Wenhao Luo
TraceMark-LDM: Authenticatable Watermarking for Latent Diffusion Models via Binary-Guided Rearrangement
Mar 30, 2025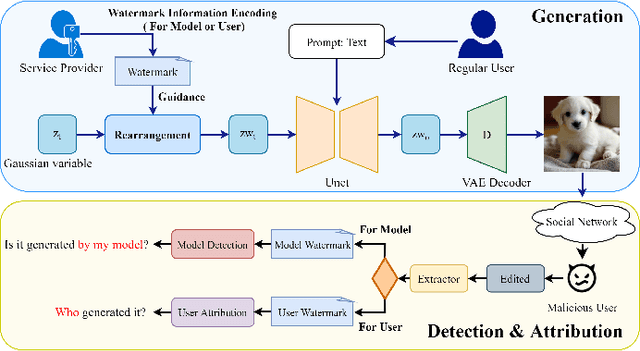
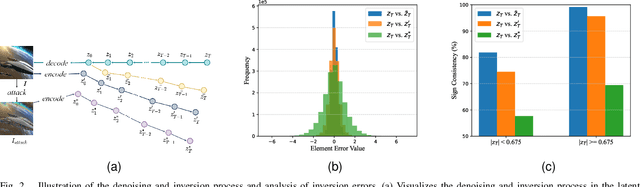
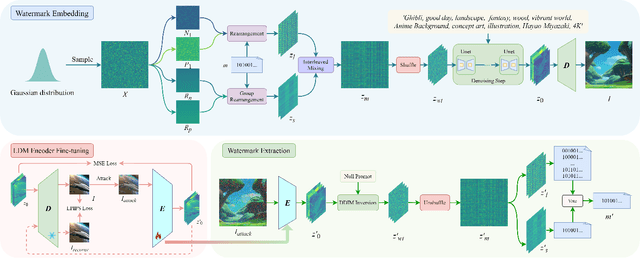
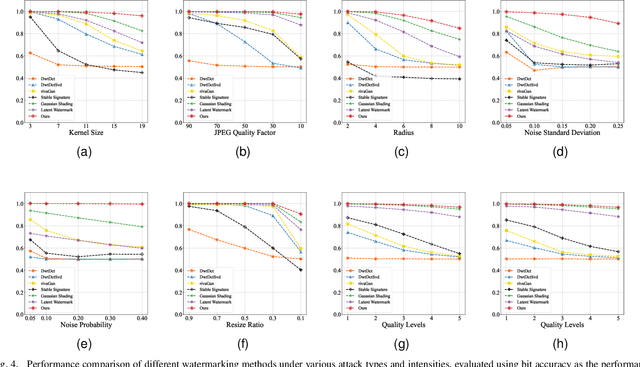
Abstract:Image generation algorithms are increasingly integral to diverse aspects of human society, driven by their practical applications. However, insufficient oversight in artificial Intelligence generated content (AIGC) can facilitate the spread of malicious content and increase the risk of copyright infringement. Among the diverse range of image generation models, the Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) is currently the most widely used, dominating the majority of the Text-to-Image model market. Currently, most attribution methods for LDMs rely on directly embedding watermarks into the generated images or their intermediate noise, a practice that compromises both the quality and the robustness of the generated content. To address these limitations, we introduce TraceMark-LDM, an novel algorithm that integrates watermarking to attribute generated images while guaranteeing non-destructive performance. Unlike current methods, TraceMark-LDM leverages watermarks as guidance to rearrange random variables sampled from a Gaussian distribution. To mitigate potential deviations caused by inversion errors, the small absolute elements are grouped and rearranged. Additionally, we fine-tune the LDM encoder to enhance the robustness of the watermark. Experimental results show that images synthesized using TraceMark-LDM exhibit superior quality and attribution accuracy compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques. Notably, TraceMark-LDM demonstrates exceptional robustness against various common attack methods, consistently outperforming SOTA methods.
Distributed Multi-robot Source Seeking in Unknown Environments with Unknown Number of Sources
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:We introduce a novel distributed source seeking framework, DIAS, designed for multi-robot systems in scenarios where the number of sources is unknown and potentially exceeds the number of robots. Traditional robotic source seeking methods typically focused on directing each robot to a specific strong source and may fall short in comprehensively identifying all potential sources. DIAS addresses this gap by introducing a hybrid controller that identifies the presence of sources and then alternates between exploration for data gathering and exploitation for guiding robots to identified sources. It further enhances search efficiency by dividing the environment into Voronoi cells and approximating source density functions based on Gaussian process regression. Additionally, DIAS can be integrated with existing source seeking algorithms. We compare DIAS with existing algorithms, including DoSS and GMES in simulated gas leakage scenarios where the number of sources outnumbers or is equal to the number of robots. The numerical results show that DIAS outperforms the baseline methods in both the efficiency of source identification by the robots and the accuracy of the estimated environmental density function.
Merry-Go-Round: Safe Control of Decentralized Multi-Robot Systems with Deadlock Prevention
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:We propose a hybrid approach for decentralized multi-robot navigation that ensures both safety and deadlock prevention. Building on a standard control formulation, we add a lightweight deadlock prevention mechanism by forming temporary "roundabouts" (circular reference paths). Each robot relies only on local, peer-to-peer communication and a controller for base collision avoidance; a roundabout is generated or joined on demand to avert deadlocks. Robots in the roundabout travel in one direction until an escape condition is met, allowing them to return to goal-oriented motion. Unlike classical decentralized methods that lack explicit deadlock resolution, our roundabout maneuver ensures system-wide forward progress while preserving safety constraints. Extensive simulations and physical robot experiments show that our method consistently outperforms or matches the success and arrival rates of other decentralized control approaches, particularly in cluttered or high-density scenarios, all with minimal centralized coordination.
DyPNIPP: Predicting Environment Dynamics for RL-based Robust Informative Path Planning
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Informative path planning (IPP) is an important planning paradigm for various real-world robotic applications such as environment monitoring. IPP involves planning a path that can learn an accurate belief of the quantity of interest, while adhering to planning constraints. Traditional IPP methods typically require high computation time during execution, giving rise to reinforcement learning (RL) based IPP methods. However, the existing RL-based methods do not consider spatio-temporal environments which involve their own challenges due to variations in environment characteristics. In this paper, we propose DyPNIPP, a robust RL-based IPP framework, designed to operate effectively across spatio-temporal environments with varying dynamics. To achieve this, DyPNIPP incorporates domain randomization to train the agent across diverse environments and introduces a dynamics prediction model to capture and adapt the agent actions to specific environment dynamics. Our extensive experiments in a wildfire environment demonstrate that DyPNIPP outperforms existing RL-based IPP algorithms by significantly improving robustness and performing across diverse environment conditions.
Integrating Online Learning and Connectivity Maintenance for Communication-Aware Multi-Robot Coordination
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel data-driven control strategy for maintaining connectivity in networked multi-robot systems. Existing approaches often rely on a pre-determined communication model specifying whether pairwise robots can communicate given their relative distance to guide the connectivity-aware control design, which may not capture real-world communication conditions. To relax that assumption, we present the concept of Data-driven Connectivity Barrier Certificates, which utilize Control Barrier Functions (CBF) and Gaussian Processes (GP) to characterize the admissible control space for pairwise robots based on communication performance observed online. This allows robots to maintain a satisfying level of pairwise communication quality (measured by the received signal strength) while in motion. Then we propose a Data-driven Connectivity Maintenance (DCM) algorithm that combines (1) online learning of the communication signal strength and (2) a bi-level optimization-based control framework for the robot team to enforce global connectivity of the realistic multi-robot communication graph and minimally deviate from their task-related motions. We provide theoretical proofs to justify the properties of our algorithm and demonstrate its effectiveness through simulations with up to 20 robots.
OffRIPP: Offline RL-based Informative Path Planning
Sep 25, 2024
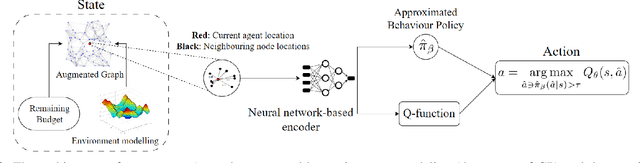
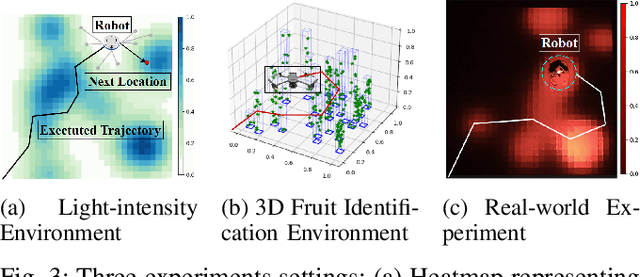
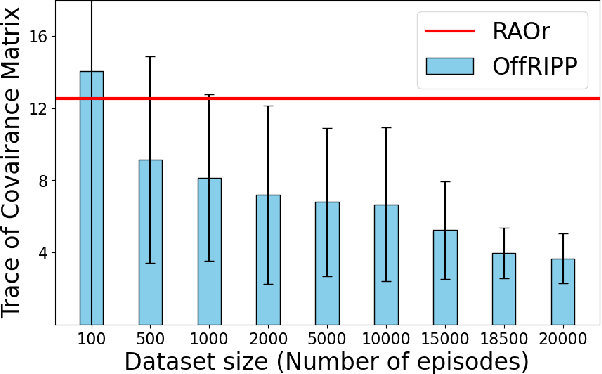
Abstract:Informative path planning (IPP) is a crucial task in robotics, where agents must design paths to gather valuable information about a target environment while adhering to resource constraints. Reinforcement learning (RL) has been shown to be effective for IPP, however, it requires environment interactions, which are risky and expensive in practice. To address this problem, we propose an offline RL-based IPP framework that optimizes information gain without requiring real-time interaction during training, offering safety and cost-efficiency by avoiding interaction, as well as superior performance and fast computation during execution -- key advantages of RL. Our framework leverages batch-constrained reinforcement learning to mitigate extrapolation errors, enabling the agent to learn from pre-collected datasets generated by arbitrary algorithms. We validate the framework through extensive simulations and real-world experiments. The numerical results show that our framework outperforms the baselines, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Courteous MPC for Autonomous Driving with CBF-inspired Risk Assessment
Aug 23, 2024



Abstract:With more autonomous vehicles (AVs) sharing roadways with human-driven vehicles (HVs), ensuring safe and courteous maneuvers that respect HVs' behavior becomes increasingly important. To promote both safety and courtesy in AV's behavior, an extension of Control Barrier Functions (CBFs)-inspired risk evaluation framework is proposed in this paper by considering both noisy observed positions and velocities of surrounding vehicles. The perceived risk by the ego vehicle can be visualized as a risk map that reflects the understanding of the surrounding environment and thus shows the potential for facilitating safe and courteous driving. By incorporating the risk evaluation framework into the Model Predictive Control (MPC) scheme, we propose a Courteous MPC for ego AV to generate courteous behaviors that 1) reduce the overall risk imposed on other vehicles and 2) respect the hard safety constraints and the original objective for efficiency. We demonstrate the performance of the proposed Courteous MPC via theoretical analysis and simulation experiments.
Safety-Critical Control with Uncertainty Quantification using Adaptive Conformal Prediction
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:Safety assurance is critical in the planning and control of robotic systems. For robots operating in the real world, the safety-critical design often needs to explicitly address uncertainties and the pre-computed guarantees often rely on the assumption of the particular distribution of the uncertainty. However, it is difficult to characterize the actual uncertainty distribution beforehand and thus the established safety guarantee may be violated due to possible distribution mismatch. In this paper, we propose a novel safe control framework that provides a high-probability safety guarantee for stochastic dynamical systems following unknown distributions of motion noise. Specifically, this framework adopts adaptive conformal prediction to dynamically quantify the prediction uncertainty from online observations and combines that with the probabilistic extension of the control barrier functions (CBFs) to characterize the uncertainty-aware control constraints. By integrating the constraints in the model predictive control scheme, it allows robots to adaptively capture the true prediction uncertainty online in a distribution-free setting and enjoys formally provable high-probability safety assurance. Simulation results on multi-robot systems with stochastic single-integrator dynamics and unicycle dynamics are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework.
Decentralized Multi-Robot Line-of-Sight Connectivity Maintenance under Uncertainty
Jun 18, 2024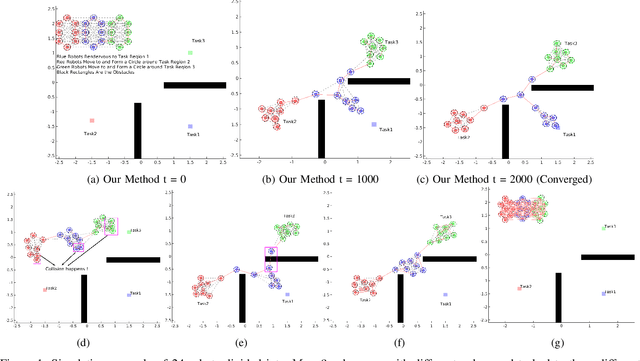



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel decentralized control method to maintain Line-of-Sight connectivity for multi-robot networks in the presence of Guassian-distributed localization uncertainty. In contrast to most existing work that assumes perfect positional information about robots or enforces overly restrictive rigid formation against uncertainty, our method enables robots to preserve Line-of-Sight connectivity with high probability under unbounded Gaussian-like positional noises while remaining minimally intrusive to the original robots' tasks. This is achieved by a motion coordination framework that jointly optimizes the set of existing Line-of-Sight edges to preserve and control revisions to the nominal task-related controllers, subject to the safety constraints and the corresponding composition of uncertainty-aware Line-of-Sight control constraints. Such compositional control constraints, expressed by our novel notion of probabilistic Line-of-Sight connectivity barrier certificates (PrLOS-CBC) for pairwise robots using control barrier functions, explicitly characterize the deterministic admissible control space for the two robots. The resulting motion ensures Line-of-Sight connectedness for the robot team with high probability. Furthermore, we propose a fully decentralized algorithm that decomposes the motion coordination framework by interleaving the composite constraint specification and solving for the resulting optimization-based controllers. The optimality of our approach is justified by the theoretical proofs. Simulation and real-world experiments results are given to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Occlusion-Free Image Based Visual Servoing using Probabilistic Control Barrier Certificates
Sep 07, 2023Abstract:Image-based visual servoing (IBVS) is a widely-used approach in robotics that employs visual information to guide robots towards desired positions. However, occlusions in this approach can lead to visual servoing failure and degrade the control performance due to the obstructed vision feature points that are essential for providing visual feedback. In this paper, we propose a Control Barrier Function (CBF) based controller that enables occlusion-free IBVS tasks by automatically adjusting the robot's configuration to keep the feature points in the field of view and away from obstacles. In particular, to account for measurement noise of the feature points, we develop the Probabilistic Control Barrier Certificates (PrCBC) using control barrier functions that encode the chance-constrained occlusion avoidance constraints under uncertainty into deterministic admissible control space for the robot, from which the resulting configuration of robot ensures that the feature points stay occlusion free from obstacles with a satisfying predefined probability. By integrating such constraints with a Model Predictive Control (MPC) framework, the sequence of optimized control inputs can be derived to achieve the primary IBVS task while enforcing the occlusion avoidance during robot movements. Simulation results are provided to validate the performance of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge