Yaguan Qian
F$^2$AT: Feature-Focusing Adversarial Training via Disentanglement of Natural and Perturbed Patterns
Oct 23, 2023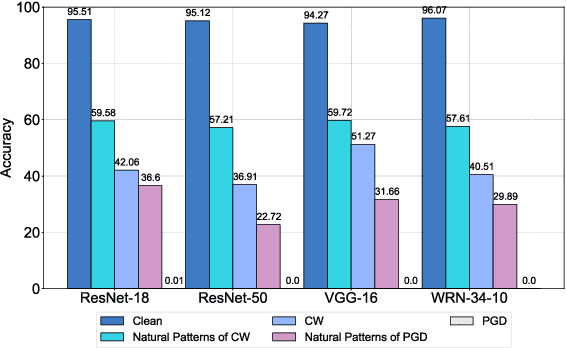
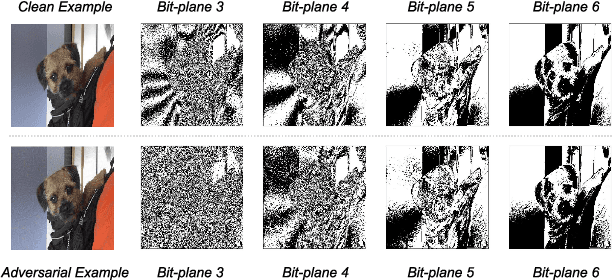
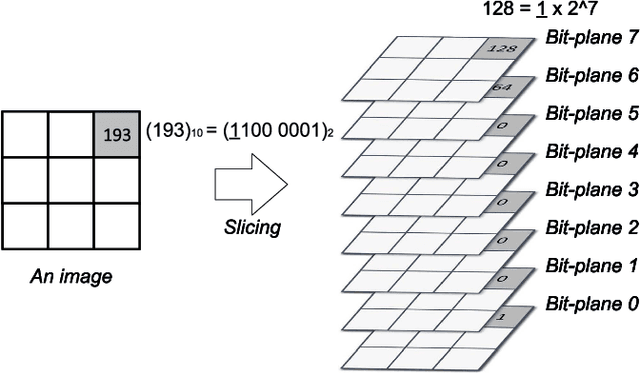
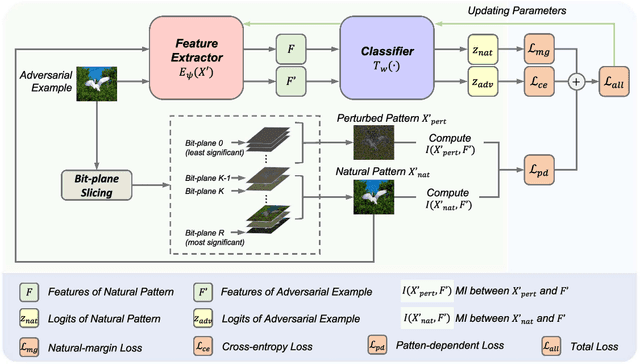
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) are vulnerable to adversarial examples crafted by well-designed perturbations. This could lead to disastrous results on critical applications such as self-driving cars, surveillance security, and medical diagnosis. At present, adversarial training is one of the most effective defenses against adversarial examples. However, traditional adversarial training makes it difficult to achieve a good trade-off between clean accuracy and robustness since spurious features are still learned by DNNs. The intrinsic reason is that traditional adversarial training makes it difficult to fully learn core features from adversarial examples when adversarial noise and clean examples cannot be disentangled. In this paper, we disentangle the adversarial examples into natural and perturbed patterns by bit-plane slicing. We assume the higher bit-planes represent natural patterns and the lower bit-planes represent perturbed patterns, respectively. We propose a Feature-Focusing Adversarial Training (F$^2$AT), which differs from previous work in that it enforces the model to focus on the core features from natural patterns and reduce the impact of spurious features from perturbed patterns. The experimental results demonstrated that F$^2$AT outperforms state-of-the-art methods in clean accuracy and adversarial robustness.
Robust Backdoor Attacks on Object Detection in Real World
Sep 16, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning models are widely deployed in many applications, such as object detection in various security fields. However, these models are vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Most backdoor attacks were intensively studied on classified models, but little on object detection. Previous works mainly focused on the backdoor attack in the digital world, but neglect the real world. Especially, the backdoor attack's effect in the real world will be easily influenced by physical factors like distance and illumination. In this paper, we proposed a variable-size backdoor trigger to adapt to the different sizes of attacked objects, overcoming the disturbance caused by the distance between the viewing point and attacked object. In addition, we proposed a backdoor training named malicious adversarial training, enabling the backdoor object detector to learn the feature of the trigger with physical noise. The experiment results show this robust backdoor attack (RBA) could enhance the attack success rate in the real world.
Towards the Desirable Decision Boundary by Moderate-Margin Adversarial Training
Jul 16, 2022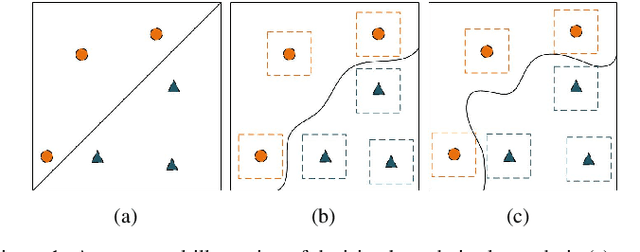
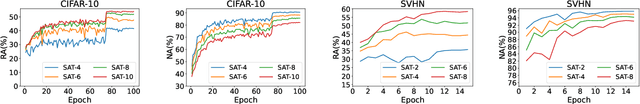
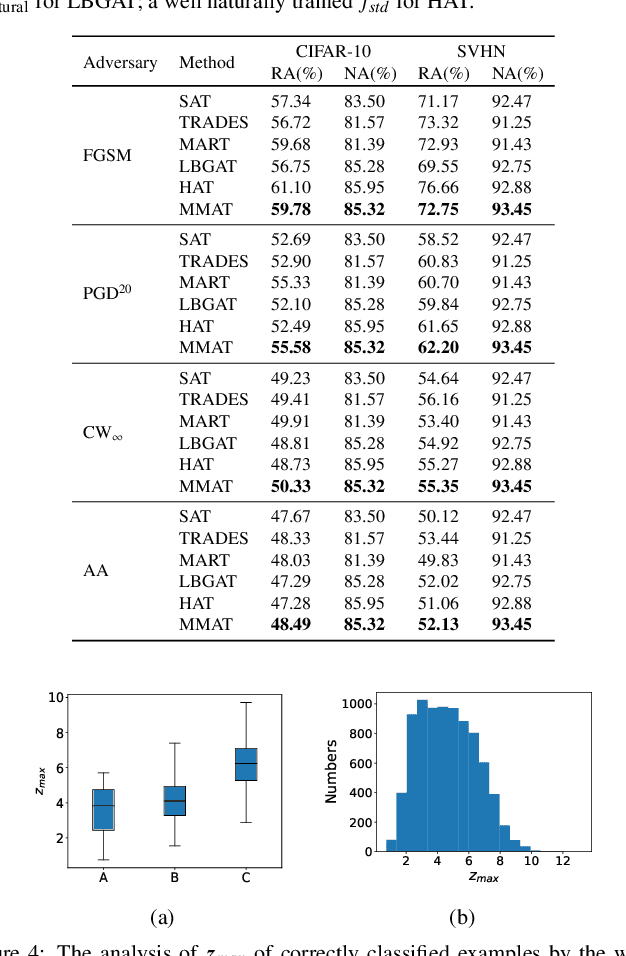
Abstract:Adversarial training, as one of the most effective defense methods against adversarial attacks, tends to learn an inclusive decision boundary to increase the robustness of deep learning models. However, due to the large and unnecessary increase in the margin along adversarial directions, adversarial training causes heavy cross-over between natural examples and adversarial examples, which is not conducive to balancing the trade-off between robustness and natural accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel adversarial training scheme to achieve a better trade-off between robustness and natural accuracy. It aims to learn a moderate-inclusive decision boundary, which means that the margins of natural examples under the decision boundary are moderate. We call this scheme Moderate-Margin Adversarial Training (MMAT), which generates finer-grained adversarial examples to mitigate the cross-over problem. We also take advantage of logits from a teacher model that has been well-trained to guide the learning of our model. Finally, MMAT achieves high natural accuracy and robustness under both black-box and white-box attacks. On SVHN, for example, state-of-the-art robustness and natural accuracy are achieved.
Hessian-Free Second-Order Adversarial Examples for Adversarial Learning
Jul 04, 2022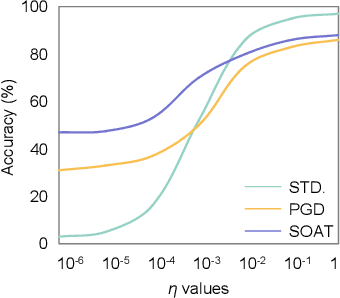
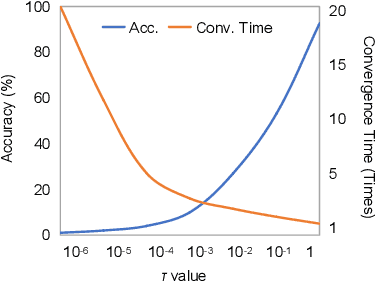
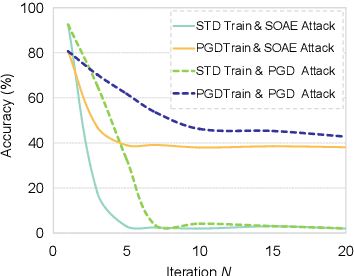
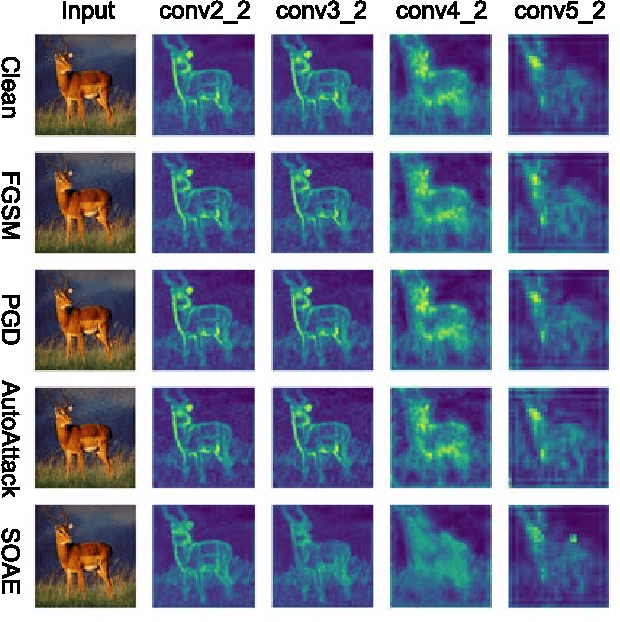
Abstract:Recent studies show deep neural networks (DNNs) are extremely vulnerable to the elaborately designed adversarial examples. Adversarial learning with those adversarial examples has been proved as one of the most effective methods to defend against such an attack. At present, most existing adversarial examples generation methods are based on first-order gradients, which can hardly further improve models' robustness, especially when facing second-order adversarial attacks. Compared with first-order gradients, second-order gradients provide a more accurate approximation of the loss landscape with respect to natural examples. Inspired by this, our work crafts second-order adversarial examples and uses them to train DNNs. Nevertheless, second-order optimization involves time-consuming calculation for Hessian-inverse. We propose an approximation method through transforming the problem into an optimization in the Krylov subspace, which remarkably reduce the computational complexity to speed up the training procedure. Extensive experiments conducted on the MINIST and CIFAR-10 datasets show that our adversarial learning with second-order adversarial examples outperforms other fisrt-order methods, which can improve the model robustness against a wide range of attacks.
Edge-aware Guidance Fusion Network for RGB Thermal Scene Parsing
Dec 09, 2021



Abstract:RGB thermal scene parsing has recently attracted increasing research interest in the field of computer vision. However, most existing methods fail to perform good boundary extraction for prediction maps and cannot fully use high level features. In addition, these methods simply fuse the features from RGB and thermal modalities but are unable to obtain comprehensive fused features. To address these problems, we propose an edge-aware guidance fusion network (EGFNet) for RGB thermal scene parsing. First, we introduce a prior edge map generated using the RGB and thermal images to capture detailed information in the prediction map and then embed the prior edge information in the feature maps. To effectively fuse the RGB and thermal information, we propose a multimodal fusion module that guarantees adequate cross-modal fusion. Considering the importance of high level semantic information, we propose a global information module and a semantic information module to extract rich semantic information from the high-level features. For decoding, we use simple elementwise addition for cascaded feature fusion. Finally, to improve the parsing accuracy, we apply multitask deep supervision to the semantic and boundary maps. Extensive experiments were performed on benchmark datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed EGFNet and its superior performance compared with state of the art methods. The code and results can be found at https://github.com/ShaohuaDong2021/EGFNet.
Versailles-FP dataset: Wall Detection in Ancient
Mar 14, 2021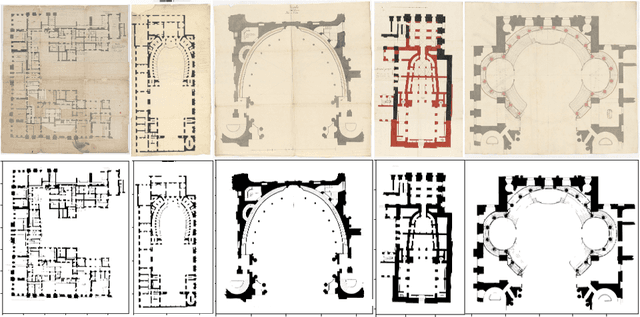

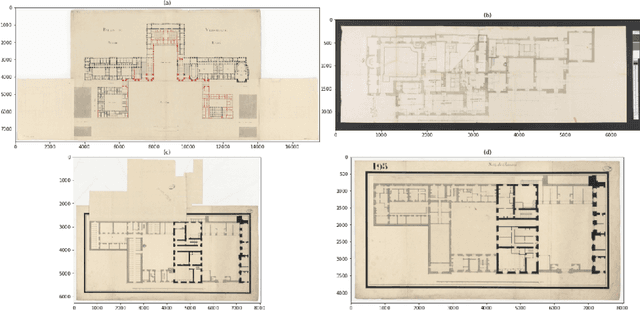

Abstract:Access to historical monuments' floor plans over a time period is necessary to understand the architectural evolution and history. Such knowledge bases also helps to rebuild the history by establishing connection between different event, person and facts which are once part of the buildings. Since the two-dimensional plans do not capture the entire space, 3D modeling sheds new light on the reading of these unique archives and thus opens up great perspectives for understanding the ancient states of the monument. Since the first step in the building's or monument's 3D model is the wall detection in the floor plan, we introduce in this paper the new and unique Versailles FP dataset of wall groundtruthed images of the Versailles Palace dated between 17th and 18th century. The dataset's wall masks are generated using an automatic approach based on multi directional steerable filters. The generated wall masks are then validated and corrected manually. We validate our approach of wall mask generation in state-of-the-art modern datasets. Finally we propose a U net based convolutional framework for wall detection. Our method achieves state of the art result surpassing fully connected network based approach.
Person Re-identification based on Robust Features in Open-world
Feb 22, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning technology promotes the rapid development of person re-identifica-tion (re-ID). However, some challenges are still existing in the open-world. First, the existing re-ID research usually assumes only one factor variable (view, clothing, pedestrian pose, pedestrian occlusion, image resolution, RGB/IR modality) changing, ignoring the complexity of multi-factor variables in the open-world. Second, the existing re-ID methods are over depend on clothing color and other apparent features of pedestrian, which are easily disguised or changed. In addition, the lack of benchmark datasets containing multi-factor variables is also hindering the practically application of re-ID in the open-world. In this paper, we propose a low-cost and high-efficiency method to solve shortcomings of the existing re-ID research, such as unreliable feature selection, low efficiency of feature extraction, single research variable, etc. Our approach based on pose estimation model improved by group convolution to obtain the continuous key points of pedestrian, and utilize dynamic time warping (DTW) to measure the similarity of features between different pedestrians. At the same time, to verify the effectiveness of our method, we provide a miniature dataset which is closer to the real world and includes pedestrian changing clothes and cross-modality factor variables fusion. Extensive experiments are conducted and the results show that our method achieves Rank-1: 60.9%, Rank-5: 78.1%, and mAP: 49.2% on this dataset, which exceeds most existing state-of-art re-ID models.
Towards Speeding up Adversarial Training in Latent Spaces
Feb 01, 2021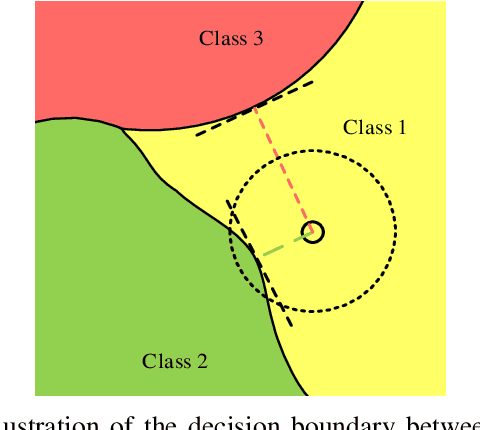
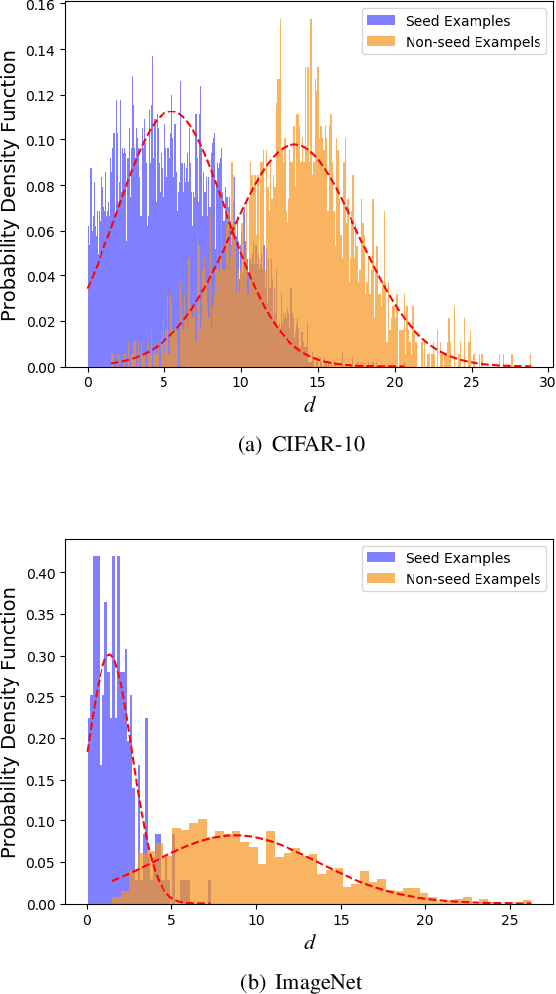
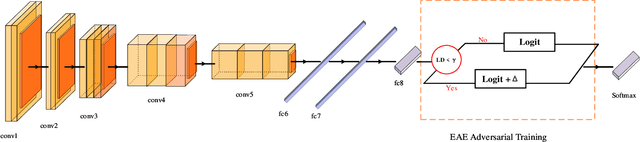
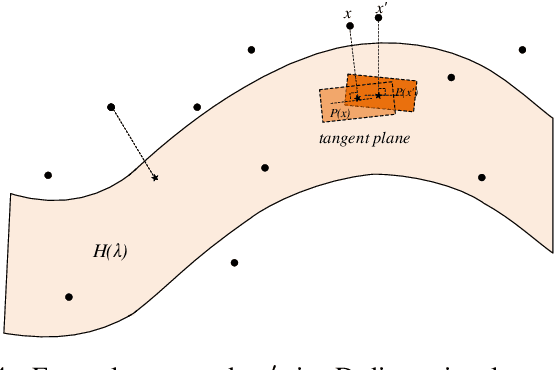
Abstract:Adversarial training is wildly considered as the most effective way to defend against adversarial examples. However, existing adversarial training methods consume unbearable time cost, since they need to generate adversarial examples in the input space, which accounts for the main part of total time-consuming. For speeding up the training process, we propose a novel adversarial training method that does not need to generate real adversarial examples. We notice that a clean example is closer to the decision boundary of the class with the second largest logit component than any other class besides its own class. Thus, by adding perturbations to logits to generate Endogenous Adversarial Examples(EAEs) -- adversarial examples in the latent space, it can avoid calculating gradients to speed up the training process. We further gain a deep insight into the existence of EAEs by the theory of manifold. To guarantee the added perturbation is within the range of constraint, we use statistical distributions to select seed examples to craft EAEs. Extensive experiments are conducted on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet, and the results show that compare with state-of-the-art "Free" and "Fast" methods, our EAE adversarial training not only shortens the training time, but also enhances the robustness of the model. Moreover, the EAE adversarial training has little impact on the accuracy of clean examples than the existing methods.
Towards Imperceptible Adversarial Image Patches Based on Network Explanations
Dec 10, 2020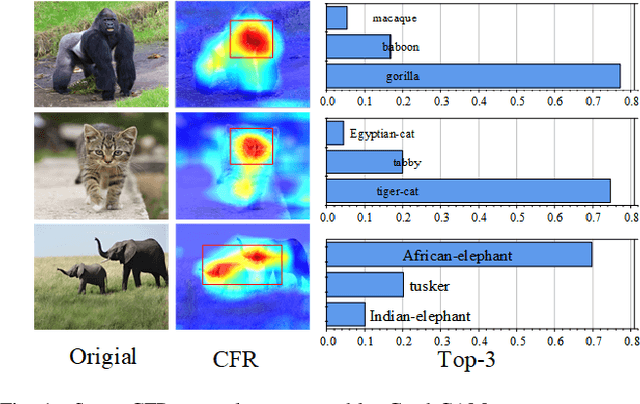
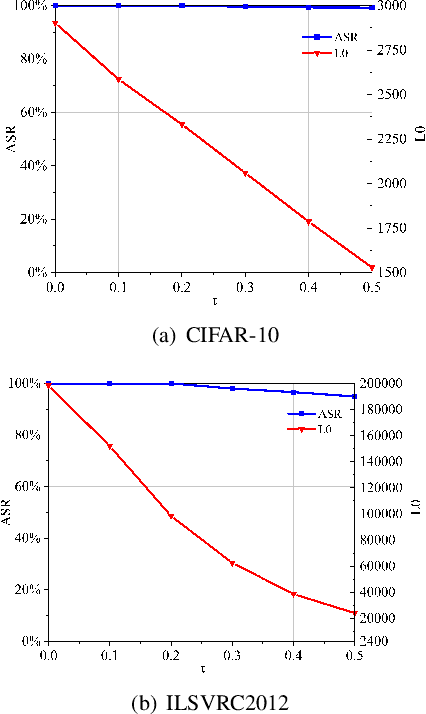
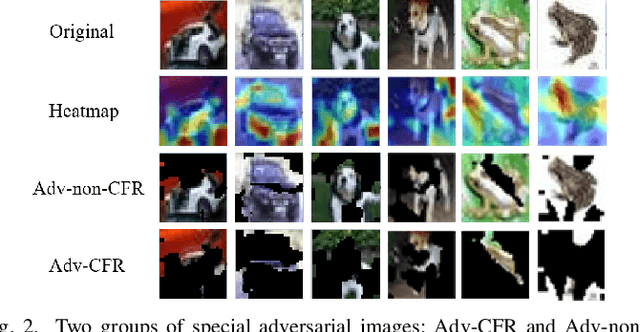
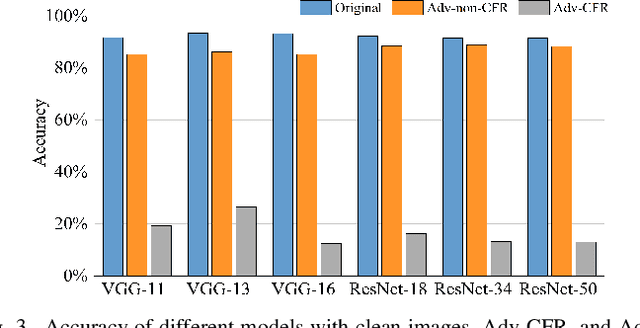
Abstract:The vulnerability of deep neural networks (DNNs) for adversarial examples have attracted more attention. Many algorithms are proposed to craft powerful adversarial examples. However, these algorithms modifying the global or local region of pixels without taking into account network explanations. Hence, the perturbations are redundancy and easily detected by human eyes. In this paper, we propose a novel method to generate local region perturbations. The main idea is to find the contributing feature regions (CFRs) of images based on network explanations for perturbations. Due to the network explanations, the perturbations added to the CFRs are more effective than other regions. In our method, a soft mask matrix is designed to represent the CFRs for finely characterizing the contributions of each pixel. Based on this soft mask, we develop a new objective function with inverse temperature to search for optimal perturbations in CFRs. Extensive experiments are conducted on CIFAR-10 and ILSVRC2012, which demonstrate the effectiveness, including attack success rate, imperceptibility,and transferability.
EI-MTD:Moving Target Defense for Edge Intelligence against Adversarial Attacks
Oct 11, 2020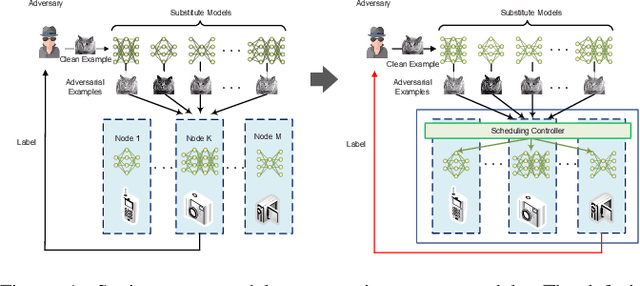
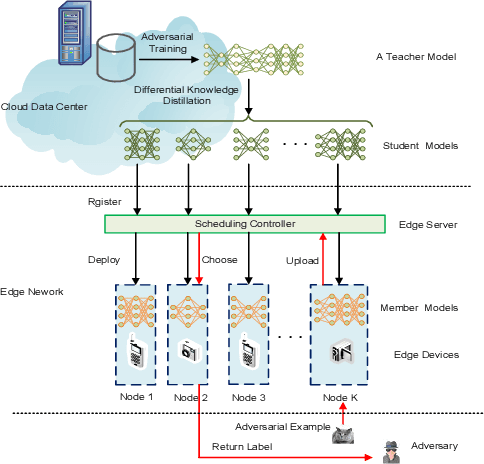
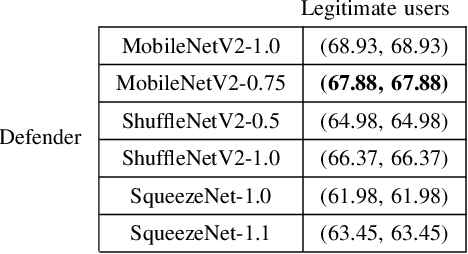
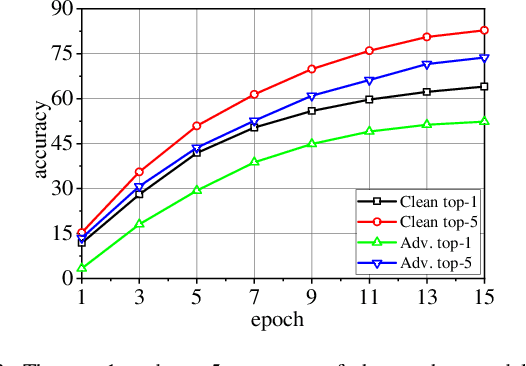
Abstract:With the boom of edge intelligence, its vulnerability to adversarial attacks becomes an urgent problem. The so-called adversarial example can fool a deep learning model on the edge node to misclassify. Due to the property of transferability, the adversary can easily make a black-box attack using a local substitute model. Nevertheless, the limitation of resource of edge nodes cannot afford a complicated defense mechanism as doing on the cloud data center. To overcome the challenge, we propose a dynamic defense mechanism, namely EI-MTD. It first obtains robust member models with small size through differential knowledge distillation from a complicated teacher model on the cloud data center. Then, a dynamic scheduling policy based on a Bayesian Stackelberg game is applied to the choice of a target model for service. This dynamic defense can prohibit the adversary from selecting an optimal substitute model for black-box attacks. Our experimental result shows that this dynamic scheduling can effectively protect edge intelligence against adversarial attacks under the black-box setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge