Yihong Luo
Noise Consistency Training: A Native Approach for One-Step Generator in Learning Additional Controls
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:The pursuit of efficient and controllable high-quality content generation remains a central challenge in artificial intelligence-generated content (AIGC). While one-step generators, enabled by diffusion distillation techniques, offer excellent generation quality and computational efficiency, adapting them to new control conditions--such as structural constraints, semantic guidelines, or external inputs--poses a significant challenge. Conventional approaches often necessitate computationally expensive modifications to the base model and subsequent diffusion distillation. This paper introduces Noise Consistency Training (NCT), a novel and lightweight approach to directly integrate new control signals into pre-trained one-step generators without requiring access to original training images or retraining the base diffusion model. NCT operates by introducing an adapter module and employs a noise consistency loss in the noise space of the generator. This loss aligns the adapted model's generation behavior across noises that are conditionally dependent to varying degrees, implicitly guiding it to adhere to the new control. Theoretically, this training objective can be understood as minimizing the distributional distance between the adapted generator and the conditional distribution induced by the new conditions. NCT is modular, data-efficient, and easily deployable, relying only on the pre-trained one-step generator and a control signal model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that NCT achieves state-of-the-art controllable generation in a single forward pass, surpassing existing multi-step and distillation-based methods in both generation quality and computational efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/Luo-Yihong/NCT
Rewards Are Enough for Fast Photo-Realistic Text-to-image Generation
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Aligning generated images to complicated text prompts and human preferences is a central challenge in Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content (AIGC). With reward-enhanced diffusion distillation emerging as a promising approach that boosts controllability and fidelity of text-to-image models, we identify a fundamental paradigm shift: as conditions become more specific and reward signals stronger, the rewards themselves become the dominant force in generation. In contrast, the diffusion losses serve as an overly expensive form of regularization. To thoroughly validate our hypothesis, we introduce R0, a novel conditional generation approach via regularized reward maximization. Instead of relying on tricky diffusion distillation losses, R0 proposes a new perspective that treats image generations as an optimization problem in data space which aims to search for valid images that have high compositional rewards. By innovative designs of the generator parameterization and proper regularization techniques, we train state-of-the-art few-step text-to-image generative models with R0 at scales. Our results challenge the conventional wisdom of diffusion post-training and conditional generation by demonstrating that rewards play a dominant role in scenarios with complex conditions. We hope our findings can contribute to further research into human-centric and reward-centric generation paradigms across the broader field of AIGC. Code is available at https://github.com/Luo-Yihong/R0.
Learning Few-Step Diffusion Models by Trajectory Distribution Matching
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Accelerating diffusion model sampling is crucial for efficient AIGC deployment. While diffusion distillation methods -- based on distribution matching and trajectory matching -- reduce sampling to as few as one step, they fall short on complex tasks like text-to-image generation. Few-step generation offers a better balance between speed and quality, but existing approaches face a persistent trade-off: distribution matching lacks flexibility for multi-step sampling, while trajectory matching often yields suboptimal image quality. To bridge this gap, we propose learning few-step diffusion models by Trajectory Distribution Matching (TDM), a unified distillation paradigm that combines the strengths of distribution and trajectory matching. Our method introduces a data-free score distillation objective, aligning the student's trajectory with the teacher's at the distribution level. Further, we develop a sampling-steps-aware objective that decouples learning targets across different steps, enabling more adjustable sampling. This approach supports both deterministic sampling for superior image quality and flexible multi-step adaptation, achieving state-of-the-art performance with remarkable efficiency. Our model, TDM, outperforms existing methods on various backbones, such as SDXL and PixArt-$\alpha$, delivering superior quality and significantly reduced training costs. In particular, our method distills PixArt-$\alpha$ into a 4-step generator that outperforms its teacher on real user preference at 1024 resolution. This is accomplished with 500 iterations and 2 A800 hours -- a mere 0.01% of the teacher's training cost. In addition, our proposed TDM can be extended to accelerate text-to-video diffusion. Notably, TDM can outperform its teacher model (CogVideoX-2B) by using only 4 NFE on VBench, improving the total score from 80.91 to 81.65. Project page: https://tdm-t2x.github.io/
Adding Additional Control to One-Step Diffusion with Joint Distribution Matching
Mar 09, 2025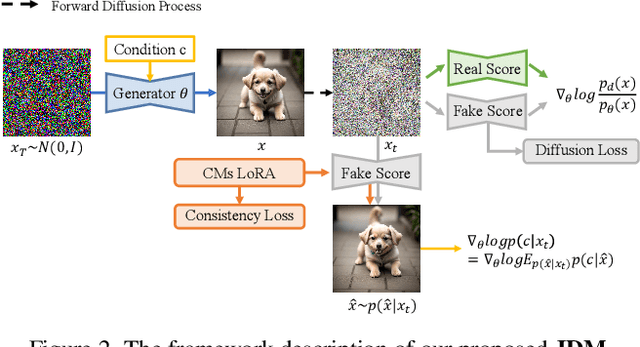
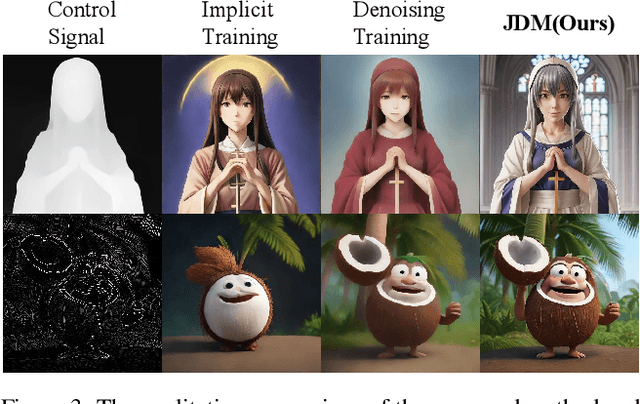
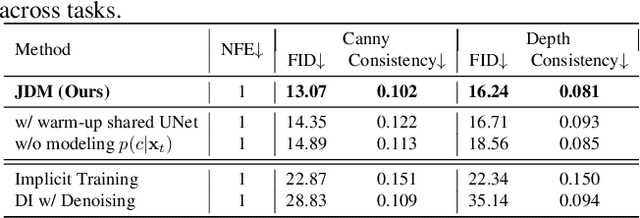

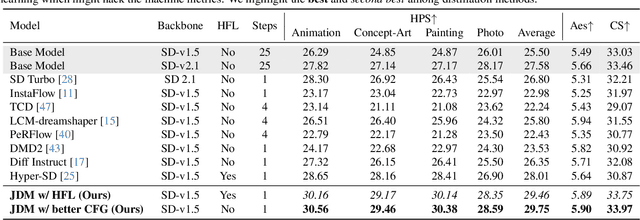
Abstract:While diffusion distillation has enabled one-step generation through methods like Variational Score Distillation, adapting distilled models to emerging new controls -- such as novel structural constraints or latest user preferences -- remains challenging. Conventional approaches typically requires modifying the base diffusion model and redistilling it -- a process that is both computationally intensive and time-consuming. To address these challenges, we introduce Joint Distribution Matching (JDM), a novel approach that minimizes the reverse KL divergence between image-condition joint distributions. By deriving a tractable upper bound, JDM decouples fidelity learning from condition learning. This asymmetric distillation scheme enables our one-step student to handle controls unknown to the teacher model and facilitates improved classifier-free guidance (CFG) usage and seamless integration of human feedback learning (HFL). Experimental results demonstrate that JDM surpasses baseline methods such as multi-step ControlNet by mere one-step in most cases, while achieving state-of-the-art performance in one-step text-to-image synthesis through improved usage of CFG or HFL integration.
Decoupled Graph Energy-based Model for Node Out-of-Distribution Detection on Heterophilic Graphs
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Despite extensive research efforts focused on OOD detection on images, OOD detection on nodes in graph learning remains underexplored. The dependence among graph nodes hinders the trivial adaptation of existing approaches on images that assume inputs to be i.i.d. sampled, since many unique features and challenges specific to graphs are not considered, such as the heterophily issue. Recently, GNNSafe, which considers node dependence, adapted energy-based detection to the graph domain with state-of-the-art performance, however, it has two serious issues: 1) it derives node energy from classification logits without specifically tailored training for modeling data distribution, making it less effective at recognizing OOD data; 2) it highly relies on energy propagation, which is based on homophily assumption and will cause significant performance degradation on heterophilic graphs, where the node tends to have dissimilar distribution with its neighbors. To address the above issues, we suggest training EBMs by MLE to enhance data distribution modeling and remove energy propagation to overcome the heterophily issues. However, training EBMs via MLE requires performing MCMC sampling on both node feature and node neighbors, which is challenging due to the node interdependence and discrete graph topology. To tackle the sampling challenge, we introduce DeGEM, which decomposes the learning process into two parts: a graph encoder that leverages topology information for node representations and an energy head that operates in latent space. Extensive experiments validate that DeGEM, without OOD exposure during training, surpasses previous state-of-the-art methods, achieving an average AUROC improvement of 6.71% on homophilic graphs and 20.29% on heterophilic graphs, and even outperform methods trained with OOD exposure. Our code is available at: https://github.com/draym28/DeGEM.
Fast Graph Sharpness-Aware Minimization for Enhancing and Accelerating Few-Shot Node Classification
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown superior performance in node classification. However, GNNs perform poorly in the Few-Shot Node Classification (FSNC) task that requires robust generalization to make accurate predictions for unseen classes with limited labels. To tackle the challenge, we propose the integration of Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM)--a technique designed to enhance model generalization by finding a flat minimum of the loss landscape--into GNN training. The standard SAM approach, however, consists of two forward-backward steps in each training iteration, doubling the computational cost compared to the base optimizer (e.g., Adam). To mitigate this drawback, we introduce a novel algorithm, Fast Graph Sharpness-Aware Minimization (FGSAM), that integrates the rapid training of Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) with the superior performance of GNNs. Specifically, we utilize GNNs for parameter perturbation while employing MLPs to minimize the perturbed loss so that we can find a flat minimum with good generalization more efficiently. Moreover, our method reutilizes the gradient from the perturbation phase to incorporate graph topology into the minimization process at almost zero additional cost. To further enhance training efficiency, we develop FGSAM+ that executes exact perturbations periodically. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed algorithm outperforms the standard SAM with lower computational costs in FSNC tasks. In particular, our FGSAM+ as a SAM variant offers a faster optimization than the base optimizer in most cases. In addition to FSNC, our proposed methods also demonstrate competitive performance in the standard node classification task for heterophilic graphs, highlighting the broad applicability. The code is available at https://github.com/draym28/FGSAM_NeurIPS24.
You Only Sample Once: Taming One-Step Text-To-Image Synthesis by Self-Cooperative Diffusion GANs
Mar 29, 2024



Abstract:We introduce YOSO, a novel generative model designed for rapid, scalable, and high-fidelity one-step image synthesis. This is achieved by integrating the diffusion process with GANs. Specifically, we smooth the distribution by the denoising generator itself, performing self-cooperative learning. We show that our method can serve as a one-step generation model training from scratch with competitive performance. Moreover, we show that our method can be extended to finetune pre-trained text-to-image diffusion for high-quality one-step text-to-image synthesis even with LoRA fine-tuning. In particular, we provide the first diffusion transformer that can generate images in one step trained on 512 resolution, with the capability of adapting to 1024 resolution without explicit training. Our code is provided at https://github.com/Luo-Yihong/YOSO.
Energy-Calibrated VAE with Test Time Free Lunch
Nov 21, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel generative model that utilizes a conditional Energy-Based Model (EBM) for enhancing Variational Autoencoder (VAE), termed Energy-Calibrated VAE (EC-VAE). Specifically, VAEs often suffer from blurry generated samples due to the lack of a tailored training on the samples generated in the generative direction. On the other hand, EBMs can generate high-quality samples but require expensive Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling. To address these issues, we introduce a conditional EBM for calibrating the generative direction of VAE during training, without requiring it for the generation at test time. In particular, we train EC-VAE upon both the input data and the calibrated samples with adaptive weight to enhance efficacy while avoiding MCMC sampling at test time. Furthermore, we extend the calibration idea of EC-VAE to variational learning and normalizing flows, and apply EC-VAE to an additional application of zero-shot image restoration via neural transport prior and range-null theory. We evaluate the proposed method with two applications, including image generation and zero-shot image restoration, and the experimental results show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance over single-step non-adversarial generation.
LSGNN: Towards General Graph Neural Network in Node Classification by Local Similarity
May 07, 2023Abstract:Heterophily has been considered as an issue that hurts the performance of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). To address this issue, some existing work uses a graph-level weighted fusion of the information of multi-hop neighbors to include more nodes with homophily. However, the heterophily might differ among nodes, which requires to consider the local topology. Motivated by it, we propose to use the local similarity (LocalSim) to learn node-level weighted fusion, which can also serve as a plug-and-play module. For better fusion, we propose a novel and efficient Initial Residual Difference Connection (IRDC) to extract more informative multi-hop information. Moreover, we provide theoretical analysis on the effectiveness of LocalSim representing node homophily on synthetic graphs. Extensive evaluations over real benchmark datasets show that our proposed method, namely Local Similarity Graph Neural Network (LSGNN), can offer comparable or superior state-of-the-art performance on both homophilic and heterophilic graphs. Meanwhile, the plug-and-play model can significantly boost the performance of existing GNNs. Our code is provided at https://github.com/draym28/LSGNN.
TO-FLOW: Efficient Continuous Normalizing Flows with Temporal Optimization adjoint with Moving Speed
Mar 28, 2022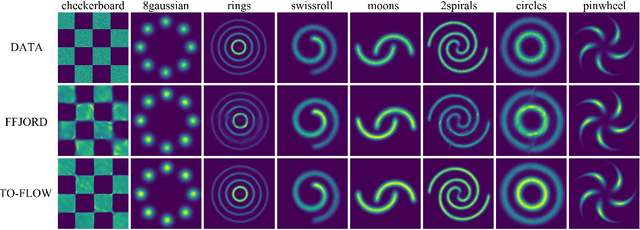
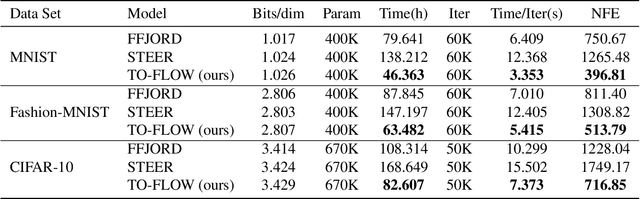
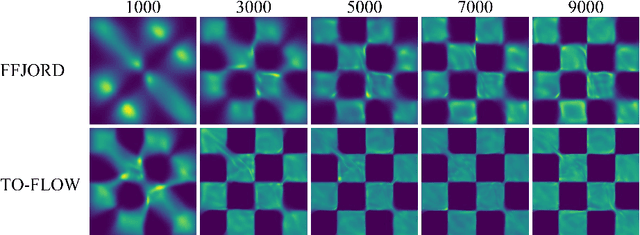
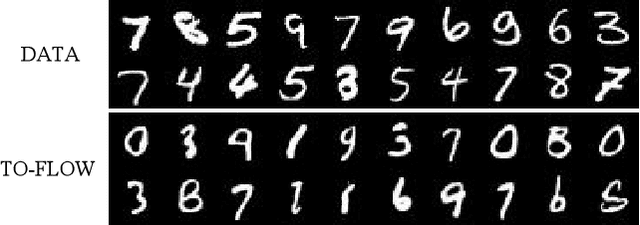
Abstract:Continuous normalizing flows (CNFs) construct invertible mappings between an arbitrary complex distribution and an isotropic Gaussian distribution using Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (neural ODEs). It has not been tractable on large datasets due to the incremental complexity of the neural ODE training. Optimal Transport theory has been applied to regularize the dynamics of the ODE to speed up training in recent works. In this paper, a temporal optimization is proposed by optimizing the evolutionary time for forward propagation of the neural ODE training. In this appoach, we optimize the network weights of the CNF alternately with evolutionary time by coordinate descent. Further with temporal regularization, stability of the evolution is ensured. This approach can be used in conjunction with the original regularization approach. We have experimentally demonstrated that the proposed approach can significantly accelerate training without sacrifying performance over baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge