Yidi Chen
RankLLM: A Python Package for Reranking with LLMs
May 25, 2025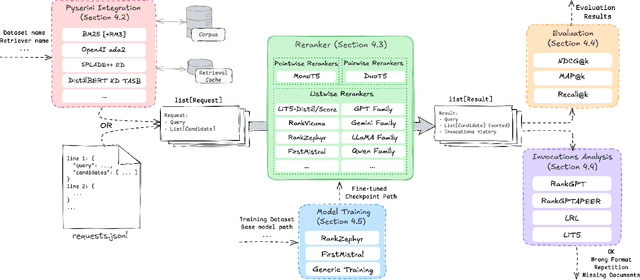
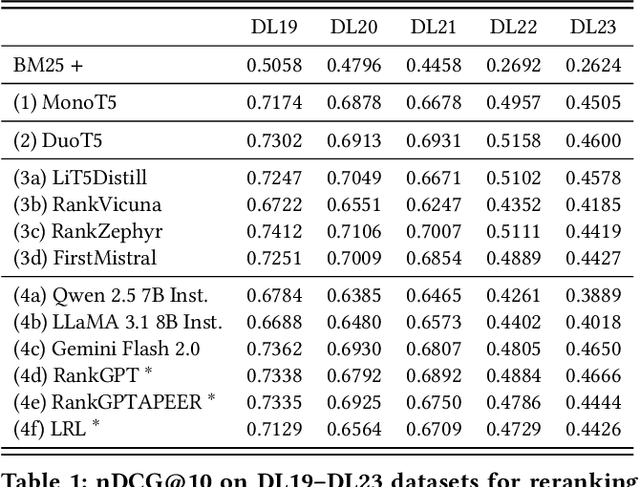
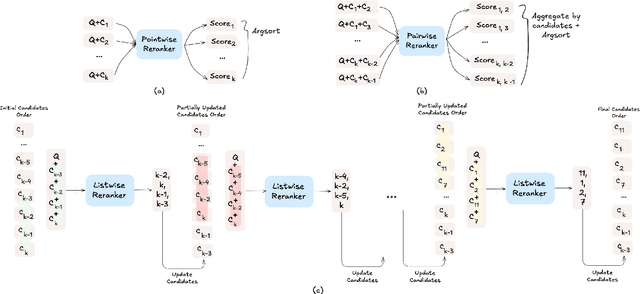
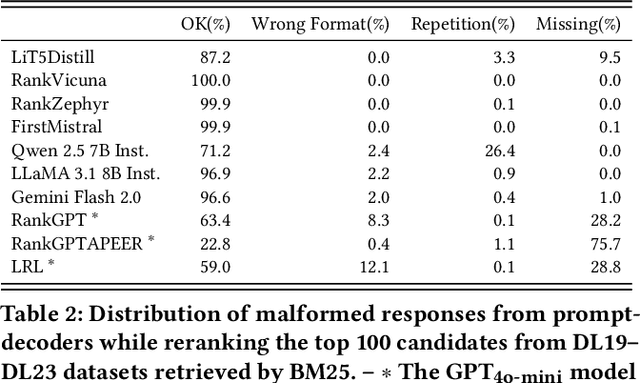
Abstract:The adoption of large language models (LLMs) as rerankers in multi-stage retrieval systems has gained significant traction in academia and industry. These models refine a candidate list of retrieved documents, often through carefully designed prompts, and are typically used in applications built on retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). This paper introduces RankLLM, an open-source Python package for reranking that is modular, highly configurable, and supports both proprietary and open-source LLMs in customized reranking workflows. To improve usability, RankLLM features optional integration with Pyserini for retrieval and provides integrated evaluation for multi-stage pipelines. Additionally, RankLLM includes a module for detailed analysis of input prompts and LLM responses, addressing reliability concerns with LLM APIs and non-deterministic behavior in Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models. This paper presents the architecture of RankLLM, along with a detailed step-by-step guide and sample code. We reproduce results from RankGPT, LRL, RankVicuna, RankZephyr, and other recent models. RankLLM integrates with common inference frameworks and a wide range of LLMs. This compatibility allows for quick reproduction of reported results, helping to speed up both research and real-world applications. The complete repository is available at rankllm.ai, and the package can be installed via PyPI.
GEMeX: A Large-Scale, Groundable, and Explainable Medical VQA Benchmark for Chest X-ray Diagnosis
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Medical Visual Question Answering (VQA) is an essential technology that integrates computer vision and natural language processing to automatically respond to clinical inquiries about medical images. However, current medical VQA datasets exhibit two significant limitations: (1) they often lack visual and textual explanations for answers, which impedes their ability to satisfy the comprehension needs of patients and junior doctors; (2) they typically offer a narrow range of question formats, inadequately reflecting the diverse requirements encountered in clinical scenarios. These limitations pose significant challenges to the development of a reliable and user-friendly Med-VQA system. To address these challenges, we introduce a large-scale, Groundable, and Explainable Medical VQA benchmark for chest X-ray diagnosis (GEMeX), featuring several innovative components: (1) A multi-modal explainability mechanism that offers detailed visual and textual explanations for each question-answer pair, thereby enhancing answer comprehensibility; (2) Four distinct question types, open-ended, closed-ended, single-choice, and multiple-choice, that better reflect diverse clinical needs. We evaluated 10 representative large vision language models on GEMeX and found that they underperformed, highlighting the dataset's complexity. However, after fine-tuning a baseline model using the training set, we observed a significant performance improvement, demonstrating the dataset's effectiveness. The project is available at www.med-vqa.com/GEMeX.
MedSAM-U: Uncertainty-Guided Auto Multi-Prompt Adaptation for Reliable MedSAM
Sep 02, 2024



Abstract:The Medical Segment Anything Model (MedSAM) has shown remarkable performance in medical image segmentation, drawing significant attention in the field. However, its sensitivity to varying prompt types and locations poses challenges. This paper addresses these challenges by focusing on the development of reliable prompts that enhance MedSAM's accuracy. We introduce MedSAM-U, an uncertainty-guided framework designed to automatically refine multi-prompt inputs for more reliable and precise medical image segmentation. Specifically, we first train a Multi-Prompt Adapter integrated with MedSAM, creating MPA-MedSAM, to adapt to diverse multi-prompt inputs. We then employ uncertainty-guided multi-prompt to effectively estimate the uncertainties associated with the prompts and their initial segmentation results. In particular, a novel uncertainty-guided prompts adaptation technique is then applied automatically to derive reliable prompts and their corresponding segmentation outcomes. We validate MedSAM-U using datasets from multiple modalities to train a universal image segmentation model. Compared to MedSAM, experimental results on five distinct modal datasets demonstrate that the proposed MedSAM-U achieves an average performance improvement of 1.7\% to 20.5\% across uncertainty-guided prompts.
MedRG: Medical Report Grounding with Multi-modal Large Language Model
Apr 10, 2024



Abstract:Medical Report Grounding is pivotal in identifying the most relevant regions in medical images based on a given phrase query, a critical aspect in medical image analysis and radiological diagnosis. However, prevailing visual grounding approaches necessitate the manual extraction of key phrases from medical reports, imposing substantial burdens on both system efficiency and physicians. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework, Medical Report Grounding (MedRG), an end-to-end solution for utilizing a multi-modal Large Language Model to predict key phrase by incorporating a unique token, BOX, into the vocabulary to serve as an embedding for unlocking detection capabilities. Subsequently, the vision encoder-decoder jointly decodes the hidden embedding and the input medical image, generating the corresponding grounding box. The experimental results validate the effectiveness of MedRG, surpassing the performance of the existing state-of-the-art medical phrase grounding methods. This study represents a pioneering exploration of the medical report grounding task, marking the first-ever endeavor in this domain.
Uncertainty-informed Mutual Learning for Joint Medical Image Classification and Segmentation
Mar 30, 2023



Abstract:Classification and segmentation are crucial in medical image analysis as they enable accurate diagnosis and disease monitoring. However, current methods often prioritize the mutual learning features and shared model parameters, while neglecting the reliability of features and performances. In this paper, we propose a novel Uncertainty-informed Mutual Learning (UML) framework for reliable and interpretable medical image analysis. Our UML introduces reliability to joint classification and segmentation tasks, leveraging mutual learning with uncertainty to improve performance. To achieve this, we first use evidential deep learning to provide image-level and pixel-wise confidences. Then, an Uncertainty Navigator Decoder is constructed for better using mutual features and generating segmentation results. Besides, an Uncertainty Instructor is proposed to screen reliable masks for classification. Overall, UML could produce confidence estimation in features and performance for each link (classification and segmentation). The experiments on the public datasets demonstrate that our UML outperforms existing methods in terms of both accuracy and robustness. Our UML has the potential to explore the development of more reliable and explainable medical image analysis models. We will release the codes for reproduction after acceptance.
EvidenceCap: Towards trustworthy medical image segmentation via evidential identity cap
Jan 01, 2023



Abstract:Medical image segmentation (MIS) is essential for supporting disease diagnosis and treatment effect assessment. Despite considerable advances in artificial intelligence (AI) for MIS, clinicians remain skeptical of its utility, maintaining low confidence in such black box systems, with this problem being exacerbated by low generalization for out-of-distribution (OOD) data. To move towards effective clinical utilization, we propose a foundation model named EvidenceCap, which makes the box transparent in a quantifiable way by uncertainty estimation. EvidenceCap not only makes AI visible in regions of uncertainty and OOD data, but also enhances the reliability, robustness, and computational efficiency of MIS. Uncertainty is modeled explicitly through subjective logic theory to gather strong evidence from features. We show the effectiveness of EvidenceCap in three segmentation datasets and apply it to the clinic. Our work sheds light on clinical safe applications and explainable AI, and can contribute towards trustworthiness in the medical domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge