Xiaoming Wu
Graph is a Substrate Across Data Modalities
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Graphs provide a natural representation of relational structure that arises across diverse domains. Despite this ubiquity, graph structure is typically learned in a modality- and task-isolated manner, where graph representations are constructed within individual task contexts and discarded thereafter. As a result, structural regularities across modalities and tasks are repeatedly reconstructed rather than accumulated at the level of intermediate graph representations. This motivates a representation-learning question: how should graph structure be organized so that it can persist and accumulate across heterogeneous modalities and tasks? We adopt a representation-centric perspective in which graph structure is treated as a structural substrate that persists across learning contexts. To instantiate this perspective, we propose G-Substrate, a graph substrate framework that organizes learning around shared graph structures. G-Substrate comprises two complementary mechanisms: a unified structural schema that ensures compatibility among graph representations across heterogeneous modalities and tasks, and an interleaved role-based training strategy that exposes the same graph structure to multiple functional roles during learning. Experiments across multiple domains, modalities, and tasks show that G-Substrate outperforms task-isolated and naive multi-task learning methods.
FedeCouple: Fine-Grained Balancing of Global-Generalization and Local-Adaptability in Federated Learning
Nov 12, 2025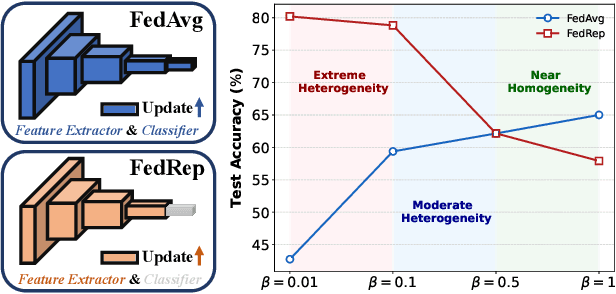
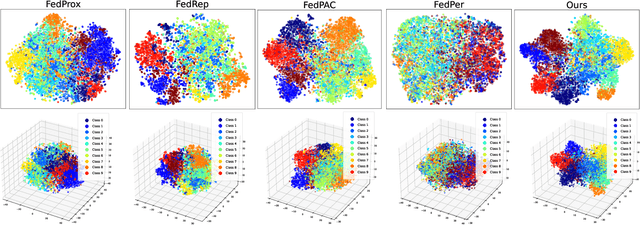
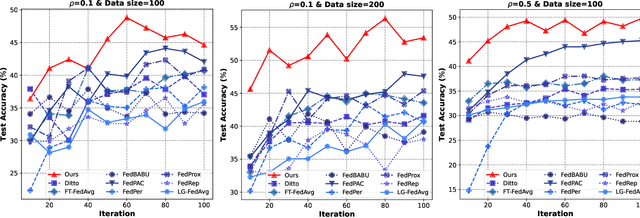
Abstract:In privacy-preserving mobile network transmission scenarios with heterogeneous client data, personalized federated learning methods that decouple feature extractors and classifiers have demonstrated notable advantages in enhancing learning capability. However, many existing approaches primarily focus on feature space consistency and classification personalization during local training, often neglecting the local adaptability of the extractor and the global generalization of the classifier. This oversight results in insufficient coordination and weak coupling between the components, ultimately degrading the overall model performance. To address this challenge, we propose FedeCouple, a federated learning method that balances global generalization and local adaptability at a fine-grained level. Our approach jointly learns global and local feature representations while employing dynamic knowledge distillation to enhance the generalization of personalized classifiers. We further introduce anchors to refine the feature space; their strict locality and non-transmission inherently preserve privacy and reduce communication overhead. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical analysis proving that FedeCouple converges for nonconvex objectives, with iterates approaching a stationary point as the number of communication rounds increases. Extensive experiments conducted on five image-classification datasets demonstrate that FedeCouple consistently outperforms nine baseline methods in effectiveness, stability, scalability, and security. Notably, in experiments evaluating effectiveness, FedeCouple surpasses the best baseline by a significant margin of 4.3%.
Choice Outweighs Effort: Facilitating Complementary Knowledge Fusion in Federated Learning via Re-calibration and Merit-discrimination
Aug 25, 2025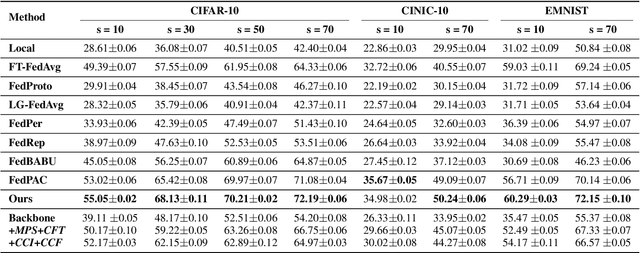
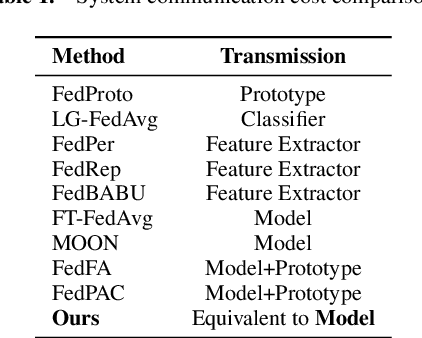
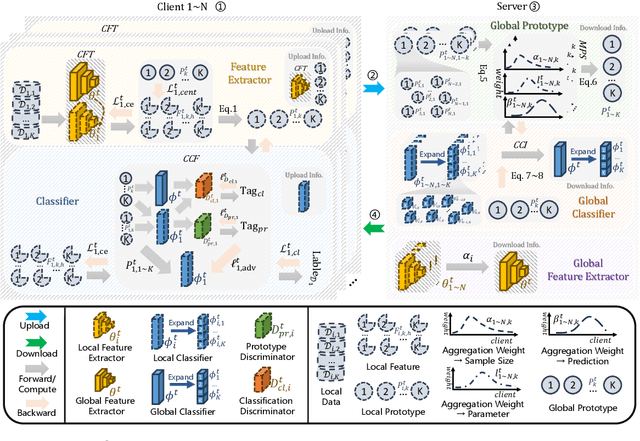
Abstract:Cross-client data heterogeneity in federated learning induces biases that impede unbiased consensus condensation and the complementary fusion of generalization- and personalization-oriented knowledge. While existing approaches mitigate heterogeneity through model decoupling and representation center loss, they often rely on static and restricted metrics to evaluate local knowledge and adopt global alignment too rigidly, leading to consensus distortion and diminished model adaptability. To address these limitations, we propose FedMate, a method that implements bilateral optimization: On the server side, we construct a dynamic global prototype, with aggregation weights calibrated by holistic integration of sample size, current parameters, and future prediction; a category-wise classifier is then fine-tuned using this prototype to preserve global consistency. On the client side, we introduce complementary classification fusion to enable merit-based discrimination training and incorporate cost-aware feature transmission to balance model performance and communication efficiency. Experiments on five datasets of varying complexity demonstrate that FedMate outperforms state-of-the-art methods in harmonizing generalization and adaptation. Additionally, semantic segmentation experiments on autonomous driving datasets validate the method's real-world scalability.
FedSaaS: Class-Consistency Federated Semantic Segmentation via Global Prototype Supervision and Local Adversarial Harmonization
May 14, 2025Abstract:Federated semantic segmentation enables pixel-level classification in images through collaborative learning while maintaining data privacy. However, existing research commonly overlooks the fine-grained class relationships within the semantic space when addressing heterogeneous problems, particularly domain shift. This oversight results in ambiguities between class representation. To overcome this challenge, we propose a novel federated segmentation framework that strikes class consistency, termed FedSaaS. Specifically, we introduce class exemplars as a criterion for both local- and global-level class representations. On the server side, the uploaded class exemplars are leveraged to model class prototypes, which supervise global branch of clients, ensuring alignment with global-level representation. On the client side, we incorporate an adversarial mechanism to harmonize contributions of global and local branches, leading to consistent output. Moreover, multilevel contrastive losses are employed on both sides to enforce consistency between two-level representations in the same semantic space. Extensive experiments on several driving scene segmentation datasets demonstrate that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods, significantly improving average segmentation accuracy and effectively addressing the class-consistency representation problem.
BianCang: A Traditional Chinese Medicine Large Language Model
Nov 17, 2024



Abstract:The rise of large language models (LLMs) has driven significant progress in medical applications, including traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). However, current medical LLMs struggle with TCM diagnosis and syndrome differentiation due to substantial differences between TCM and modern medical theory, and the scarcity of specialized, high-quality corpora. This paper addresses these challenges by proposing BianCang, a TCM-specific LLM, using a two-stage training process that first injects domain-specific knowledge and then aligns it through targeted stimulation. To enhance diagnostic and differentiation capabilities, we constructed pre-training corpora, instruction-aligned datasets based on real hospital records, and the ChP-TCM dataset derived from the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. We compiled extensive TCM and medical corpora for continuous pre-training and supervised fine-tuning, building a comprehensive dataset to refine the model's understanding of TCM. Evaluations across 11 test sets involving 29 models and 4 tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of BianCang, offering valuable insights for future research. Code, datasets, and models are available at https://github.com/QLU-NLP/BianCang.
FedSiam-DA: Dual-aggregated Federated Learning via Siamese Network under Non-IID Data
Nov 18, 2022Abstract:Federated learning is a distributed learning that allows each client to keep the original data locally and only upload the parameters of the local model to the server. Despite federated learning can address data island, it remains challenging to train with data heterogeneous in a real application. In this paper, we propose FedSiam-DA, a novel dual-aggregated contrastive federated learning approach, to personalize both local and global models, under various settings of data heterogeneity. Firstly, based on the idea of contrastive learning in the siamese network, FedSiam-DA regards the local and global model as different branches of the siamese network during the local training and controls the update direction of the model by constantly changing model similarity to personalize the local model. Secondly, FedSiam-DA introduces dynamic weights based on model similarity for each local model and exercises the dual-aggregated mechanism to further improve the generalization of the global model. Moreover, we provide extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, the results demonstrate that FedSiam-DA achieves outperforming several previous FL approaches on heterogeneous datasets.
A Framework Based on Generational and Environmental Response Strategies for Dynamic Multi-objective Optimization
Jul 06, 2022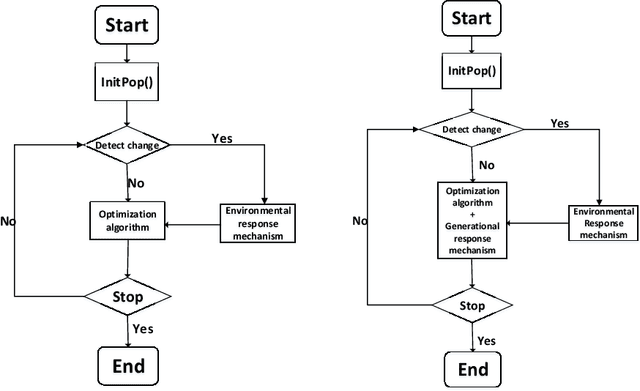
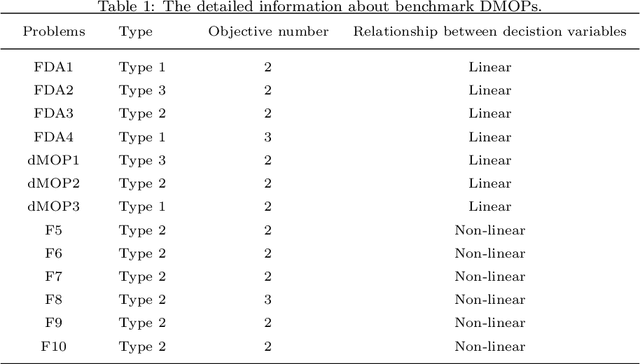
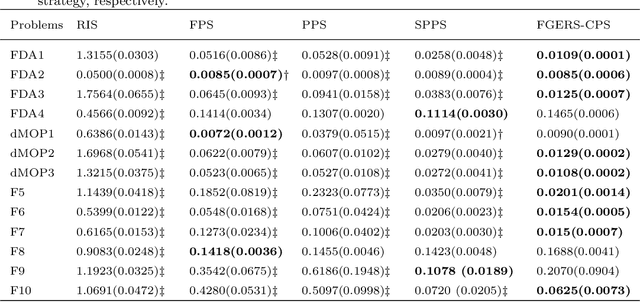
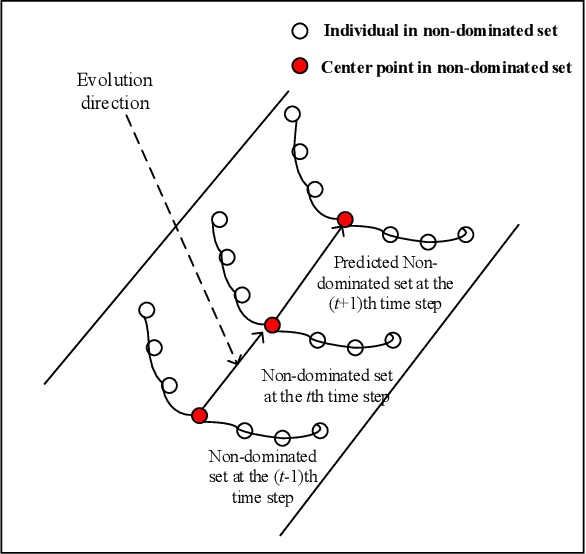
Abstract:Due to the dynamics and uncertainty of the dynamic multi-objective optimization problems (DMOPs), it is difficult for algorithms to find a satisfactory solution set before the next environmental change, especially for some complex environments. One reason may be that the information in the environmental static stage can not be used well in the traditional framework. In this paper, a novel framework based on generational and environmental response strategies (FGERS) is proposed, in which response strategies are run both in the environmental change stage and the environmental static stage to obtain population evolution information of those both stages. Unlike in the traditional framework, response strategies are only run in the environmental change stage. For simplicity, the feed-forward center point strategy was chosen to be the response strategy in the novel dynamic framework (FGERS-CPS). FGERS-CPS is not only to predict change trend of the optimum solution set in the environmental change stage, but to predict the evolution trend of the population after several generations in the environmental static stage. Together with the feed-forward center point strategy, a simple memory strategy and adaptive diversity maintenance strategy were used to form the complete FGERS-CPS. On 13 DMOPs with various characteristics, FGERS-CPS was compared with four classical response strategies in the traditional framework. Experimental results show that FGERS-CPS is effective for DMOPs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge