance on HMMT 2025 from 40% to nearly 70% with 0.5m tokens at test time, outperforming both comparably sized models and many larger reasoning LLMs. Finally, we also show that models trained with RC can more effectively leverage existing scaffolds to further scale test-time performance, due to the improved summary-conditioned generation abilities learned through training.
POPE: Learning to Reason on Hard Problems via Privileged On-Policy Exploration
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has improved the reasoning abilities of large language models (LLMs), yet state-of-the-art methods still fail to learn on many training problems. On hard problems, on-policy RL rarely explores even a single correct rollout, yielding zero reward and no learning signal for driving improvement. We find that natural solutions to remedy this exploration problem from classical RL, such as entropy bonuses, more permissive clipping of the importance ratio, or direct optimization of pass@k objectives, do not resolve this issue and often destabilize optimization without improving solvability. A natural alternative is to leverage transfer from easier problems. However, we show that mixing easy and hard problems during RL training is counterproductive due to ray interference, where optimization focuses on already-solvable problems in a way that actively inhibits progress on harder ones. To address this challenge, we introduce Privileged On-Policy Exploration (POPE), an approach that leverages human- or other oracle solutions as privileged information to guide exploration on hard problems, unlike methods that use oracle solutions as training targets (e.g., off-policy RL methods or warmstarting from SFT). POPE augments hard problems with prefixes of oracle solutions, enabling RL to obtain non-zero rewards during guided rollouts. Crucially, the resulting behaviors transfer back to the original, unguided problems through a synergy between instruction-following and reasoning. Empirically, POPE expands the set of solvable problems and substantially improves performance on challenging reasoning benchmarks.
RLAD: Training LLMs to Discover Abstractions for Solving Reasoning Problems
Oct 02, 2025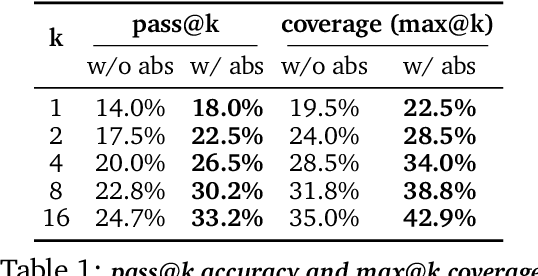
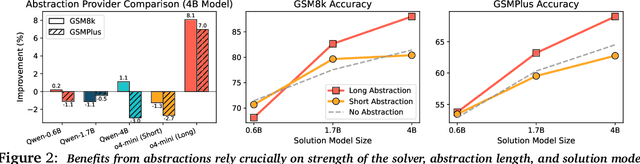
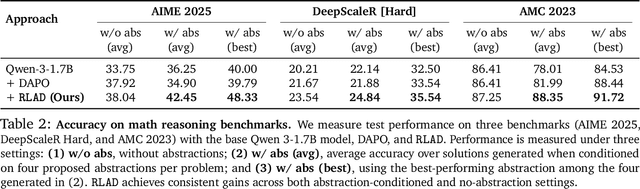
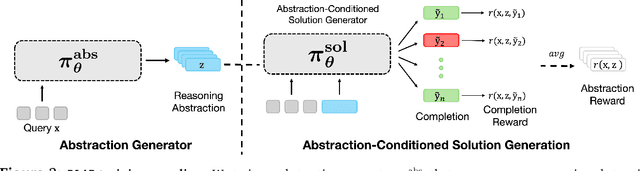
Abstract:Reasoning requires going beyond pattern matching or memorization of solutions to identify and implement "algorithmic procedures" that can be used to deduce answers to hard problems. Doing so requires realizing the most relevant primitives, intermediate results, or shared procedures, and building upon them. While RL post-training on long chains of thought ultimately aims to uncover this kind of algorithmic behavior, most reasoning traces learned by large models fail to consistently capture or reuse procedures, instead drifting into verbose and degenerate exploration. To address more effective reasoning, we introduce reasoning abstractions: concise natural language descriptions of procedural and factual knowledge that guide the model toward learning successful reasoning. We train models to be capable of proposing multiple abstractions given a problem, followed by RL that incentivizes building a solution while using the information provided by these abstractions. This results in a two-player RL training paradigm, abbreviated as RLAD, that jointly trains an abstraction generator and a solution generator. This setup effectively enables structured exploration, decouples learning signals of abstraction proposal and solution generation, and improves generalization to harder problems. We also show that allocating more test-time compute to generating abstractions is more beneficial for performance than generating more solutions at large test budgets, illustrating the role of abstractions in guiding meaningful exploration.
Optimizing Test-Time Compute via Meta Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:Training models to effectively use test-time compute is crucial for improving the reasoning performance of LLMs. Current methods mostly do so via fine-tuning on search traces or running RL with 0/1 outcome reward, but do these approaches efficiently utilize test-time compute? Would these approaches continue to scale as the budget improves? In this paper, we try to answer these questions. We formalize the problem of optimizing test-time compute as a meta-reinforcement learning (RL) problem, which provides a principled perspective on spending test-time compute. This perspective enables us to view the long output stream from the LLM as consisting of several episodes run at test time and leads us to use a notion of cumulative regret over output tokens as a way to measure the efficacy of test-time compute. Akin to how RL algorithms can best tradeoff exploration and exploitation over training, minimizing cumulative regret would also provide the best balance between exploration and exploitation in the token stream. While we show that state-of-the-art models do not minimize regret, one can do so by maximizing a dense reward bonus in conjunction with the outcome 0/1 reward RL. This bonus is the ''progress'' made by each subsequent block in the output stream, quantified by the change in the likelihood of eventual success. Using these insights, we develop Meta Reinforcement Fine-Tuning, or MRT, a new class of fine-tuning methods for optimizing test-time compute. MRT leads to a 2-3x relative gain in performance and roughly a 1.5x gain in token efficiency for math reasoning compared to outcome-reward RL.
Harnessing Webpage UIs for Text-Rich Visual Understanding
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Text-rich visual understanding-the ability to process environments where dense textual content is integrated with visuals-is crucial for multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to interact effectively with structured environments. To enhance this capability, we propose synthesizing general multimodal instructions from webpage UIs using text-based large language models (LLMs). Despite lacking direct visual input, text-based LLMs are able to process structured text representations from webpage accessibility trees. These instructions are then paired with UI screenshots to train multimodal models. We introduce MultiUI, a dataset containing 7.3 million samples from 1 million websites, covering diverse multimodal tasks and UI layouts. Models trained on MultiUI not only excel in web UI tasks-achieving up to a 48\% improvement on VisualWebBench and a 19.1\% boost in action accuracy on a web agent dataset Mind2Web-but also generalize surprisingly well to non-web UI tasks and even to non-UI domains, such as document understanding, OCR, and chart interpretation. These results highlight the broad applicability of web UI data for advancing text-rich visual understanding across various scenarios.
Recursive Introspection: Teaching Language Model Agents How to Self-Improve
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:A central piece in enabling intelligent agentic behavior in foundation models is to make them capable of introspecting upon their behavior, reasoning, and correcting their mistakes as more computation or interaction is available. Even the strongest proprietary large language models (LLMs) do not quite exhibit the ability of continually improving their responses sequentially, even in scenarios where they are explicitly told that they are making a mistake. In this paper, we develop RISE: Recursive IntroSpEction, an approach for fine-tuning LLMs to introduce this capability, despite prior work hypothesizing that this capability may not be possible to attain. Our approach prescribes an iterative fine-tuning procedure, which attempts to teach the model how to alter its response after having executed previously unsuccessful attempts to solve a hard test-time problem, with optionally additional environment feedback. RISE poses fine-tuning for a single-turn prompt as solving a multi-turn Markov decision process (MDP), where the initial state is the prompt. Inspired by principles in online imitation learning and reinforcement learning, we propose strategies for multi-turn data collection and training so as to imbue an LLM with the capability to recursively detect and correct its previous mistakes in subsequent iterations. Our experiments show that RISE enables Llama2, Llama3, and Mistral models to improve themselves with more turns on math reasoning tasks, outperforming several single-turn strategies given an equal amount of inference-time computation. We also find that RISE scales well, often attaining larger benefits with more capable models. Our analysis shows that RISE makes meaningful improvements to responses to arrive at the correct solution for challenging prompts, without disrupting one-turn abilities as a result of expressing more complex distributions.
Guided Data Augmentation for Offline Reinforcement Learning and Imitation Learning
Oct 27, 2023Abstract:Learning from demonstration (LfD) is a popular technique that uses expert demonstrations to learn robot control policies. However, the difficulty in acquiring expert-quality demonstrations limits the applicability of LfD methods: real-world data collection is often costly, and the quality of the demonstrations depends greatly on the demonstrator's abilities and safety concerns. A number of works have leveraged data augmentation (DA) to inexpensively generate additional demonstration data, but most DA works generate augmented data in a random fashion and ultimately produce highly suboptimal data. In this work, we propose Guided Data Augmentation (GuDA), a human-guided DA framework that generates expert-quality augmented data. The key insight of GuDA is that while it may be difficult to demonstrate the sequence of actions required to produce expert data, a user can often easily identify when an augmented trajectory segment represents task progress. Thus, the user can impose a series of simple rules on the DA process to automatically generate augmented samples that approximate expert behavior. To extract a policy from GuDA, we use off-the-shelf offline reinforcement learning and behavior cloning algorithms. We evaluate GuDA on a physical robot soccer task as well as simulated D4RL navigation tasks, a simulated autonomous driving task, and a simulated soccer task. Empirically, we find that GuDA enables learning from a small set of potentially suboptimal demonstrations and substantially outperforms a DA strategy that samples augmented data randomly.
FLEE-GNN: A Federated Learning System for Edge-Enhanced Graph Neural Network in Analyzing Geospatial Resilience of Multicommodity Food Flows
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Understanding and measuring the resilience of food supply networks is a global imperative to tackle increasing food insecurity. However, the complexity of these networks, with their multidimensional interactions and decisions, presents significant challenges. This paper proposes FLEE-GNN, a novel Federated Learning System for Edge-Enhanced Graph Neural Network, designed to overcome these challenges and enhance the analysis of geospatial resilience of multicommodity food flow network, which is one type of spatial networks. FLEE-GNN addresses the limitations of current methodologies, such as entropy-based methods, in terms of generalizability, scalability, and data privacy. It combines the robustness and adaptability of graph neural networks with the privacy-conscious and decentralized aspects of federated learning on food supply network resilience analysis across geographical regions. This paper also discusses FLEE-GNN's innovative data generation techniques, experimental designs, and future directions for improvement. The results show the advancements of this approach to quantifying the resilience of multicommodity food flow networks, contributing to efforts towards ensuring global food security using AI methods. The developed FLEE-GNN has the potential to be applied in other spatial networks with spatially heterogeneous sub-network distributions.
* 10 pages, 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge