Xiyao Li
End-to-end training of Multimodal Model and ranking Model
Apr 09, 2024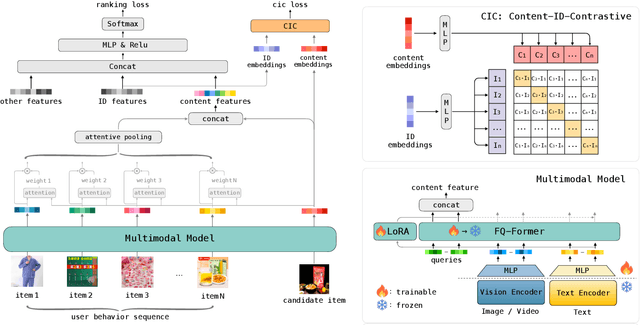
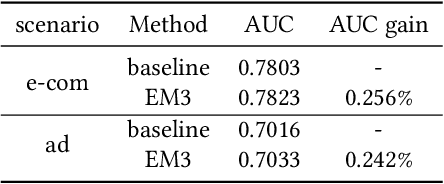
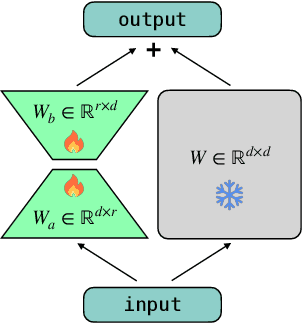
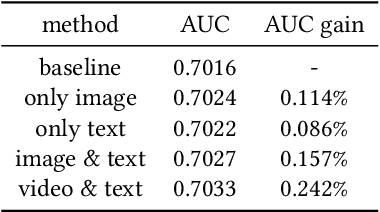
Abstract:Traditional recommender systems heavily rely on ID features, which often encounter challenges related to cold-start and generalization. Modeling pre-extracted content features can mitigate these issues, but is still a suboptimal solution due to the discrepancies between training tasks and model parameters. End-to-end training presents a promising solution for these problems, yet most of the existing works mainly focus on retrieval models, leaving the multimodal techniques under-utilized. In this paper, we propose an industrial multimodal recommendation framework named EM3: End-to-end training of Multimodal Model and ranking Model, which sufficiently utilizes multimodal information and allows personalized ranking tasks to directly train the core modules in the multimodal model to obtain more task-oriented content features, without overburdening resource consumption. First, we propose Fusion-Q-Former, which consists of transformers and a set of trainable queries, to fuse different modalities and generate fixed-length and robust multimodal embeddings. Second, in our sequential modeling for user content interest, we utilize Low-Rank Adaptation technique to alleviate the conflict between huge resource consumption and long sequence length. Third, we propose a novel Content-ID-Contrastive learning task to complement the advantages of content and ID by aligning them with each other, obtaining more task-oriented content embeddings and more generalized ID embeddings. In experiments, we implement EM3 on different ranking models in two scenario, achieving significant improvements in both offline evaluation and online A/B test, verifying the generalizability of our method. Ablation studies and visualization are also performed. Furthermore, we also conduct experiments on two public datasets to show that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods.
ProS: Prompting-to-simulate Generalized knowledge for Universal Cross-Domain Retrieval
Dec 19, 2023



Abstract:The goal of Universal Cross-Domain Retrieval (UCDR) is to achieve robust performance in generalized test scenarios, wherein data may belong to strictly unknown domains and categories during training. Recently, pre-trained models with prompt tuning have shown strong generalization capabilities and attained noteworthy achievements in various downstream tasks, such as few-shot learning and video-text retrieval. However, applying them directly to UCDR may not sufficiently to handle both domain shift (i.e., adapting to unfamiliar domains) and semantic shift (i.e., transferring to unknown categories). To this end, we propose Prompting-to-Simulate (ProS), the first method to apply prompt tuning for UCDR. ProS employs a two-step process to simulate Content-aware Dynamic Prompts (CaDP) which can impact models to produce generalized features for UCDR. Concretely, in Prompt Units Learning stage, we introduce two Prompt Units to individually capture domain and semantic knowledge in a mask-and-align way. Then, in Context-aware Simulator Learning stage, we train a Content-aware Prompt Simulator under a simulated test scenarios to produce the corresponding CaDP. Extensive experiments conducted on three benchmark datasets show that our method achieves new state-of-the-art performance without bringing excessive parameters. Our method is publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ProS
MoCoSA: Momentum Contrast for Knowledge Graph Completion with Structure-Augmented Pre-trained Language Models
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC) aims to conduct reasoning on the facts within knowledge graphs and automatically infer missing links. Existing methods can mainly be categorized into structure-based or description-based. On the one hand, structure-based methods effectively represent relational facts in knowledge graphs using entity embeddings. However, they struggle with semantically rich real-world entities due to limited structural information and fail to generalize to unseen entities. On the other hand, description-based methods leverage pre-trained language models (PLMs) to understand textual information. They exhibit strong robustness towards unseen entities. However, they have difficulty with larger negative sampling and often lag behind structure-based methods. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose Momentum Contrast for knowledge graph completion with Structure-Augmented pre-trained language models (MoCoSA), which allows the PLM to perceive the structural information by the adaptable structure encoder. To improve learning efficiency, we proposed momentum hard negative and intra-relation negative sampling. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of mean reciprocal rank (MRR), with improvements of 2.5% on WN18RR and 21% on OpenBG500.
Conductivity Imaging from Internal Measurements with Mixed Least-Squares Deep Neural Networks
Mar 29, 2023



Abstract:In this work we develop a novel approach using deep neural networks to reconstruct the conductivity distribution in elliptic problems from one internal measurement. The approach is based on a mixed reformulation of the governing equation and utilizes the standard least-squares objective to approximate the conductivity and flux simultaneously, with deep neural networks as ansatz functions. We provide a thorough analysis of the neural network approximations for both continuous and empirical losses, including rigorous error estimates that are explicit in terms of the noise level, various penalty parameters and neural network architectural parameters (depth, width and parameter bound). We also provide extensive numerical experiments in two- and multi-dimensions to illustrate distinct features of the approach, e.g., excellent stability with respect to data noise and capability of solving high-dimensional problems.
Fashion Image Retrieval with Multi-Granular Alignment
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:Fashion image retrieval task aims to search relevant clothing items of a query image from the gallery. The previous recipes focus on designing different distance-based loss functions, pulling relevant pairs to be close and pushing irrelevant images apart. However, these methods ignore fine-grained features (e.g. neckband, cuff) of clothing images. In this paper, we propose a novel fashion image retrieval method leveraging both global and fine-grained features, dubbed Multi-Granular Alignment (MGA). Specifically, we design a Fine-Granular Aggregator(FGA) to capture and aggregate detailed patterns. Then we propose Attention-based Token Alignment (ATA) to align image features at the multi-granular level in a coarse-to-fine manner. To prove the effectiveness of our proposed method, we conduct experiments on two sub-tasks (In-Shop & Consumer2Shop) of the public fashion datasets DeepFashion. The experimental results show that our MGA outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by 1.8% and 0.6% in the two sub-tasks on the R@1 metric, respectively.
Imaging Conductivity from Current Density Magnitude using Neural Networks
Apr 18, 2022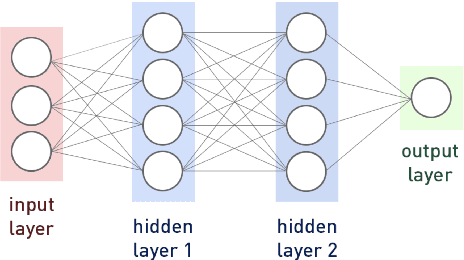
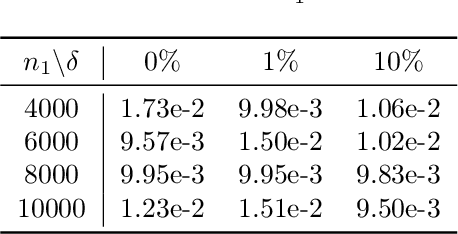
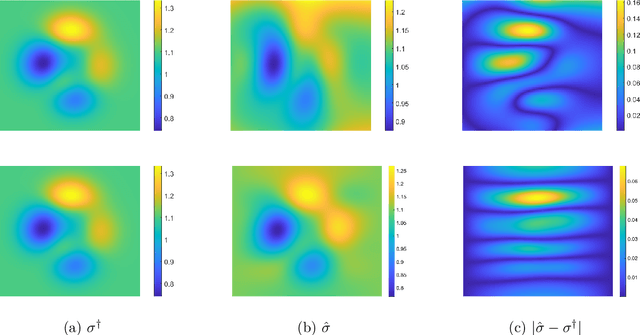
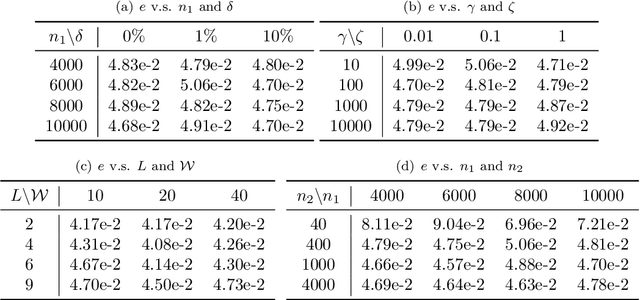
Abstract:Conductivity imaging represents one of the most important tasks in medical imaging. In this work we develop a neural network based reconstruction technique for imaging the conductivity from the magnitude of the internal current density. It is achieved by formulating the problem as a relaxed weighted least-gradient problem, and then approximating its minimizer by standard fully connected feedforward neural networks. We derive bounds on two components of the generalization error, i.e., approximation error and statistical error, explicitly in terms of properties of the neural networks (e.g., depth, total number of parameters, and the bound of the network parameters). We illustrate the performance and distinct features of the approach on several numerical experiments. Numerically, it is observed that the approach enjoys remarkable robustness with respect to the presence of data noise.
CADG: A Model Based on Cross Attention for Domain Generalization
Apr 07, 2022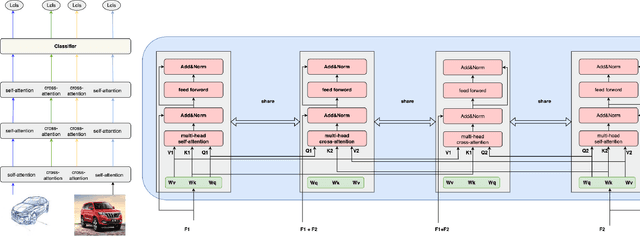
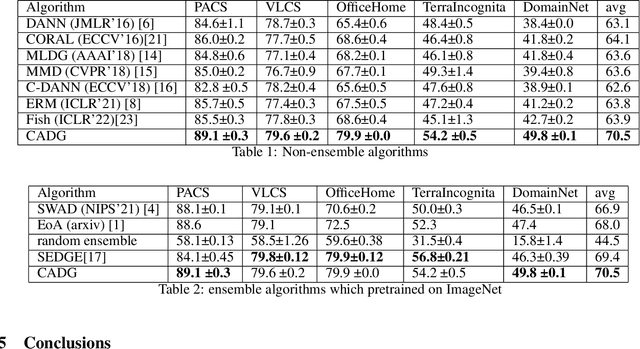
Abstract:In Domain Generalization (DG) tasks, models are trained by using only training data from the source domains to achieve generalization on an unseen target domain, this will suffer from the distribution shift problem. So it's important to learn a classifier to focus on the common representation which can be used to classify on multi-domains, so that this classifier can achieve a high performance on an unseen target domain as well. With the success of cross attention in various cross-modal tasks, we find that cross attention is a powerful mechanism to align the features come from different distributions. So we design a model named CADG (cross attention for domain generalization), wherein cross attention plays a important role, to address distribution shift problem. Such design makes the classifier can be adopted on multi-domains, so the classifier will generalize well on an unseen domain. Experiments show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on a variety of domain generalization benchmarks compared with other single model and can even achieve a better performance than some ensemble-based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge