Weifeng Su
Break the Tie: Learning Cluster-Customized Category Relationships for Categorical Data Clustering
Nov 12, 2025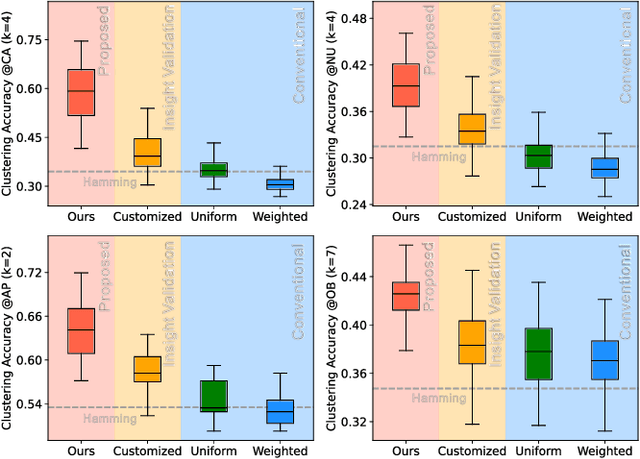
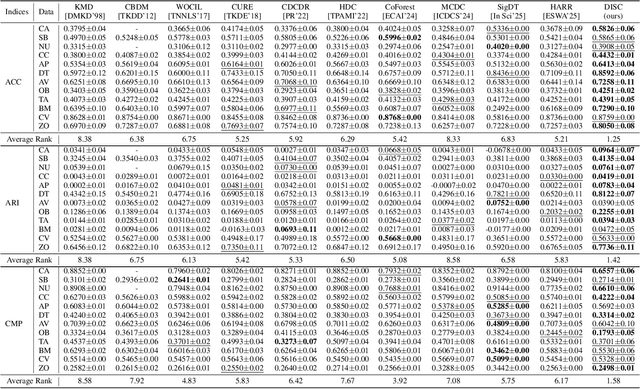
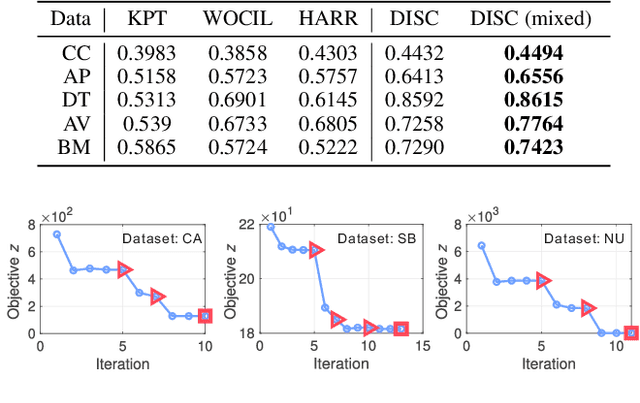
Abstract:Categorical attributes with qualitative values are ubiquitous in cluster analysis of real datasets. Unlike the Euclidean distance of numerical attributes, the categorical attributes lack well-defined relationships of their possible values (also called categories interchangeably), which hampers the exploration of compact categorical data clusters. Although most attempts are made for developing appropriate distance metrics, they typically assume a fixed topological relationship between categories when learning distance metrics, which limits their adaptability to varying cluster structures and often leads to suboptimal clustering performance. This paper, therefore, breaks the intrinsic relationship tie of attribute categories and learns customized distance metrics suitable for flexibly and accurately revealing various cluster distributions. As a result, the fitting ability of the clustering algorithm is significantly enhanced, benefiting from the learnable category relationships. Moreover, the learned category relationships are proved to be Euclidean distance metric-compatible, enabling a seamless extension to mixed datasets that include both numerical and categorical attributes. Comparative experiments on 12 real benchmark datasets with significance tests show the superior clustering accuracy of the proposed method with an average ranking of 1.25, which is significantly higher than the 5.21 ranking of the current best-performing method.
DDO-IN: Dual Domains Optimization for Implicit Neural Network to Eliminate Motion Artifact in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Mar 11, 2025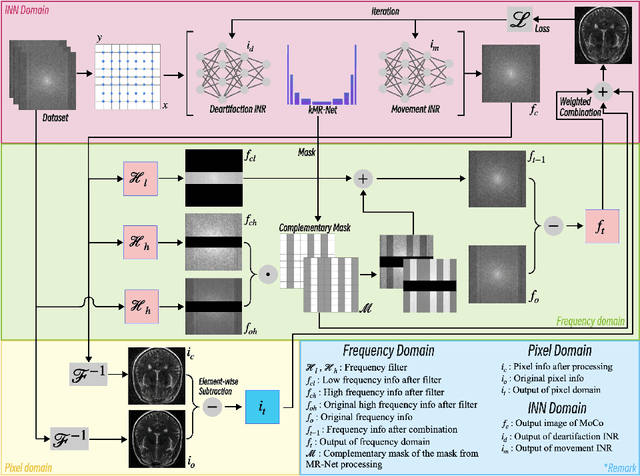
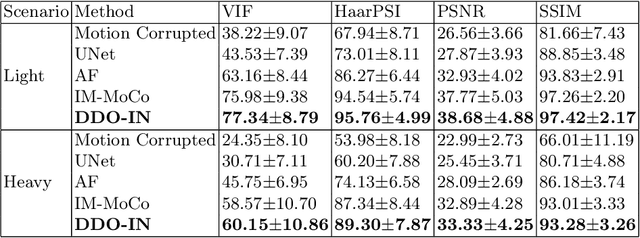
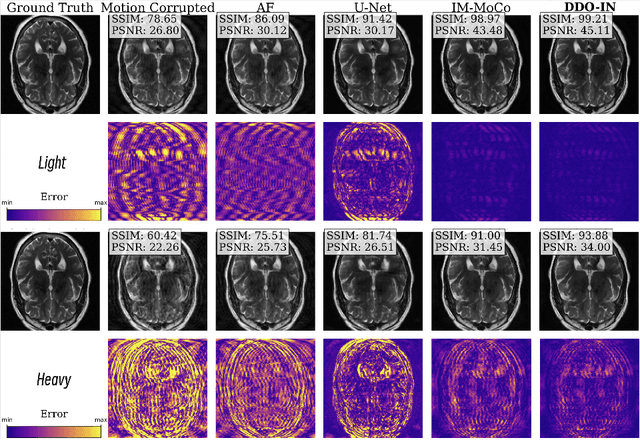
Abstract:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) motion artifacts can seriously affect clinical diagnostics, making it challenging to interpret images accurately. Existing methods for eliminating motion artifacts struggle to retain fine structural details and simultaneously lack the necessary vividness and sharpness. In this study, we present a novel dual-domain optimization (DDO) approach that integrates information from the pixel and frequency domains guiding the recovery of clean magnetic resonance images through implicit neural representations(INRs). Specifically, our approach leverages the low-frequency components in the k-space as a reference to capture accurate tissue textures, while high-frequency and pixel information contribute to recover details. Furthermore, we design complementary masks and dynamic loss weighting transitioning from global to local attention that effectively suppress artifacts while retaining useful details for reconstruction. Experimental results on the NYU fastMRI dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches in multiple evaluation metrics. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DDO-IN-A73B.
Leveraging CORAL-Correlation Consistency Network for Semi-Supervised Left Atrium MRI Segmentation
Oct 21, 2024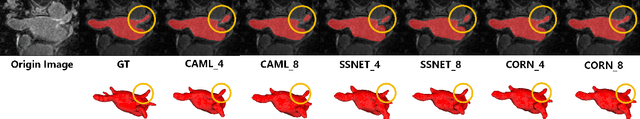
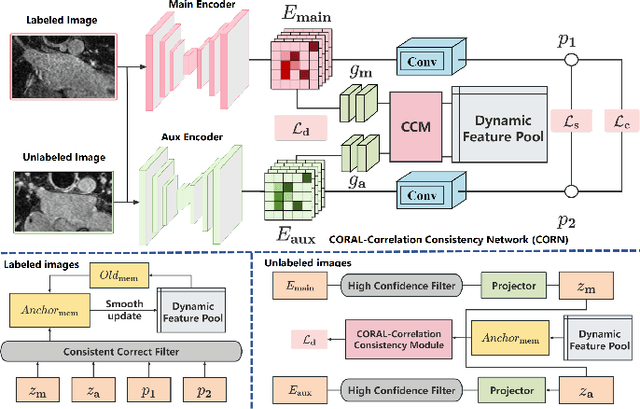
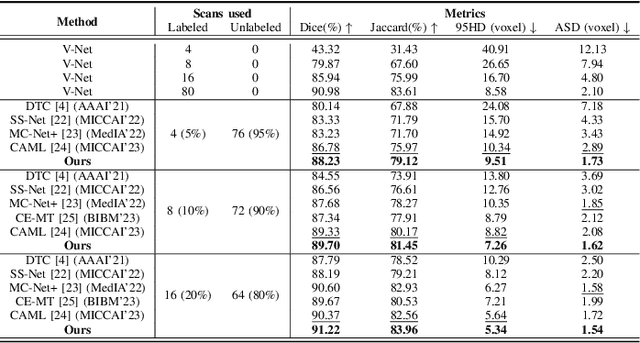
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has been widely used to learn from both a few labeled images and many unlabeled images to overcome the scarcity of labeled samples in medical image segmentation. Most current SSL-based segmentation methods use pixel values directly to identify similar features in labeled and unlabeled data. They usually fail to accurately capture the intricate attachment structures in the left atrium, such as the areas of inconsistent density or exhibit outward curvatures, adding to the complexity of the task. In this paper, we delve into this issue and introduce an effective solution, CORAL(Correlation-Aligned)-Correlation Consistency Network (CORN), to capture the global structure shape and local details of Left Atrium. Diverging from previous methods focused on each local pixel value, the CORAL-Correlation Consistency Module (CCM) in the CORN leverages second-order statistical information to capture global structural features by minimizing the distribution discrepancy between labeled and unlabeled samples in feature space. Yet, direct construction of features from unlabeled data frequently results in ``Sample Selection Bias'', leading to flawed supervision. We thus further propose the Dynamic Feature Pool (DFP) for the CCM, which utilizes a confidence-based filtering strategy to remove incorrectly selected features and regularize both teacher and student models by constraining the similarity matrix to be consistent. Extensive experiments on the Left Atrium dataset have shown that the proposed CORN outperforms previous state-of-the-art semi-supervised learning methods.
M$^3$-Impute: Mask-guided Representation Learning for Missing Value Imputation
Oct 11, 2024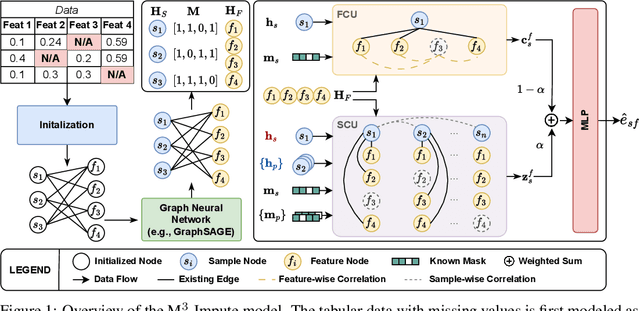
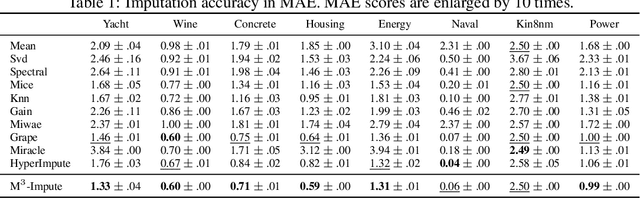
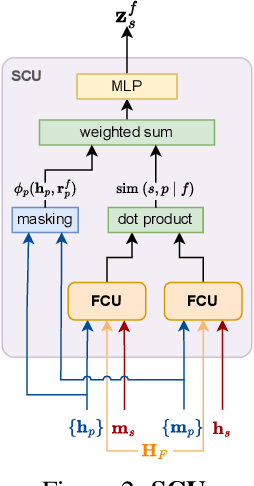
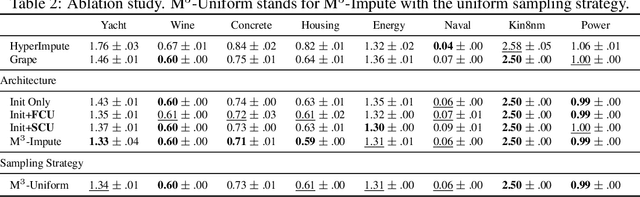
Abstract:Missing values are a common problem that poses significant challenges to data analysis and machine learning. This problem necessitates the development of an effective imputation method to fill in the missing values accurately, thereby enhancing the overall quality and utility of the datasets. Existing imputation methods, however, fall short of explicitly considering the `missingness' information in the data during the embedding initialization stage and modeling the entangled feature and sample correlations during the learning process, thus leading to inferior performance. We propose M$^3$-Impute, which aims to explicitly leverage the missingness information and such correlations with novel masking schemes. M$^3$-Impute first models the data as a bipartite graph and uses a graph neural network to learn node embeddings, where the refined embedding initialization process directly incorporates the missingness information. They are then optimized through M$^3$-Impute's novel feature correlation unit (FRU) and sample correlation unit (SRU) that effectively captures feature and sample correlations for imputation. Experiment results on 25 benchmark datasets under three different missingness settings show the effectiveness of M$^3$-Impute by achieving 20 best and 4 second-best MAE scores on average.
Fuse4Seg: Image-Level Fusion Based Multi-Modality Medical Image Segmentation
Sep 17, 2024Abstract:Although multi-modality medical image segmentation holds significant potential for enhancing the diagnosis and understanding of complex diseases by integrating diverse imaging modalities, existing methods predominantly rely on feature-level fusion strategies. We argue the current feature-level fusion strategy is prone to semantic inconsistencies and misalignments across various imaging modalities because it merges features at intermediate layers in a neural network without evaluative control. To mitigate this, we introduce a novel image-level fusion based multi-modality medical image segmentation method, Fuse4Seg, which is a bi-level learning framework designed to model the intertwined dependencies between medical image segmentation and medical image fusion. The image-level fusion process is seamlessly employed to guide and enhance the segmentation results through a layered optimization approach. Besides, the knowledge gained from the segmentation module can effectively enhance the fusion module. This ensures that the resultant fused image is a coherent representation that accurately amalgamates information from all modalities. Moreover, we construct a BraTS-Fuse benchmark based on BraTS dataset, which includes 2040 paired original images, multi-modal fusion images, and ground truth. This benchmark not only serves image-level medical segmentation but is also the largest dataset for medical image fusion to date. Extensive experiments on several public datasets and our benchmark demonstrate the superiority of our approach over prior state-of-the-art (SOTA) methodologies.
DAE-Fuse: An Adaptive Discriminative Autoencoder for Multi-Modality Image Fusion
Sep 16, 2024



Abstract:Multi-modality image fusion aims to integrate complementary data information from different imaging modalities into a single image. Existing methods often generate either blurry fused images that lose fine-grained semantic information or unnatural fused images that appear perceptually cropped from the inputs. In this work, we propose a novel two-phase discriminative autoencoder framework, termed DAE-Fuse, that generates sharp and natural fused images. In the adversarial feature extraction phase, we introduce two discriminative blocks into the encoder-decoder architecture, providing an additional adversarial loss to better guide feature extraction by reconstructing the source images. While the two discriminative blocks are adapted in the attention-guided cross-modality fusion phase to distinguish the structural differences between the fused output and the source inputs, injecting more naturalness into the results. Extensive experiments on public infrared-visible, medical image fusion, and downstream object detection datasets demonstrate our method's superiority and generalizability in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
Dynamic D2D-Assisted Federated Learning over O-RAN: Performance Analysis, MAC Scheduler, and Asymmetric User Selection
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:Existing studies on federated learning (FL) are mostly focused on system orchestration for static snapshots of the network and making static control decisions (e.g., spectrum allocation). However, real-world wireless networks are susceptible to temporal variations of wireless channel capacity and users' datasets. In this paper, we incorporate multi-granular system dynamics (MSDs) into FL, including (M1) dynamic wireless channel capacity, captured by a set of discrete-time events, called $\mathscr{D}$-Events, and (M2) dynamic datasets of users. The latter is characterized by (M2-a) modeling the dynamics of user's dataset size via an ordinary differential equation and (M2-b) introducing dynamic model drift}, formulated via a partial differential inequality} drawing concrete analytical connections between the dynamics of users' datasets and FL accuracy. We then conduct FL orchestration under MSDs by introducing dynamic cooperative FL with dedicated MAC schedulers (DCLM), exploiting the unique features of open radio access network (O-RAN). DCLM proposes (i) a hierarchical device-to-device (D2D)-assisted model training, (ii) dynamic control decisions through dedicated O-RAN MAC schedulers, and (iii) asymmetric user selection. We provide extensive theoretical analysis to study the convergence of DCLM. We then optimize the degrees of freedom (e.g., user selection and spectrum allocation) in DCLM through a highly non-convex optimization problem. We develop a systematic approach to obtain the solution for this problem, opening the door to solving a broad variety of network-aware FL optimization problems. We show the efficiency of DCLM via numerical simulations and provide a series of future directions.
Synergies Between Federated Learning and O-RAN: Towards an Elastic Virtualized Architecture for Multiple Distributed Machine Learning Services
Apr 14, 2023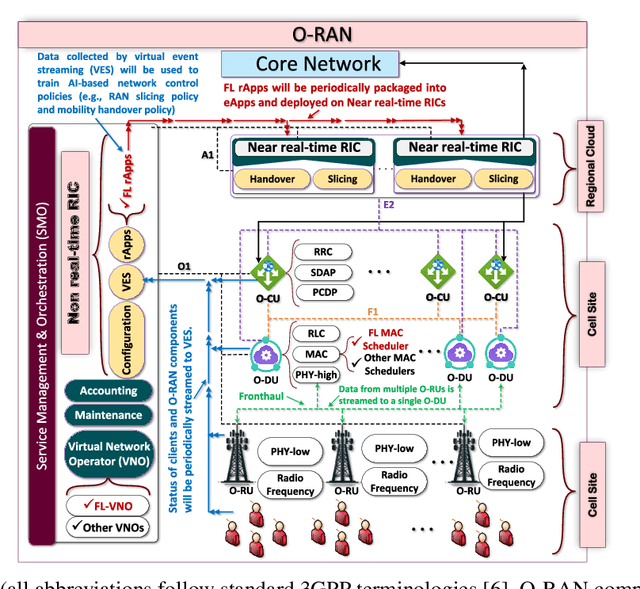
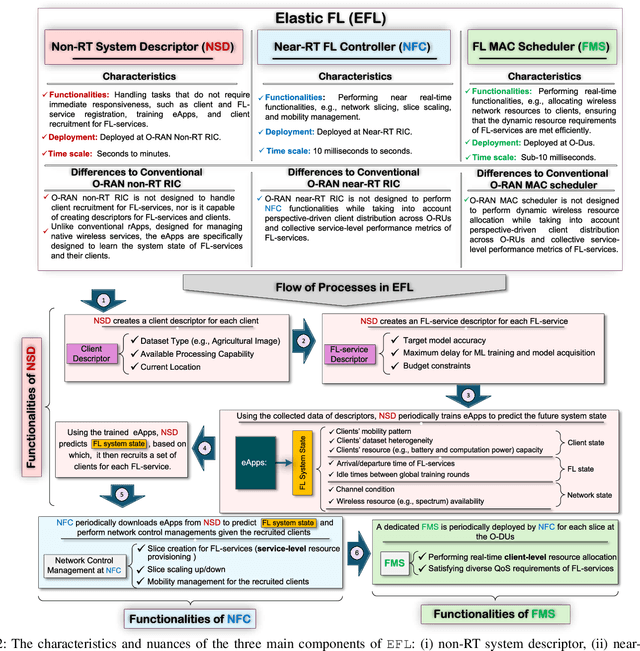
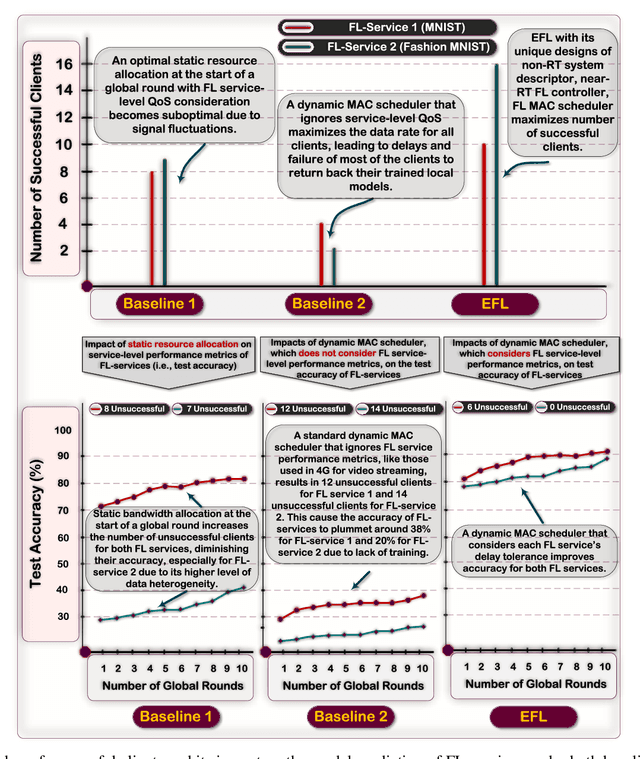
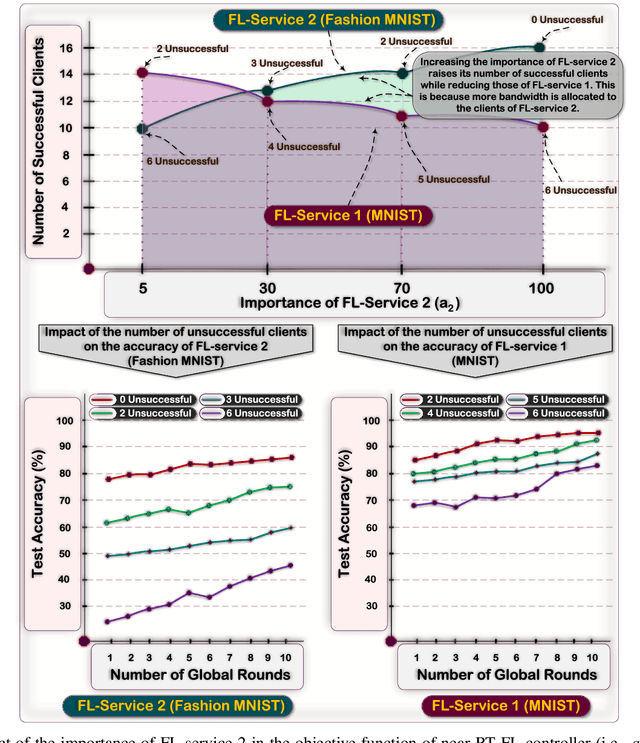
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is the most popular distributed machine learning technique. However, implementation of FL over modern wireless networks faces key challenges caused by (i) dynamics of the network conditions, (ii) coexistence of multiple FL services/tasks in the system, and (iii) concurrent execution of FL services with other network services, which are not jointly considered in prior works. Motivated by these challenges, we introduce a generic FL paradigm over next-generation (NextG) networks, called dynamic multi-service FL (DMS-FL). We identify three unexplored design considerations in DMS-FL: (i) FL service operator accumulation, (ii) wireless resource fragmentation, and (iii) signal strength fluctuations. We take the first steps towards addressing these design considerations through proposing a novel distributed ML architecture called elastic virtualized FL (EV-FL). EV-FL unleashes the full potential of Open RAN (O-RAN) systems and introduces an elastic resource provisioning methodology to execute FL services. It further constitutes a multi-time-scale FL management system that introduces three dimensions into existing FL architectures: (i) virtualization, (ii) scalability, and (iii) elasticity. Through investigating EV-FL, we reveal a series of open research directions for future work. We finally simulate EV-FL to demonstrate its potential to save wireless resources and increase fairness among FL services.
Towards Cooperative Federated Learning over Heterogeneous Edge/Fog Networks
Mar 15, 2023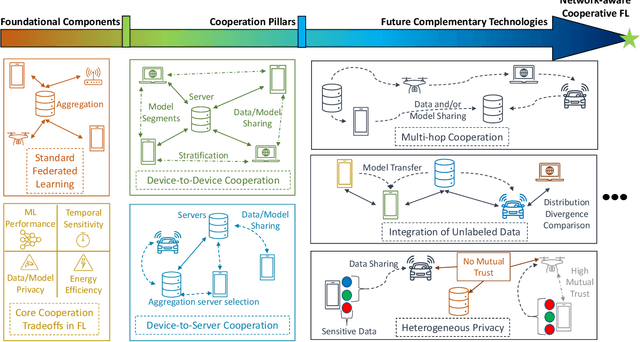
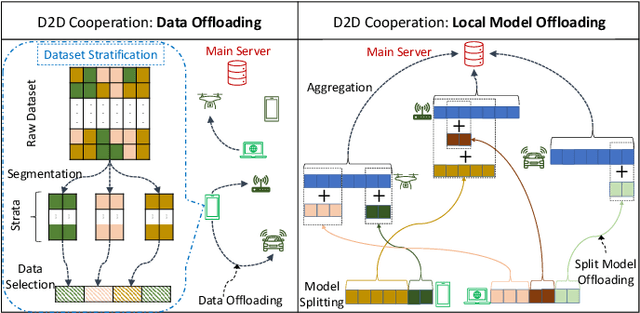
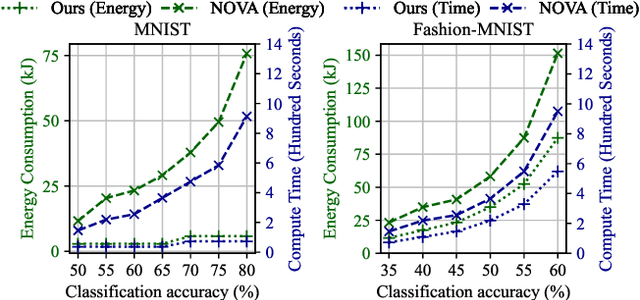
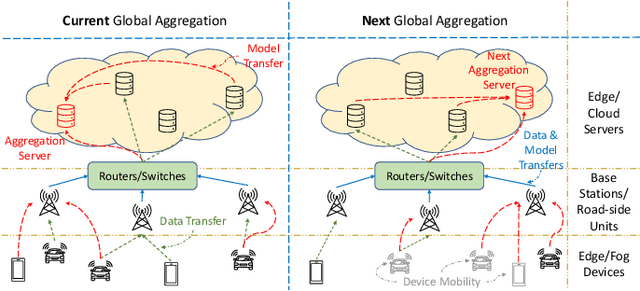
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has been promoted as a popular technique for training machine learning (ML) models over edge/fog networks. Traditional implementations of FL have largely neglected the potential for inter-network cooperation, treating edge/fog devices and other infrastructure participating in ML as separate processing elements. Consequently, FL has been vulnerable to several dimensions of network heterogeneity, such as varying computation capabilities, communication resources, data qualities, and privacy demands. We advocate for cooperative federated learning (CFL), a cooperative edge/fog ML paradigm built on device-to-device (D2D) and device-to-server (D2S) interactions. Through D2D and D2S cooperation, CFL counteracts network heterogeneity in edge/fog networks through enabling a model/data/resource pooling mechanism, which will yield substantial improvements in ML model training quality and network resource consumption. We propose a set of core methodologies that form the foundation of D2D and D2S cooperation and present preliminary experiments that demonstrate their benefits. We also discuss new FL functionalities enabled by this cooperative framework such as the integration of unlabeled data and heterogeneous device privacy into ML model training. Finally, we describe some open research directions at the intersection of cooperative edge/fog and FL.
LenAtten: An Effective Length Controlling Unit For Text Summarization
Jun 01, 2021
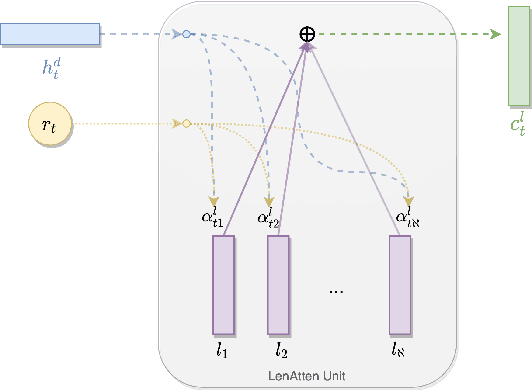
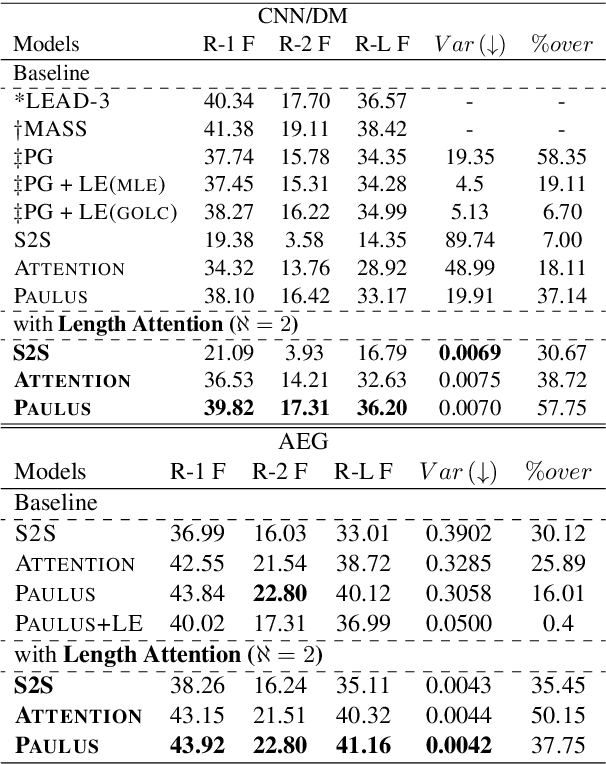
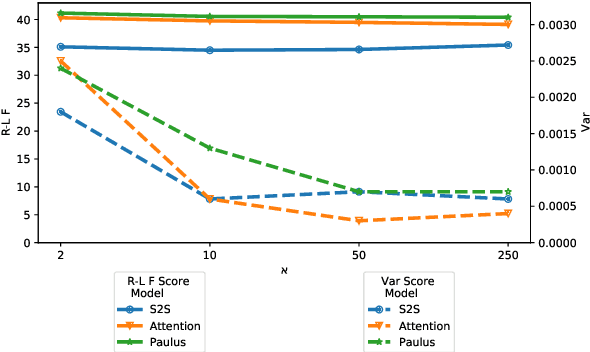
Abstract:Fixed length summarization aims at generating summaries with a preset number of words or characters. Most recent researches incorporate length information with word embeddings as the input to the recurrent decoding unit, causing a compromise between length controllability and summary quality. In this work, we present an effective length controlling unit Length Attention (LenAtten) to break this trade-off. Experimental results show that LenAtten not only brings improvements in length controllability and ROGUE scores but also has great generalization ability. In the task of generating a summary with the target length, our model is 732 times better than the best-performing length controllable summarizer in length controllability on the CNN/Daily Mail dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge