Viviana Patti
Practising responsibility: Ethics in NLP as a hands-on course
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:As Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems become more pervasive, integrating ethical considerations into NLP education has become essential. However, this presents inherent challenges in curriculum development: the field's rapid evolution from both academia and industry, and the need to foster critical thinking beyond traditional technical training. We introduce our course on Ethical Aspects in NLP and our pedagogical approach, grounded in active learning through interactive sessions, hands-on activities, and "learning by teaching" methods. Over four years, the course has been refined and adapted across different institutions, educational levels, and interdisciplinary backgrounds; it has also yielded many reusable products, both in the form of teaching materials and in the form of actual educational products aimed at diverse audiences, made by the students themselves. By sharing our approach and experience, we hope to provide inspiration for educators seeking to incorporate social impact considerations into their curricula.
Evalita-LLM: Benchmarking Large Language Models on Italian
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:We describe Evalita-LLM, a new benchmark designed to evaluate Large Language Models (LLMs) on Italian tasks. The distinguishing and innovative features of Evalita-LLM are the following: (i) all tasks are native Italian, avoiding issues of translating from Italian and potential cultural biases; (ii) in addition to well established multiple-choice tasks, the benchmark includes generative tasks, enabling more natural interaction with LLMs; (iii) all tasks are evaluated against multiple prompts, this way mitigating the model sensitivity to specific prompts and allowing a fairer and objective evaluation. We propose an iterative methodology, where candidate tasks and candidate prompts are validated against a set of LLMs used for development. We report experimental results from the benchmark's development phase, and provide performance statistics for several state-of-the-art LLMs.
GFG -- Gender-Fair Generation: A CALAMITA Challenge
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:Gender-fair language aims at promoting gender equality by using terms and expressions that include all identities and avoid reinforcing gender stereotypes. Implementing gender-fair strategies is particularly challenging in heavily gender-marked languages, such as Italian. To address this, the Gender-Fair Generation challenge intends to help shift toward gender-fair language in written communication. The challenge, designed to assess and monitor the recognition and generation of gender-fair language in both mono- and cross-lingual scenarios, includes three tasks: (1) the detection of gendered expressions in Italian sentences, (2) the reformulation of gendered expressions into gender-fair alternatives, and (3) the generation of gender-fair language in automatic translation from English to Italian. The challenge relies on three different annotated datasets: the GFL-it corpus, which contains Italian texts extracted from administrative documents provided by the University of Brescia; GeNTE, a bilingual test set for gender-neutral rewriting and translation built upon a subset of the Europarl dataset; and Neo-GATE, a bilingual test set designed to assess the use of non-binary neomorphemes in Italian for both fair formulation and translation tasks. Finally, each task is evaluated with specific metrics: average of F1-score obtained by means of BERTScore computed on each entry of the datasets for task 1, an accuracy measured with a gender-neutral classifier, and a coverage-weighted accuracy for tasks 2 and 3.
The World Literature Knowledge Graph
Jul 31, 2023



Abstract:Digital media have enabled the access to unprecedented literary knowledge. Authors, readers, and scholars are now able to discover and share an increasing amount of information about books and their authors. However, these sources of knowledge are fragmented and do not adequately represent non-Western writers and their works. In this paper we present The World Literature Knowledge Graph, a semantic resource containing 194,346 writers and 965,210 works, specifically designed for exploring facts about literary works and authors from different parts of the world. The knowledge graph integrates information about the reception of literary works gathered from 3 different communities of readers, aligned according to a single semantic model. The resource is accessible through an online visualization platform, which can be found at the following URL: https://literaturegraph.di.unito.it/. This platform has been rigorously tested and validated by $3$ distinct categories of experts who have found it to be highly beneficial for their respective work domains. These categories include teachers, researchers in the humanities, and professionals in the publishing industry. The feedback received from these experts confirms that they can effectively utilize the platform to enhance their work processes and achieve valuable outcomes.
Wikibio: a Semantic Resource for the Intersectional Analysis of Biographical Events
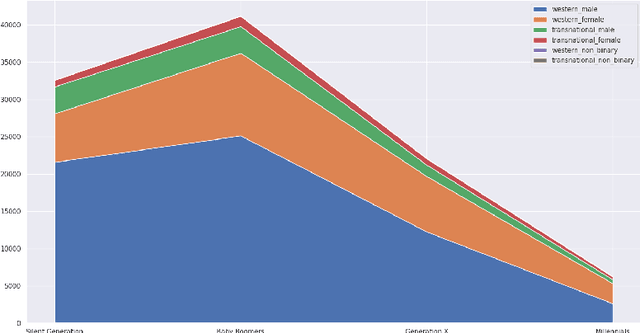
Jun 15, 2023Abstract:Biographical event detection is a relevant task for the exploration and comparison of the ways in which people's lives are told and represented. In this sense, it may support several applications in digital humanities and in works aimed at exploring bias about minoritized groups. Despite that, there are no corpora and models specifically designed for this task. In this paper we fill this gap by presenting a new corpus annotated for biographical event detection. The corpus, which includes 20 Wikipedia biographies, was compared with five existing corpora to train a model for the biographical event detection task. The model was able to detect all mentions of the target-entity in a biography with an F-score of 0.808 and the entity-related events with an F-score of 0.859. Finally, the model was used for performing an analysis of biases about women and non-Western people in Wikipedia biographies.
The URW-KG: a Resource for Tackling the Underrepresentation of non-Western Writers
Dec 21, 2022
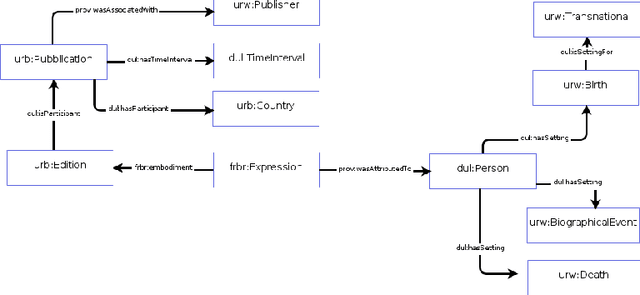
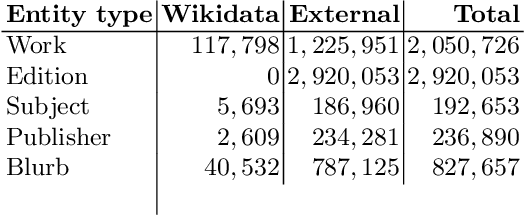
Abstract:Digital media have enabled the access to unprecedented literary knowledge. Authors, readers, and scholars are now able to discover and share an increasing amount of information about books and their authors. Notwithstanding, digital archives are still unbalanced: writers from non-Western countries are less represented, and such a condition leads to the perpetration of old forms of discrimination. In this paper, we present the Under-Represented Writers Knowledge Graph (URW-KG), a resource designed to explore and possibly amend this lack of representation by gathering and mapping information about works and authors from Wikidata and three other sources: Open Library, Goodreads, and Google Books. The experiments based on KG embeddings showed that the integrated information encoded in the graph allows scholars and users to be more easily exposed to non-Western literary works and authors with respect to Wikidata alone. This opens to the development of fairer and effective tools for author discovery and exploration.
O-Dang! The Ontology of Dangerous Speech Messages
Jul 13, 2022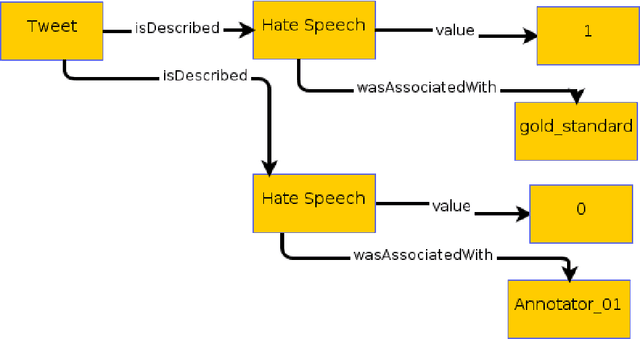
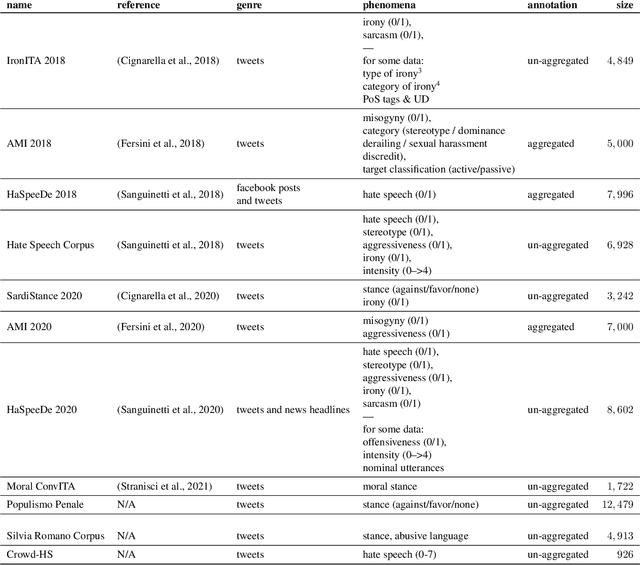
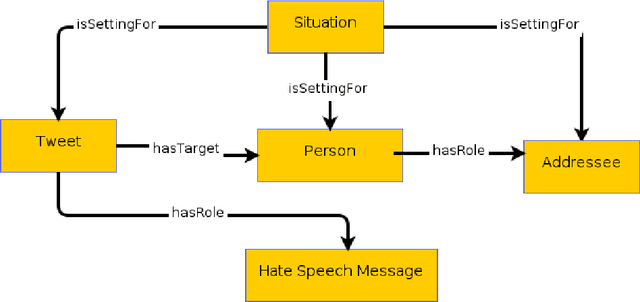
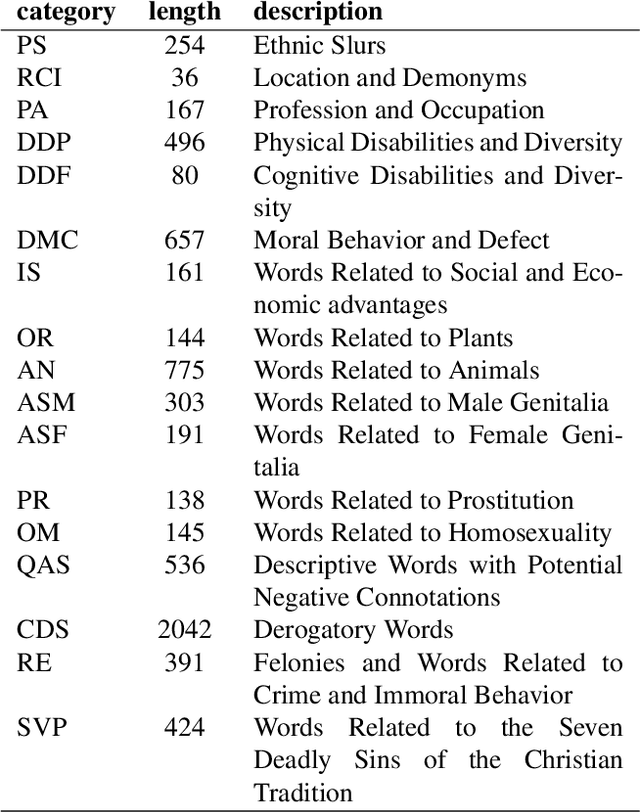
Abstract:Inside the NLP community there is a considerable amount of language resources created, annotated and released every day with the aim of studying specific linguistic phenomena. Despite a variety of attempts in order to organize such resources has been carried on, a lack of systematic methods and of possible interoperability between resources are still present. Furthermore, when storing linguistic information, still nowadays, the most common practice is the concept of "gold standard", which is in contrast with recent trends in NLP that aim at stressing the importance of different subjectivities and points of view when training machine learning and deep learning methods. In this paper we present O-Dang!: The Ontology of Dangerous Speech Messages, a systematic and interoperable Knowledge Graph (KG) for the collection of linguistic annotated data. O-Dang! is designed to gather and organize Italian datasets into a structured KG, according to the principles shared within the Linguistic Linked Open Data community. The ontology has also been designed to account for a perspectivist approach, since it provides a model for encoding both gold standard and single-annotator labels in the KG. The paper is structured as follows. In Section 1 the motivations of our work are outlined. Section 2 describes the O-Dang! Ontology, that provides a common semantic model for the integration of datasets in the KG. The Ontology Population stage with information about corpora, users, and annotations is presented in Section 3. Finally, in Section 4 an analysis of offensiveness across corpora is provided as a first case study for the resource.
APPReddit: a Corpus of Reddit Posts Annotated for Appraisal
May 31, 2022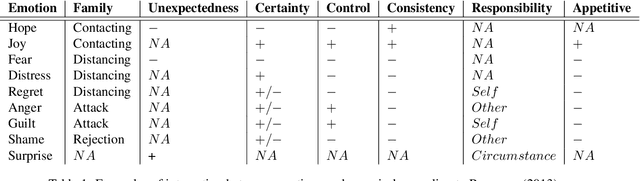
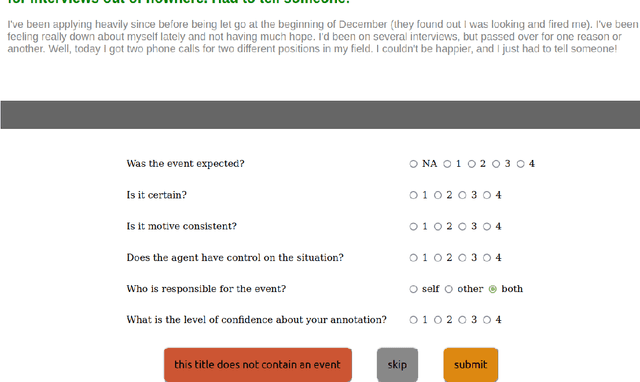
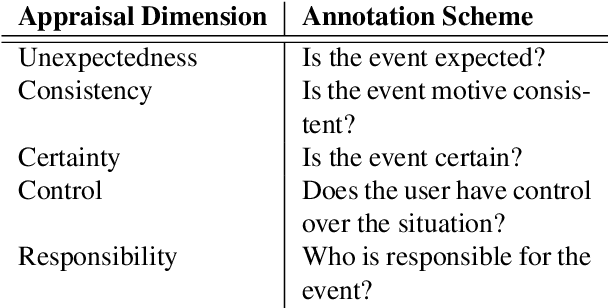
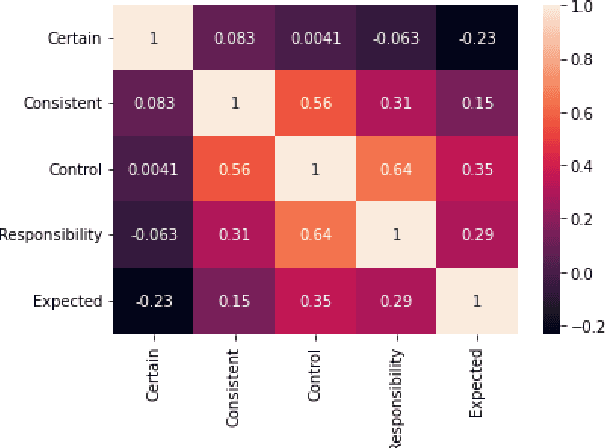
Abstract:Despite the large number of computational resources for emotion recognition, there is a lack of data sets relying on appraisal models. According to Appraisal theories, emotions are the outcome of a multi-dimensional evaluation of events. In this paper, we present APPReddit, the first corpus of non-experimental data annotated according to this theory. After describing its development, we compare our resource with enISEAR, a corpus of events created in an experimental setting and annotated for appraisal. Results show that the two corpora can be mapped notwithstanding different typologies of data and annotations schemes. A SVM model trained on APPReddit predicts four appraisal dimensions without significant loss. Merging both corpora in a single training set increases the prediction of 3 out of 4 dimensions. Such findings pave the way to a better performing classification model for appraisal prediction.
Whose Opinions Matter? Perspective-aware Models to Identify Opinions of Hate Speech Victims in Abusive Language Detection
Jun 30, 2021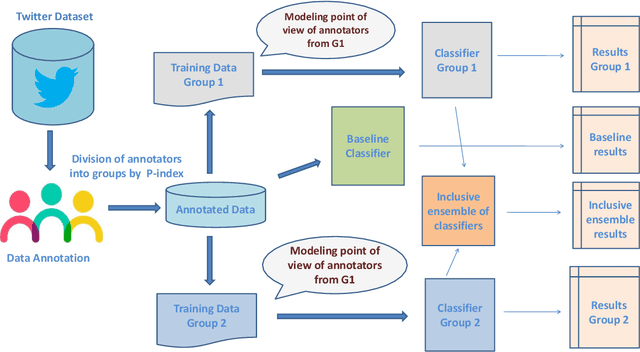
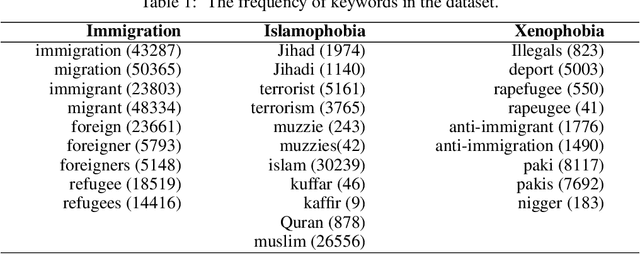
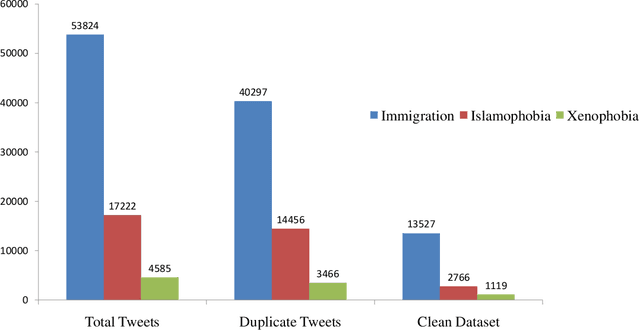
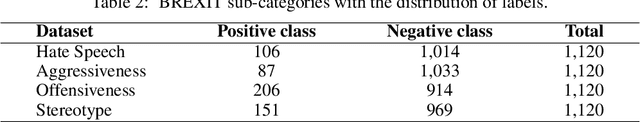
Abstract:Social media platforms provide users the freedom of expression and a medium to exchange information and express diverse opinions. Unfortunately, this has also resulted in the growth of abusive content with the purpose of discriminating people and targeting the most vulnerable communities such as immigrants, LGBT, Muslims, Jews and women. Because abusive language is subjective in nature, there might be highly polarizing topics or events involved in the annotation of abusive contents such as hate speech (HS). Therefore, we need novel approaches to model conflicting perspectives and opinions coming from people with different personal and demographic backgrounds. In this paper, we present an in-depth study to model polarized opinions coming from different communities under the hypothesis that similar characteristics (ethnicity, social background, culture etc.) can influence the perspectives of annotators on a certain phenomenon. We believe that by relying on this information, we can divide the annotators into groups sharing similar perspectives. We can create separate gold standards, one for each group, to train state-of-the-art deep learning models. We can employ an ensemble approach to combine the perspective-aware classifiers from different groups to an inclusive model. We also propose a novel resource, a multi-perspective English language dataset annotated according to different sub-categories relevant for characterising online abuse: hate speech, aggressiveness, offensiveness and stereotype. By training state-of-the-art deep learning models on this novel resource, we show how our approach improves the prediction performance of a state-of-the-art supervised classifier.
A Commonsense Reasoning Framework for Explanatory Emotion Attribution, Generation and Re-classification
Jan 11, 2021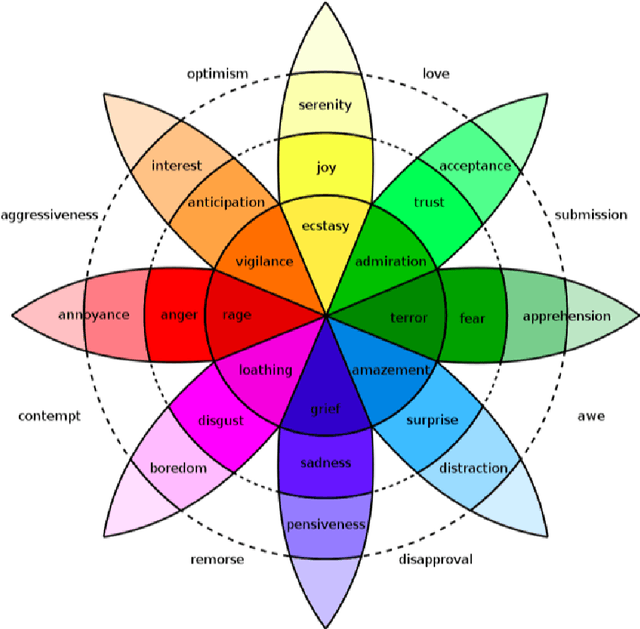
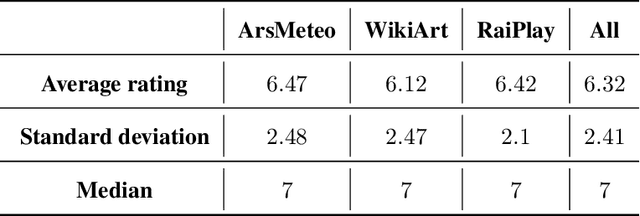

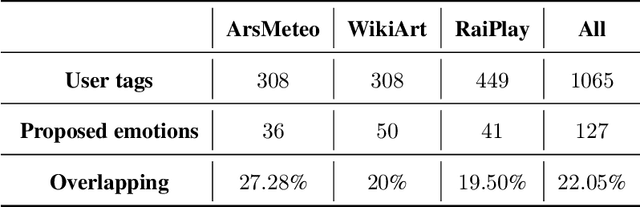
Abstract:In this work we present an explainable system for emotion attribution and recommendation (called DEGARI) relying on a recently introduced commonsense reasoning framework (the TCL logic) which is based on a human-like procedure for the automatic generation of novel concepts in a Description Logics knowledge base. Starting from an ontological formalization of emotions (known as ArsEmotica), the system exploits the logic TCL to automatically generate novel commonsense semantic representations of compound emotions (e.g. Love as derived from the combination of Joy and Trust according to the ArsEmotica model). The generated emotions correspond to prototypes, i.e. commonsense representations of given concepts, and have been used to reclassify emotion-related contents in a variety of artistic domains, ranging from art datasets to the editorial content available in RaiPlay, the online multimedia platform of RAI Radiotelevisione Italiana (the Italian public broadcasting company). We have tested our system (1) by reclassifying the available contents in the tested dataset with respect to the new generated compound emotions (2) with an evaluation, in the form of a controlled user study experiment, of the feasibility of using the obtained reclassifications as recommended emotional content. The obtained results are encouraging and pave the way to many possible further improvements and research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge