Weiye Zhao
SPARK: A Modular Benchmark for Humanoid Robot Safety
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces the Safe Protective and Assistive Robot Kit (SPARK), a comprehensive benchmark designed to ensure safety in humanoid autonomy and teleoperation. Humanoid robots pose significant safety risks due to their physical capabilities of interacting with complex environments. The physical structures of humanoid robots further add complexity to the design of general safety solutions. To facilitate the safe deployment of complex robot systems, SPARK can be used as a toolbox that comes with state-of-the-art safe control algorithms in a modular and composable robot control framework. Users can easily configure safety criteria and sensitivity levels to optimize the balance between safety and performance. To accelerate humanoid safety research and development, SPARK provides a simulation benchmark that compares safety approaches in a variety of environments, tasks, and robot models. Furthermore, SPARK allows quick deployment of synthesized safe controllers on real robots. For hardware deployment, SPARK supports Apple Vision Pro (AVP) or a Motion Capture System as external sensors, while also offering interfaces for seamless integration with alternative hardware setups. This paper demonstrates SPARK's capability with both simulation experiments and case studies with a Unitree G1 humanoid robot. Leveraging these advantages of SPARK, users and researchers can significantly improve the safety of their humanoid systems as well as accelerate relevant research. The open-source code is available at https://github.com/intelligent-control-lab/spark.
Continual Learning and Lifting of Koopman Dynamics for Linear Control of Legged Robots
Nov 21, 2024Abstract:The control of legged robots, particularly humanoid and quadruped robots, presents significant challenges due to their high-dimensional and nonlinear dynamics. While linear systems can be effectively controlled using methods like Model Predictive Control (MPC), the control of nonlinear systems remains complex. One promising solution is the Koopman Operator, which approximates nonlinear dynamics with a linear model, enabling the use of proven linear control techniques. However, achieving accurate linearization through data-driven methods is difficult due to issues like approximation error, domain shifts, and the limitations of fixed linear state-space representations. These challenges restrict the scalability of Koopman-based approaches. This paper addresses these challenges by proposing a continual learning algorithm designed to iteratively refine Koopman dynamics for high-dimensional legged robots. The key idea is to progressively expand the dataset and latent space dimension, enabling the learned Koopman dynamics to converge towards accurate approximations of the true system dynamics. Theoretical analysis shows that the linear approximation error of our method converges monotonically. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves high control performance on robots like Unitree G1/H1/A1/Go2 and ANYmal D, across various terrains using simple linear MPC controllers. This work is the first to successfully apply linearized Koopman dynamics for locomotion control of high-dimensional legged robots, enabling a scalable model-based control solution.
Absolute State-wise Constrained Policy Optimization: High-Probability State-wise Constraints Satisfaction
Oct 02, 2024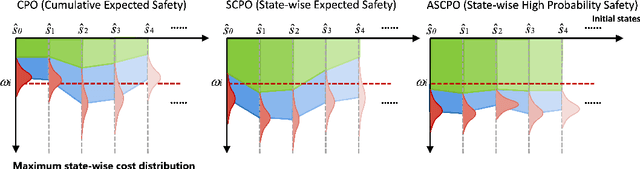

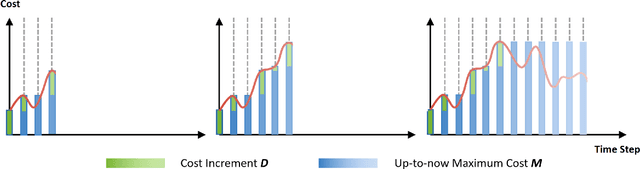

Abstract:Enforcing state-wise safety constraints is critical for the application of reinforcement learning (RL) in real-world problems, such as autonomous driving and robot manipulation. However, existing safe RL methods only enforce state-wise constraints in expectation or enforce hard state-wise constraints with strong assumptions. The former does not exclude the probability of safety violations, while the latter is impractical. Our insight is that although it is intractable to guarantee hard state-wise constraints in a model-free setting, we can enforce state-wise safety with high probability while excluding strong assumptions. To accomplish the goal, we propose Absolute State-wise Constrained Policy Optimization (ASCPO), a novel general-purpose policy search algorithm that guarantees high-probability state-wise constraint satisfaction for stochastic systems. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by training neural network policies for extensive robot locomotion tasks, where the agent must adhere to various state-wise safety constraints. Our results show that ASCPO significantly outperforms existing methods in handling state-wise constraints across challenging continuous control tasks, highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
WeHelp: A Shared Autonomy System for Wheelchair Users
Sep 19, 2024

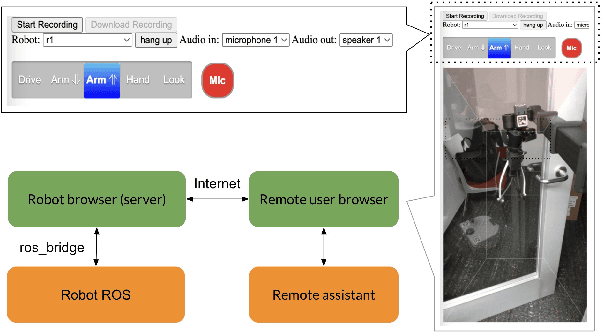

Abstract:There is a large population of wheelchair users. Most of the wheelchair users need help with daily tasks. However, according to recent reports, their needs are not properly satisfied due to the lack of caregivers. Therefore, in this project, we develop WeHelp, a shared autonomy system aimed for wheelchair users. A robot with a WeHelp system has three modes, following mode, remote control mode and tele-operation mode. In the following mode, the robot follows the wheelchair user automatically via visual tracking. The wheelchair user can ask the robot to follow them from behind, by the left or by the right. When the wheelchair user asks for help, the robot will recognize the command via speech recognition, and then switch to the teleoperation mode or remote control mode. In the teleoperation mode, the wheelchair user takes over the robot with a joy stick and controls the robot to complete some complex tasks for their needs, such as opening doors, moving obstacles on the way, reaching objects on a high shelf or on the low ground, etc. In the remote control mode, a remote assistant takes over the robot and helps the wheelchair user complete some complex tasks for their needs. Our evaluation shows that the pipeline is useful and practical for wheelchair users. Source code and demo of the paper are available at \url{https://github.com/Walleclipse/WeHelp}.
Physics-Aware Combinatorial Assembly Planning using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:Combinatorial assembly uses standardized unit primitives to build objects that satisfy user specifications. Lego is a widely used platform for combinatorial assembly, in which people use unit primitives (ie Lego bricks) to build highly customizable 3D objects. This paper studies sequence planning for physical combinatorial assembly using Lego. Given the shape of the desired object, we want to find a sequence of actions for placing Lego bricks to build the target object. In particular, we aim to ensure the planned assembly sequence is physically executable. However, assembly sequence planning (ASP) for combinatorial assembly is particularly challenging due to its combinatorial nature, ie the vast number of possible combinations and complex constraints. To address the challenges, we employ deep reinforcement learning to learn a construction policy for placing unit primitives sequentially to build the desired object. Specifically, we design an online physics-aware action mask that efficiently filters out invalid actions and guides policy learning. In the end, we demonstrate that the proposed method successfully plans physically valid assembly sequences for constructing different Lego structures. The generated construction plan can be executed in real.
Meta-Control: Automatic Model-based Control Synthesis for Heterogeneous Robot Skills
May 18, 2024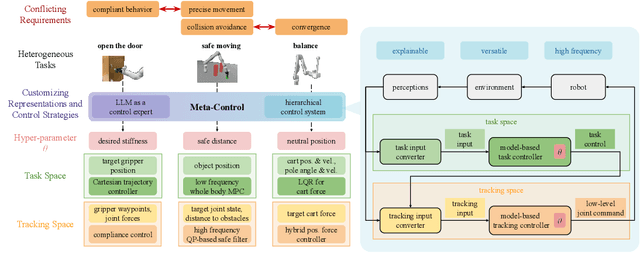
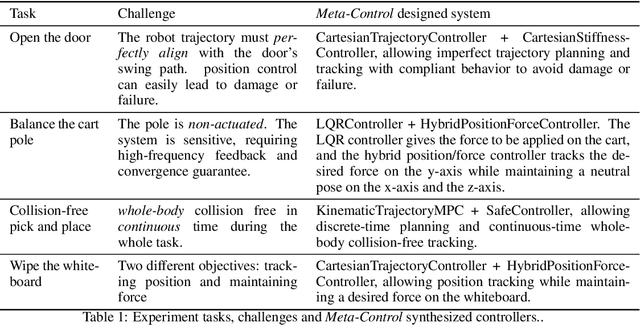
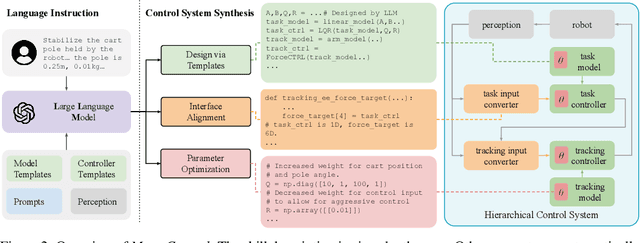
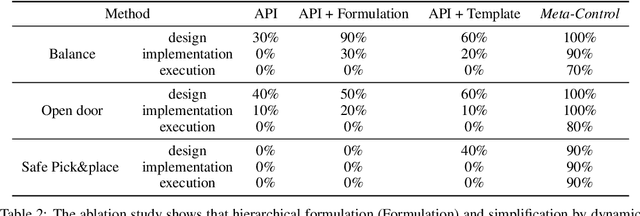
Abstract:The requirements for real-world manipulation tasks are diverse and often conflicting; some tasks necessitate force constraints or collision avoidance, while others demand high-frequency feedback. Satisfying these varied requirements with a fixed state-action representation and control strategy is challenging, impeding the development of a universal robotic foundation model. In this work, we propose Meta-Control, the first LLM-enabled automatic control synthesis approach that creates customized state representations and control strategies tailored to specific tasks. Meta-Control leverages a generic hierarchical control framework to address a wide range of heterogeneous tasks. Our core insight is the decomposition of the state space into an abstract task space and a concrete tracking space. By harnessing LLM's extensive common sense and control knowledge, we enable the LLM to design these spaces, including states, dynamic models, and controllers, using pre-defined but abstract templates. Meta-Control stands out for its fully model-based nature, allowing for rigorous analysis, efficient parameter tuning, and reliable execution. It not only utilizes decades of control expertise encapsulated within LLMs to facilitate heterogeneous control but also ensures formal guarantees such as safety and stability. Our method is validated both in real-world scenarios and simulations across diverse tasks with conflicting requirements, such as collision avoidance versus convergence and compliance versus high precision. Videos and additional results are at meta-control-paper.github.io
Implicit Safe Set Algorithm for Provably Safe Reinforcement Learning
May 04, 2024Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has demonstrated remarkable performance in many continuous control tasks. However, a significant obstacle to the real-world application of DRL is the lack of safety guarantees. Although DRL agents can satisfy system safety in expectation through reward shaping, designing agents to consistently meet hard constraints (e.g., safety specifications) at every time step remains a formidable challenge. In contrast, existing work in the field of safe control provides guarantees on persistent satisfaction of hard safety constraints. However, these methods require explicit analytical system dynamics models to synthesize safe control, which are typically inaccessible in DRL settings. In this paper, we present a model-free safe control algorithm, the implicit safe set algorithm, for synthesizing safeguards for DRL agents that ensure provable safety throughout training. The proposed algorithm synthesizes a safety index (barrier certificate) and a subsequent safe control law solely by querying a black-box dynamic function (e.g., a digital twin simulator). Moreover, we theoretically prove that the implicit safe set algorithm guarantees finite time convergence to the safe set and forward invariance for both continuous-time and discrete-time systems. We validate the proposed algorithm on the state-of-the-art Safety Gym benchmark, where it achieves zero safety violations while gaining $95\% \pm 9\%$ cumulative reward compared to state-of-the-art safe DRL methods. Furthermore, the resulting algorithm scales well to high-dimensional systems with parallel computing.
Learning Predictive Safety Filter via Decomposition of Robust Invariant Set
Nov 12, 2023


Abstract:Ensuring safety of nonlinear systems under model uncertainty and external disturbances is crucial, especially for real-world control tasks. Predictive methods such as robust model predictive control (RMPC) require solving nonconvex optimization problems online, which leads to high computational burden and poor scalability. Reinforcement learning (RL) works well with complex systems, but pays the price of losing rigorous safety guarantee. This paper presents a theoretical framework that bridges the advantages of both RMPC and RL to synthesize safety filters for nonlinear systems with state- and action-dependent uncertainty. We decompose the robust invariant set (RIS) into two parts: a target set that aligns with terminal region design of RMPC, and a reach-avoid set that accounts for the rest of RIS. We propose a policy iteration approach for robust reach-avoid problems and establish its monotone convergence. This method sets the stage for an adversarial actor-critic deep RL algorithm, which simultaneously synthesizes a reach-avoid policy network, a disturbance policy network, and a reach-avoid value network. The learned reach-avoid policy network is utilized to generate nominal trajectories for online verification, which filters potentially unsafe actions that may drive the system into unsafe regions when worst-case disturbances are applied. We formulate a second-order cone programming (SOCP) approach for online verification using system level synthesis, which optimizes for the worst-case reach-avoid value of any possible trajectories. The proposed safety filter requires much lower computational complexity than RMPC and still enjoys persistent robust safety guarantee. The effectiveness of our method is illustrated through a numerical example.
Absolute Policy Optimization
Oct 20, 2023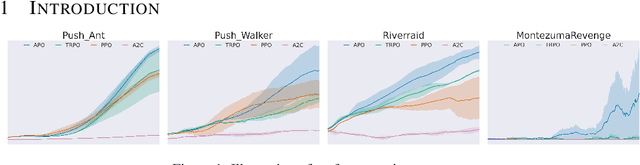

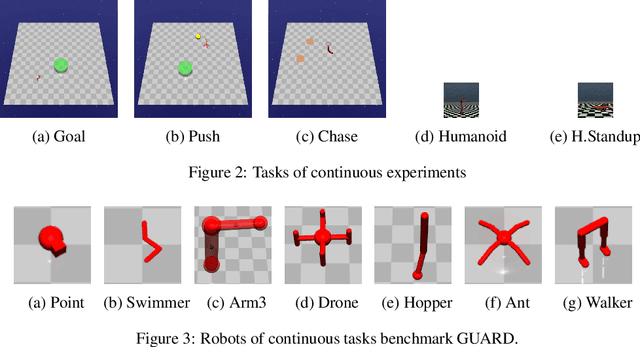
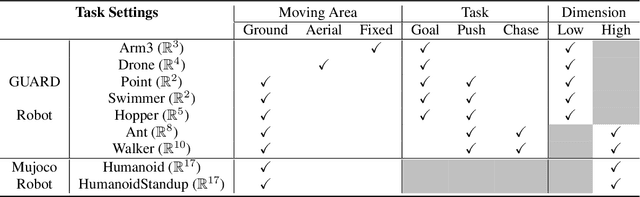
Abstract:In recent years, trust region on-policy reinforcement learning has achieved impressive results in addressing complex control tasks and gaming scenarios. However, contemporary state-of-the-art algorithms within this category primarily emphasize improvement in expected performance, lacking the ability to control over the worst-case performance outcomes. To address this limitation, we introduce a novel objective function; by optimizing which, it will lead to guaranteed monotonic improvement in the lower bound of near-total performance samples (absolute performance). Considering this groundbreaking theoretical advancement, we then refine this theoretically grounded algorithm through a series of approximations, resulting in a practical solution called Absolute Policy Optimization (APO). Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach across challenging continuous control benchmark tasks and extend its applicability to mastering Atari games. Our findings reveal that APO significantly outperforms state-of-the-art policy gradient algorithms, resulting in substantial improvements in both expected performance and worst-case performance.
Learn With Imagination: Safe Set Guided State-wise Constrained Policy Optimization
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (RL) excels in various control tasks, yet the absence of safety guarantees hampers its real-world applicability. In particular, explorations during learning usually results in safety violations, while the RL agent learns from those mistakes. On the other hand, safe control techniques ensure persistent safety satisfaction but demand strong priors on system dynamics, which is usually hard to obtain in practice. To address these problems, we present Safe Set Guided State-wise Constrained Policy Optimization (S-3PO), a pioneering algorithm generating state-wise safe optimal policies with zero training violations, i.e., learning without mistakes. S-3PO first employs a safety-oriented monitor with black-box dynamics to ensure safe exploration. It then enforces a unique cost for the RL agent to converge to optimal behaviors within safety constraints. S-3PO outperforms existing methods in high-dimensional robotics tasks, managing state-wise constraints with zero training violation. This innovation marks a significant stride towards real-world safe RL deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge