Ye Yao
TraceMark-LDM: Authenticatable Watermarking for Latent Diffusion Models via Binary-Guided Rearrangement
Mar 30, 2025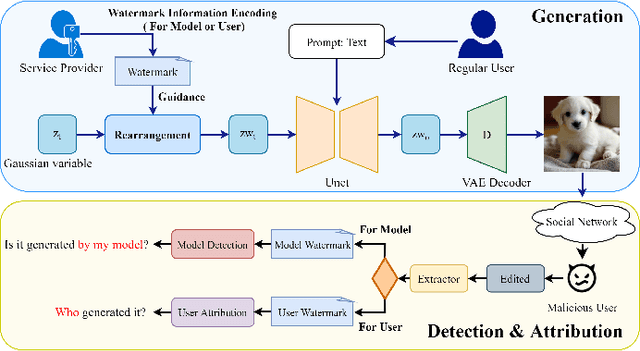
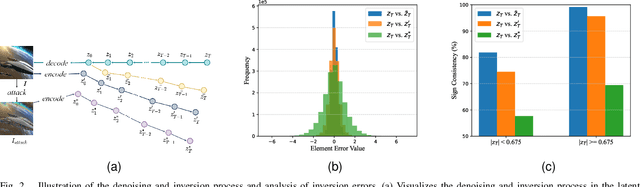
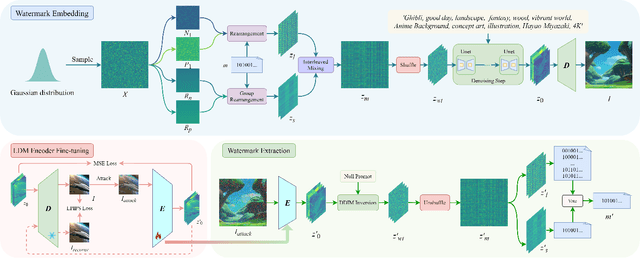
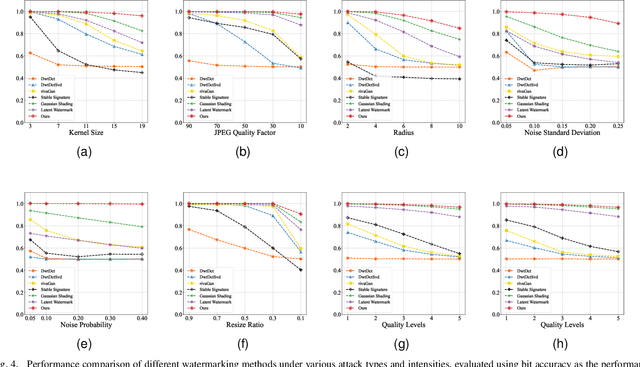
Abstract:Image generation algorithms are increasingly integral to diverse aspects of human society, driven by their practical applications. However, insufficient oversight in artificial Intelligence generated content (AIGC) can facilitate the spread of malicious content and increase the risk of copyright infringement. Among the diverse range of image generation models, the Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) is currently the most widely used, dominating the majority of the Text-to-Image model market. Currently, most attribution methods for LDMs rely on directly embedding watermarks into the generated images or their intermediate noise, a practice that compromises both the quality and the robustness of the generated content. To address these limitations, we introduce TraceMark-LDM, an novel algorithm that integrates watermarking to attribute generated images while guaranteeing non-destructive performance. Unlike current methods, TraceMark-LDM leverages watermarks as guidance to rearrange random variables sampled from a Gaussian distribution. To mitigate potential deviations caused by inversion errors, the small absolute elements are grouped and rearranged. Additionally, we fine-tune the LDM encoder to enhance the robustness of the watermark. Experimental results show that images synthesized using TraceMark-LDM exhibit superior quality and attribution accuracy compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques. Notably, TraceMark-LDM demonstrates exceptional robustness against various common attack methods, consistently outperforming SOTA methods.
Dense Feature Interaction Network for Image Inpainting Localization
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Image inpainting, which is the task of filling in missing areas in an image, is a common image editing technique. Inpainting can be used to conceal or alter image contents in malicious manipulation of images, driving the need for research in image inpainting detection. Existing methods mostly rely on a basic encoder-decoder structure, which often results in a high number of false positives or misses the inpainted regions, especially when dealing with targets of varying semantics and scales. Additionally, the absence of an effective approach to capture boundary artifacts leads to less accurate edge localization. In this paper, we describe a new method for inpainting detection based on a Dense Feature Interaction Network (DeFI-Net). DeFI-Net uses a novel feature pyramid architecture to capture and amplify multi-scale representations across various stages, thereby improving the detection of image inpainting by better revealing feature-level interactions. Additionally, the network can adaptively direct the lower-level features, which carry edge and shape information, to refine the localization of manipulated regions while integrating the higher-level semantic features. Using DeFI-Net, we develop a method combining complementary representations to accurately identify inpainted areas. Evaluation on five image inpainting datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in detecting inpainting across diverse models.
DeepTFP: Mobile Time Series Data Analytics based Traffic Flow Prediction
Oct 01, 2017
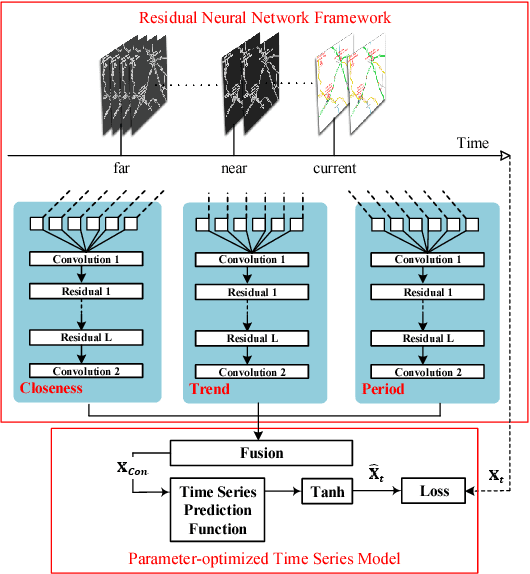
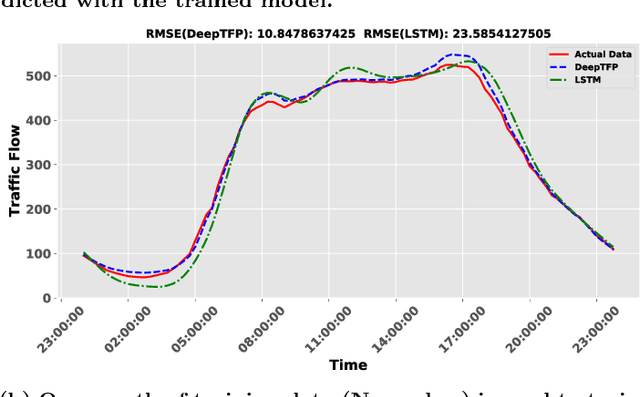
Abstract:Traffic flow prediction is an important research issue to avoid traffic congestion in transportation systems. Traffic congestion avoiding can be achieved by knowing traffic flow and then conducting transportation planning. Achieving traffic flow prediction is challenging as the prediction is affected by many complex factors such as inter-region traffic, vehicles' relations, and sudden events. However, as the mobile data of vehicles has been widely collected by sensor-embedded devices in transportation systems, it is possible to predict the traffic flow by analysing mobile data. This study proposes a deep learning based prediction algorithm, DeepTFP, to collectively predict the traffic flow on each and every traffic road of a city. This algorithm uses three deep residual neural networks to model temporal closeness, period, and trend properties of traffic flow. Each residual neural network consists of a branch of residual convolutional units. DeepTFP aggregates the outputs of the three residual neural networks to optimize the parameters of a time series prediction model. Contrast experiments on mobile time series data from the transportation system of England demonstrate that the proposed DeepTFP outperforms the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) architecture based method in prediction accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge