Swati Agarwal
Predicting ATP binding sites in protein sequences using Deep Learning and Natural Language Processing
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:Predicting ATP-Protein Binding sites in genes is of great significance in the field of Biology and Medicine. The majority of research in this field has been conducted through time- and resource-intensive 'wet experiments' in laboratories. Over the years, researchers have been investigating computational methods computational methods to accomplish the same goals, utilising the strength of advanced Deep Learning and NLP algorithms. In this paper, we propose to develop methods to classify ATP-Protein binding sites. We conducted various experiments mainly using PSSMs and several word embeddings as features. We used 2D CNNs and LightGBM classifiers as our chief Deep Learning Algorithms. The MP3Vec and BERT models have also been subjected to testing in our study. The outcomes of our experiments demonstrated improvement over the state-of-the-art benchmarks.
Probing Semantic Grounding in Language Models of Code with Representational Similarity Analysis
Jul 15, 2022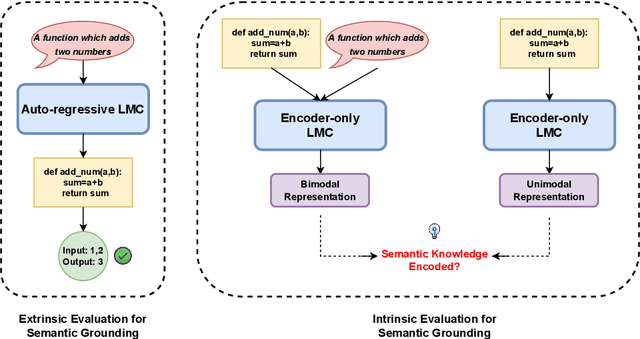
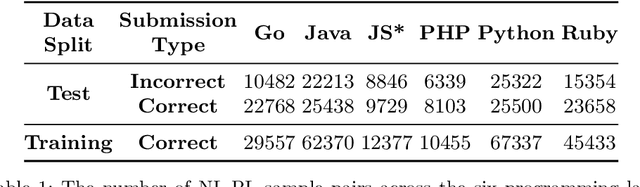
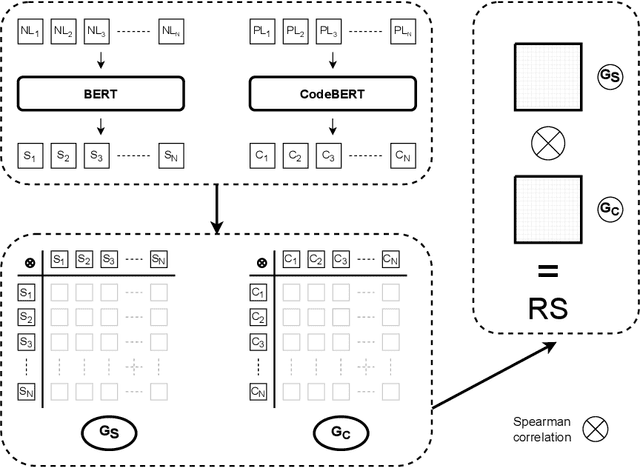
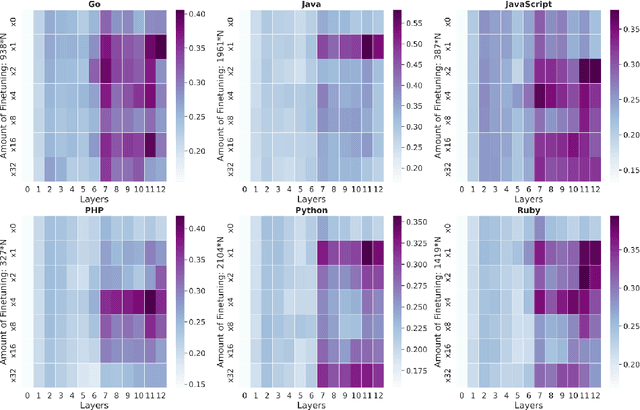
Abstract:Representational Similarity Analysis is a method from cognitive neuroscience, which helps in comparing representations from two different sources of data. In this paper, we propose using Representational Similarity Analysis to probe the semantic grounding in language models of code. We probe representations from the CodeBERT model for semantic grounding by using the data from the IBM CodeNet dataset. Through our experiments, we show that current pre-training methods do not induce semantic grounding in language models of code, and instead focus on optimizing form-based patterns. We also show that even a little amount of fine-tuning on semantically relevant tasks increases the semantic grounding in CodeBERT significantly. Our ablations with the input modality to the CodeBERT model show that using bimodal inputs (code and natural language) over unimodal inputs (only code) gives better semantic grounding and sample efficiency during semantic fine-tuning. Finally, our experiments with semantic perturbations in code reveal that CodeBERT is able to robustly distinguish between semantically correct and incorrect code.
BPGC at SemEval-2020 Task 11: Propaganda Detection in News Articles with Multi-Granularity Knowledge Sharing and Linguistic Features based Ensemble Learning
May 31, 2020
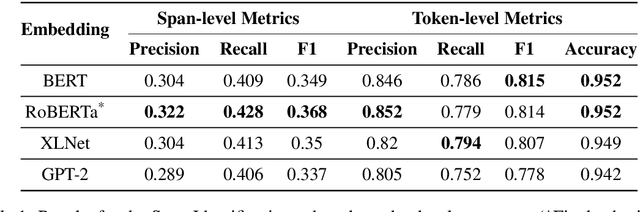
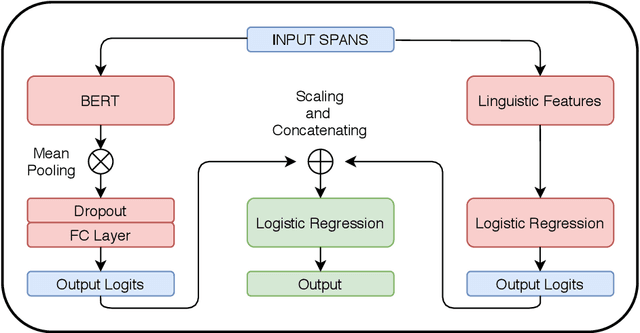
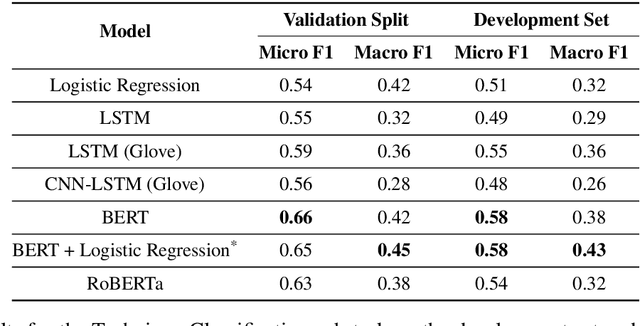
Abstract:Propaganda spreads the ideology and beliefs of like-minded people, brainwashing their audiences, and sometimes leading to violence. SemEval 2020 Task-11 aims to design automated systems for news propaganda detection. Task-11 consists of two sub-tasks, namely, Span Identification - given any news article, the system tags those specific fragments which contain at least one propaganda technique; and Technique Classification - correctly classify a given propagandist statement amongst 14 propaganda techniques. For sub-task 1, we use contextual embeddings extracted from pre-trained transformer models to represent the text data at various granularities and propose a multi-granularity knowledge sharing approach. For sub-task 2, we use an ensemble of BERT and logistic regression classifiers with linguistic features. Our results reveal that the linguistic features are the strong indicators for covering minority classes in a highly imbalanced dataset.
Malware Detection using Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Apr 04, 2019



Abstract:Research shows that over the last decade, malware has been growing exponentially, causing substantial financial losses to various organizations. Different anti-malware companies have been proposing solutions to defend attacks from these malware. The velocity, volume, and the complexity of malware are posing new challenges to the anti-malware community. Current state-of-the-art research shows that recently, researchers and anti-virus organizations started applying machine learning and deep learning methods for malware analysis and detection. We have used opcode frequency as a feature vector and applied unsupervised learning in addition to supervised learning for malware classification. The focus of this tutorial is to present our work on detecting malware with 1) various machine learning algorithms and 2) deep learning models. Our results show that the Random Forest outperforms Deep Neural Network with opcode frequency as a feature. Also in feature reduction, Deep Auto-Encoders are overkill for the dataset, and elementary function like Variance Threshold perform better than others. In addition to the proposed methodologies, we will also discuss the additional issues and the unique challenges in the domain, open research problems, limitations, and future directions.
* 11 Pages and 3 Figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge