Yizhuo Yang
M4Human: A Large-Scale Multimodal mmWave Radar Benchmark for Human Mesh Reconstruction
Dec 17, 2025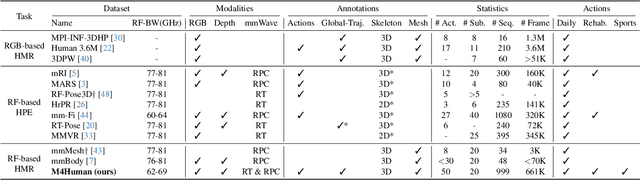
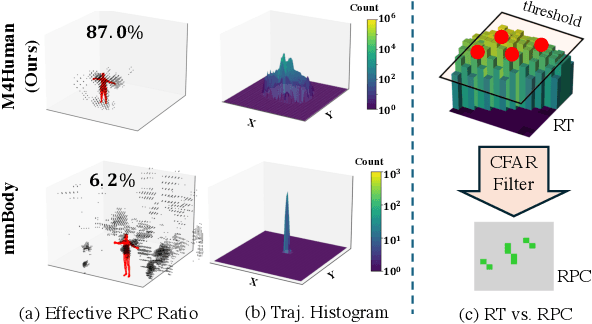
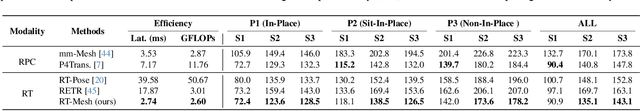
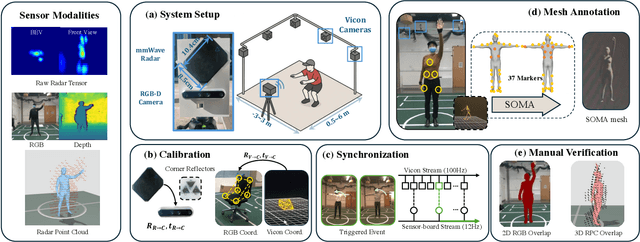
Abstract:Human mesh reconstruction (HMR) provides direct insights into body-environment interaction, which enables various immersive applications. While existing large-scale HMR datasets rely heavily on line-of-sight RGB input, vision-based sensing is limited by occlusion, lighting variation, and privacy concerns. To overcome these limitations, recent efforts have explored radio-frequency (RF) mmWave radar for privacy-preserving indoor human sensing. However, current radar datasets are constrained by sparse skeleton labels, limited scale, and simple in-place actions. To advance the HMR research community, we introduce M4Human, the current largest-scale (661K-frame) ($9\times$ prior largest) multimodal benchmark, featuring high-resolution mmWave radar, RGB, and depth data. M4Human provides both raw radar tensors (RT) and processed radar point clouds (RPC) to enable research across different levels of RF signal granularity. M4Human includes high-quality motion capture (MoCap) annotations with 3D meshes and global trajectories, and spans 20 subjects and 50 diverse actions, including in-place, sit-in-place, and free-space sports or rehabilitation movements. We establish benchmarks on both RT and RPC modalities, as well as multimodal fusion with RGB-D modalities. Extensive results highlight the significance of M4Human for radar-based human modeling while revealing persistent challenges under fast, unconstrained motion. The dataset and code will be released after the paper publication.
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection for Autonomous Robots via Mahalanobis SVDD with Audio-IMU Fusion
May 09, 2025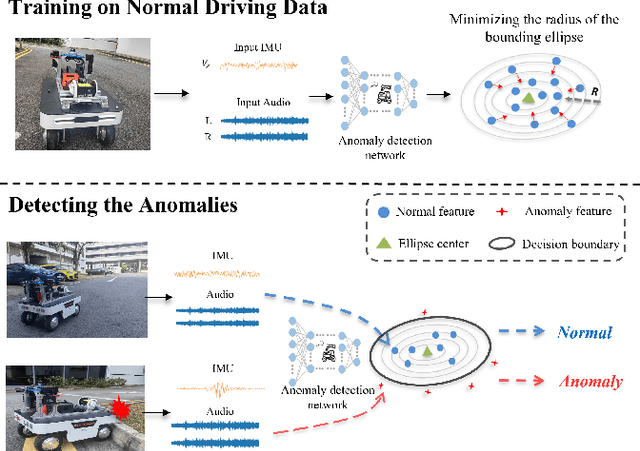
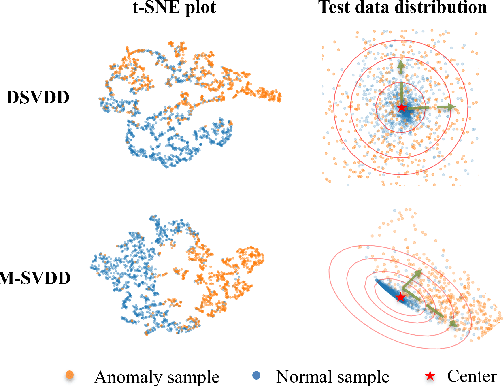
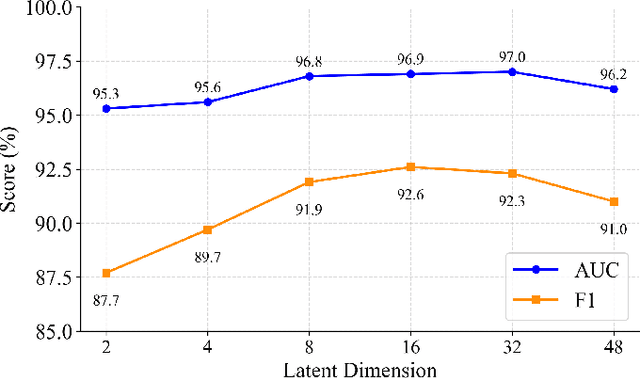
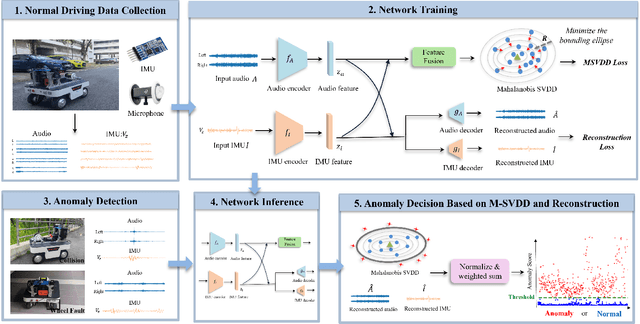
Abstract:Reliable anomaly detection is essential for ensuring the safety of autonomous robots, particularly when conventional detection systems based on vision or LiDAR become unreliable in adverse or unpredictable conditions. In such scenarios, alternative sensing modalities are needed to provide timely and robust feedback. To this end, we explore the use of audio and inertial measurement unit (IMU) sensors to detect underlying anomalies in autonomous mobile robots, such as collisions and internal mechanical faults. Furthermore, to address the challenge of limited labeled anomaly data, we propose an unsupervised anomaly detection framework based on Mahalanobis Support Vector Data Description (M-SVDD). In contrast to conventional SVDD methods that rely on Euclidean distance and assume isotropic feature distributions, our approach employs the Mahalanobis distance to adaptively scale feature dimensions and capture inter-feature correlations, enabling more expressive decision boundaries. In addition, a reconstruction-based auxiliary branch is introduced to preserve feature diversity and prevent representation collapse, further enhancing the robustness of anomaly detection. Extensive experiments on a collected mobile robot dataset and four public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, as shown in the video https://youtu.be/yh1tn6DDD4A. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/jamesyang7/M-SVDD.
Following Is All You Need: Robot Crowd Navigation Using People As Planners
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Navigating in crowded environments requires the robot to be equipped with high-level reasoning and planning techniques. Existing works focus on developing complex and heavyweight planners while ignoring the role of human intelligence. Since humans are highly capable agents who are also widely available in a crowd navigation setting, we propose an alternative scheme where the robot utilises people as planners to benefit from their effective planning decisions and social behaviours. Through a set of rule-based evaluations, we identify suitable human leaders who exhibit the potential to guide the robot towards its goal. Using a simple base planner, the robot follows the selected leader through shorthorizon subgoals that are designed to be straightforward to achieve. We demonstrate through both simulated and real-world experiments that our novel framework generates safe and efficient robot plans compared to existing planners, even without predictive or data-driven modules. Our method also brings human-like robot behaviours without explicitly defining traffic rules and social norms. Code will be available at https://github.com/centiLinda/PeopleAsPlanner.git.
AV-DTEC: Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Fusion for Drone Trajectory Estimation and Classification
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:The increasing use of compact UAVs has created significant threats to public safety, while traditional drone detection systems are often bulky and costly. To address these challenges, we propose AV-DTEC, a lightweight self-supervised audio-visual fusion-based anti-UAV system. AV-DTEC is trained using self-supervised learning with labels generated by LiDAR, and it simultaneously learns audio and visual features through a parallel selective state-space model. With the learned features, a specially designed plug-and-play primary-auxiliary feature enhancement module integrates visual features into audio features for better robustness in cross-lighting conditions. To reduce reliance on auxiliary features and align modalities, we propose a teacher-student model that adaptively adjusts the weighting of visual features. AV-DTEC demonstrates exceptional accuracy and effectiveness in real-world multi-modality data. The code and trained models are publicly accessible on GitHub \url{https://github.com/AmazingDay1/AV-DETC}.
Unsupervised UAV 3D Trajectories Estimation with Sparse Point Clouds
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Compact UAV systems, while advancing delivery and surveillance, pose significant security challenges due to their small size, which hinders detection by traditional methods. This paper presents a cost-effective, unsupervised UAV detection method using spatial-temporal sequence processing to fuse multiple LiDAR scans for accurate UAV tracking in real-world scenarios. Our approach segments point clouds into foreground and background, analyzes spatial-temporal data, and employs a scoring mechanism to enhance detection accuracy. Tested on a public dataset, our solution placed 4th in the CVPR 2024 UG2+ Challenge, demonstrating its practical effectiveness. We plan to open-source all designs, code, and sample data for the research community github.com/lianghanfang/UnLiDAR-UAV-Est.
Learning Dynamic Weight Adjustment for Spatial-Temporal Trajectory Planning in Crowd Navigation
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:Robot navigation in dense human crowds poses a significant challenge due to the complexity of human behavior in dynamic and obstacle-rich environments. In this work, we propose a dynamic weight adjustment scheme using a neural network to predict the optimal weights of objectives in an optimization-based motion planner. We adopt a spatial-temporal trajectory planner and incorporate diverse objectives to achieve a balance among safety, efficiency, and goal achievement in complex and dynamic environments. We design the network structure, observation encoding, and reward function to effectively train the policy network using reinforcement learning, allowing the robot to adapt its behavior in real time based on environmental and pedestrian information. Simulation results show improved safety compared to the fixed-weight planner and the state-of-the-art learning-based methods, and verify the ability of the learned policy to adaptively adjust the weights based on the observed situations. The approach's feasibility is demonstrated in a navigation task using an autonomous delivery robot across a crowded corridor over a 300 m distance.
AV-PedAware: Self-Supervised Audio-Visual Fusion for Dynamic Pedestrian Awareness
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:In this study, we introduce AV-PedAware, a self-supervised audio-visual fusion system designed to improve dynamic pedestrian awareness for robotics applications. Pedestrian awareness is a critical requirement in many robotics applications. However, traditional approaches that rely on cameras and LIDARs to cover multiple views can be expensive and susceptible to issues such as changes in illumination, occlusion, and weather conditions. Our proposed solution replicates human perception for 3D pedestrian detection using low-cost audio and visual fusion. This study represents the first attempt to employ audio-visual fusion to monitor footstep sounds for the purpose of predicting the movements of pedestrians in the vicinity. The system is trained through self-supervised learning based on LIDAR-generated labels, making it a cost-effective alternative to LIDAR-based pedestrian awareness. AV-PedAware achieves comparable results to LIDAR-based systems at a fraction of the cost. By utilizing an attention mechanism, it can handle dynamic lighting and occlusions, overcoming the limitations of traditional LIDAR and camera-based systems. To evaluate our approach's effectiveness, we collected a new multimodal pedestrian detection dataset and conducted experiments that demonstrate the system's ability to provide reliable 3D detection results using only audio and visual data, even in extreme visual conditions. We will make our collected dataset and source code available online for the community to encourage further development in the field of robotics perception systems.
Robust Loop Closure by Textual Cues in Challenging Environments
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Loop closure is an important task in robot navigation. However, existing methods mostly rely on some implicit or heuristic features of the environment, which can still fail to work in common environments such as corridors, tunnels, and warehouses. Indeed, navigating in such featureless, degenerative, and repetitive (FDR) environments would also pose a significant challenge even for humans, but explicit text cues in the surroundings often provide the best assistance. This inspires us to propose a multi-modal loop closure method based on explicit human-readable textual cues in FDR environments. Specifically, our approach first extracts scene text entities based on Optical Character Recognition (OCR), then creates a local map of text cues based on accurate LiDAR odometry and finally identifies loop closure events by a graph-theoretic scheme. Experiment results demonstrate that this approach has superior performance over existing methods that rely solely on visual and LiDAR sensors. To benefit the community, we release the source code and datasets at \url{https://github.com/TongxingJin/TXTLCD}.
ULOC: Learning to Localize in Complex Large-Scale Environments with Ultra-Wideband Ranges
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:While UWB-based methods can achieve high localization accuracy in small-scale areas, their accuracy and reliability are significantly challenged in large-scale environments. In this paper, we propose a learning-based framework named ULOC for Ultra-Wideband (UWB) based localization in such complex large-scale environments. First, anchors are deployed in the environment without knowledge of their actual position. Then, UWB observations are collected when the vehicle travels in the environment. At the same time, map-consistent pose estimates are developed from registering (onboard self-localization) data with the prior map to provide the training labels. We then propose a network based on MAMBA that learns the ranging patterns of UWBs over a complex large-scale environment. The experiment demonstrates that our solution can ensure high localization accuracy on a large scale compared to the state-of-the-art. We release our source code to benefit the community at https://github.com/brytsknguyen/uloc.
MMAUD: A Comprehensive Multi-Modal Anti-UAV Dataset for Modern Miniature Drone Threats
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:In response to the evolving challenges posed by small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), which possess the potential to transport harmful payloads or independently cause damage, we introduce MMAUD: a comprehensive Multi-Modal Anti-UAV Dataset. MMAUD addresses a critical gap in contemporary threat detection methodologies by focusing on drone detection, UAV-type classification, and trajectory estimation. MMAUD stands out by combining diverse sensory inputs, including stereo vision, various Lidars, Radars, and audio arrays. It offers a unique overhead aerial detection vital for addressing real-world scenarios with higher fidelity than datasets captured on specific vantage points using thermal and RGB. Additionally, MMAUD provides accurate Leica-generated ground truth data, enhancing credibility and enabling confident refinement of algorithms and models, which has never been seen in other datasets. Most existing works do not disclose their datasets, making MMAUD an invaluable resource for developing accurate and efficient solutions. Our proposed modalities are cost-effective and highly adaptable, allowing users to experiment and implement new UAV threat detection tools. Our dataset closely simulates real-world scenarios by incorporating ambient heavy machinery sounds. This approach enhances the dataset's applicability, capturing the exact challenges faced during proximate vehicular operations. It is expected that MMAUD can play a pivotal role in advancing UAV threat detection, classification, trajectory estimation capabilities, and beyond. Our dataset, codes, and designs will be available in https://github.com/ntu-aris/MMAUD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge