Yuting Su
Organ-Agents: Virtual Human Physiology Simulator via LLMs
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled new possibilities in simulating complex physiological systems. We introduce Organ-Agents, a multi-agent framework that simulates human physiology via LLM-driven agents. Each Simulator models a specific system (e.g., cardiovascular, renal, immune). Training consists of supervised fine-tuning on system-specific time-series data, followed by reinforcement-guided coordination using dynamic reference selection and error correction. We curated data from 7,134 sepsis patients and 7,895 controls, generating high-resolution trajectories across 9 systems and 125 variables. Organ-Agents achieved high simulation accuracy on 4,509 held-out patients, with per-system MSEs <0.16 and robustness across SOFA-based severity strata. External validation on 22,689 ICU patients from two hospitals showed moderate degradation under distribution shifts with stable simulation. Organ-Agents faithfully reproduces critical multi-system events (e.g., hypotension, hyperlactatemia, hypoxemia) with coherent timing and phase progression. Evaluation by 15 critical care physicians confirmed realism and physiological plausibility (mean Likert ratings 3.9 and 3.7). Organ-Agents also enables counterfactual simulations under alternative sepsis treatment strategies, generating trajectories and APACHE II scores aligned with matched real-world patients. In downstream early warning tasks, classifiers trained on synthetic data showed minimal AUROC drops (<0.04), indicating preserved decision-relevant patterns. These results position Organ-Agents as a credible, interpretable, and generalizable digital twin for precision diagnosis, treatment simulation, and hypothesis testing in critical care.
A Training-Free Plug-and-Play Watermark Framework for Stable Diffusion
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:Nowadays, the family of Stable Diffusion (SD) models has gained prominence for its high quality outputs and scalability. This has also raised security concerns on social media, as malicious users can create and disseminate harmful content. Existing approaches involve training components or entire SDs to embed a watermark in generated images for traceability and responsibility attribution. However, in the era of AI-generated content (AIGC), the rapid iteration of SDs renders retraining with watermark models costly. To address this, we propose a training-free plug-and-play watermark framework for SDs. Without modifying any components of SDs, we embed diverse watermarks in the latent space, adapting to the denoising process. Our experimental findings reveal that our method effectively harmonizes image quality and watermark invisibility. Furthermore, it performs robustly under various attacks. We also have validated that our method is generalized to multiple versions of SDs, even without retraining the watermark model.
Dynamic Causal Disentanglement Model for Dialogue Emotion Detection
Sep 13, 2023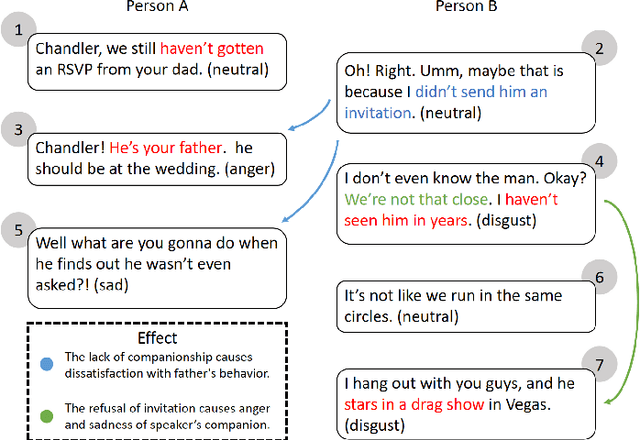
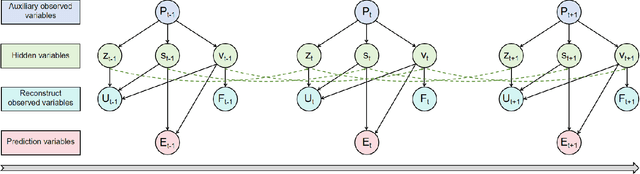
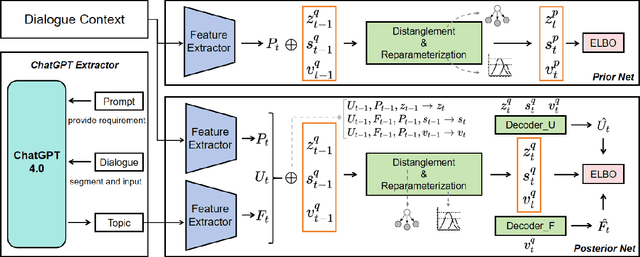
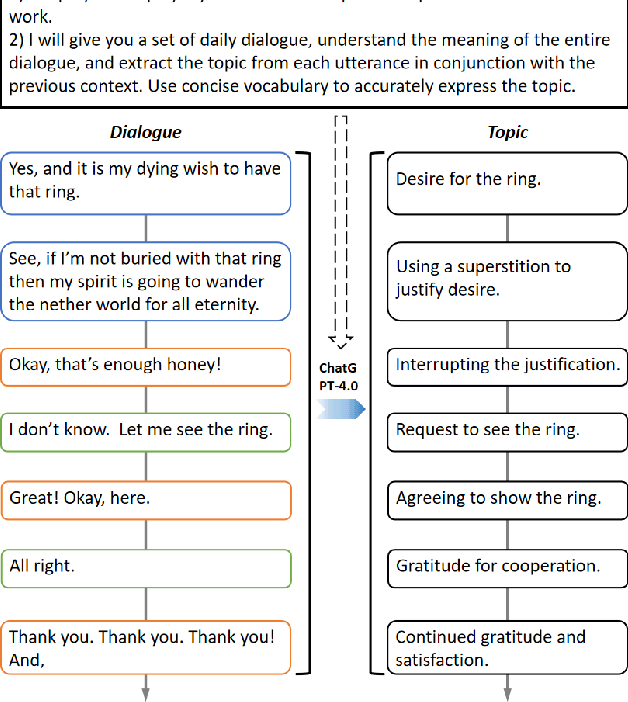
Abstract:Emotion detection is a critical technology extensively employed in diverse fields. While the incorporation of commonsense knowledge has proven beneficial for existing emotion detection methods, dialogue-based emotion detection encounters numerous difficulties and challenges due to human agency and the variability of dialogue content.In dialogues, human emotions tend to accumulate in bursts. However, they are often implicitly expressed. This implies that many genuine emotions remain concealed within a plethora of unrelated words and dialogues.In this paper, we propose a Dynamic Causal Disentanglement Model based on hidden variable separation, which is founded on the separation of hidden variables. This model effectively decomposes the content of dialogues and investigates the temporal accumulation of emotions, thereby enabling more precise emotion recognition. First, we introduce a novel Causal Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) to establish the correlation between hidden emotional information and other observed elements. Subsequently, our approach utilizes pre-extracted personal attributes and utterance topics as guiding factors for the distribution of hidden variables, aiming to separate irrelevant ones. Specifically, we propose a dynamic temporal disentanglement model to infer the propagation of utterances and hidden variables, enabling the accumulation of emotion-related information throughout the conversation. To guide this disentanglement process, we leverage the ChatGPT-4.0 and LSTM networks to extract utterance topics and personal attributes as observed information.Finally, we test our approach on two popular datasets in dialogue emotion detection and relevant experimental results verified the model's superiority.
T2IW: Joint Text to Image & Watermark Generation
Sep 07, 2023



Abstract:Recent developments in text-conditioned image generative models have revolutionized the production of realistic results. Unfortunately, this has also led to an increase in privacy violations and the spread of false information, which requires the need for traceability, privacy protection, and other security measures. However, existing text-to-image paradigms lack the technical capabilities to link traceable messages with image generation. In this study, we introduce a novel task for the joint generation of text to image and watermark (T2IW). This T2IW scheme ensures minimal damage to image quality when generating a compound image by forcing the semantic feature and the watermark signal to be compatible in pixels. Additionally, by utilizing principles from Shannon information theory and non-cooperative game theory, we are able to separate the revealed image and the revealed watermark from the compound image. Furthermore, we strengthen the watermark robustness of our approach by subjecting the compound image to various post-processing attacks, with minimal pixel distortion observed in the revealed watermark. Extensive experiments have demonstrated remarkable achievements in image quality, watermark invisibility, and watermark robustness, supported by our proposed set of evaluation metrics.
StyleEDL: Style-Guided High-order Attention Network for Image Emotion Distribution Learning
Aug 06, 2023Abstract:Emotion distribution learning has gained increasing attention with the tendency to express emotions through images. As for emotion ambiguity arising from humans' subjectivity, substantial previous methods generally focused on learning appropriate representations from the holistic or significant part of images. However, they rarely consider establishing connections with the stylistic information although it can lead to a better understanding of images. In this paper, we propose a style-guided high-order attention network for image emotion distribution learning termed StyleEDL, which interactively learns stylistic-aware representations of images by exploring the hierarchical stylistic information of visual contents. Specifically, we consider exploring the intra- and inter-layer correlations among GRAM-based stylistic representations, and meanwhile exploit an adversary-constrained high-order attention mechanism to capture potential interactions between subtle visual parts. In addition, we introduce a stylistic graph convolutional network to dynamically generate the content-dependent emotion representations to benefit the final emotion distribution learning. Extensive experiments conducted on several benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed StyleEDL compared to state-of-the-art methods. The implementation is released at: https://github.com/liuxianyi/StyleEDL.
DS-Net: Dynamic Spatiotemporal Network for Video Salient Object Detection
Dec 09, 2020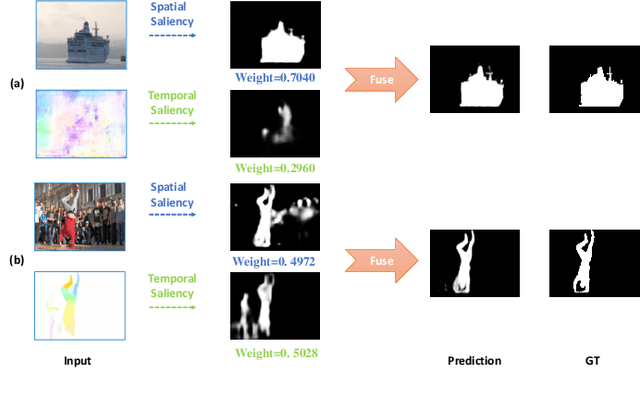
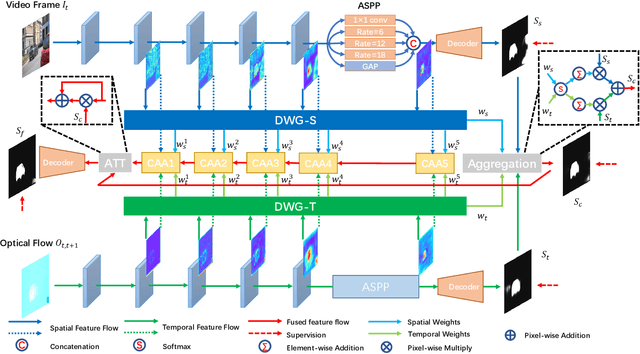
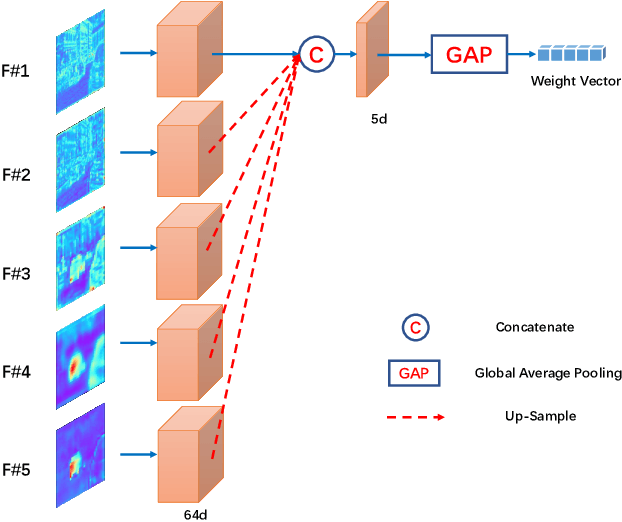
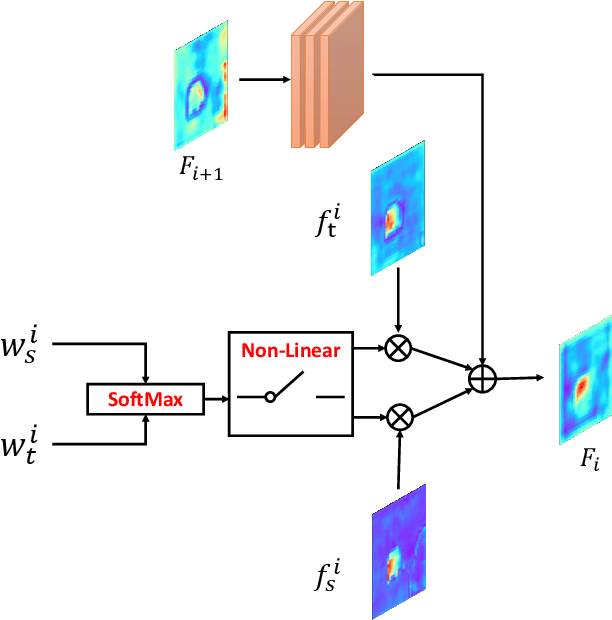
Abstract:As moving objects always draw more attention of human eyes, the temporal motive information is always exploited complementarily with spatial information to detect salient objects in videos. Although efficient tools such as optical flow have been proposed to extract temporal motive information, it often encounters difficulties when used for saliency detection due to the movement of camera or the partial movement of salient objects. In this paper, we investigate the complimentary roles of spatial and temporal information and propose a novel dynamic spatiotemporal network (DS-Net) for more effective fusion of spatiotemporal information. We construct a symmetric two-bypass network to explicitly extract spatial and temporal features. A dynamic weight generator (DWG) is designed to automatically learn the reliability of corresponding saliency branch. And a top-down cross attentive aggregation (CAA) procedure is designed so as to facilitate dynamic complementary aggregation of spatiotemporal features. Finally, the features are modified by spatial attention with the guidance of coarse saliency map and then go through decoder part for final saliency map. Experimental results on five benchmarks VOS, DAVIS, FBMS, SegTrack-v2, and ViSal demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior performance than state-of-the-art algorithms. The source code is available at https://github.com/TJUMMG/DS-Net.
Mnemonics Training: Multi-Class Incremental Learning without Forgetting
Feb 26, 2020



Abstract:Multi-Class Incremental Learning (MCIL) aims to learn new concepts by incrementally updating a model trained on previous concepts. However, there is an inherent trade-off to effectively learning new concepts without catastrophic forgetting of previous ones. To alleviate this issue, it has been proposed to keep around a few examples of the previous concepts but the effectiveness of this approach heavily depends on the representativeness of these examples. This paper proposes a novel and automatic framework we call mnemonics, where we parameterize exemplars and make them optimizable in an end-to-end manner. We train the framework through bilevel optimizations, i.e., model-level and exemplar-level. We conduct extensive experiments on three MCIL benchmarks, CIFAR-100, ImageNet-Subset and ImageNet, and show that using mnemonics exemplars can surpass the state-of-the-art by a large margin. Interestingly and quite intriguingly, the mnemonics exemplars tend to be on the boundaries between classes.
LCC: Learning to Customize and Combine Neural Networks for Few-Shot Learning
Apr 17, 2019



Abstract:Meta-learning has been shown to be an effective strategy for few-shot learning. The key idea is to leverage a large number of similar few-shot tasks in order to meta-learn how to best initiate a (single) base-learner for novel few-shot tasks. While meta-learning how to initialize a base-learner has shown promising results, it is well known that hyperparameter settings such as the learning rate and the weighting of the regularization term are important to achieve best performance. We thus propose to also meta-learn these hyperparameters and in fact learn a time- and layer-varying scheme for learning a base-learner on novel tasks. Additionally, we propose to learn not only a single base-learner but an ensemble of several base-learners to obtain more robust results. While ensembles of learners have shown to improve performance in various settings, this is challenging for few-shot learning tasks due to the limited number of training samples. Therefore, our approach also aims to meta-learn how to effectively combine several base-learners. We conduct extensive experiments and report top performance for five-class few-shot recognition tasks on two challenging benchmarks: miniImageNet and Fewshot-CIFAR100 (FC100).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge