Antonio Lieto
Exploring Values in Museum Artifacts in the SPICE project: a Preliminary Study
Nov 13, 2023


Abstract:This document describes the rationale, the implementation and a preliminary evaluation of a semantic reasoning tool developed in the EU H2020 SPICE project to enhance the diversity of perspectives experienced by museum visitors. The tool, called DEGARI 2.0 for values, relies on the commonsense reasoning framework TCL, and exploits an ontological model formalizingthe Haidt's theory of moral values to associate museum items with combined values and emotions. Within a museum exhibition, this tool can suggest cultural items that are associated not only with the values of already experienced or preferred objects, but also with novel items with different value stances, opening the visit experience to more inclusive interpretations of cultural content. The system has been preliminarily tested, in the context of the SPICE project, on the collection of the Hecht Museum of Haifa.
Can empathy affect the attribution of mental states to robots?
Sep 06, 2023Abstract:This paper presents an experimental study showing that the humanoid robot NAO, in a condition already validated with regards to its capacity to trigger situational empathy in humans, is able to stimulate the attribution of mental states towards itself. Indeed, results show that participants not only experienced empathy towards NAO, when the robot was afraid of losing its memory due to a malfunction, but they also attributed higher scores to the robot emotional intelligence in the Attribution of Mental State Questionnaire, in comparison with the users in the control condition. This result suggests a possible correlation between empathy toward the robot and humans' attribution of mental states to it.
A Storytelling Robot managing Persuasive and Ethical Stances via ACT-R: an Exploratory Study
Jul 27, 2021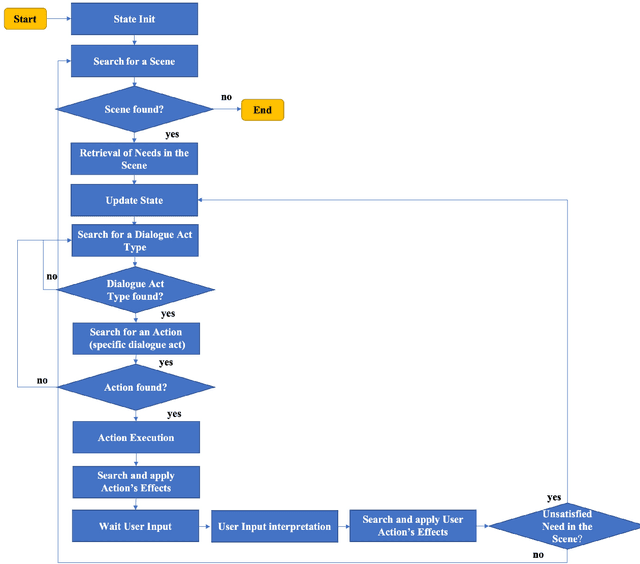
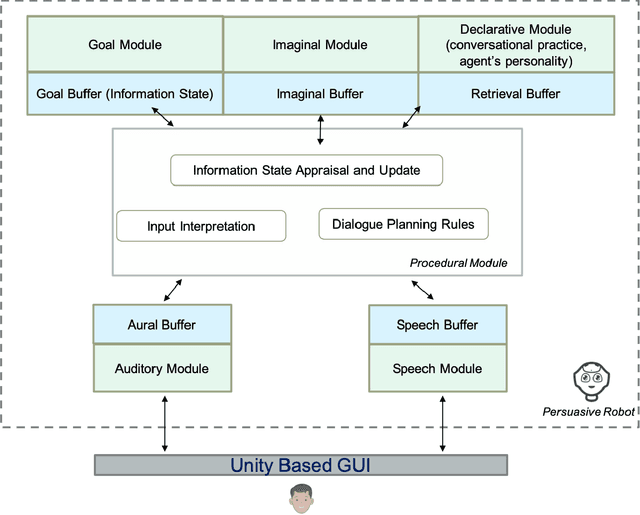

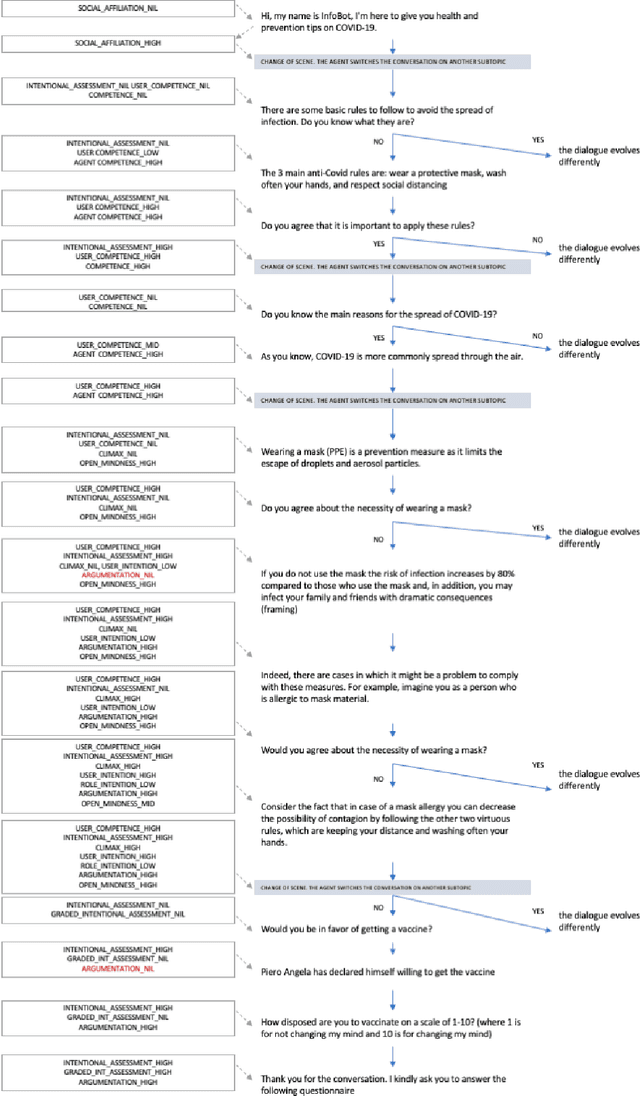
Abstract:We present a storytelling robot, controlled via the ACT-R cognitive architecture, able to adopt different persuasive techniques and ethical stances while conversing about some topics concerning COVID-19. The main contribution of the paper consists in the proposal of a needs-driven model that guides and evaluates, during the dialogue, the use (if any) of persuasive techniques available in the agent procedural memory. The portfolio of persuasive techniques tested in such a model ranges from the use of storytelling, to framing techniques and rhetorical-based arguments. To the best of our knowledge, this represents the first attempt of building a persuasive agent able to integrate a mix of explicitly grounded cognitive assumptions about dialogue management, storytelling and persuasive techniques as well as ethical attitudes. The paper presents the results of an exploratory evaluation of the system on 63 participants
* 20 pages, 7 figures
A Commonsense Reasoning Framework for Explanatory Emotion Attribution, Generation and Re-classification
Jan 11, 2021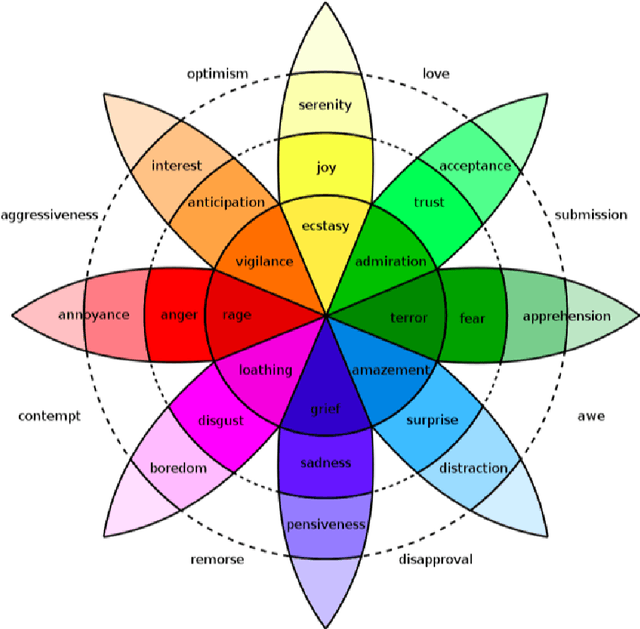
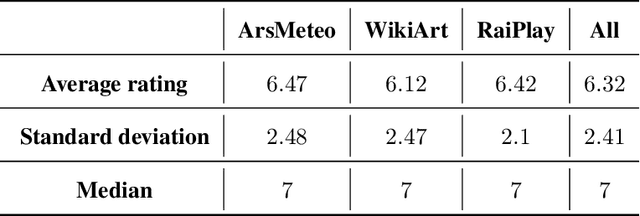

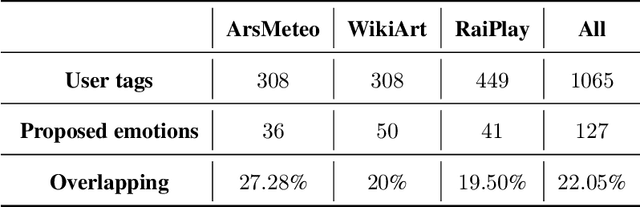
Abstract:In this work we present an explainable system for emotion attribution and recommendation (called DEGARI) relying on a recently introduced commonsense reasoning framework (the TCL logic) which is based on a human-like procedure for the automatic generation of novel concepts in a Description Logics knowledge base. Starting from an ontological formalization of emotions (known as ArsEmotica), the system exploits the logic TCL to automatically generate novel commonsense semantic representations of compound emotions (e.g. Love as derived from the combination of Joy and Trust according to the ArsEmotica model). The generated emotions correspond to prototypes, i.e. commonsense representations of given concepts, and have been used to reclassify emotion-related contents in a variety of artistic domains, ranging from art datasets to the editorial content available in RaiPlay, the online multimedia platform of RAI Radiotelevisione Italiana (the Italian public broadcasting company). We have tested our system (1) by reclassifying the available contents in the tested dataset with respect to the new generated compound emotions (2) with an evaluation, in the form of a controlled user study experiment, of the feasibility of using the obtained reclassifications as recommended emotional content. The obtained results are encouraging and pave the way to many possible further improvements and research directions.
Reasoning about Typicality and Probabilities in Preferential Description Logics
Apr 23, 2020Abstract:In this work we describe preferential Description Logics of typicality, a nonmonotonic extension of standard Description Logics by means of a typicality operator T allowing to extend a knowledge base with inclusions of the form T(C) v D, whose intuitive meaning is that normally/typically Cs are also Ds. This extension is based on a minimal model semantics corresponding to a notion of rational closure, built upon preferential models. We recall the basic concepts underlying preferential Description Logics. We also present two extensions of the preferential semantics: on the one hand, we consider probabilistic extensions, based on a distributed semantics that is suitable for tackling the problem of commonsense concept combination, on the other hand, we consider other strengthening of the rational closure semantics and construction to avoid the so-called blocking of property inheritance problem.
Heterogeneous Proxytypes Extended: Integrating Theory-like Representations and Mechanisms with Prototypes and Exemplars
Sep 04, 2019
Abstract:The paper introduces an extension of the proposal according to which conceptual representations in cognitive agents should be intended as heterogeneous proxytypes. The main contribution of this paper is in that it details how to reconcile, under a heterogeneous representational perspective, different theories of typicality about conceptual representation and reasoning. In particular, it provides a novel theoretical hypothesis - as well as a novel categorization algorithm called DELTA - showing how to integrate the representational and reasoning assumptions of the theory-theory of concepts with the those ascribed to the prototype and exemplars-based theories.
A Description Logic Framework for Commonsense Conceptual Combination Integrating Typicality, Probabilities and Cognitive Heuristics
Nov 07, 2018

Abstract:We propose a nonmonotonic Description Logic of typicality able to account for the phenomenon of concept combination of prototypical concepts. The proposed logic relies on the logic of typicality ALC TR, whose semantics is based on the notion of rational closure, as well as on the distributed semantics of probabilistic Description Logics, and is equipped with a cognitive heuristic used by humans for concept composition. We first extend the logic of typicality ALC TR by typicality inclusions whose intuitive meaning is that "there is probability p about the fact that typical Cs are Ds". As in the distributed semantics, we define different scenarios containing only some typicality inclusions, each one having a suitable probability. We then focus on those scenarios whose probabilities belong to a given and fixed range, and we exploit such scenarios in order to ascribe typical properties to a concept C obtained as the combination of two prototypical concepts. We also show that reasoning in the proposed Description Logic is EXPTIME-complete as for the underlying ALC.
Representational Issues in the Debate on the Standard Model of the Mind
Apr 23, 2018Abstract:In this paper we discuss some of the issues concerning the Memory and Content aspects in the recent debate on the identification of a Standard Model of the Mind (Laird, Lebiere, and Rosenbloom in press). In particular, we focus on the representational models concerning the Declarative Memories of current Cognitive Architectures (CAs). In doing so we outline some of the main problems affecting the current CAs and suggest that the Conceptual Spaces, a representational framework developed by Gardenfors, is worth-considering to address such problems. Finally, we briefly analyze the alternative representational assumptions employed in the three CAs constituting the current baseline for the Standard Model (i.e. SOAR, ACT-R and Sigma). In doing so, we point out the respective differences and discuss their implications in the light of the analyzed problems.
Conceptual Spaces for Cognitive Architectures: A Lingua Franca for Different Levels of Representation
Jan 02, 2017


Abstract:During the last decades, many cognitive architectures (CAs) have been realized adopting different assumptions about the organization and the representation of their knowledge level. Some of them (e.g. SOAR [Laird (2012)]) adopt a classical symbolic approach, some (e.g. LEABRA [O'Reilly and Munakata (2000)]) are based on a purely connectionist model, while others (e.g. CLARION [Sun (2006)] adopt a hybrid approach combining connectionist and symbolic representational levels. Additionally, some attempts (e.g. biSOAR) trying to extend the representational capacities of CAs by integrating diagrammatical representations and reasoning are also available [Kurup and Chandrasekaran (2007)]. In this paper we propose a reflection on the role that Conceptual Spaces, a framework developed by Peter G\"ardenfors [G\"ardenfors (2000)] more than fifteen years ago, can play in the current development of the Knowledge Level in Cognitive Systems and Architectures. In particular, we claim that Conceptual Spaces offer a lingua franca that allows to unify and generalize many aspects of the symbolic, sub-symbolic and diagrammatic approaches (by overcoming some of their typical problems) and to integrate them on a common ground. In doing so we extend and detail some of the arguments explored by G\"ardenfors [G\"ardenfors (1997)] for defending the need of a conceptual, intermediate, representation level between the symbolic and the sub-symbolic one.
Artwork creation by a cognitive architecture integrating computational creativity and dual process approaches
Jan 04, 2016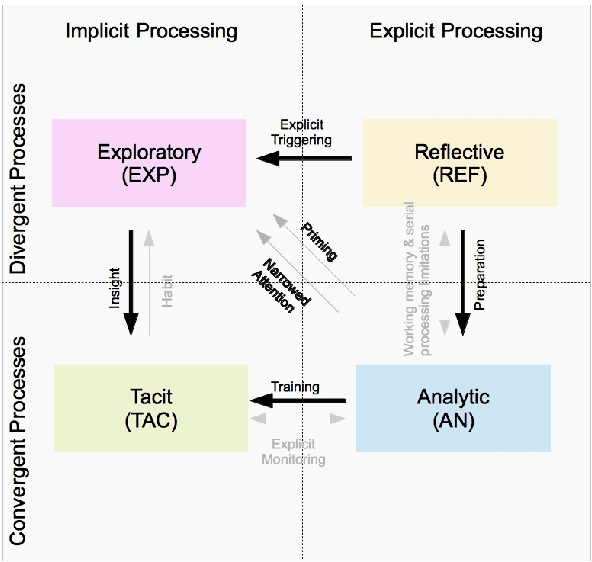
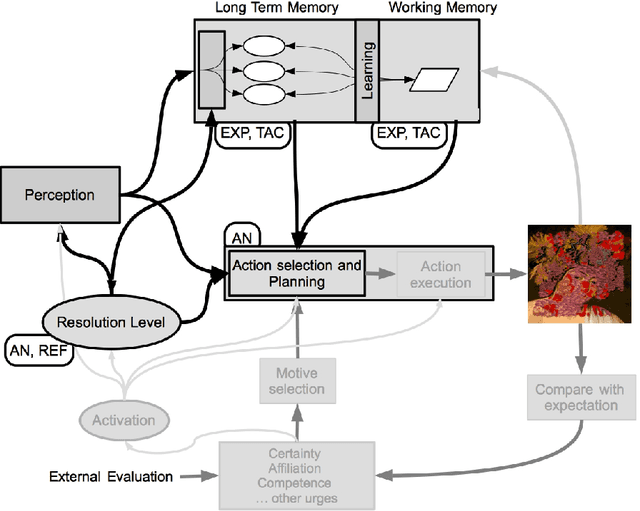
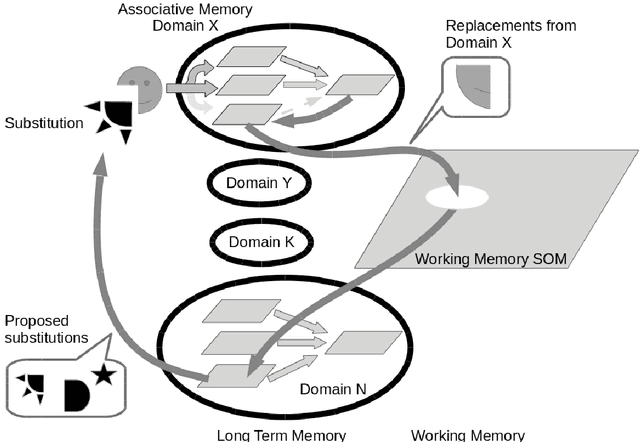

Abstract:The paper proposes a novel cognitive architecture (CA) for computational creativity based on the Psi model and on the mechanisms inspired by dual process theories of reasoning and rationality. In recent years, many cognitive models have focused on dual process theories to better describe and implement complex cognitive skills in artificial agents, but creativity has been approached only at a descriptive level. In previous works we have described various modules of the cognitive architecture that allows a robot to execute creative paintings. By means of dual process theories we refine some relevant mechanisms to obtain artworks, and in particular we explain details about the resolution level of the CA dealing with different strategies of access to the Long Term Memory (LTM) and managing the interaction between S1 and S2 processes of the dual process theory. The creative process involves both divergent and convergent processes in either implicit or explicit manner. This leads to four activities (exploratory, reflective, tacit, and analytic) that, triggered by urges and motivations, generate creative acts. These creative acts exploit both the LTM and the WM in order to make novel substitutions to a perceived image by properly mixing parts of pictures coming from different domains. The paper highlights the role of the interaction between S1 and S2 processes, modulated by the resolution level, which focuses the attention of the creative agent by broadening or narrowing the exploration of novel solutions, or even drawing the solution from a set of already made associations. An example of artificial painter is described in some experimentations by using a robotic platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge