Peiguang Jing
VIIS: Visible and Infrared Information Synthesis for Severe Low-light Image Enhancement
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Images captured in severe low-light circumstances often suffer from significant information absence. Existing singular modality image enhancement methods struggle to restore image regions lacking valid information. By leveraging light-impervious infrared images, visible and infrared image fusion methods have the potential to reveal information hidden in darkness. However, they primarily emphasize inter-modal complementation but neglect intra-modal enhancement, limiting the perceptual quality of output images. To address these limitations, we propose a novel task, dubbed visible and infrared information synthesis (VIIS), which aims to achieve both information enhancement and fusion of the two modalities. Given the difficulty in obtaining ground truth in the VIIS task, we design an information synthesis pretext task (ISPT) based on image augmentation. We employ a diffusion model as the framework and design a sparse attention-based dual-modalities residual (SADMR) conditioning mechanism to enhance information interaction between the two modalities. This mechanism enables features with prior knowledge from both modalities to adaptively and iteratively attend to each modality's information during the denoising process. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our model qualitatively and quantitatively outperforms not only the state-of-the-art methods in relevant fields but also the newly designed baselines capable of both information enhancement and fusion. The code is available at https://github.com/Chenz418/VIIS.
Depth-induced Saliency Comparison Network for Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease via Jointly Analysis of Visual Stimuli and Eye Movements
Mar 15, 2024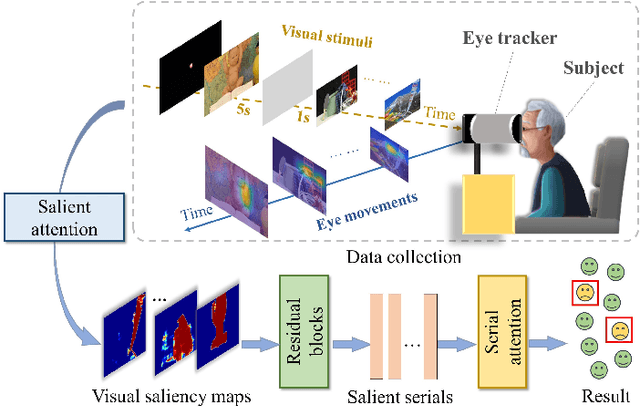
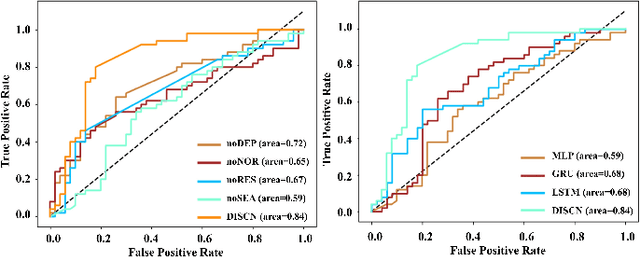
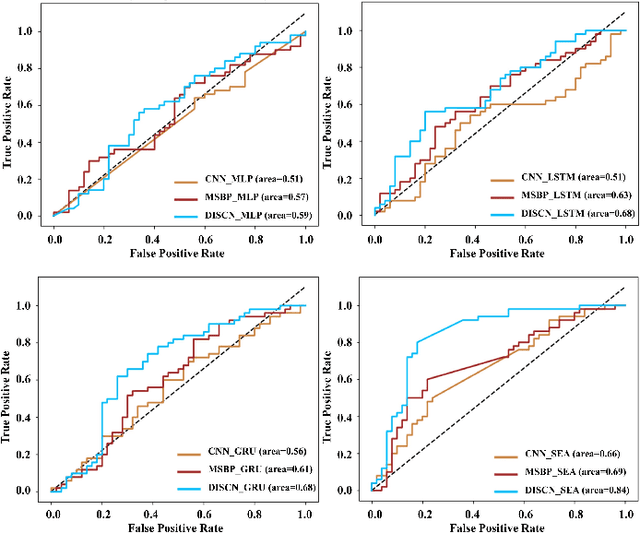
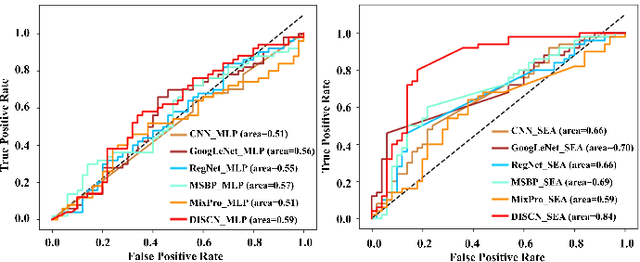
Abstract:Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is very important for following medical treatments, and eye movements under special visual stimuli may serve as a potential non-invasive biomarker for detecting cognitive abnormalities of AD patients. In this paper, we propose an Depth-induced saliency comparison network (DISCN) for eye movement analysis, which may be used for diagnosis the Alzheimers disease. In DISCN, a salient attention module fuses normal eye movements with RGB and depth maps of visual stimuli using hierarchical salient attention (SAA) to evaluate comprehensive saliency maps, which contain information from both visual stimuli and normal eye movement behaviors. In addition, we introduce serial attention module (SEA) to emphasis the most abnormal eye movement behaviors to reduce personal bias for a more robust result. According to our experiments, the DISCN achieves consistent validity in classifying the eye movements between the AD patients and normal controls.
StyleEDL: Style-Guided High-order Attention Network for Image Emotion Distribution Learning
Aug 06, 2023Abstract:Emotion distribution learning has gained increasing attention with the tendency to express emotions through images. As for emotion ambiguity arising from humans' subjectivity, substantial previous methods generally focused on learning appropriate representations from the holistic or significant part of images. However, they rarely consider establishing connections with the stylistic information although it can lead to a better understanding of images. In this paper, we propose a style-guided high-order attention network for image emotion distribution learning termed StyleEDL, which interactively learns stylistic-aware representations of images by exploring the hierarchical stylistic information of visual contents. Specifically, we consider exploring the intra- and inter-layer correlations among GRAM-based stylistic representations, and meanwhile exploit an adversary-constrained high-order attention mechanism to capture potential interactions between subtle visual parts. In addition, we introduce a stylistic graph convolutional network to dynamically generate the content-dependent emotion representations to benefit the final emotion distribution learning. Extensive experiments conducted on several benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed StyleEDL compared to state-of-the-art methods. The implementation is released at: https://github.com/liuxianyi/StyleEDL.
Deep Learning-based Eye-Tracking Analysis for Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Using 3D Comprehensive Visual Stimuli
Mar 13, 2023Abstract:Alzheimer's Disease (AD) causes a continuous decline in memory, thinking, and judgment. Traditional diagnoses are usually based on clinical experience, which is limited by some realistic factors. In this paper, we focus on exploiting deep learning techniques to diagnose AD based on eye-tracking behaviors. Visual attention, as typical eye-tracking behavior, is of great clinical value to detect cognitive abnormalities in AD patients. To better analyze the differences in visual attention between AD patients and normals, we first conduct a 3D comprehensive visual task on a non-invasive eye-tracking system to collect visual attention heatmaps. We then propose a multi-layered comparison convolution neural network (MC-CNN) to distinguish the visual attention differences between AD patients and normals. In MC-CNN, the multi-layered representations of heatmaps are obtained by hierarchical convolution to better encode eye-movement behaviors, which are further integrated into a distance vector to benefit the comprehensive visual task. Extensive experimental results on the collected dataset demonstrate that MC-CNN achieves consistent validity in classifying AD patients and normals with eye-tracking data.
DS-Net: Dynamic Spatiotemporal Network for Video Salient Object Detection
Dec 09, 2020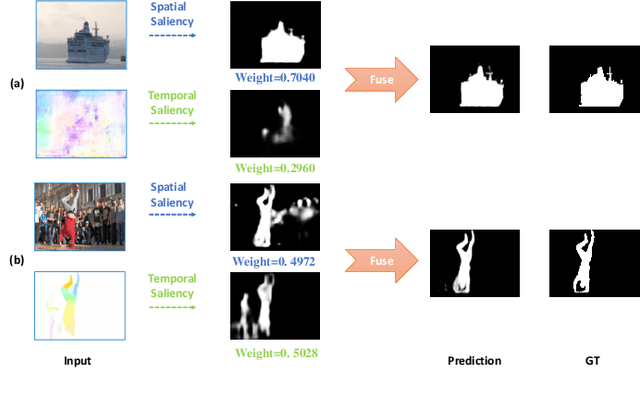
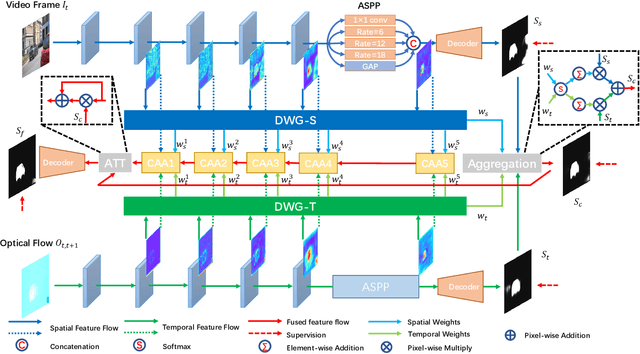
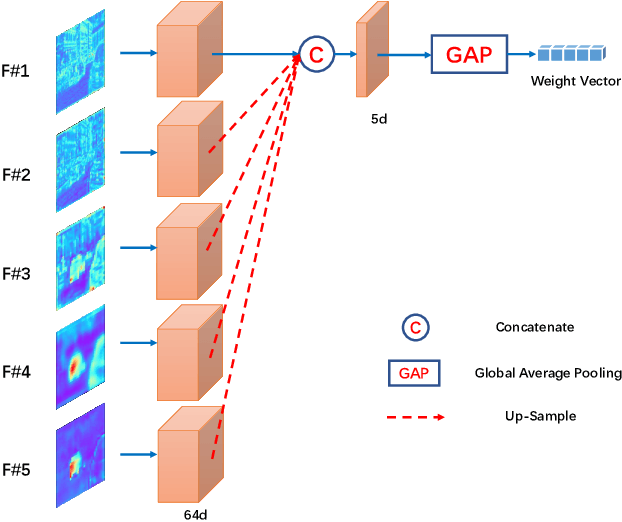
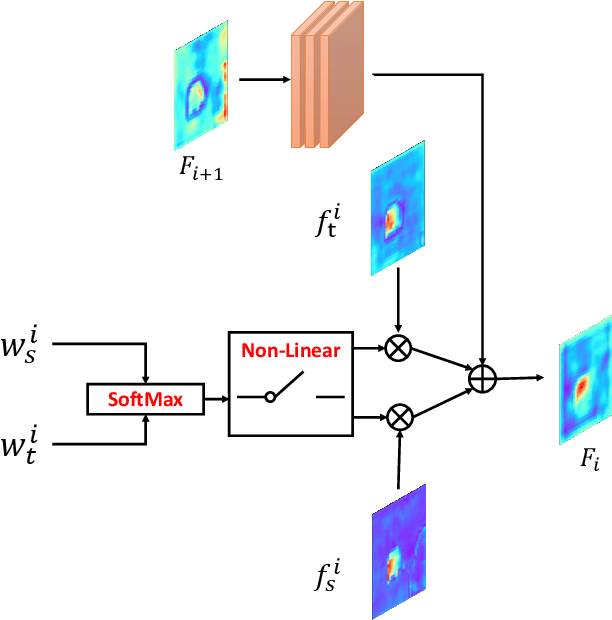
Abstract:As moving objects always draw more attention of human eyes, the temporal motive information is always exploited complementarily with spatial information to detect salient objects in videos. Although efficient tools such as optical flow have been proposed to extract temporal motive information, it often encounters difficulties when used for saliency detection due to the movement of camera or the partial movement of salient objects. In this paper, we investigate the complimentary roles of spatial and temporal information and propose a novel dynamic spatiotemporal network (DS-Net) for more effective fusion of spatiotemporal information. We construct a symmetric two-bypass network to explicitly extract spatial and temporal features. A dynamic weight generator (DWG) is designed to automatically learn the reliability of corresponding saliency branch. And a top-down cross attentive aggregation (CAA) procedure is designed so as to facilitate dynamic complementary aggregation of spatiotemporal features. Finally, the features are modified by spatial attention with the guidance of coarse saliency map and then go through decoder part for final saliency map. Experimental results on five benchmarks VOS, DAVIS, FBMS, SegTrack-v2, and ViSal demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior performance than state-of-the-art algorithms. The source code is available at https://github.com/TJUMMG/DS-Net.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge