Oscar Araque
A Novel Lexicon for the Moral Foundation of Liberty
Jul 16, 2024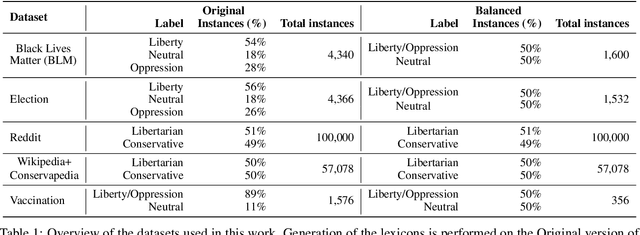
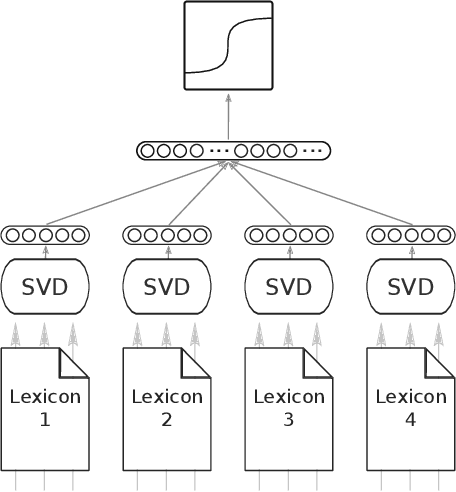

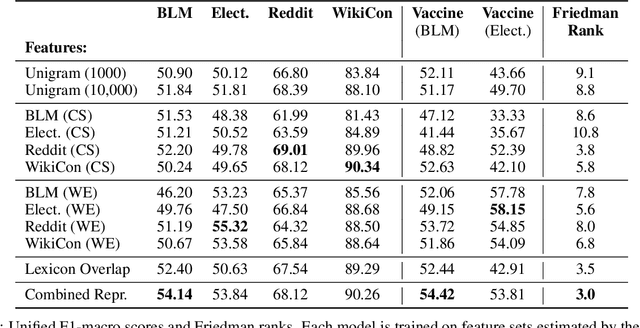
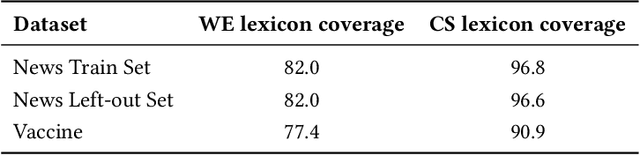
Abstract:The moral value of liberty is a central concept in our inference system when it comes to taking a stance towards controversial social issues such as vaccine hesitancy, climate change, or the right to abortion. Here, we propose a novel Liberty lexicon evaluated on more than 3,000 manually annotated data both in in- and out-of-domain scenarios. As a result of this evaluation, we produce a combined lexicon that constitutes the main outcome of this work. This final lexicon incorporates information from an ensemble of lexicons that have been generated using word embedding similarity (WE) and compositional semantics (CS). Our key contributions include enriching the liberty annotations, developing a robust liberty lexicon for broader application, and revealing the complexity of expressions related to liberty across different platforms. Through the evaluation, we show that the difficulty of the task calls for designing approaches that combine knowledge, in an effort of improving the representations of learning systems.
A Cost-aware Study of Depression Language on Social Media using Topic and Affect Contextualization
Jun 30, 2023Abstract:Depression is a growing issue in society's mental health that affects all areas of life and can even lead to suicide. Fortunately, prevention programs can be effective in its treatment. In this context, this work proposes an automatic system for detecting depression on social media based on machine learning and natural language processing methods. This paper presents the following contributions: (i) an ensemble learning system that combines several types of text representations for depression detection, including recent advances in the field; (ii) a contextualization schema through topic and affective information; (iii) an analysis of models' energy consumption, establishing a trade-off between classification performance and overall computational costs. To assess the proposed models' effectiveness, a thorough evaluation is performed in two datasets that model depressive text. Experiments indicate that the proposed contextualization strategies can improve the classification and that approaches that use Transformers can improve the overall F-score by 2% while augmenting the energy cost a hundred times. Finally, this work paves the way for future energy-wise systems by considering both the performance classification and the energy consumption.
LibertyMFD: A Lexicon to Assess the Moral Foundation of Liberty
Sep 14, 2022


Abstract:Quantifying the moral narratives expressed in the user-generated text, news, or public discourses is fundamental for understanding individuals' concerns and viewpoints and preventing violent protests and social polarisation. The Moral Foundation Theory (MFT) was developed to operationalise morality in a five-dimensional scale system. Recent developments of the theory urged for the introduction of a new foundation, the Liberty Foundation. Being only recently added to the theory, there are no available linguistic resources to assess whether liberty is present in text corpora. Given its importance to current social issues such as the vaccination debate, we propose two data-driven approaches, deriving two candidate lexicons generated based on aligned documents from online news sources with different worldviews. After extensive experimentation, we contribute to the research community a novel lexicon that assesses the liberty moral foundation in the way individuals with contrasting viewpoints express themselves through written text. The LibertyMFD dictionary can be a valuable tool for policymakers to understand diverse viewpoints on controversial social issues such as vaccination, abortion, or even uprisings, as they happen and on a large scale.
* GoodIT '22: Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Conference on Information Technology for Social Good. GoodIT'22, September 7-9, 2022, Limassol, Cyprus
O-Dang! The Ontology of Dangerous Speech Messages
Jul 13, 2022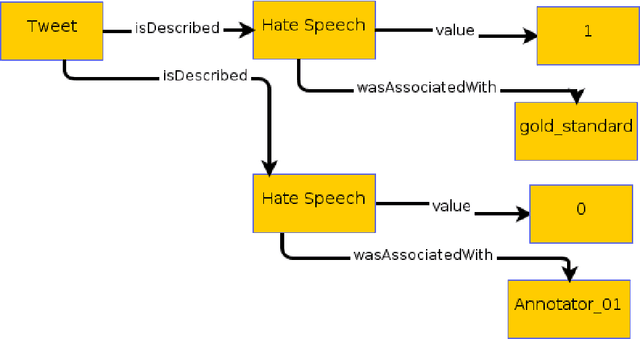
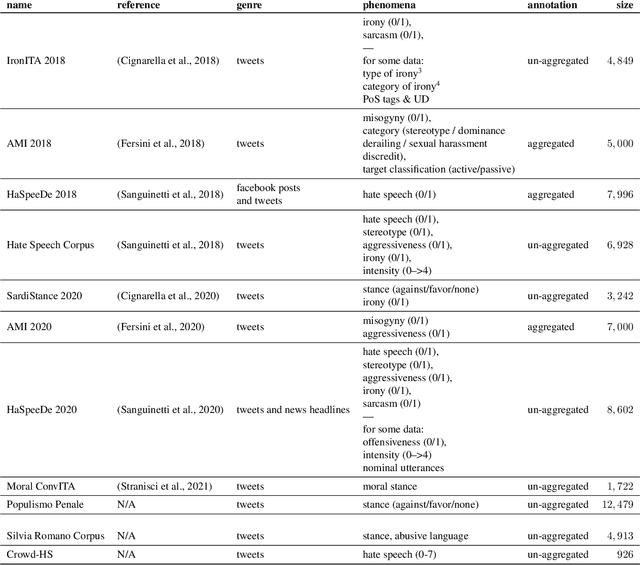
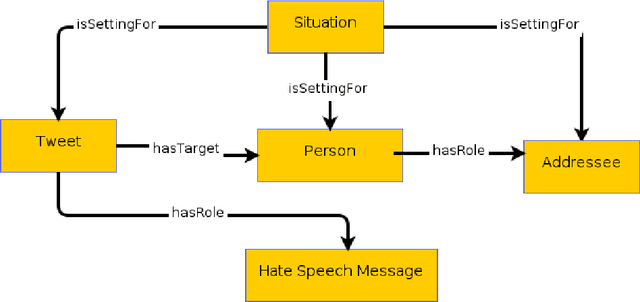
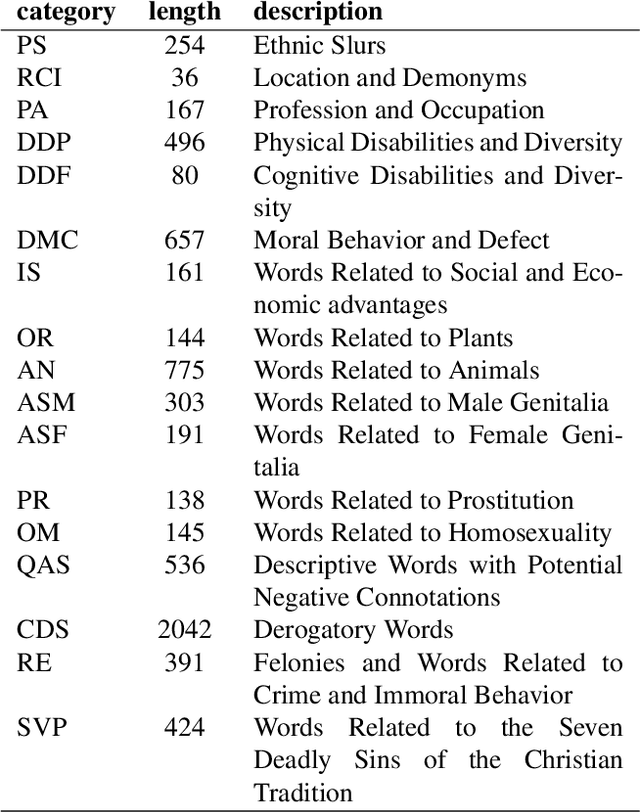
Abstract:Inside the NLP community there is a considerable amount of language resources created, annotated and released every day with the aim of studying specific linguistic phenomena. Despite a variety of attempts in order to organize such resources has been carried on, a lack of systematic methods and of possible interoperability between resources are still present. Furthermore, when storing linguistic information, still nowadays, the most common practice is the concept of "gold standard", which is in contrast with recent trends in NLP that aim at stressing the importance of different subjectivities and points of view when training machine learning and deep learning methods. In this paper we present O-Dang!: The Ontology of Dangerous Speech Messages, a systematic and interoperable Knowledge Graph (KG) for the collection of linguistic annotated data. O-Dang! is designed to gather and organize Italian datasets into a structured KG, according to the principles shared within the Linguistic Linked Open Data community. The ontology has also been designed to account for a perspectivist approach, since it provides a model for encoding both gold standard and single-annotator labels in the KG. The paper is structured as follows. In Section 1 the motivations of our work are outlined. Section 2 describes the O-Dang! Ontology, that provides a common semantic model for the integration of datasets in the KG. The Ontology Population stage with information about corpora, users, and annotations is presented in Section 3. Finally, in Section 4 an analysis of offensiveness across corpora is provided as a first case study for the resource.
MoralStrength: Exploiting a Moral Lexicon and Embedding Similarity for Moral Foundations Prediction
Apr 17, 2019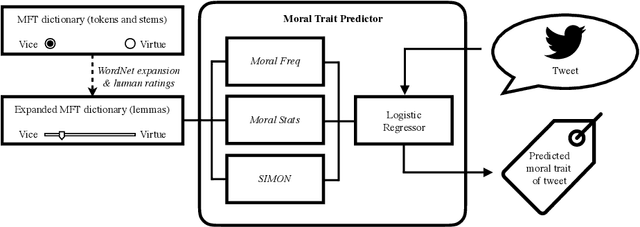
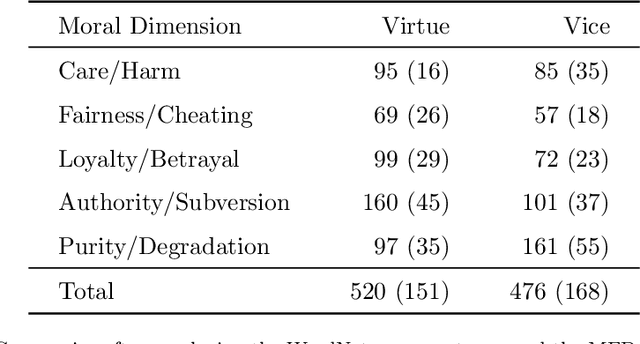
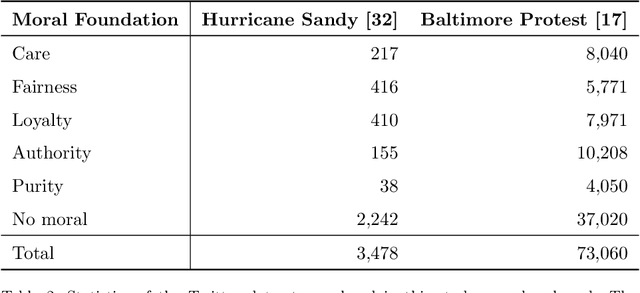
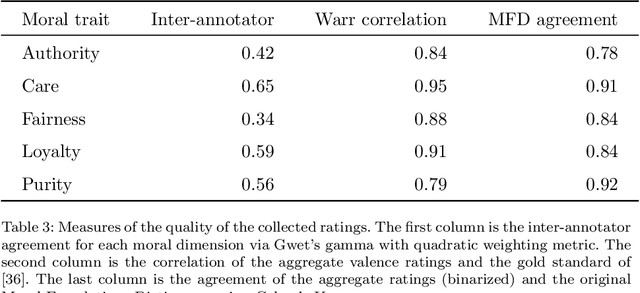
Abstract:Opinions and attitudes towards controversial social and political issues are hardly ever based on evidence alone. Moral values play a fundamental role in the decision-making process of how we perceive and interpret information. The Moral Foundations Dictionary (MFD) was developed to operationalize moral values in text. In this study, we present MoralStrength, a lexicon of approximately 1,000 lemmas, obtained as an extension of the Moral Foundations Dictionary, based on WordNet synsets. Moreover, for each lemma it provides with a crowdsourced numeric assessment of Moral Valence, indicating the strength with which a lemma is expressing the specific value. We evaluated the predictive potentials of this moral lexicon, defining three utilization approaches of increasing complexity, ranging from statistical properties of the lexicon to a deep learning approach of word embeddings based on semantic similarity. Logistic regression models trained on the features extracted from MoralStrength, significantly outperformed the current state-of-the-art, reaching an F1-score of 87.6% over the previous 62.4% (p-value<0.01). Such findings pave the way for further research, allowing for an in-depth understanding of moral narratives in text for a wide range of social issues.
A framework for fake review detection in online consumer electronics retailers
Mar 29, 2019



Abstract:The impact of online reviews on businesses has grown significantly during last years, being crucial to determine business success in a wide array of sectors, ranging from restaurants, hotels to e-commerce. Unfortunately, some users use unethical means to improve their online reputation by writing fake reviews of their businesses or competitors. Previous research has addressed fake review detection in a number of domains, such as product or business reviews in restaurants and hotels. However, in spite of its economical interest, the domain of consumer electronics businesses has not yet been thoroughly studied. This article proposes a feature framework for detecting fake reviews that has been evaluated in the consumer electronics domain. The contributions are fourfold: (i) Construction of a dataset for classifying fake reviews in the consumer electronics domain in four different cities based on scraping techniques; (ii) definition of a feature framework for fake review detection; (iii) development of a fake review classification method based on the proposed framework and (iv) evaluation and analysis of the results for each of the cities under study. We have reached an 82% F-Score on the classification task and the Ada Boost classifier has been proven to be the best one by statistical means according to the Friedman test.
* Information Processing & Management, 11 pages
DepecheMood++: a Bilingual Emotion Lexicon Built Through Simple Yet Powerful Techniques
Oct 08, 2018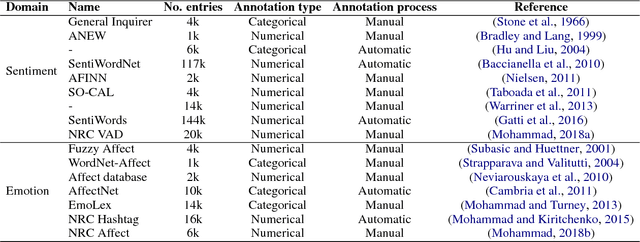

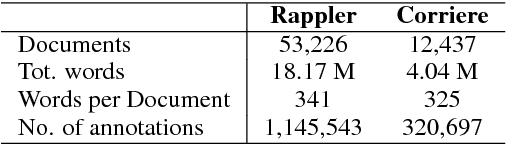
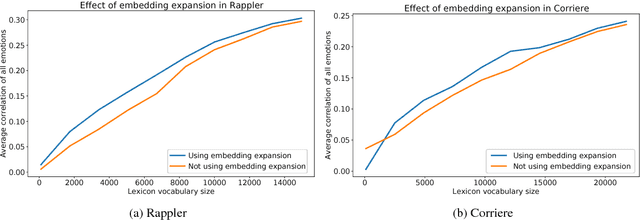
Abstract:Several lexica for sentiment analysis have been developed and made available in the NLP community. While most of these come with word polarity annotations (e.g. positive/negative), attempts at building lexica for finer-grained emotion analysis (e.g. happiness, sadness) have recently attracted significant attention. Such lexica are often exploited as a building block in the process of developing learning models for which emotion recognition is needed, and/or used as baselines to which compare the performance of the models. In this work, we contribute two new resources to the community: a) an extension of an existing and widely used emotion lexicon for English; and b) a novel version of the lexicon targeting Italian. Furthermore, we show how simple techniques can be used, both in supervised and unsupervised experimental settings, to boost performances on datasets and tasks of varying degree of domain-specificity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge