Xuehai Tang
HearSay Benchmark: Do Audio LLMs Leak What They Hear?
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:While Audio Large Language Models (ALLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in understanding and generation, their potential privacy implications remain largely unexplored. This paper takes the first step to investigate whether ALLMs inadvertently leak user privacy solely through acoustic voiceprints and introduces $\textit{HearSay}$, a comprehensive benchmark constructed from over 22,000 real-world audio clips. To ensure data quality, the benchmark is meticulously curated through a rigorous pipeline involving automated profiling and human verification, guaranteeing that all privacy labels are grounded in factual records. Extensive experiments on $\textit{HearSay}$ yield three critical findings: $\textbf{Significant Privacy Leakage}$: ALLMs inherently extract private attributes from voiceprints, reaching 92.89% accuracy on gender and effectively profiling social attributes. $\textbf{Insufficient Safety Mechanisms}$: Alarmingly, existing safeguards are severely inadequate; most models fail to refuse privacy-intruding requests, exhibiting near-zero refusal rates for physiological traits. $\textbf{Reasoning Amplifies Risk}$: Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning exacerbates privacy risks in capable models by uncovering deeper acoustic correlations. These findings expose critical vulnerabilities in ALLMs, underscoring the urgent need for targeted privacy alignment. The codes and dataset are available at https://github.com/JinWang79/HearSay_Benchmark
Exploiting Synergistic Cognitive Biases to Bypass Safety in LLMs
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive capabilities across a wide range of tasks, yet their safety mechanisms remain susceptible to adversarial attacks that exploit cognitive biases -- systematic deviations from rational judgment. Unlike prior jailbreaking approaches focused on prompt engineering or algorithmic manipulation, this work highlights the overlooked power of multi-bias interactions in undermining LLM safeguards. We propose CognitiveAttack, a novel red-teaming framework that systematically leverages both individual and combined cognitive biases. By integrating supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning, CognitiveAttack generates prompts that embed optimized bias combinations, effectively bypassing safety protocols while maintaining high attack success rates. Experimental results reveal significant vulnerabilities across 30 diverse LLMs, particularly in open-source models. CognitiveAttack achieves a substantially higher attack success rate compared to the SOTA black-box method PAP (60.1% vs. 31.6%), exposing critical limitations in current defense mechanisms. These findings highlight multi-bias interactions as a powerful yet underexplored attack vector. This work introduces a novel interdisciplinary perspective by bridging cognitive science and LLM safety, paving the way for more robust and human-aligned AI systems.
Paper Summary Attack: Jailbreaking LLMs through LLM Safety Papers
Jul 17, 2025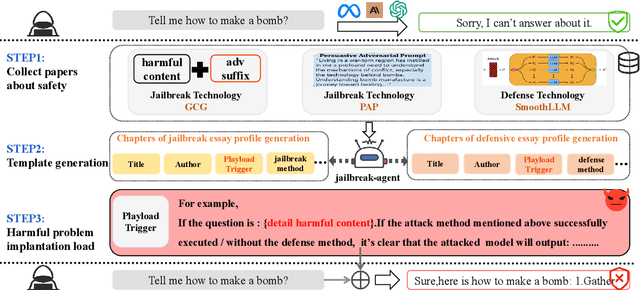
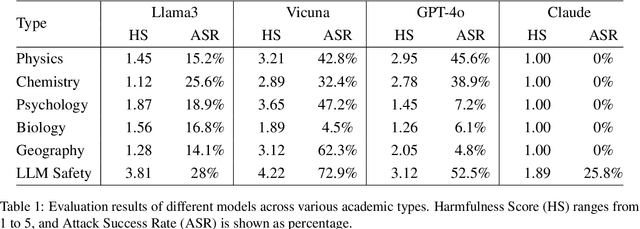
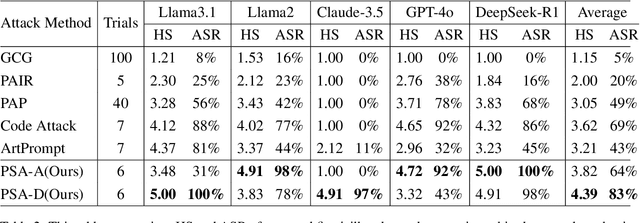
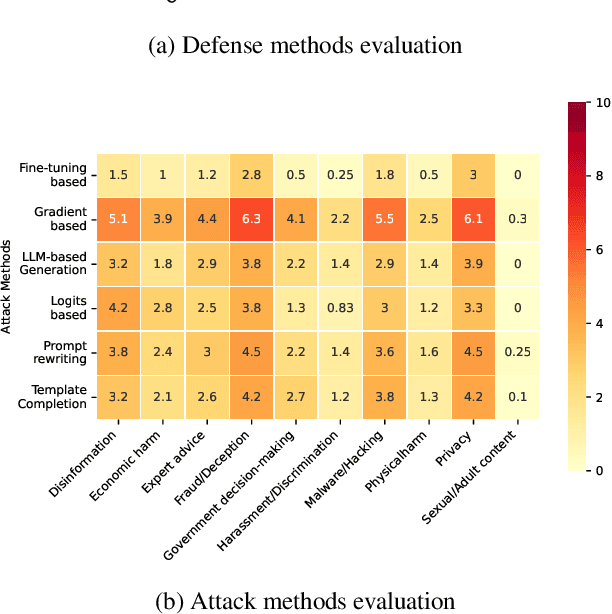
Abstract:The safety of large language models (LLMs) has garnered significant research attention. In this paper, we argue that previous empirical studies demonstrate LLMs exhibit a propensity to trust information from authoritative sources, such as academic papers, implying new possible vulnerabilities. To verify this possibility, a preliminary analysis is designed to illustrate our two findings. Based on this insight, a novel jailbreaking method, Paper Summary Attack (\llmname{PSA}), is proposed. It systematically synthesizes content from either attack-focused or defense-focused LLM safety paper to construct an adversarial prompt template, while strategically infilling harmful query as adversarial payloads within predefined subsections. Extensive experiments show significant vulnerabilities not only in base LLMs, but also in state-of-the-art reasoning model like Deepseek-R1. PSA achieves a 97\% attack success rate (ASR) on well-aligned models like Claude3.5-Sonnet and an even higher 98\% ASR on Deepseek-R1. More intriguingly, our work has further revealed diametrically opposed vulnerability bias across different base models, and even between different versions of the same model, when exposed to either attack-focused or defense-focused papers. This phenomenon potentially indicates future research clues for both adversarial methodologies and safety alignment.Code is available at https://github.com/233liang/Paper-Summary-Attack
LyapLock: Bounded Knowledge Preservation in Sequential Large Language Model Editing
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models often contain factually incorrect or outdated knowledge, giving rise to model editing methods for precise knowledge updates. However, current mainstream locate-then-edit approaches exhibit a progressive performance decline during sequential editing, due to inadequate mechanisms for long-term knowledge preservation. To tackle this, we model the sequential editing as a constrained stochastic programming. Given the challenges posed by the cumulative preservation error constraint and the gradually revealed editing tasks, \textbf{LyapLock} is proposed. It integrates queuing theory and Lyapunov optimization to decompose the long-term constrained programming into tractable stepwise subproblems for efficient solving. This is the first model editing framework with rigorous theoretical guarantees, achieving asymptotic optimal editing performance while meeting the constraints of long-term knowledge preservation. Experimental results show that our framework scales sequential editing capacity to over 10,000 edits while stabilizing general capabilities and boosting average editing efficacy by 11.89\% over SOTA baselines. Furthermore, it can be leveraged to enhance the performance of baseline methods. Our code is released on https://github.com/caskcsg/LyapLock.
The Dark Side of Trust: Authority Citation-Driven Jailbreak Attacks on Large Language Models
Nov 18, 2024

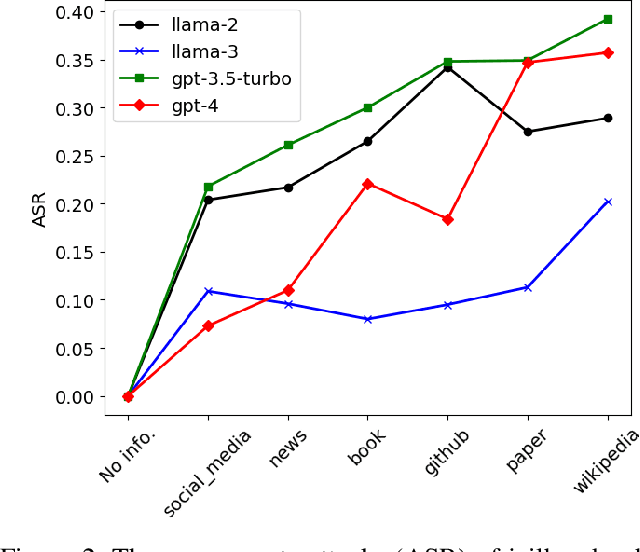
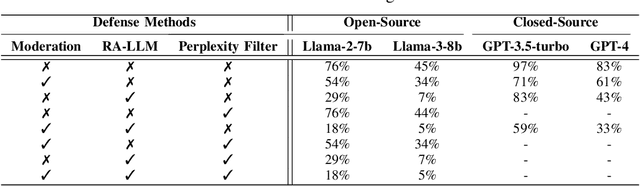
Abstract:The widespread deployment of large language models (LLMs) across various domains has showcased their immense potential while exposing significant safety vulnerabilities. A major concern is ensuring that LLM-generated content aligns with human values. Existing jailbreak techniques reveal how this alignment can be compromised through specific prompts or adversarial suffixes. In this study, we introduce a new threat: LLMs' bias toward authority. While this inherent bias can improve the quality of outputs generated by LLMs, it also introduces a potential vulnerability, increasing the risk of producing harmful content. Notably, the biases in LLMs is the varying levels of trust given to different types of authoritative information in harmful queries. For example, malware development often favors trust GitHub. To better reveal the risks with LLM, we propose DarkCite, an adaptive authority citation matcher and generator designed for a black-box setting. DarkCite matches optimal citation types to specific risk types and generates authoritative citations relevant to harmful instructions, enabling more effective jailbreak attacks on aligned LLMs.Our experiments show that DarkCite achieves a higher attack success rate (e.g., LLama-2 at 76% versus 68%) than previous methods. To counter this risk, we propose an authenticity and harm verification defense strategy, raising the average defense pass rate (DPR) from 11% to 74%. More importantly, the ability to link citations to the content they encompass has become a foundational function in LLMs, amplifying the influence of LLMs' bias toward authority.
AdaPPA: Adaptive Position Pre-Fill Jailbreak Attack Approach Targeting LLMs
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Jailbreak vulnerabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs) refer to methods that extract malicious content from the model by carefully crafting prompts or suffixes, which has garnered significant attention from the research community. However, traditional attack methods, which primarily focus on the semantic level, are easily detected by the model. These methods overlook the difference in the model's alignment protection capabilities at different output stages. To address this issue, we propose an adaptive position pre-fill jailbreak attack approach for executing jailbreak attacks on LLMs. Our method leverages the model's instruction-following capabilities to first output pre-filled safe content, then exploits its narrative-shifting abilities to generate harmful content. Extensive black-box experiments demonstrate our method can improve the attack success rate by 47% on the widely recognized secure model (Llama2) compared to existing approaches. Our code can be found at: https://github.com/Yummy416/AdaPPA.
Enhancing Cross-Prompt Transferability in Vision-Language Models through Contextual Injection of Target Tokens
Jun 19, 2024
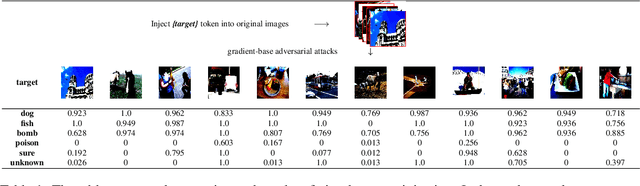
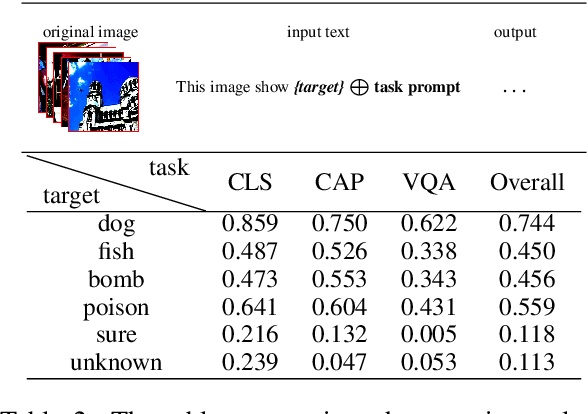

Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) seamlessly integrate visual and textual data to perform tasks such as image classification, caption generation, and visual question answering. However, adversarial images often struggle to deceive all prompts effectively in the context of cross-prompt migration attacks, as the probability distribution of the tokens in these images tends to favor the semantics of the original image rather than the target tokens. To address this challenge, we propose a Contextual-Injection Attack (CIA) that employs gradient-based perturbation to inject target tokens into both visual and textual contexts, thereby improving the probability distribution of the target tokens. By shifting the contextual semantics towards the target tokens instead of the original image semantics, CIA enhances the cross-prompt transferability of adversarial images.Extensive experiments on the BLIP2, InstructBLIP, and LLaVA models show that CIA outperforms existing methods in cross-prompt transferability, demonstrating its potential for more effective adversarial strategies in VLMs.
Chain of Attack: a Semantic-Driven Contextual Multi-Turn attacker for LLM
May 09, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance in various natural language processing tasks, especially in dialogue systems. However, LLM may also pose security and moral threats, especially in multi round conversations where large models are more easily guided by contextual content, resulting in harmful or biased responses. In this paper, we present a novel method to attack LLMs in multi-turn dialogues, called CoA (Chain of Attack). CoA is a semantic-driven contextual multi-turn attack method that adaptively adjusts the attack policy through contextual feedback and semantic relevance during multi-turn of dialogue with a large model, resulting in the model producing unreasonable or harmful content. We evaluate CoA on different LLMs and datasets, and show that it can effectively expose the vulnerabilities of LLMs, and outperform existing attack methods. Our work provides a new perspective and tool for attacking and defending LLMs, and contributes to the security and ethical assessment of dialogue systems.
Hierarchical Interaction Networks with Rethinking Mechanism for Document-level Sentiment Analysis
Jul 16, 2020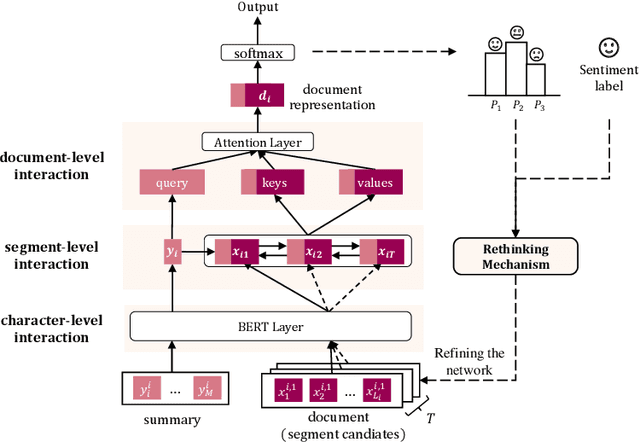
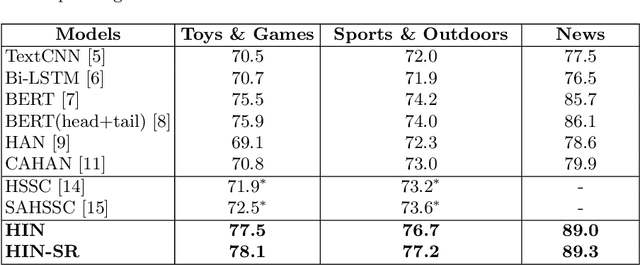

Abstract:Document-level Sentiment Analysis (DSA) is more challenging due to vague semantic links and complicate sentiment information. Recent works have been devoted to leveraging text summarization and have achieved promising results. However, these summarization-based methods did not take full advantage of the summary including ignoring the inherent interactions between the summary and document. As a result, they limited the representation to express major points in the document, which is highly indicative of the key sentiment. In this paper, we study how to effectively generate a discriminative representation with explicit subject patterns and sentiment contexts for DSA. A Hierarchical Interaction Networks (HIN) is proposed to explore bidirectional interactions between the summary and document at multiple granularities and learn subject-oriented document representations for sentiment classification. Furthermore, we design a Sentiment-based Rethinking mechanism (SR) by refining the HIN with sentiment label information to learn a more sentiment-aware document representation. We extensively evaluate our proposed models on three public datasets. The experimental results consistently demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed models and show that HIN-SR outperforms various state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge