Wenning Wei
Fine-Tuning Large Multimodal Models for Automatic Pronunciation Assessment
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Automatic Pronunciation Assessment (APA) is critical for Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL), requiring evaluation across multiple granularities and aspects. Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) present new opportunities for APA, but their effectiveness in fine-grained assessment remains uncertain. This work investigates fine-tuning LMMs for APA using the Speechocean762 dataset and a private corpus. Fine-tuning significantly outperforms zero-shot settings and achieves competitive results on single-granularity tasks compared to public and commercial systems. The model performs well at word and sentence levels, while phoneme-level assessment remains challenging. We also observe that the Pearson Correlation Coefficient (PCC) reaches 0.9, whereas Spearman's rank Correlation Coefficient (SCC) remains around 0.6, suggesting that SCC better reflects ordinal consistency. These findings highlight both the promise and limitations of LMMs for APA and point to future work on fine-grained modeling and rank-aware evaluation.
Exploring the Potential of Large Multimodal Models as Effective Alternatives for Pronunciation Assessment
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance across a wide range of domains. This paper explores their potential in pronunciation assessment tasks, with a particular focus on evaluating the capabilities of the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) model, specifically GPT-4o. Our study investigates its ability to process speech and audio for pronunciation assessment across multiple levels of granularity and dimensions, with an emphasis on feedback generation and scoring. For our experiments, we use the publicly available Speechocean762 dataset. The evaluation focuses on two key aspects: multi-level scoring and the practicality of the generated feedback. Scoring results are compared against the manual scores provided in the Speechocean762 dataset, while feedback quality is assessed using Large Language Models (LLMs). The findings highlight the effectiveness of integrating LMMs with traditional methods for pronunciation assessment, offering insights into the model's strengths and identifying areas for further improvement.
MuLanTTS: The Microsoft Speech Synthesis System for Blizzard Challenge 2023
Sep 12, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present MuLanTTS, the Microsoft end-to-end neural text-to-speech (TTS) system designed for the Blizzard Challenge 2023. About 50 hours of audiobook corpus for French TTS as hub task and another 2 hours of speaker adaptation as spoke task are released to build synthesized voices for different test purposes including sentences, paragraphs, homographs, lists, etc. Building upon DelightfulTTS, we adopt contextual and emotion encoders to adapt the audiobook data to enrich beyond sentences for long-form prosody and dialogue expressiveness. Regarding the recording quality, we also apply denoise algorithms and long audio processing for both corpora. For the hub task, only the 50-hour single speaker data is used for building the TTS system, while for the spoke task, a multi-speaker source model is used for target speaker fine tuning. MuLanTTS achieves mean scores of quality assessment 4.3 and 4.5 in the respective tasks, statistically comparable with natural speech while keeping good similarity according to similarity assessment. The excellent and similarity in this year's new and dense statistical evaluation show the effectiveness of our proposed system in both tasks.
On Addressing Practical Challenges for RNN-Transducer
May 04, 2021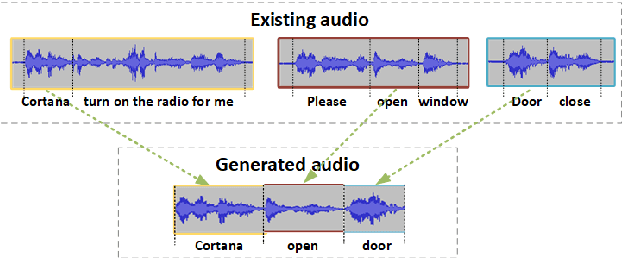


Abstract:In this paper, several works are proposed to address practical challenges for deploying RNN Transducer (RNN-T) based speech recognition system. These challenges are adapting a well-trained RNN-T model to a new domain without collecting the audio data, obtaining time stamps and confidence scores at word level. The first challenge is solved with a splicing data method which concatenates the speech segments extracted from the source domain data. To get the time stamp, a phone prediction branch is added to the RNN-T model by sharing the encoder for the purpose of force alignment. Finally, we obtain word-level confidence scores by utilizing several types of features calculated during decoding and from confusion network. Evaluated with Microsoft production data, the splicing data adaptation method improves the baseline and adaption with the text to speech method by 58.03% and 15.25% relative word error rate reduction, respectively. The proposed time stamping method can get less than 50ms word timing difference on average while maintaining the recognition accuracy of the RNN-T model. We also obtain high confidence annotation performance with limited computation cost.
Developing RNN-T Models Surpassing High-Performance Hybrid Models with Customization Capability
Jul 30, 2020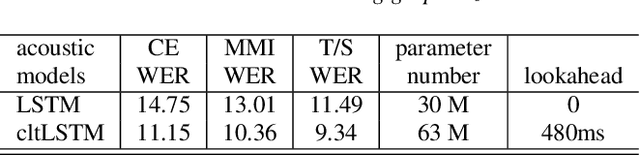
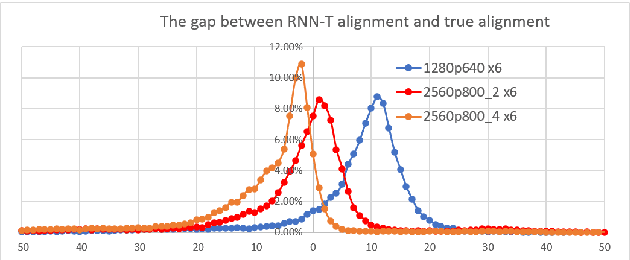
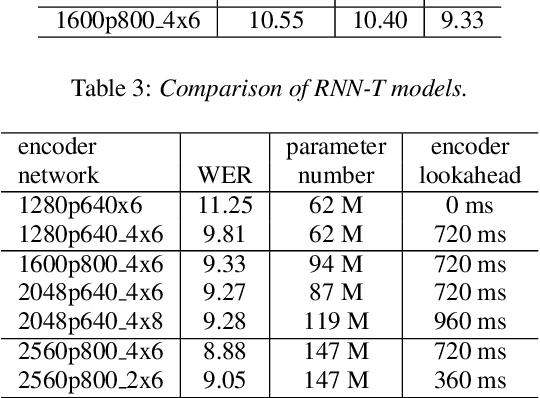
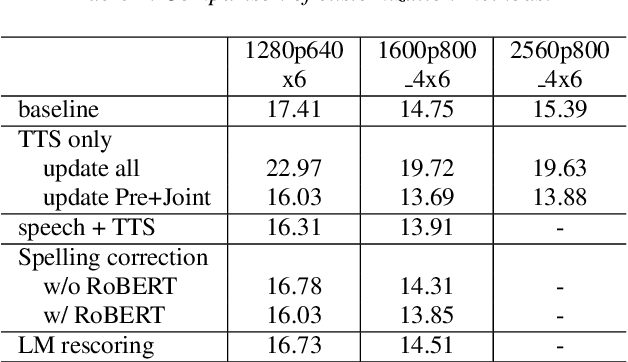
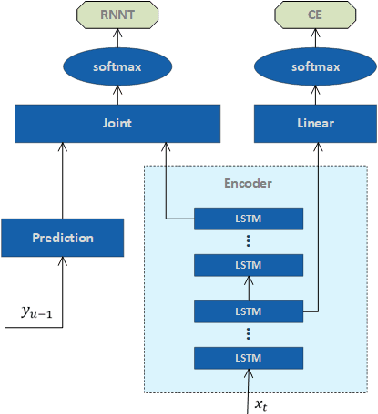
Abstract:Because of its streaming nature, recurrent neural network transducer (RNN-T) is a very promising end-to-end (E2E) model that may replace the popular hybrid model for automatic speech recognition. In this paper, we describe our recent development of RNN-T models with reduced GPU memory consumption during training, better initialization strategy, and advanced encoder modeling with future lookahead. When trained with Microsoft's 65 thousand hours of anonymized training data, the developed RNN-T model surpasses a very well trained hybrid model with both better recognition accuracy and lower latency. We further study how to customize RNN-T models to a new domain, which is important for deploying E2E models to practical scenarios. By comparing several methods leveraging text-only data in the new domain, we found that updating RNN-T's prediction and joint networks using text-to-speech generated from domain-specific text is the most effective.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge