Xiaoyun Yang
CUE-Net: Violence Detection Video Analytics with Spatial Cropping, Enhanced UniformerV2 and Modified Efficient Additive Attention
Apr 27, 2024



Abstract:In this paper we introduce CUE-Net, a novel architecture designed for automated violence detection in video surveillance. As surveillance systems become more prevalent due to technological advances and decreasing costs, the challenge of efficiently monitoring vast amounts of video data has intensified. CUE-Net addresses this challenge by combining spatial Cropping with an enhanced version of the UniformerV2 architecture, integrating convolutional and self-attention mechanisms alongside a novel Modified Efficient Additive Attention mechanism (which reduces the quadratic time complexity of self-attention) to effectively and efficiently identify violent activities. This approach aims to overcome traditional challenges such as capturing distant or partially obscured subjects within video frames. By focusing on both local and global spatiotemporal features, CUE-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance on the RWF-2000 and RLVS datasets, surpassing existing methods.
DTFD-MIL: Double-Tier Feature Distillation Multiple Instance Learning for Histopathology Whole Slide Image Classification
Mar 22, 2022



Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) has been increasingly used in the classification of histopathology whole slide images (WSIs). However, MIL approaches for this specific classification problem still face unique challenges, particularly those related to small sample cohorts. In these, there are limited number of WSI slides (bags), while the resolution of a single WSI is huge, which leads to a large number of patches (instances) cropped from this slide. To address this issue, we propose to virtually enlarge the number of bags by introducing the concept of pseudo-bags, on which a double-tier MIL framework is built to effectively use the intrinsic features. Besides, we also contribute to deriving the instance probability under the framework of attention-based MIL, and utilize the derivation to help construct and analyze the proposed framework. The proposed method outperforms other latest methods on the CAMELYON-16 by substantially large margins, and is also better in performance on the TCGA lung cancer dataset. The proposed framework is ready to be extended for wider MIL applications. The code is available at: https://github.com/hrzhang1123/DTFD-MIL
3D Dense Face Alignment with Fused Features by Aggregating CNNs and GCNs
Mar 09, 2022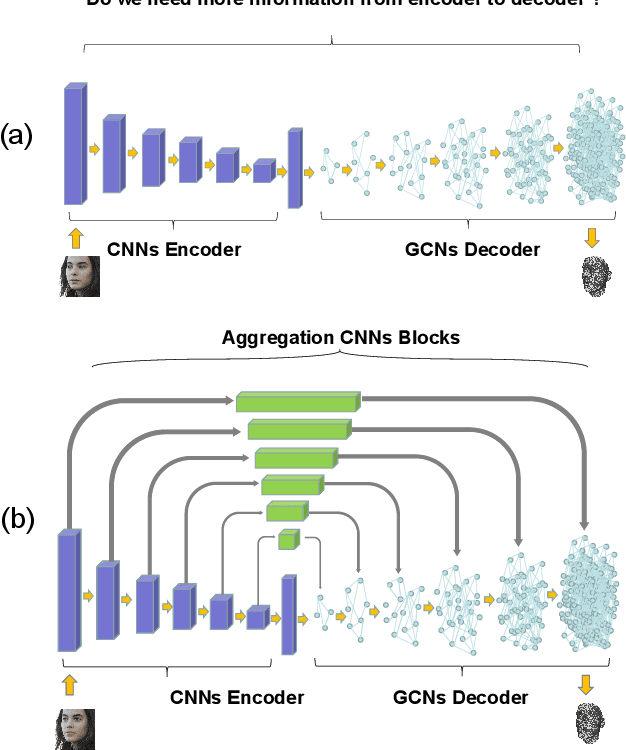
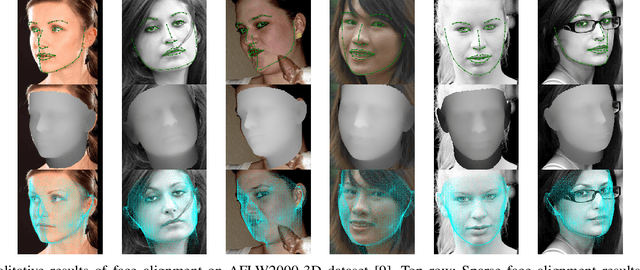
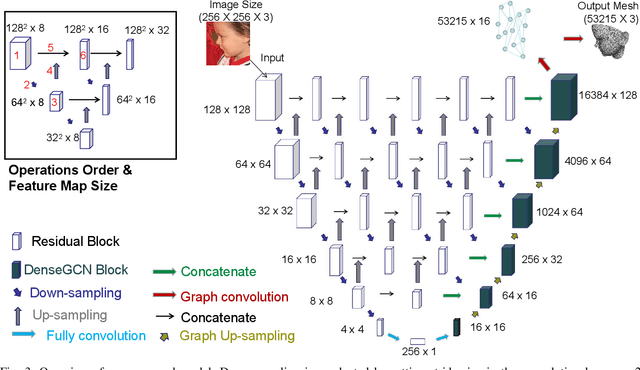
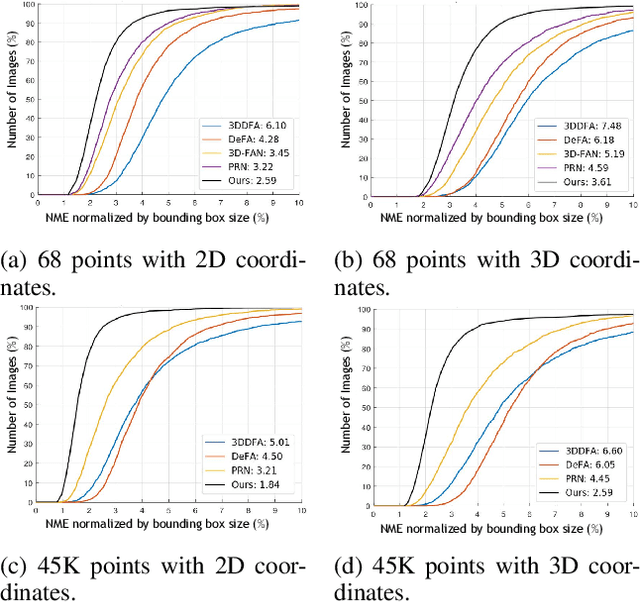
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel multi-level aggregation network to regress the coordinates of the vertices of a 3D face from a single 2D image in an end-to-end manner. This is achieved by seamlessly combining standard convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with Graph Convolution Networks (GCNs). By iteratively and hierarchically fusing the features across different layers and stages of the CNNs and GCNs, our approach can provide a dense face alignment and 3D face reconstruction simultaneously for the benefit of direct feature learning of 3D face mesh. Experiments on several challenging datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches on both 2D and 3D face alignment tasks.
Counting with Adaptive Auxiliary Learning
Mar 08, 2022



Abstract:This paper proposes an adaptive auxiliary task learning based approach for object counting problems. Unlike existing auxiliary task learning based methods, we develop an attention-enhanced adaptively shared backbone network to enable both task-shared and task-tailored features learning in an end-to-end manner. The network seamlessly combines standard Convolution Neural Network (CNN) and Graph Convolution Network (GCN) for feature extraction and feature reasoning among different domains of tasks. Our approach gains enriched contextual information by iteratively and hierarchically fusing the features across different task branches of the adaptive CNN backbone. The whole framework pays special attention to the objects' spatial locations and varied density levels, informed by object (or crowd) segmentation and density level segmentation auxiliary tasks. In particular, thanks to the proposed dilated contrastive density loss function, our network benefits from individual and regional context supervision in terms of pixel-independent and pixel-dependent feature learning mechanisms, along with strengthened robustness. Experiments on seven challenging multi-domain datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance to the state-of-the-art auxiliary task learning based counting methods. Our code is made publicly available at: https://github.com/smallmax00/Counting_With_Adaptive_Auxiliary
BI-GCN: Boundary-Aware Input-Dependent Graph Convolution Network for Biomedical Image Segmentation
Oct 31, 2021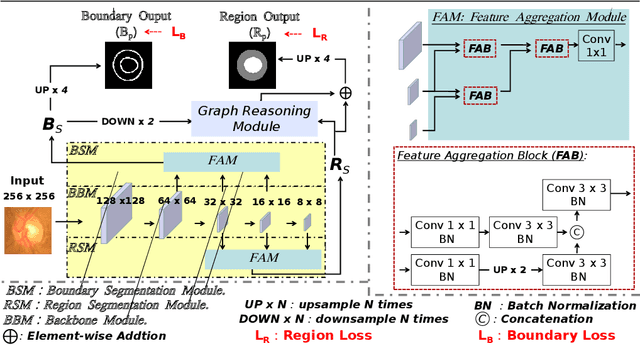
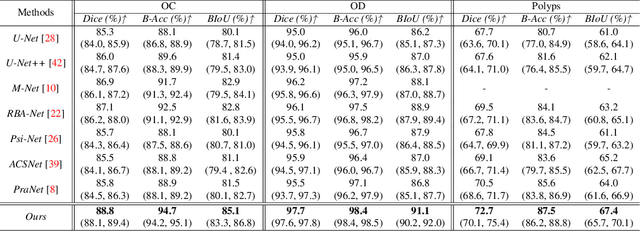

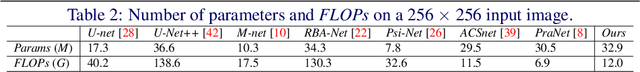
Abstract:Segmentation is an essential operation of image processing. The convolution operation suffers from a limited receptive field, while global modelling is fundamental to segmentation tasks. In this paper, we apply graph convolution into the segmentation task and propose an improved \textit{Laplacian}. Different from existing methods, our \textit{Laplacian} is data-dependent, and we introduce two attention diagonal matrices to learn a better vertex relationship. In addition, it takes advantage of both region and boundary information when performing graph-based information propagation. Specifically, we model and reason about the boundary-aware region-wise correlations of different classes through learning graph representations, which is capable of manipulating long range semantic reasoning across various regions with the spatial enhancement along the object's boundary. Our model is well-suited to obtain global semantic region information while also accommodates local spatial boundary characteristics simultaneously. Experiments on two types of challenging datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on the segmentation of polyps in colonoscopy images and of the optic disc and optic cup in colour fundus images.
Video Annotation for Visual Tracking via Selection and Refinement
Aug 09, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning based visual trackers entail offline pre-training on large volumes of video datasets with accurate bounding box annotations that are labor-expensive to achieve. We present a new framework to facilitate bounding box annotations for video sequences, which investigates a selection-and-refinement strategy to automatically improve the preliminary annotations generated by tracking algorithms. A temporal assessment network (T-Assess Net) is proposed which is able to capture the temporal coherence of target locations and select reliable tracking results by measuring their quality. Meanwhile, a visual-geometry refinement network (VG-Refine Net) is also designed to further enhance the selected tracking results by considering both target appearance and temporal geometry constraints, allowing inaccurate tracking results to be corrected. The combination of the above two networks provides a principled approach to ensure the quality of automatic video annotation. Experiments on large scale tracking benchmarks demonstrate that our method can deliver highly accurate bounding box annotations and significantly reduce human labor by 94.0%, yielding an effective means to further boost tracking performance with augmented training data.
Spatial Uncertainty-Aware Semi-Supervised Crowd Counting
Aug 02, 2021



Abstract:Semi-supervised approaches for crowd counting attract attention, as the fully supervised paradigm is expensive and laborious due to its request for a large number of images of dense crowd scenarios and their annotations. This paper proposes a spatial uncertainty-aware semi-supervised approach via regularized surrogate task (binary segmentation) for crowd counting problems. Different from existing semi-supervised learning-based crowd counting methods, to exploit the unlabeled data, our proposed spatial uncertainty-aware teacher-student framework focuses on high confident regions' information while addressing the noisy supervision from the unlabeled data in an end-to-end manner. Specifically, we estimate the spatial uncertainty maps from the teacher model's surrogate task to guide the feature learning of the main task (density regression) and the surrogate task of the student model at the same time. Besides, we introduce a simple yet effective differential transformation layer to enforce the inherent spatial consistency regularization between the main task and the surrogate task in the student model, which helps the surrogate task to yield more reliable predictions and generates high-quality uncertainty maps. Thus, our model can also address the task-level perturbation problems that occur spatial inconsistency between the primary and surrogate tasks in the student model. Experimental results on four challenging crowd counting datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance to the state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods.
A Video Is Worth Three Views: Trigeminal Transformers for Video-based Person Re-identification
Apr 05, 2021
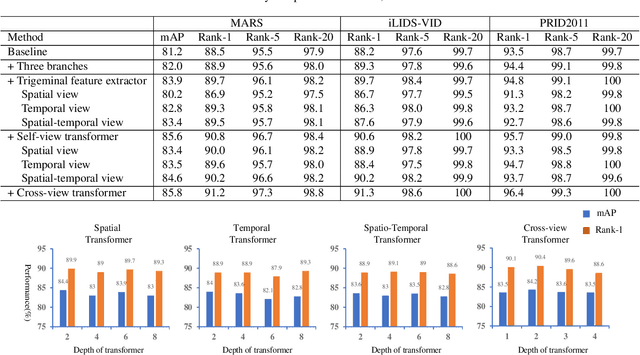

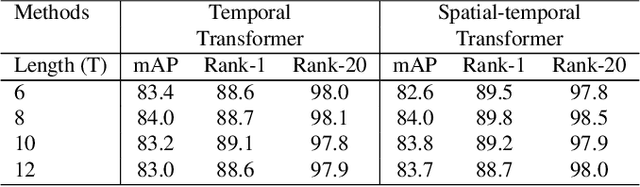
Abstract:Video-based person re-identification (Re-ID) aims to retrieve video sequences of the same person under non-overlapping cameras. Previous methods usually focus on limited views, such as spatial, temporal or spatial-temporal view, which lack of the observations in different feature domains. To capture richer perceptions and extract more comprehensive video representations, in this paper we propose a novel framework named Trigeminal Transformers (TMT) for video-based person Re-ID. More specifically, we design a trigeminal feature extractor to jointly transform raw video data into spatial, temporal and spatial-temporal domain. Besides, inspired by the great success of vision transformer, we introduce the transformer structure for video-based person Re-ID. In our work, three self-view transformers are proposed to exploit the relationships between local features for information enhancement in spatial, temporal and spatial-temporal domains. Moreover, a cross-view transformer is proposed to aggregate the multi-view features for comprehensive video representations. The experimental results indicate that our approach can achieve better performance than other state-of-the-art approaches on public Re-ID benchmarks. We will release the code for model reproduction.
Watching You: Global-guided Reciprocal Learning for Video-based Person Re-identification
Apr 01, 2021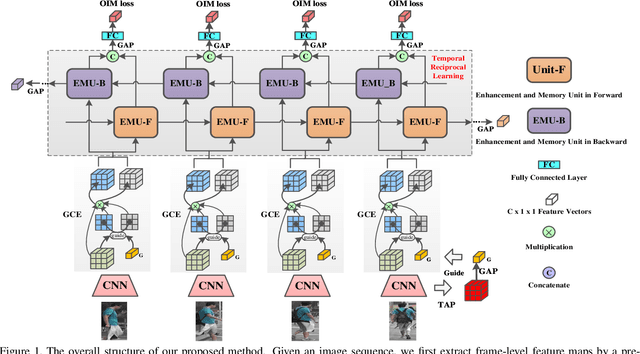
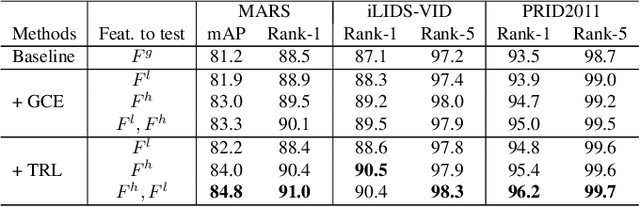
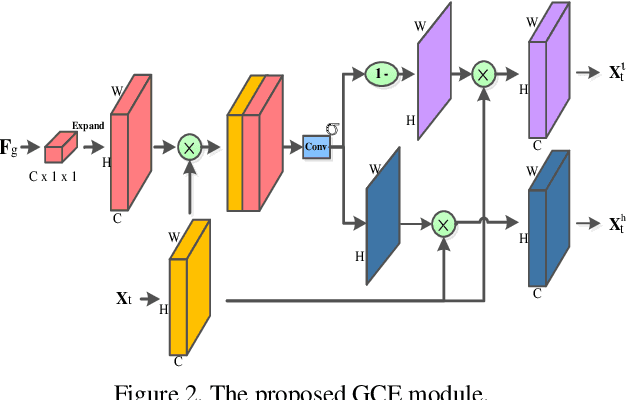
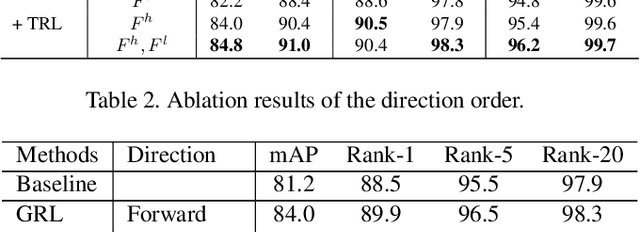
Abstract:Video-based person re-identification (Re-ID) aims to automatically retrieve video sequences of the same person under non-overlapping cameras. To achieve this goal, it is the key to fully utilize abundant spatial and temporal cues in videos. Existing methods usually focus on the most conspicuous image regions, thus they may easily miss out fine-grained clues due to the person varieties in image sequences. To address above issues, in this paper, we propose a novel Global-guided Reciprocal Learning (GRL) framework for video-based person Re-ID. Specifically, we first propose a Global-guided Correlation Estimation (GCE) to generate feature correlation maps of local features and global features, which help to localize the high- and low-correlation regions for identifying the same person. After that, the discriminative features are disentangled into high-correlation features and low-correlation features under the guidance of the global representations. Moreover, a novel Temporal Reciprocal Learning (TRL) mechanism is designed to sequentially enhance the high-correlation semantic information and accumulate the low-correlation sub-critical clues. Extensive experiments are conducted on three public benchmarks. The experimental results indicate that our approach can achieve better performance than other state-of-the-art approaches. The code is released at https://github.com/flysnowtiger/GRL.
Transformer Tracking
Mar 29, 2021



Abstract:Correlation acts as a critical role in the tracking field, especially in recent popular Siamese-based trackers. The correlation operation is a simple fusion manner to consider the similarity between the template and the search region. However, the correlation operation itself is a local linear matching process, leading to lose semantic information and fall into local optimum easily, which may be the bottleneck of designing high-accuracy tracking algorithms. Is there any better feature fusion method than correlation? To address this issue, inspired by Transformer, this work presents a novel attention-based feature fusion network, which effectively combines the template and search region features solely using attention. Specifically, the proposed method includes an ego-context augment module based on self-attention and a cross-feature augment module based on cross-attention. Finally, we present a Transformer tracking (named TransT) method based on the Siamese-like feature extraction backbone, the designed attention-based fusion mechanism, and the classification and regression head. Experiments show that our TransT achieves very promising results on six challenging datasets, especially on large-scale LaSOT, TrackingNet, and GOT-10k benchmarks. Our tracker runs at approximatively 50 fps on GPU. Code and models are available at https://github.com/chenxin-dlut/TransT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge