Weizhi Meng
Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning from Partial Decryption Verifiable Threshold Multi-Client Functional Encryption
Nov 17, 2025



Abstract:In federated learning, multiple parties can cooperate to train the model without directly exchanging their own private data, but the gradient leakage problem still threatens the privacy security and model integrity. Although the existing scheme uses threshold cryptography to mitigate the inference attack, it can not guarantee the verifiability of the aggregation results, making the system vulnerable to the threat of poisoning attack. We construct a partial decryption verifiable threshold multi client function encryption scheme, and apply it to Federated learning to implement the federated learning verifiable threshold security aggregation protocol (VTSAFL). VTSAFL empowers clients to verify aggregation results, concurrently minimizing both computational and communication overhead. The size of the functional key and partial decryption results of the scheme are constant, which provides efficiency guarantee for large-scale deployment. The experimental results on MNIST dataset show that vtsafl can achieve the same accuracy as the existing scheme, while reducing the total training time by more than 40%, and reducing the communication overhead by up to 50%. This efficiency is critical for overcoming the resource constraints inherent in Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
TraceMark-LDM: Authenticatable Watermarking for Latent Diffusion Models via Binary-Guided Rearrangement
Mar 30, 2025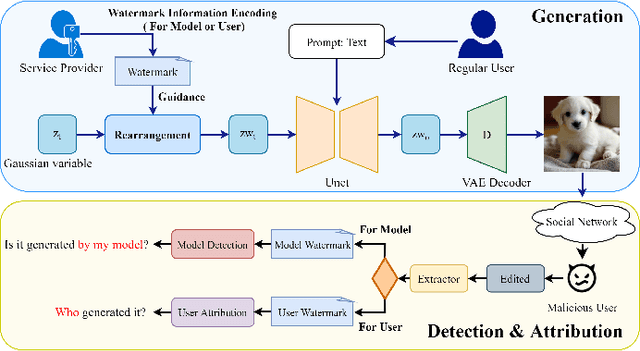
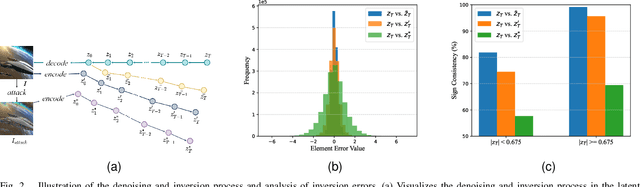
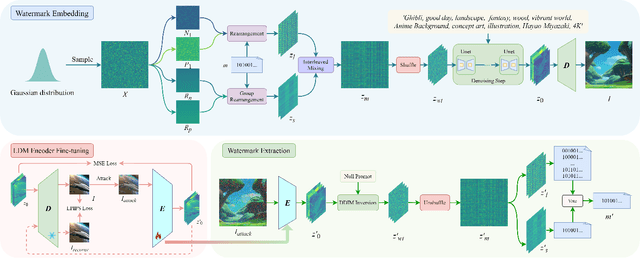
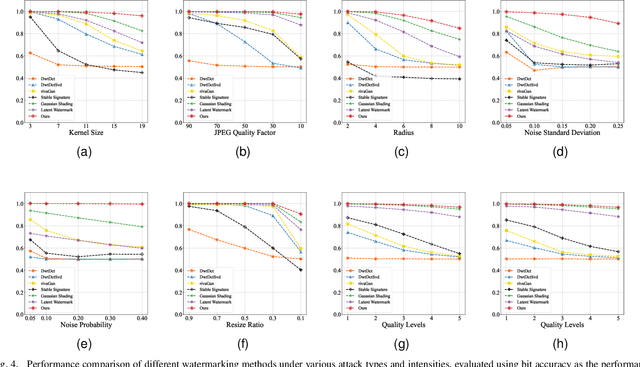
Abstract:Image generation algorithms are increasingly integral to diverse aspects of human society, driven by their practical applications. However, insufficient oversight in artificial Intelligence generated content (AIGC) can facilitate the spread of malicious content and increase the risk of copyright infringement. Among the diverse range of image generation models, the Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) is currently the most widely used, dominating the majority of the Text-to-Image model market. Currently, most attribution methods for LDMs rely on directly embedding watermarks into the generated images or their intermediate noise, a practice that compromises both the quality and the robustness of the generated content. To address these limitations, we introduce TraceMark-LDM, an novel algorithm that integrates watermarking to attribute generated images while guaranteeing non-destructive performance. Unlike current methods, TraceMark-LDM leverages watermarks as guidance to rearrange random variables sampled from a Gaussian distribution. To mitigate potential deviations caused by inversion errors, the small absolute elements are grouped and rearranged. Additionally, we fine-tune the LDM encoder to enhance the robustness of the watermark. Experimental results show that images synthesized using TraceMark-LDM exhibit superior quality and attribution accuracy compared to state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques. Notably, TraceMark-LDM demonstrates exceptional robustness against various common attack methods, consistently outperforming SOTA methods.
Stealthy Voice Eavesdropping with Acoustic Metamaterials: Unraveling a New Privacy Threat
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:We present SuperEar, a novel privacy threat based on acoustic metamaterials. Unlike previous research, SuperEar can surreptitiously track and eavesdrop on the phone calls of a moving outdoor target from a safe distance. To design this attack, SuperEar overcomes the challenges faced by traditional acoustic metamaterials, including low low-frequency gain and audio distortion during reconstruction. It successfully magnifies the speech signal by approximately 20 times, allowing the sound to be captured from the earpiece of the target phone. In addition, SuperEar optimizes the trade-off between the number and size of acoustic metamaterials, improving the portability and concealability of the interceptor while ensuring effective interception performance. This makes it highly suitable for outdoor tracking and eavesdropping scenarios. Through extensive experimentation, we have evaluated SuperEar and our results show that it can achieve an eavesdropping accuracy of over 80% within a range of 4.5 meters in the aforementioned scenario, thus validating its great potential in real-world applications.
Protecting User Privacy in Online Settings via Supervised Learning
Apr 06, 2023



Abstract:Companies that have an online presence-in particular, companies that are exclusively digital-often subscribe to this business model: collect data from the user base, then expose the data to advertisement agencies in order to turn a profit. Such companies routinely market a service as "free", while obfuscating the fact that they tend to "charge" users in the currency of personal information rather than money. However, online companies also gather user data for more principled purposes, such as improving the user experience and aggregating statistics. The problem is the sale of user data to third parties. In this work, we design an intelligent approach to online privacy protection that leverages supervised learning. By detecting and blocking data collection that might infringe on a user's privacy, we can restore a degree of digital privacy to the user. In our evaluation, we collect a dataset of network requests and measure the performance of several classifiers that adhere to the supervised learning paradigm. The results of our evaluation demonstrate the feasibility and potential of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge