Cheng Dai
Co-PLNet: A Collaborative Point-Line Network for Prompt-Guided Wireframe Parsing
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Wireframe parsing aims to recover line segments and their junctions to form a structured geometric representation useful for downstream tasks such as Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). Existing methods predict lines and junctions separately and reconcile them post-hoc, causing mismatches and reduced robustness. We present Co-PLNet, a point-line collaborative framework that exchanges spatial cues between the two tasks, where early detections are converted into spatial prompts via a Point-Line Prompt Encoder (PLP-Encoder), which encodes geometric attributes into compact and spatially aligned maps. A Cross-Guidance Line Decoder (CGL-Decoder) then refines predictions with sparse attention conditioned on complementary prompts, enforcing point-line consistency and efficiency. Experiments on Wireframe and YorkUrban show consistent improvements in accuracy and robustness, together with favorable real-time efficiency, demonstrating our effectiveness for structured geometry perception.
ProSG: Using Prompt Synthetic Gradients to Alleviate Prompt Forgetting of RNN-like Language Models
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:RNN-like language models are getting renewed attention from NLP researchers in recent years and several models have made significant progress, which demonstrates performance comparable to traditional transformers. However, due to the recurrent nature of RNNs, this kind of language model can only store information in a set of fixed-length state vectors. As a consequence, they still suffer from forgetfulness though after a lot of improvements and optimizations, when given complex instructions or prompts. As the prompted generation is the main and most concerned function of LMs, solving the problem of forgetting in the process of generation is no wonder of vital importance. In this paper, focusing on easing the prompt forgetting during generation, we proposed an architecture to teach the model memorizing prompt during generation by synthetic gradient. To force the model to memorize the prompt, we derive the states that encode the prompt, then transform it into model parameter modification using low-rank gradient approximation, which hard-codes the prompt into model parameters temporarily. We construct a dataset for experiments, and the results have demonstrated the effectiveness of our method in solving the problem of forgetfulness in the process of prompted generation. We will release all the code upon acceptance.
CADG: A Model Based on Cross Attention for Domain Generalization
Apr 07, 2022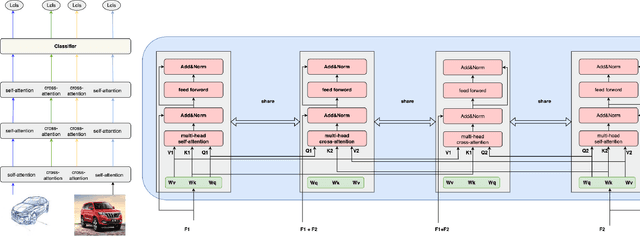
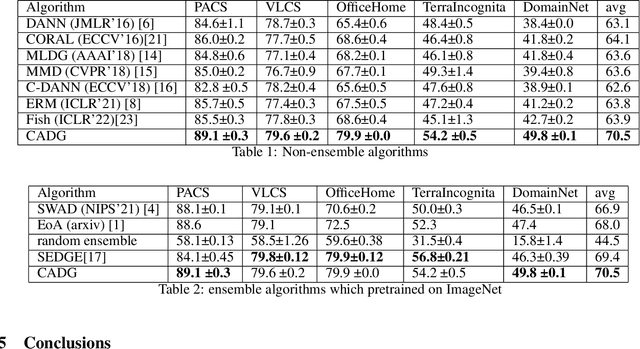
Abstract:In Domain Generalization (DG) tasks, models are trained by using only training data from the source domains to achieve generalization on an unseen target domain, this will suffer from the distribution shift problem. So it's important to learn a classifier to focus on the common representation which can be used to classify on multi-domains, so that this classifier can achieve a high performance on an unseen target domain as well. With the success of cross attention in various cross-modal tasks, we find that cross attention is a powerful mechanism to align the features come from different distributions. So we design a model named CADG (cross attention for domain generalization), wherein cross attention plays a important role, to address distribution shift problem. Such design makes the classifier can be adopted on multi-domains, so the classifier will generalize well on an unseen domain. Experiments show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on a variety of domain generalization benchmarks compared with other single model and can even achieve a better performance than some ensemble-based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge