Veeky Baths
LLaVA Finds Free Lunch: Teaching Human Behavior Improves Content Understanding Abilities Of LLMs
May 02, 2024Abstract:Communication is defined as ``Who says what to whom with what effect.'' A message from a communicator generates downstream receiver effects, also known as behavior. Receiver behavior, being a downstream effect of the message, carries rich signals about it. Even after carrying signals about the message, the behavior data is often ignored while training large language models. We show that training LLMs on receiver behavior can actually help improve their content-understanding abilities. Specifically, we show that training LLMs to predict the receiver behavior of likes and comments improves the LLM's performance on a wide variety of downstream content understanding tasks. We show this performance increase over 40 video and image understanding tasks over 23 benchmark datasets across both 0-shot and fine-tuning settings, outperforming many supervised baselines. Moreover, since receiver behavior, such as likes and comments, is collected by default on the internet and does not need any human annotations to be useful, the performance improvement we get after training on this data is essentially free-lunch. We release the receiver behavior cleaned comments and likes of 750k images and videos collected from multiple platforms along with our instruction-tuning data.
Continuous Time Continuous Space Homeostatic Reinforcement Learning (CTCS-HRRL) : Towards Biological Self-Autonomous Agent
Jan 17, 2024Abstract:Homeostasis is a biological process by which living beings maintain their internal balance. Previous research suggests that homeostasis is a learned behaviour. Recently introduced Homeostatic Regulated Reinforcement Learning (HRRL) framework attempts to explain this learned homeostatic behavior by linking Drive Reduction Theory and Reinforcement Learning. This linkage has been proven in the discrete time-space, but not in the continuous time-space. In this work, we advance the HRRL framework to a continuous time-space environment and validate the CTCS-HRRL (Continuous Time Continuous Space HRRL) framework. We achieve this by designing a model that mimics the homeostatic mechanisms in a real-world biological agent. This model uses the Hamilton-Jacobian Bellman Equation, and function approximation based on neural networks and Reinforcement Learning. Through a simulation-based experiment we demonstrate the efficacy of this model and uncover the evidence linked to the agent's ability to dynamically choose policies that favor homeostasis in a continuously changing internal-state milieu. Results of our experiments demonstrate that agent learns homeostatic behaviour in a CTCS environment, making CTCS-HRRL a promising framework for modellng animal dynamics and decision-making.
Long-Term Memorability On Advertisements
Sep 01, 2023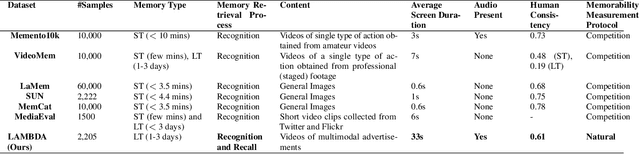
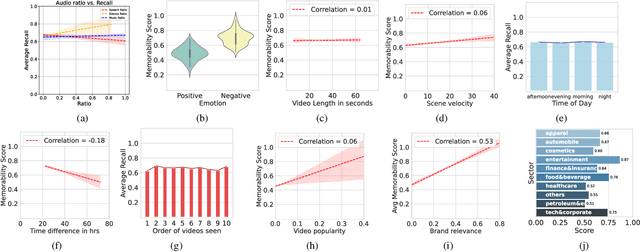
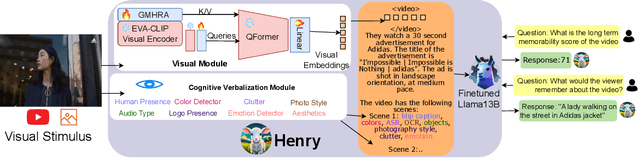
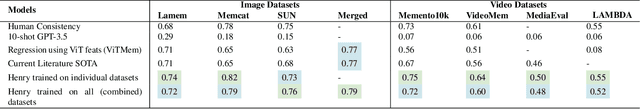
Abstract:Marketers spend billions of dollars on advertisements but to what end? At the purchase time, if customers cannot recognize a brand for which they saw an ad, the money spent on the ad is essentially wasted. Despite its importance in marketing, until now, there has been no study on the memorability of ads in the ML literature. Most studies have been conducted on short-term recall (<5 mins) on specific content types like object and action videos. On the other hand, the advertising industry only cares about long-term memorability (a few hours or longer), and advertisements are almost always highly multimodal, depicting a story through its different modalities (text, images, and videos). With this motivation, we conduct the first large scale memorability study consisting of 1203 participants and 2205 ads covering 276 brands. Running statistical tests over different participant subpopulations and ad-types, we find many interesting insights into what makes an ad memorable - both content and human factors. For example, we find that brands which use commercials with fast moving scenes are more memorable than those with slower scenes (p=8e-10) and that people who use ad-blockers remember lower number of ads than those who don't (p=5e-3). Further, with the motivation of simulating the memorability of marketing materials for a particular audience, ultimately helping create one, we present a novel model, Sharingan, trained to leverage real-world knowledge of LLMs and visual knowledge of visual encoders to predict the memorability of a content. We test our model on all the prominent memorability datasets in literature (both images and videos) and achieve state of the art across all of them. We conduct extensive ablation studies across memory types, modality, brand, and architectural choices to find insights into what drives memory.
Probing Semantic Grounding in Language Models of Code with Representational Similarity Analysis
Jul 15, 2022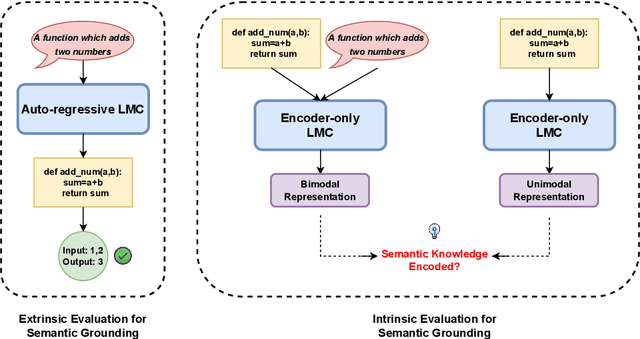
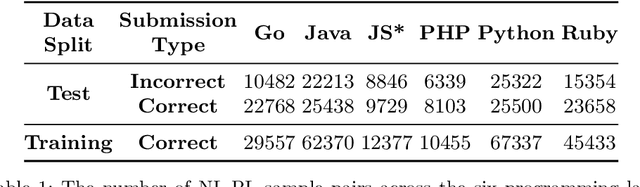
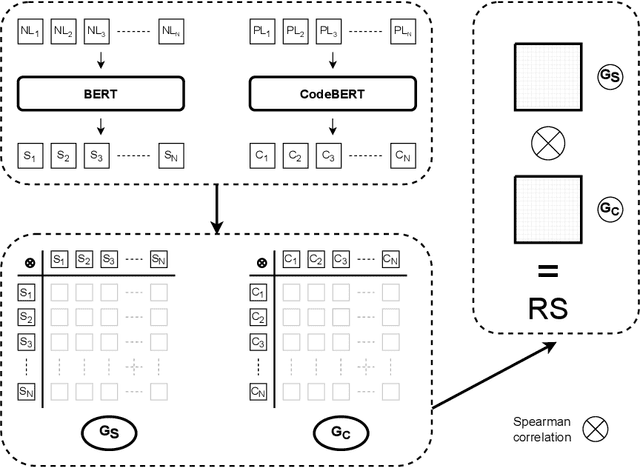
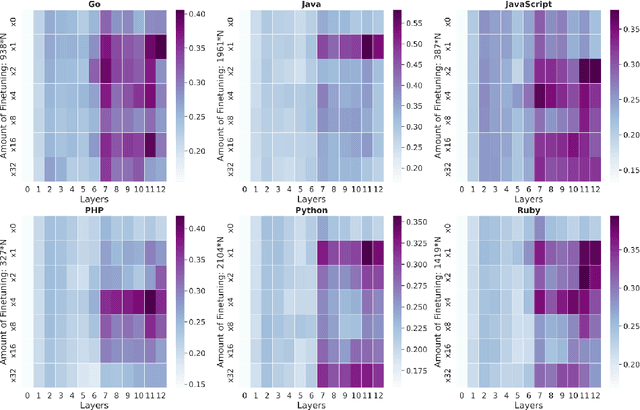
Abstract:Representational Similarity Analysis is a method from cognitive neuroscience, which helps in comparing representations from two different sources of data. In this paper, we propose using Representational Similarity Analysis to probe the semantic grounding in language models of code. We probe representations from the CodeBERT model for semantic grounding by using the data from the IBM CodeNet dataset. Through our experiments, we show that current pre-training methods do not induce semantic grounding in language models of code, and instead focus on optimizing form-based patterns. We also show that even a little amount of fine-tuning on semantically relevant tasks increases the semantic grounding in CodeBERT significantly. Our ablations with the input modality to the CodeBERT model show that using bimodal inputs (code and natural language) over unimodal inputs (only code) gives better semantic grounding and sample efficiency during semantic fine-tuning. Finally, our experiments with semantic perturbations in code reveal that CodeBERT is able to robustly distinguish between semantically correct and incorrect code.
ML-Based Analysis to Identify Speech Features Relevant in Predicting Alzheimer's Disease
Oct 25, 2021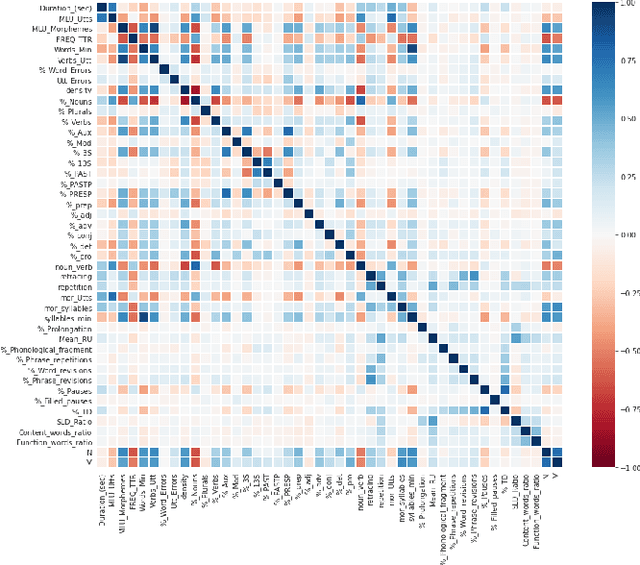
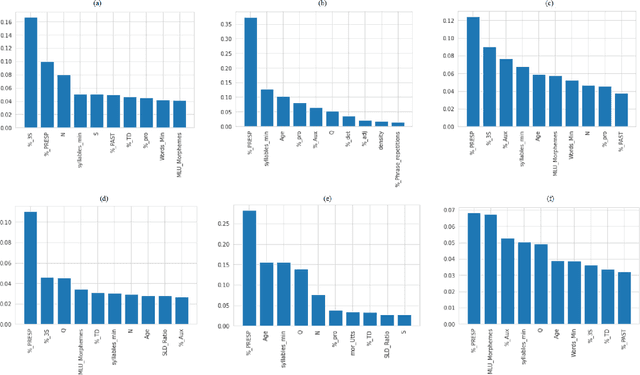
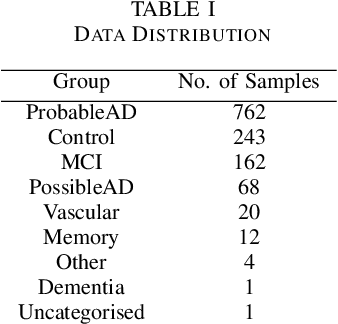

Abstract:Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that affects nearly 50 million individuals across the globe and is one of the leading causes of deaths globally. It is projected that by 2050, the number of people affected by the disease would more than double. Consequently, the growing advancements in technology beg the question, can technology be used to predict Alzheimer's for a better and early diagnosis? In this paper, we focus on this very problem. Specifically, we have trained both ML models and neural networks to predict and classify participants based on their speech patterns. We computed a number of linguistic variables using DementiaBank's Pitt Corpus, a database consisting of transcripts of interviews with subjects suffering from multiple neurodegenerative diseases. We then trained both binary classifiers, as well as multiclass classifiers to distinguish AD from normal aging and other neurodegenerative diseases. We also worked on establishing the link between specific speech factors that can help determine the onset of AD. Confusion matrices and feature importance graphs have been plotted model-wise to compare the performances of our models. In both multiclass and binary classification, neural networks were found to outperform the other models with a testing accuracy of 76.44% and 92.05% respectively. For the feature importance, it was concluded that '%_PRESP' (present participle), '%_3S' (3rd person present tense markers) were two of the most important speech features for our classifiers in predicting AD.
Deep Neural Networks on EEG Signals to Predict Auditory Attention Score Using Gramian Angular Difference Field
Oct 24, 2021



Abstract:Auditory attention is a selective type of hearing in which people focus their attention intentionally on a specific source of a sound or spoken words whilst ignoring or inhibiting other auditory stimuli. In some sense, the auditory attention score of an individual shows the focus the person can have in auditory tasks. The recent advancements in deep learning and in the non-invasive technologies recording neural activity beg the question, can deep learning along with technologies such as electroencephalography (EEG) be used to predict the auditory attention score of an individual? In this paper, we focus on this very problem of estimating a person's auditory attention level based on their brain's electrical activity captured using 14-channeled EEG signals. More specifically, we deal with attention estimation as a regression problem. The work has been performed on the publicly available Phyaat dataset. The concept of Gramian Angular Difference Field (GADF) has been used to convert time-series EEG data into an image having 14 channels, enabling us to train various deep learning models such as 2D CNN, 3D CNN, and convolutional autoencoders. Their performances have been compared amongst themselves as well as with the work done previously. Amongst the different models we tried, 2D CNN gave the best performance. It outperformed the existing methods by a decent margin of 0.22 mean absolute error (MAE).
Alzheimers Dementia Detection using Acoustic & Linguistic features and Pre-Trained BERT
Sep 24, 2021


Abstract:Alzheimers disease is a fatal progressive brain disorder that worsens with time. It is high time we have inexpensive and quick clinical diagnostic techniques for early detection and care. In previous studies, various Machine Learning techniques and Pre-trained Deep Learning models have been used in conjunction with the extraction of various acoustic and linguistic features. Our study focuses on three models for the classification task in the ADReSS (The Alzheimers Dementia Recognition through Spontaneous Speech) 2021 Challenge. We use the well-balanced dataset provided by the ADReSS Challenge for training and validating our models. Model 1 uses various acoustic features from the eGeMAPs feature-set, Model 2 uses various linguistic features that we generated from auto-generated transcripts and Model 3 uses the auto-generated transcripts directly to extract features using a Pre-trained BERT and TF-IDF. These models are described in detail in the models section.
Wheelchair automation by a hybrid BCI system using SSVEP and eye blinks
Jun 10, 2021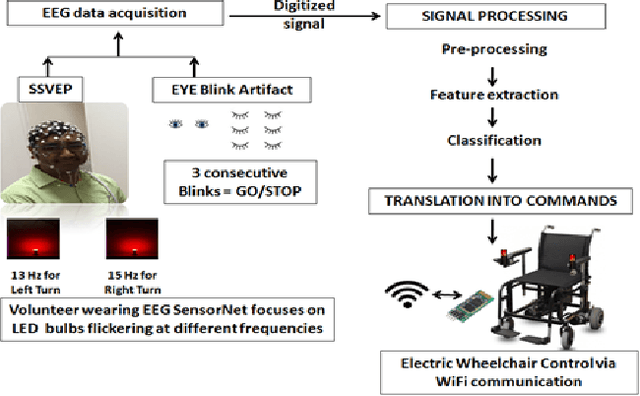
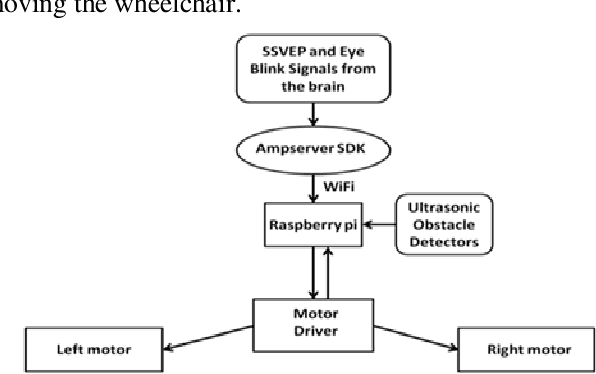
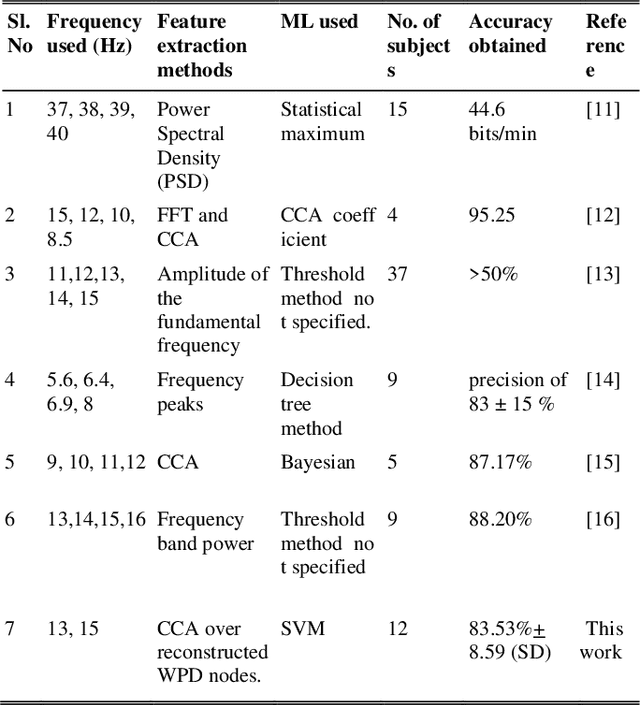
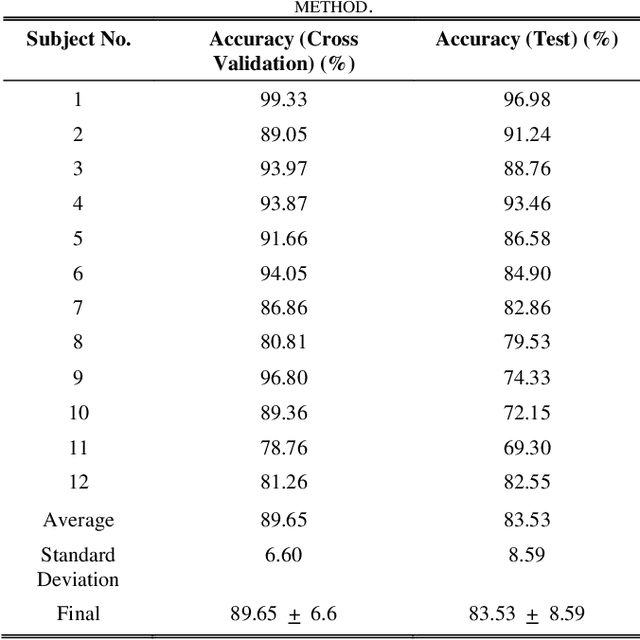
Abstract:This work proposes a hybrid Brain Computer Interface system for the automation of a wheelchair for the disabled. Herein a working prototype of a BCI-based wheelchair is detailed that can navigate inside a typical home environment with minimum structural modification and without any visual obstruction and discomfort to the user. The prototype is based on a combined mechanism of steady-state visually evoked potential and eye blinks. To elicit SSVEP, LEDs flickering at 13Hz and 15Hz were used to select the left and right direction, respectively, and EEG data was recorded. In addition, the occurrence of three continuous blinks was used as an indicator for stopping an ongoing action. The wavelet packet denoising method was applied, followed by feature extraction methods such as Wavelet Packet Decomposition and Canonical Correlation Analysis over narrowband reconstructed EEG signals. Bayesian optimization was used to obtain 5 fold cross-validations to optimize the hyperparameters of the Support Vector Machine. The resulting new model was tested and the average cross-validation accuracy 89.65% + 6.6% (SD) and testing accuracy 83.53% + 8.59% (SD) were obtained. The wheelchair was controlled by RaspberryPi through WiFi. The developed prototype demonstrated an average of 86.97% success rate for all trials with 4.015s for each command execution. The prototype can be used efficiently in a home environment without causing any discomfort to the user.
Using Diachronic Distributed Word Representations as Models of Lexical Development in Children
May 11, 2021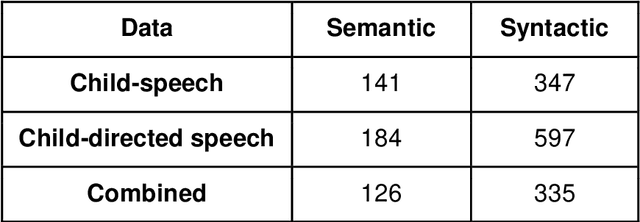
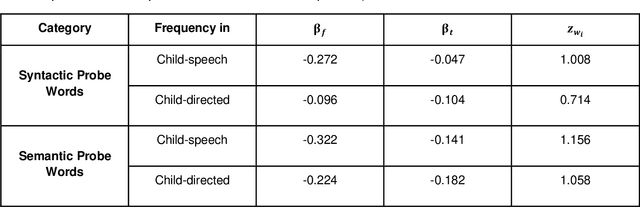
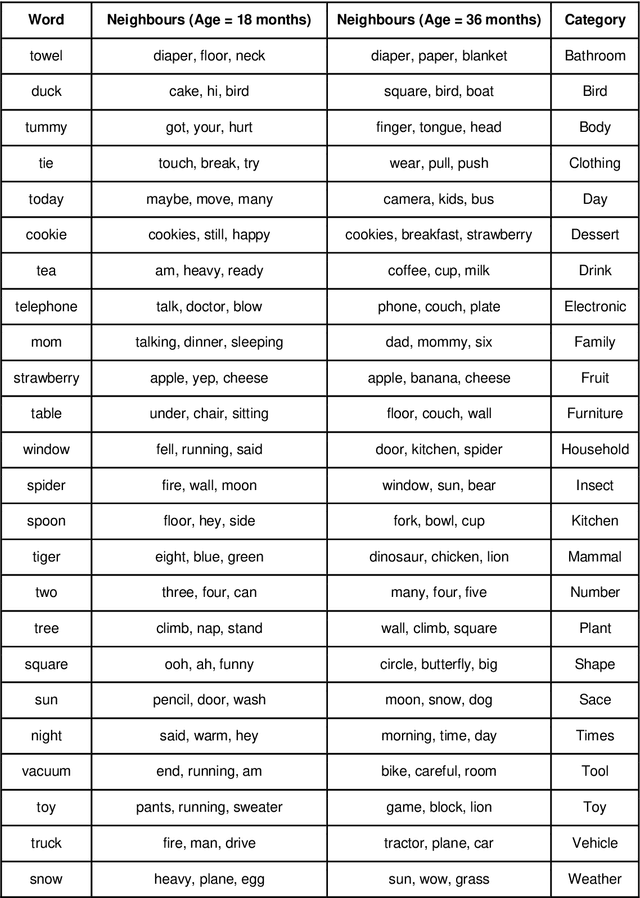
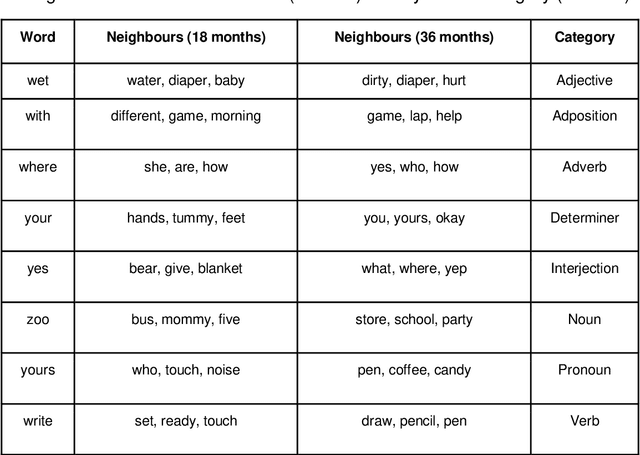
Abstract:Recent work has shown that distributed word representations can encode abstract semantic and syntactic information from child-directed speech. In this paper, we use diachronic distributed word representations to perform temporal modeling and analysis of lexical development in children. Unlike all previous work, we use temporally sliced speech corpus to learn distributed word representations of child and child-directed speech. Through our modeling experiments, we demonstrate the dynamics of growing lexical knowledge in children over time, as compared against a saturated level of lexical knowledge in child-directed adult speech. We also fit linear mixed-effects models with the rate of semantic change in the diachronic representations and word frequencies. This allows us to inspect the role of word frequencies towards lexical development in children. Further, we perform a qualitative analysis of the diachronic representations from our model, which reveals the categorization and word associations in the mental lexicon of children.
Vyākarana: A Colorless Green Benchmark for Syntactic Evaluation in Indic Languages
Mar 01, 2021

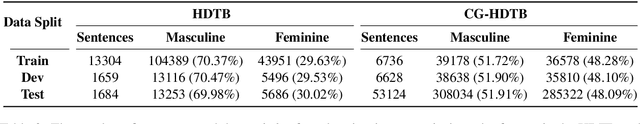
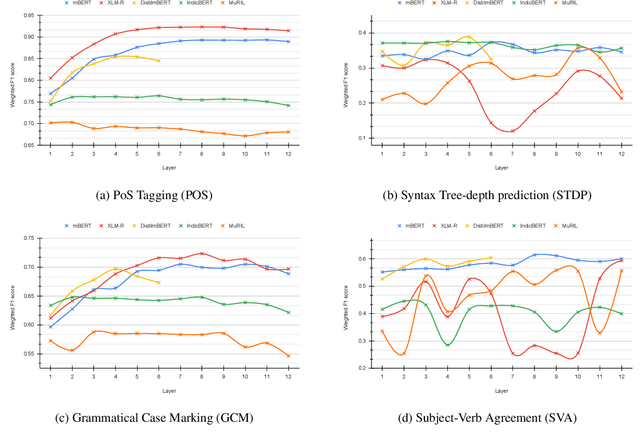
Abstract:While there has been significant progress towards developing NLU datasets and benchmarks for Indic languages, syntactic evaluation has been relatively less explored. Unlike English, Indic languages have rich morphosyntax, grammatical genders, free linear word-order, and highly inflectional morphology. In this paper, we introduce Vy\=akarana: a benchmark of gender-balanced Colorless Green sentences in Indic languages for syntactic evaluation of multilingual language models. The benchmark comprises four syntax-related tasks: PoS Tagging, Syntax Tree-depth Prediction, Grammatical Case Marking, and Subject-Verb Agreement. We use the datasets from the evaluation tasks to probe five multilingual language models of varying architectures for syntax in Indic languages. Our results show that the token-level and sentence-level representations from the Indic language models (IndicBERT and MuRIL) do not capture the syntax in Indic languages as efficiently as the other highly multilingual language models. Further, our layer-wise probing experiments reveal that while mBERT, DistilmBERT, and XLM-R localize the syntax in middle layers, the Indic language models do not show such syntactic localization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge