Yun Ni
Cosmos-Reason1: From Physical Common Sense To Embodied Reasoning
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Physical AI systems need to perceive, understand, and perform complex actions in the physical world. In this paper, we present the Cosmos-Reason1 models that can understand the physical world and generate appropriate embodied decisions (e.g., next step action) in natural language through long chain-of-thought reasoning processes. We begin by defining key capabilities for Physical AI reasoning, with a focus on physical common sense and embodied reasoning. To represent physical common sense, we use a hierarchical ontology that captures fundamental knowledge about space, time, and physics. For embodied reasoning, we rely on a two-dimensional ontology that generalizes across different physical embodiments. Building on these capabilities, we develop two multimodal large language models, Cosmos-Reason1-8B and Cosmos-Reason1-56B. We curate data and train our models in four stages: vision pre-training, general supervised fine-tuning (SFT), Physical AI SFT, and Physical AI reinforcement learning (RL) as the post-training. To evaluate our models, we build comprehensive benchmarks for physical common sense and embodied reasoning according to our ontologies. Evaluation results show that Physical AI SFT and reinforcement learning bring significant improvements. To facilitate the development of Physical AI, we will make our code and pre-trained models available under the NVIDIA Open Model License at https://github.com/nvidia-cosmos/cosmos-reason1.
FLIQS: One-Shot Mixed-Precision Floating-Point and Integer Quantization Search
Aug 07, 2023


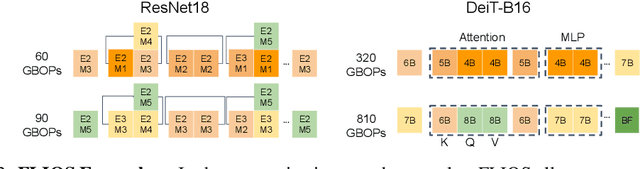
Abstract:Quantization has become a mainstream compression technique for reducing model size, computational requirements, and energy consumption for modern deep neural networks (DNNs). With the improved numerical support in recent hardware, including multiple variants of integer and floating point, mixed-precision quantization has become necessary to achieve high-quality results with low model cost. Prior mixed-precision quantization methods have performed a post-training quantization search, which compromises on accuracy, or a differentiable quantization search, which leads to high memory usage from branching. Therefore, we propose the first one-shot mixed-precision quantization search that eliminates the need for retraining in both integer and low-precision floating point models. We evaluate our floating-point and integer quantization search (FLIQS) on multiple convolutional networks and vision transformer models to discover Pareto-optimal models. Our approach discovers models that improve upon uniform precision, manual mixed-precision, and recent integer quantization search methods. With the proposed integer quantization search, we increase the accuracy of ResNet-18 on ImageNet by 1.31% points and ResNet-50 by 0.90% points with equivalent model cost over previous methods. Additionally, for the first time, we explore a novel mixed-precision floating-point search and improve MobileNetV2 by up to 0.98% points compared to prior state-of-the-art FP8 models. Finally, we extend FLIQS to simultaneously search a joint quantization and neural architecture space and improve the ImageNet accuracy by 2.69% points with similar model cost on a MobileNetV2 search space.
Animal Kingdom: A Large and Diverse Dataset for Animal Behavior Understanding
Apr 18, 2022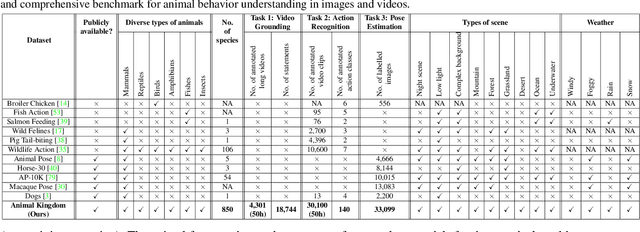
Abstract:Understanding animals' behaviors is significant for a wide range of applications. However, existing animal behavior datasets have limitations in multiple aspects, including limited numbers of animal classes, data samples and provided tasks, and also limited variations in environmental conditions and viewpoints. To address these limitations, we create a large and diverse dataset, Animal Kingdom, that provides multiple annotated tasks to enable a more thorough understanding of natural animal behaviors. The wild animal footages used in our dataset record different times of the day in extensive range of environments containing variations in backgrounds, viewpoints, illumination and weather conditions. More specifically, our dataset contains 50 hours of annotated videos to localize relevant animal behavior segments in long videos for the video grounding task, 30K video sequences for the fine-grained multi-label action recognition task, and 33K frames for the pose estimation task, which correspond to a diverse range of animals with 850 species across 6 major animal classes. Such a challenging and comprehensive dataset shall be able to facilitate the community to develop, adapt, and evaluate various types of advanced methods for animal behavior analysis. Moreover, we propose a Collaborative Action Recognition (CARe) model that learns general and specific features for action recognition with unseen new animals. This method achieves promising performance in our experiments. Our dataset can be found at https://sutdcv.github.io/Animal-Kingdom.
UAV-Human: A Large Benchmark for Human Behavior Understanding with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Apr 12, 2021



Abstract:Human behavior understanding with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is of great significance for a wide range of applications, which simultaneously brings an urgent demand of large, challenging, and comprehensive benchmarks for the development and evaluation of UAV-based models. However, existing benchmarks have limitations in terms of the amount of captured data, types of data modalities, categories of provided tasks, and diversities of subjects and environments. Here we propose a new benchmark - UAVHuman - for human behavior understanding with UAVs, which contains 67,428 multi-modal video sequences and 119 subjects for action recognition, 22,476 frames for pose estimation, 41,290 frames and 1,144 identities for person re-identification, and 22,263 frames for attribute recognition. Our dataset was collected by a flying UAV in multiple urban and rural districts in both daytime and nighttime over three months, hence covering extensive diversities w.r.t subjects, backgrounds, illuminations, weathers, occlusions, camera motions, and UAV flying attitudes. Such a comprehensive and challenging benchmark shall be able to promote the research of UAV-based human behavior understanding, including action recognition, pose estimation, re-identification, and attribute recognition. Furthermore, we propose a fisheye-based action recognition method that mitigates the distortions in fisheye videos via learning unbounded transformations guided by flat RGB videos. Experiments show the efficacy of our method on the UAV-Human dataset. The project page: https://github.com/SUTDCV/UAV-Human
Accurate Light Field Depth Estimation with Superpixel Regularization over Partially Occluded Regions
Aug 07, 2017



Abstract:Depth estimation is a fundamental problem for light field photography applications. Numerous methods have been proposed in recent years, which either focus on crafting cost terms for more robust matching, or on analyzing the geometry of scene structures embedded in the epipolar-plane images. Significant improvements have been made in terms of overall depth estimation error; however, current state-of-the-art methods still show limitations in handling intricate occluding structures and complex scenes with multiple occlusions. To address these challenging issues, we propose a very effective depth estimation framework which focuses on regularizing the initial label confidence map and edge strength weights. Specifically, we first detect partially occluded boundary regions (POBR) via superpixel based regularization. Series of shrinkage/reinforcement operations are then applied on the label confidence map and edge strength weights over the POBR. We show that after weight manipulations, even a low-complexity weighted least squares model can produce much better depth estimation than state-of-the-art methods in terms of average disparity error rate, occlusion boundary precision-recall rate, and the preservation of intricate visual features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge