Xinyue Hao
Avenir-Web: Human-Experience-Imitating Multimodal Web Agents with Mixture of Grounding Experts
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Despite advances in multimodal large language models, autonomous web agents still struggle to reliably execute long-horizon tasks on complex and dynamic web interfaces. Existing agents often suffer from inaccurate element grounding, the absence of site-specific procedural knowledge, and unstable long-term task tracking and memory, particularly when operating over complex Document Object Model structures. To address these limitations, we introduce Avenir-Web, a web agent that achieves a new open-source state of the art on the Online-Mind2Web benchmark in real-world deployment. Avenir-Web leverages a Mixture of Grounding Experts, Experience-Imitation Planning for incorporating procedural priors, and a task-tracking checklist combined with adaptive memory to enable robust and seamless interaction across diverse user interface paradigms. We evaluate Avenir-Web on Online-Mind2Web, a rigorous benchmark of live and user-centered web tasks. Our results demonstrate that Avenir-Web significantly surpasses prior open-source agents and attains performance parity with top-tier proprietary models, thereby establishing a new open-source state of the art for reliable web agents on live websites.
Progressive Data Dropout: An Embarrassingly Simple Approach to Faster Training
May 28, 2025Abstract:The success of the machine learning field has reliably depended on training on large datasets. While effective, this trend comes at an extraordinary cost. This is due to two deeply intertwined factors: the size of models and the size of datasets. While promising research efforts focus on reducing the size of models, the other half of the equation remains fairly mysterious. Indeed, it is surprising that the standard approach to training remains to iterate over and over, uniformly sampling the training dataset. In this paper we explore a series of alternative training paradigms that leverage insights from hard-data-mining and dropout, simple enough to implement and use that can become the new training standard. The proposed Progressive Data Dropout reduces the number of effective epochs to as little as 12.4% of the baseline. This savings actually do not come at any cost for accuracy. Surprisingly, the proposed method improves accuracy by up to 4.82%. Our approach requires no changes to model architecture or optimizer, and can be applied across standard training pipelines, thus posing an excellent opportunity for wide adoption. Code can be found here: https://github.com/bazyagami/LearningWithRevision
Principles of Visual Tokens for Efficient Video Understanding
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Video understanding has made huge strides in recent years, relying largely on the power of the transformer architecture. As this architecture is notoriously expensive and video is highly redundant, research into improving efficiency has become particularly relevant. This has led to many creative solutions, including token merging and token selection. While most methods succeed in reducing the cost of the model and maintaining accuracy, an interesting pattern arises: most methods do not outperform the random sampling baseline. In this paper we take a closer look at this phenomenon and make several observations. First, we develop an oracle for the value of tokens which exposes a clear Pareto distribution where most tokens have remarkably low value, and just a few carry most of the perceptual information. Second, we analyze why this oracle is extremely hard to learn, as it does not consistently coincide with visual cues. Third, we observe that easy videos need fewer tokens to maintain accuracy. We build on these and further insights to propose a lightweight video model we call LITE that can select a small number of tokens effectively, outperforming state-of-the-art and existing baselines across datasets (Kinetics400 and Something-Something-V2) in the challenging trade-off of computation (GFLOPs) vs accuracy.
Watt For What: Rethinking Deep Learning's Energy-Performance Relationship
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:Deep learning models have revolutionized various fields, from image recognition to natural language processing, by achieving unprecedented levels of accuracy. However, their increasing energy consumption has raised concerns about their environmental impact, disadvantaging smaller entities in research and exacerbating global energy consumption. In this paper, we explore the trade-off between model accuracy and electricity consumption, proposing a metric that penalizes large consumption of electricity. We conduct a comprehensive study on the electricity consumption of various deep learning models across different GPUs, presenting a detailed analysis of their accuracy-efficiency trade-offs. By evaluating accuracy per unit of electricity consumed, we demonstrate how smaller, more energy-efficient models can significantly expedite research while mitigating environmental concerns. Our results highlight the potential for a more sustainable approach to deep learning, emphasizing the importance of optimizing models for efficiency. This research also contributes to a more equitable research landscape, where smaller entities can compete effectively with larger counterparts. This advocates for the adoption of efficient deep learning practices to reduce electricity consumption, safeguarding the environment for future generations whilst also helping ensure a fairer competitive landscape.
IROS 2019 Lifelong Robotic Vision Challenge -- Lifelong Object Recognition Report
Apr 26, 2020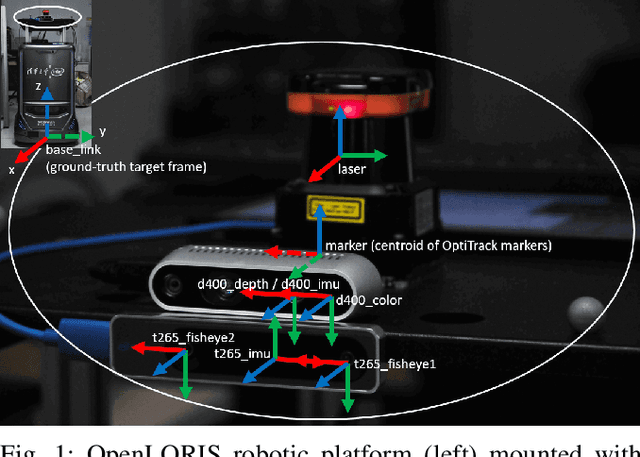
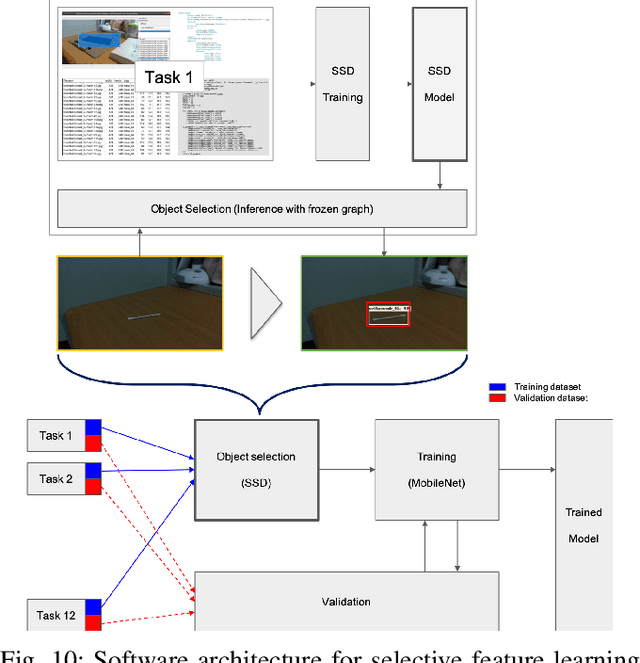
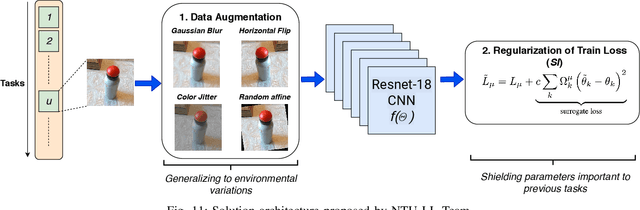
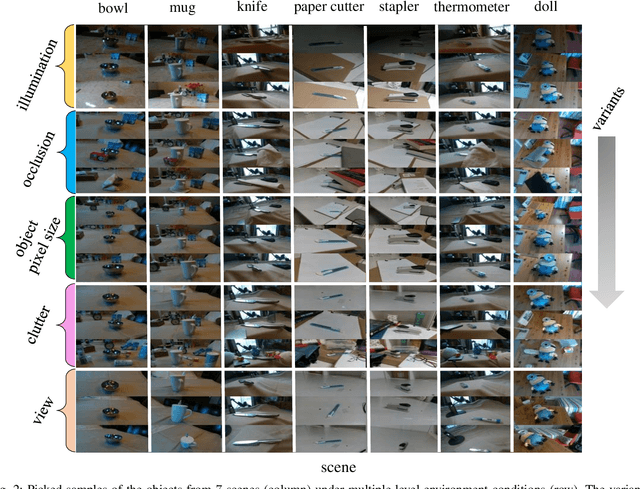
Abstract:This report summarizes IROS 2019-Lifelong Robotic Vision Competition (Lifelong Object Recognition Challenge) with methods and results from the top $8$ finalists (out of over~$150$ teams). The competition dataset (L)ifel(O)ng (R)obotic V(IS)ion (OpenLORIS) - Object Recognition (OpenLORIS-object) is designed for driving lifelong/continual learning research and application in robotic vision domain, with everyday objects in home, office, campus, and mall scenarios. The dataset explicitly quantifies the variants of illumination, object occlusion, object size, camera-object distance/angles, and clutter information. Rules are designed to quantify the learning capability of the robotic vision system when faced with the objects appearing in the dynamic environments in the contest. Individual reports, dataset information, rules, and released source code can be found at the project homepage: "https://lifelong-robotic-vision.github.io/competition/".
OpenLORIS-Object: A Dataset and Benchmark towards Lifelong Object Recognition
Nov 15, 2019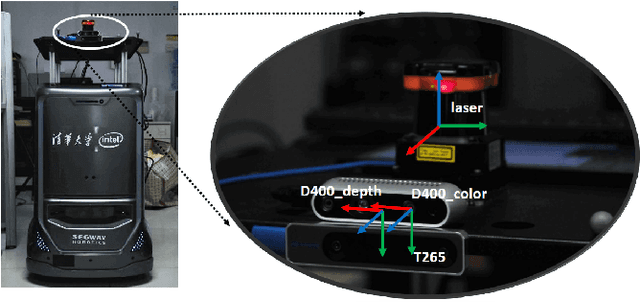
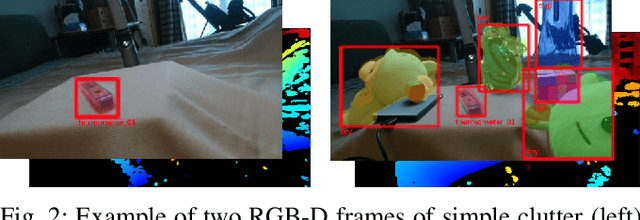
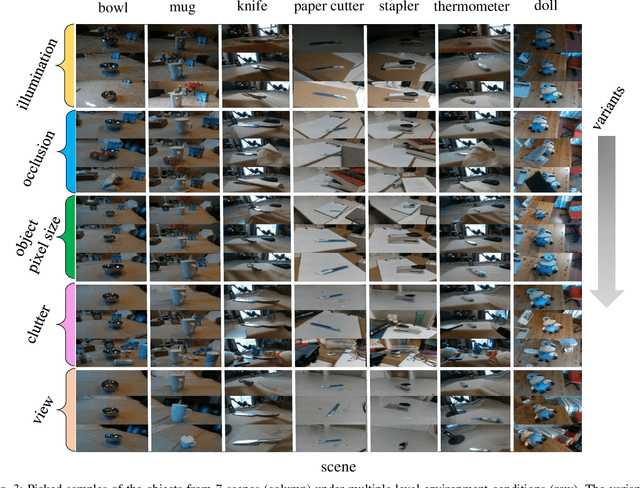
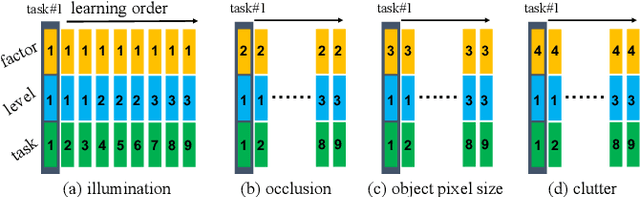
Abstract:The recent breakthroughs in computer vision have benefited from the availability of large representative datasets (e.g. ImageNet and COCO) for training. Yet, robotic vision poses unique challenges for applying visual algorithms developed from these standard computer vision datasets due to their implicit assumption over non-varying distributions for a fixed set of tasks. Fully retraining models each time a new task becomes available is infeasible due to computational, storage and sometimes privacy issues, while na\"{i}ve incremental strategies have been shown to suffer from catastrophic forgetting. It is crucial for the robots to operate continuously under open-set and detrimental conditions with adaptive visual perceptual systems, where lifelong learning is a fundamental capability. However, very few datasets and benchmarks are available to evaluate and compare emerging techniques. To fill this gap, we provide a new lifelong robotic vision dataset ("OpenLORIS-Object") collected via RGB-D cameras mounted on mobile robots. The dataset embeds the challenges faced by a robot in the real-life application and provides new benchmarks for validating lifelong object recognition algorithms. Moreover, we have provided a testbed of $9$ state-of-the-art lifelong learning algorithms. Each of them involves $48$ tasks with $4$ evaluation metrics over the OpenLORIS-Object dataset. The results demonstrate that the object recognition task in the ever-changing difficulty environments is far from being solved and the bottlenecks are at the forward/backward transfer designs. Our dataset and benchmark are publicly available at \href{https://lifelong-robotic-vision.github.io/dataset/Data_Object-Recognition.html}{\underline{this url}}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge