Depth-induced Saliency Comparison Network for Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease via Jointly Analysis of Visual Stimuli and Eye Movements
Paper and Code
Mar 15, 2024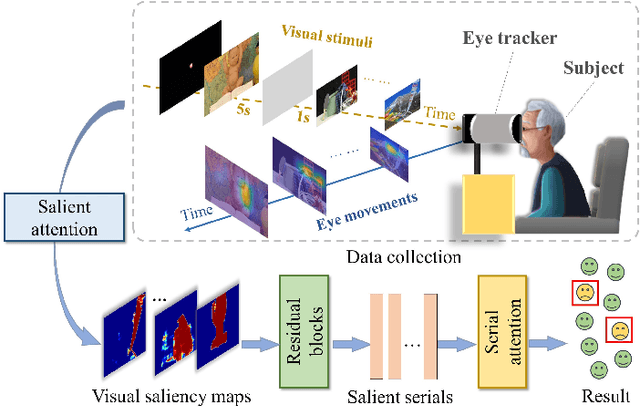
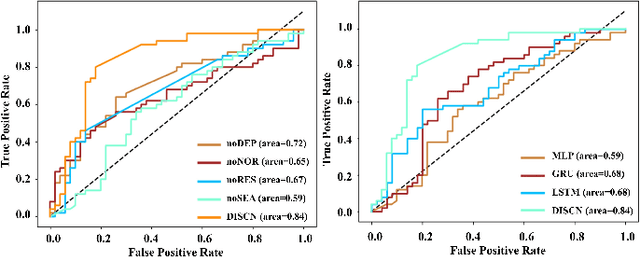
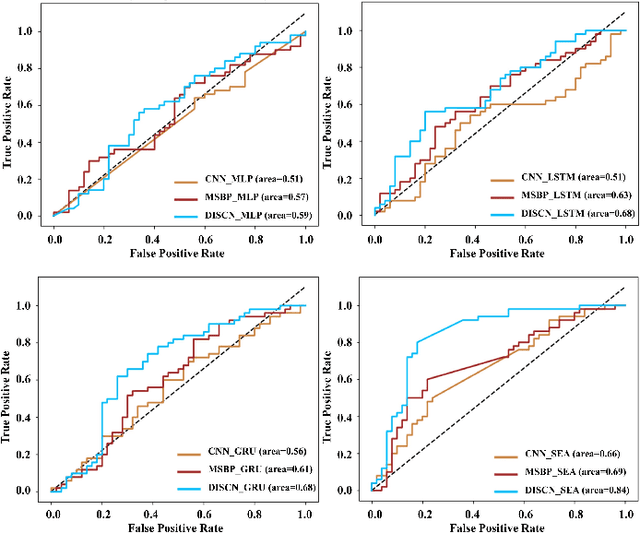
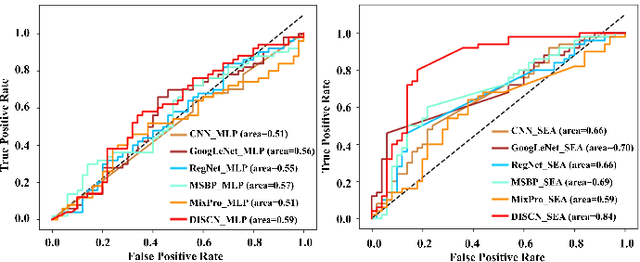
Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is very important for following medical treatments, and eye movements under special visual stimuli may serve as a potential non-invasive biomarker for detecting cognitive abnormalities of AD patients. In this paper, we propose an Depth-induced saliency comparison network (DISCN) for eye movement analysis, which may be used for diagnosis the Alzheimers disease. In DISCN, a salient attention module fuses normal eye movements with RGB and depth maps of visual stimuli using hierarchical salient attention (SAA) to evaluate comprehensive saliency maps, which contain information from both visual stimuli and normal eye movement behaviors. In addition, we introduce serial attention module (SEA) to emphasis the most abnormal eye movement behaviors to reduce personal bias for a more robust result. According to our experiments, the DISCN achieves consistent validity in classifying the eye movements between the AD patients and normal controls.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge