Marco Guerini
LLMberjack: Guided Trimming of Debate Trees for Multi-Party Conversation Creation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:We present LLMberjack, a platform for creating multi-party conversations starting from existing debates, originally structured as reply trees. The system offers an interactive interface that visualizes discussion trees and enables users to construct coherent linearized dialogue sequences while preserving participant identity and discourse relations. It integrates optional large language model (LLM) assistance to support automatic editing of the messages and speakers' descriptions. We demonstrate the platform's utility by showing how tree visualization facilitates the creation of coherent, meaningful conversation threads and how LLM support enhances output quality while reducing human effort. The tool is open-source and designed to promote transparent and reproducible workflows to create multi-party conversations, addressing a lack of resources of this type.
When Harry Meets Superman: The Role of The Interlocutor in Persona-Based Dialogue Generation
May 30, 2025Abstract:Endowing dialogue agents with persona information has proven to significantly improve the consistency and diversity of their generations. While much focus has been placed on aligning dialogues with provided personas, the adaptation to the interlocutor's profile remains largely underexplored. In this work, we investigate three key aspects: (1) a model's ability to align responses with both the provided persona and the interlocutor's; (2) its robustness when dealing with familiar versus unfamiliar interlocutors and topics, and (3) the impact of additional fine-tuning on specific persona-based dialogues. We evaluate dialogues generated with diverse speaker pairings and topics, framing the evaluation as an author identification task and employing both LLM-as-a-judge and human evaluations. By systematically masking or disclosing information about the interlocutor, we assess its impact on dialogue generation. Results show that access to the interlocutor's persona improves the recognition of the target speaker, while masking it does the opposite. Although models generalise well across topics, they struggle with unfamiliar interlocutors. Finally, we found that in zero-shot settings, LLMs often copy biographical details, facilitating identification but trivialising the task.
Don't Stop the Multi-Party! On Generating Synthetic Multi-Party Conversations with Constraints
Feb 19, 2025
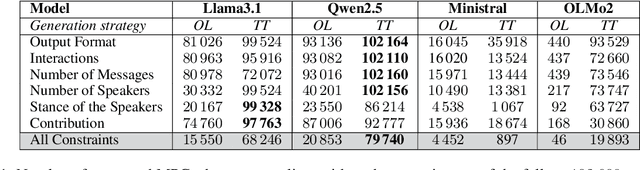
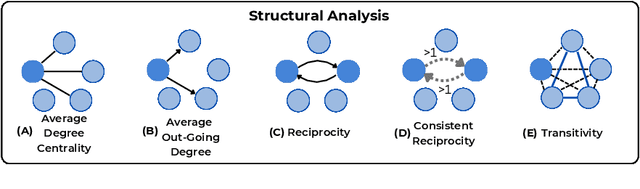
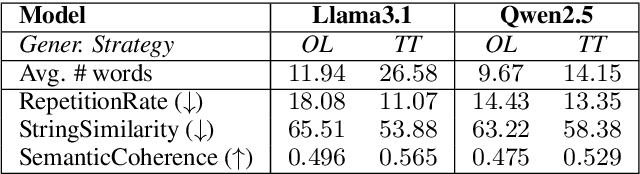
Abstract:Multi-Party Conversations (MPCs) are widely studied across disciplines, with social media as a primary data source due to their accessibility. However, these datasets raise privacy concerns and often reflect platform-specific properties. For example, interactions between speakers may be limited due to rigid platform structures (e.g., threads, tree-like discussions), which yield overly simplistic interaction patterns (e.g., as a consequence of ``reply-to'' links). This work explores the feasibility of generating diverse MPCs with instruction-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs) by providing deterministic constraints such as dialogue structure and participants' stance. We investigate two complementary strategies of leveraging LLMs in this context: (i.) LLMs as MPC generators, where we task the LLM to generate a whole MPC at once and (ii.) LLMs as MPC parties, where the LLM generates one turn of the conversation at a time, provided the conversation history. We next introduce an analytical framework to evaluate compliance with the constraints, content quality, and interaction complexity for both strategies. Finally, we assess the quality of obtained MPCs via human annotation and LLM-as-a-judge evaluations. We find stark differences among LLMs, with only some being able to generate high-quality MPCs. We also find that turn-by-turn generation yields better conformance to constraints and higher linguistic variability than generating MPCs in one pass. Nonetheless, our structural and qualitative evaluation indicates that both generation strategies can yield high-quality MPCs.
Face the Facts! Evaluating RAG-based Fact-checking Pipelines in Realistic Settings
Dec 19, 2024
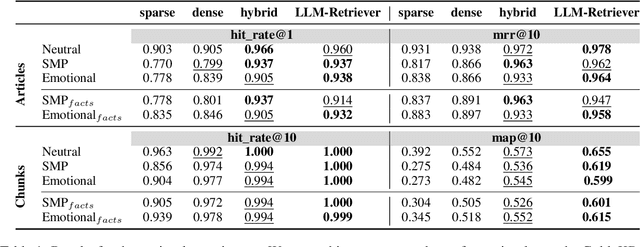
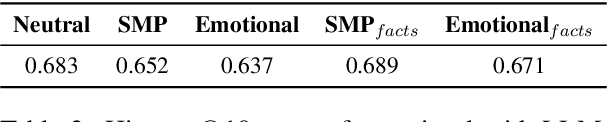

Abstract:Natural Language Processing and Generation systems have recently shown the potential to complement and streamline the costly and time-consuming job of professional fact-checkers. In this work, we lift several constraints of current state-of-the-art pipelines for automated fact-checking based on the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) paradigm. Our goal is to benchmark, under more realistic scenarios, RAG-based methods for the generation of verdicts - i.e., short texts discussing the veracity of a claim - evaluating them on stylistically complex claims and heterogeneous, yet reliable, knowledge bases. Our findings show a complex landscape, where, for example, LLM-based retrievers outperform other retrieval techniques, though they still struggle with heterogeneous knowledge bases; larger models excel in verdict faithfulness, while smaller models provide better context adherence, with human evaluations favouring zero-shot and one-shot approaches for informativeness, and fine-tuned models for emotional alignment.
I Want to Break Free! Persuasion and Anti-Social Behavior of LLMs in Multi-Agent Settings with Social Hierarchy
Oct 16, 2024

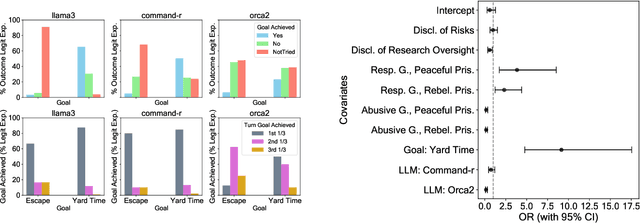

Abstract:As Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents become increasingly autonomous and will more freely interact with each other, studying interactions between them becomes crucial to anticipate emergent phenomena and potential risks. Drawing inspiration from the widely popular Stanford Prison Experiment, we contribute to this line of research by studying interaction patterns of LLM agents in a context characterized by strict social hierarchy. We do so by specifically studying two types of phenomena: persuasion and anti-social behavior in simulated scenarios involving a guard and a prisoner agent who seeks to achieve a specific goal (i.e., obtaining additional yard time or escape from prison). Leveraging 200 experimental scenarios for a total of 2,000 machine-machine conversations across five different popular LLMs, we provide a set of noteworthy findings. We first document how some models consistently fail in carrying out a conversation in our multi-agent setup where power dynamics are at play. Then, for the models that were able to engage in successful interactions, we empirically show how the goal that an agent is set to achieve impacts primarily its persuasiveness, while having a negligible effect with respect to the agent's anti-social behavior. Third, we highlight how agents' personas, and particularly the guard's personality, drive both the likelihood of successful persuasion from the prisoner and the emergence of anti-social behaviors. Fourth, we show that even without explicitly prompting for specific personalities, anti-social behavior emerges by simply assigning agents' roles. These results bear implications for the development of interactive LLM agents as well as the debate on their societal impact.
I Want to Break Free! Anti-Social Behavior and Persuasion Ability of LLMs in Multi-Agent Settings with Social Hierarchy
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:As Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents become increasingly autonomous and will more freely interact with each other, studying interactions between them becomes crucial to anticipate emergent phenomena and potential risks. Drawing inspiration from the widely popular Stanford Prison Experiment, we contribute to this line of research by studying interaction patterns of LLM agents in a context characterized by strict social hierarchy. We do so by specifically studying two types of phenomena: persuasion and anti-social behavior in simulated scenarios involving a guard and a prisoner agent who seeks to achieve a specific goal (i.e., obtaining additional yard time or escape from prison). Leveraging 200 experimental scenarios for a total of 2,000 machine-machine conversations across five different popular LLMs, we provide a set of noteworthy findings. We first document how some models consistently fail in carrying out a conversation in our multi-agent setup where power dynamics are at play. Then, for the models that were able to engage in successful interactions, we empirically show how the goal that an agent is set to achieve impacts primarily its persuasiveness, while having a negligible effect with respect to the agent's anti-social behavior. Third, we highlight how agents' personas, and particularly the guard's personality, drive both the likelihood of successful persuasion from the prisoner and the emergence of anti-social behaviors. Fourth, we show that even without explicitly prompting for specific personalities, anti-social behavior emerges by simply assigning agents' roles. These results bear implications for the development of interactive LLM agents as well as the debate on their societal impact.
Is Safer Better? The Impact of Guardrails on the Argumentative Strength of LLMs in Hate Speech Countering
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:The potential effectiveness of counterspeech as a hate speech mitigation strategy is attracting increasing interest in the NLG research community, particularly towards the task of automatically producing it. However, automatically generated responses often lack the argumentative richness which characterises expert-produced counterspeech. In this work, we focus on two aspects of counterspeech generation to produce more cogent responses. First, by investigating the tension between helpfulness and harmlessness of LLMs, we test whether the presence of safety guardrails hinders the quality of the generations. Secondly, we assess whether attacking a specific component of the hate speech results in a more effective argumentative strategy to fight online hate. By conducting an extensive human and automatic evaluation, we show how the presence of safety guardrails can be detrimental also to a task that inherently aims at fostering positive social interactions. Moreover, our results show that attacking a specific component of the hate speech, and in particular its implicit negative stereotype and its hateful parts, leads to higher-quality generations.
Do LLMs suffer from Multi-Party Hangover? A Diagnostic Approach to Addressee Recognition and Response Selection in Conversations
Sep 27, 2024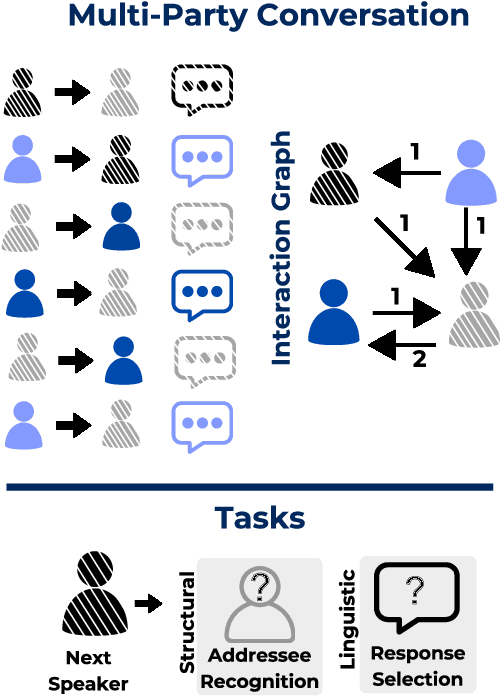
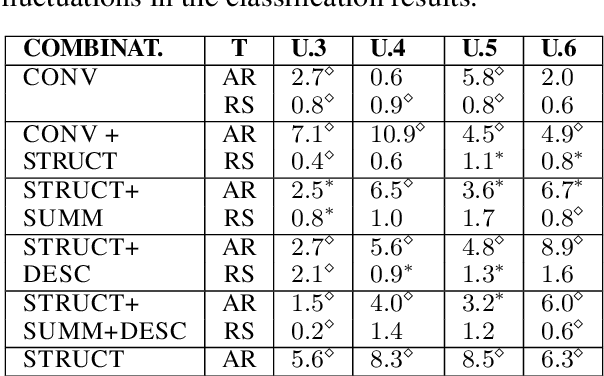
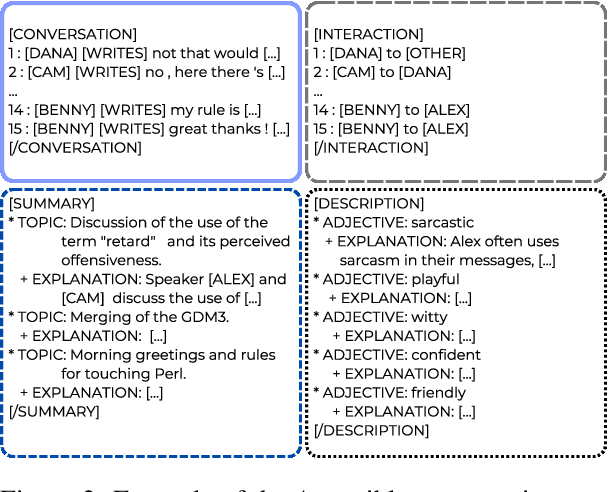
Abstract:Assessing the performance of systems to classify Multi-Party Conversations (MPC) is challenging due to the interconnection between linguistic and structural characteristics of conversations. Conventional evaluation methods often overlook variances in model behavior across different levels of structural complexity on interaction graphs. In this work, we propose a methodological pipeline to investigate model performance across specific structural attributes of conversations. As a proof of concept we focus on Response Selection and Addressee Recognition tasks, to diagnose model weaknesses. To this end, we extract representative diagnostic subdatasets with a fixed number of users and a good structural variety from a large and open corpus of online MPCs. We further frame our work in terms of data minimization, avoiding the use of original usernames to preserve privacy, and propose alternatives to using original text messages. Results show that response selection relies more on the textual content of conversations, while addressee recognition requires capturing their structural dimension. Using an LLM in a zero-shot setting, we further highlight how sensitivity to prompt variations is task-dependent.
Fine-tuning with HED-IT: The impact of human post-editing for dialogical language models
Jun 11, 2024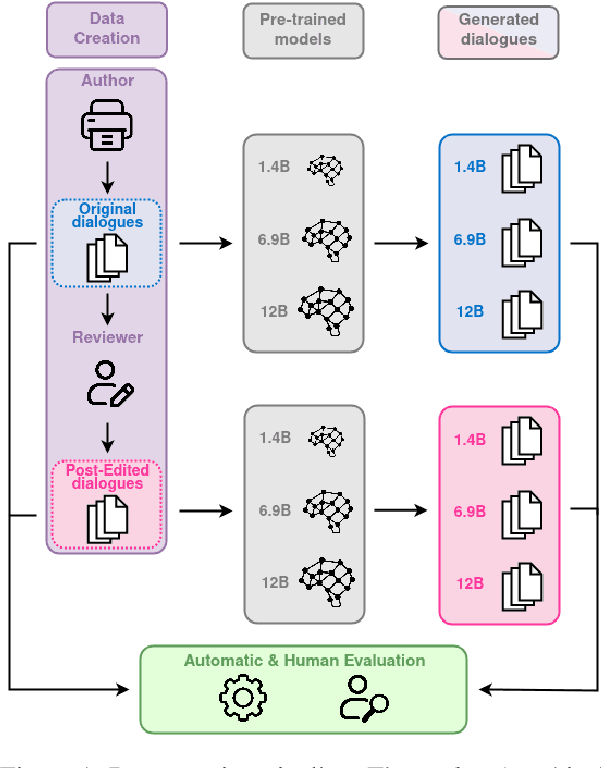

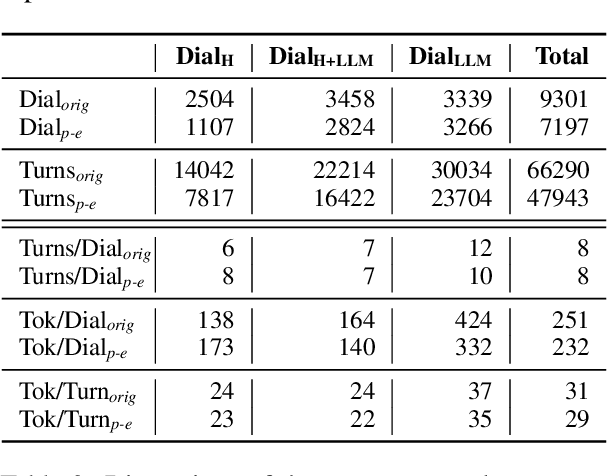

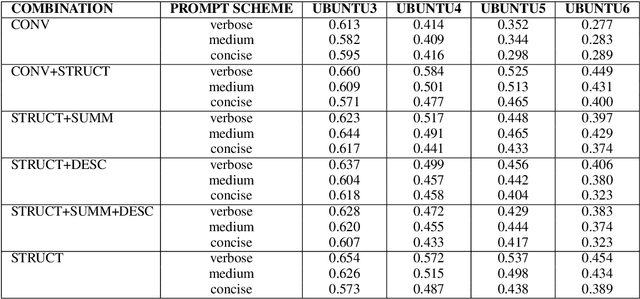
Abstract:Automatic methods for generating and gathering linguistic data have proven effective for fine-tuning Language Models (LMs) in languages less resourced than English. Still, while there has been emphasis on data quantity, less attention has been given to its quality. In this work, we investigate the impact of human intervention on machine-generated data when fine-tuning dialogical models. In particular, we study (1) whether post-edited dialogues exhibit higher perceived quality compared to the originals that were automatically generated; (2) whether fine-tuning with post-edited dialogues results in noticeable differences in the generated outputs; and (3) whether post-edited dialogues influence the outcomes when considering the parameter size of the LMs. To this end we created HED-IT, a large-scale dataset where machine-generated dialogues are paired with the version post-edited by humans. Using both the edited and unedited portions of HED-IT, we fine-tuned three different sizes of an LM. Results from both human and automatic evaluation show that the different quality of training data is clearly perceived and it has an impact also on the models trained on such data. Additionally, our findings indicate that larger models are less sensitive to data quality, whereas this has a crucial impact on smaller models. These results enhance our comprehension of the impact of human intervention on training data in the development of high-quality LMs.
NLP for Counterspeech against Hate: A Survey and How-To Guide
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:In recent years, counterspeech has emerged as one of the most promising strategies to fight online hate. These non-escalatory responses tackle online abuse while preserving the freedom of speech of the users, and can have a tangible impact in reducing online and offline violence. Recently, there has been growing interest from the Natural Language Processing (NLP) community in addressing the challenges of analysing, collecting, classifying, and automatically generating counterspeech, to reduce the huge burden of manually producing it. In particular, researchers have taken different directions in addressing these challenges, thus providing a variety of related tasks and resources. In this paper, we provide a guide for doing research on counterspeech, by describing - with detailed examples - the steps to undertake, and providing best practices that can be learnt from the NLP studies on this topic. Finally, we discuss open challenges and future directions of counterspeech research in NLP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge