Yiqun Hui
RecFlow: An Industrial Full Flow Recommendation Dataset
Oct 28, 2024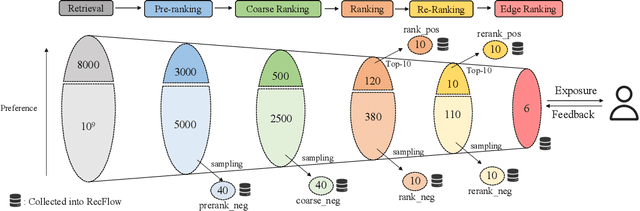
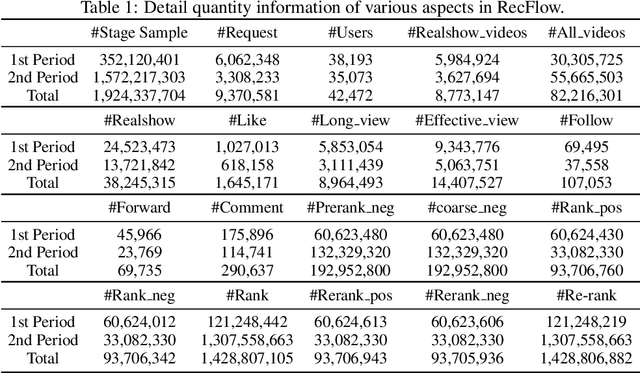
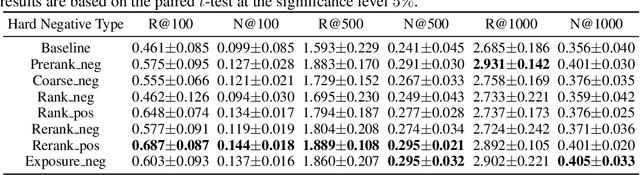
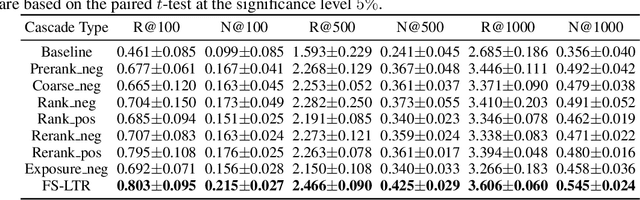
Abstract:Industrial recommendation systems (RS) rely on the multi-stage pipeline to balance effectiveness and efficiency when delivering items from a vast corpus to users. Existing RS benchmark datasets primarily focus on the exposure space, where novel RS algorithms are trained and evaluated. However, when these algorithms transition to real world industrial RS, they face a critical challenge of handling unexposed items which are a significantly larger space than the exposed one. This discrepancy profoundly impacts their practical performance. Additionally, these algorithms often overlook the intricate interplay between multiple RS stages, resulting in suboptimal overall system performance. To address this issue, we introduce RecFlow, an industrial full flow recommendation dataset designed to bridge the gap between offline RS benchmarks and the real online environment. Unlike existing datasets, RecFlow includes samples not only from the exposure space but also unexposed items filtered at each stage of the RS funnel. Our dataset comprises 38M interactions from 42K users across nearly 9M items with additional 1.9B stage samples collected from 9.3M online requests over 37 days and spanning 6 stages. Leveraging the RecFlow dataset, we conduct courageous exploration experiments, showcasing its potential in designing new algorithms to enhance effectiveness by incorporating stage-specific samples. Some of these algorithms have already been deployed online, consistently yielding significant gains. We propose RecFlow as the first comprehensive benchmark dataset for the RS community, supporting research on designing algorithms at any stage, study of selection bias, debiased algorithms, multi-stage consistency and optimality, multi-task recommendation, and user behavior modeling. The RecFlow dataset, along with the corresponding source code, is available at https://github.com/RecFlow-ICLR/RecFlow.
TWIN V2: Scaling Ultra-Long User Behavior Sequence Modeling for Enhanced CTR Prediction at Kuaishou
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:The significance of modeling long-term user interests for CTR prediction tasks in large-scale recommendation systems is progressively gaining attention among researchers and practitioners. Existing work, such as SIM and TWIN, typically employs a two-stage approach to model long-term user behavior sequences for efficiency concerns. The first stage rapidly retrieves a subset of sequences related to the target item from a long sequence using a search-based mechanism namely the General Search Unit (GSU), while the second stage calculates the interest scores using the Exact Search Unit (ESU) on the retrieved results. Given the extensive length of user behavior sequences spanning the entire life cycle, potentially reaching up to 10^6 in scale, there is currently no effective solution for fully modeling such expansive user interests. To overcome this issue, we introduced TWIN-V2, an enhancement of TWIN, where a divide-and-conquer approach is applied to compress life-cycle behaviors and uncover more accurate and diverse user interests. Specifically, a hierarchical clustering method groups items with similar characteristics in life-cycle behaviors into a single cluster during the offline phase. By limiting the size of clusters, we can compress behavior sequences well beyond the magnitude of 10^5 to a length manageable for online inference in GSU retrieval. Cluster-aware target attention extracts comprehensive and multi-faceted long-term interests of users, thereby making the final recommendation results more accurate and diverse. Extensive offline experiments on a multi-billion-scale industrial dataset and online A/B tests have demonstrated the effectiveness of TWIN-V2. Under an efficient deployment framework, TWIN-V2 has been successfully deployed to the primary traffic that serves hundreds of millions of daily active users at Kuaishou.
TWIN: TWo-stage Interest Network for Lifelong User Behavior Modeling in CTR Prediction at Kuaishou
Feb 05, 2023Abstract:Life-long user behavior modeling, i.e., extracting a user's hidden interests from rich historical behaviors in months or even years, plays a central role in modern CTR prediction systems. Conventional algorithms mostly follow two cascading stages: a simple General Search Unit (GSU) for fast and coarse search over tens of thousands of long-term behaviors and an Exact Search Unit (ESU) for effective Target Attention (TA) over the small number of finalists from GSU. Although efficient, existing algorithms mostly suffer from a crucial limitation: the \textit{inconsistent} target-behavior relevance metrics between GSU and ESU. As a result, their GSU usually misses highly relevant behaviors but retrieves ones considered irrelevant by ESU. In such case, the TA in ESU, no matter how attention is allocated, mostly deviates from the real user interests and thus degrades the overall CTR prediction accuracy. To address such inconsistency, we propose \textbf{TWo-stage Interest Network (TWIN)}, where our Consistency-Preserved GSU (CP-GSU) adopts the identical target-behavior relevance metric as the TA in ESU, making the two stages twins. Specifically, to break TA's computational bottleneck and extend it from ESU to GSU, or namely from behavior length $10^2$ to length $10^4-10^5$, we build a novel attention mechanism by behavior feature splitting. For the video inherent features of a behavior, we calculate their linear projection by efficient pre-computing \& caching strategies. And for the user-item cross features, we compress each into a one-dimentional bias term in the attention score calculation to save the computational cost. The consistency between two stages, together with the effective TA-based relevance metric in CP-GSU, contributes to significant performance gain in CTR prediction.
PEPNet: Parameter and Embedding Personalized Network for Infusing with Personalized Prior Information
Feb 05, 2023Abstract:With the increase of content pages and display styles in online services such as online-shopping and video-watching websites, industrial-scale recommender systems face challenges in multi-domain and multi-task recommendations. The core of multi-task and multi-domain recommendation is to accurately capture user interests in different domains given different user behaviors. In this paper, we propose a plug-and-play \textit{\textbf{P}arameter and \textbf{E}mbedding \textbf{P}ersonalized \textbf{Net}work (\textbf{PEPNet})} for multi-task recommendation in the multi-domain setting. PEPNet takes features with strong biases as input and dynamically scales the bottom-layer embeddings and the top-layer DNN hidden units in the model through a gate mechanism. By mapping personalized priors to scaling weights ranging from 0 to 2, PEPNet introduces both parameter personalization and embedding personalization. Embedding Personalized Network (EPNet) selects and aligns embeddings with different semantics under multiple domains. Parameter Personalized Network (PPNet) influences DNN parameters to balance interdependent targets in multiple tasks. We have made a series of special engineering optimizations combining the Kuaishou training framework and the online deployment environment. We have deployed the model in Kuaishou apps, serving over 300 million daily users. Both online and offline experiments have demonstrated substantial improvements in multiple metrics. In particular, we have seen a more than 1\% online increase in three major scenarios.
Sequential Recommendation with Graph Neural Networks
Jun 27, 2021



Abstract:Sequential recommendation aims to leverage users' historical behaviors to predict their next interaction. Existing works have not yet addressed two main challenges in sequential recommendation. First, user behaviors in their rich historical sequences are often implicit and noisy preference signals, they cannot sufficiently reflect users' actual preferences. In addition, users' dynamic preferences often change rapidly over time, and hence it is difficult to capture user patterns in their historical sequences. In this work, we propose a graph neural network model called SURGE (short for SeqUential Recommendation with Graph neural nEtworks) to address these two issues. Specifically, SURGE integrates different types of preferences in long-term user behaviors into clusters in the graph by re-constructing loose item sequences into tight item-item interest graphs based on metric learning. This helps explicitly distinguish users' core interests, by forming dense clusters in the interest graph. Then, we perform cluster-aware and query-aware graph convolutional propagation and graph pooling on the constructed graph. It dynamically fuses and extracts users' current activated core interests from noisy user behavior sequences. We conduct extensive experiments on both public and proprietary industrial datasets. Experimental results demonstrate significant performance gains of our proposed method compared to state-of-the-art methods. Further studies on sequence length confirm that our method can model long behavioral sequences effectively and efficiently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge