Thiago D. Simão
Sample-Efficient Policy Space Response Oracles with Joint Experience Best Response
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) offers a scalable alternative to exact game-theoretic analysis but suffers from non-stationarity and the need to maintain diverse populations of strategies that capture non-transitive interactions. Policy Space Response Oracles (PSRO) address these issues by iteratively expanding a restricted game with approximate best responses (BRs), yet per-agent BR training makes it prohibitively expensive in many-agent or simulator-expensive settings. We introduce Joint Experience Best Response (JBR), a drop-in modification to PSRO that collects trajectories once under the current meta-strategy profile and reuses this joint dataset to compute BRs for all agents simultaneously. This amortizes environment interaction and improves the sample efficiency of best-response computation. Because JBR converts BR computation into an offline RL problem, we propose three remedies for distribution-shift bias: (i) Conservative JBR with safe policy improvement, (ii) Exploration-Augmented JBR that perturbs data collection and admits theoretical guarantees, and (iii) Hybrid BR that interleaves JBR with periodic independent BR updates. Across benchmark multi-agent environments, Exploration-Augmented JBR achieves the best accuracy-efficiency trade-off, while Hybrid BR attains near-PSRO performance at a fraction of the sample cost. Overall, JBR makes PSRO substantially more practical for large-scale strategic learning while preserving equilibrium robustness.
Perception-Based Beliefs for POMDPs with Visual Observations
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs) are a principled planning model for sequential decision-making under uncertainty. Yet, real-world problems with high-dimensional observations, such as camera images, remain intractable for traditional belief- and filtering-based solvers. To tackle this problem, we introduce the Perception-based Beliefs for POMDPs framework (PBP), which complements such solvers with a perception model. This model takes the form of an image classifier which maps visual observations to probability distributions over states. PBP incorporates these distributions directly into belief updates, so the underlying solver does not need to reason explicitly over high-dimensional observation spaces. We show that the belief update of PBP coincides with the standard belief update if the image classifier is exact. Moreover, to handle classifier imprecision, we incorporate uncertainty quantification and introduce two methods to adjust the belief update accordingly. We implement PBP using two traditional POMDP solvers and empirically show that (1) it outperforms existing end-to-end deep RL methods and (2) uncertainty quantification improves robustness of PBP against visual corruption.
Tighter Value-Function Approximations for POMDPs
Feb 10, 2025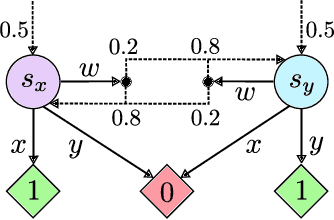
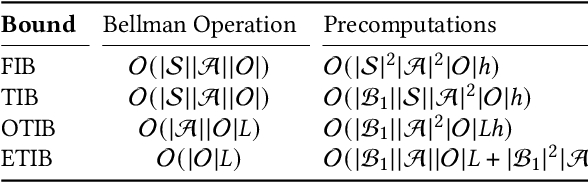
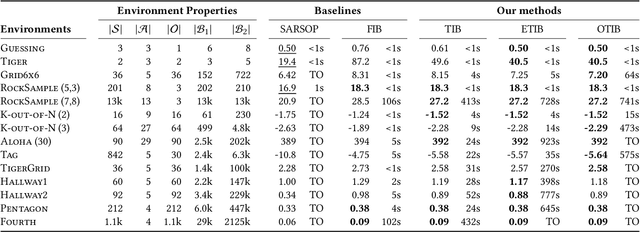
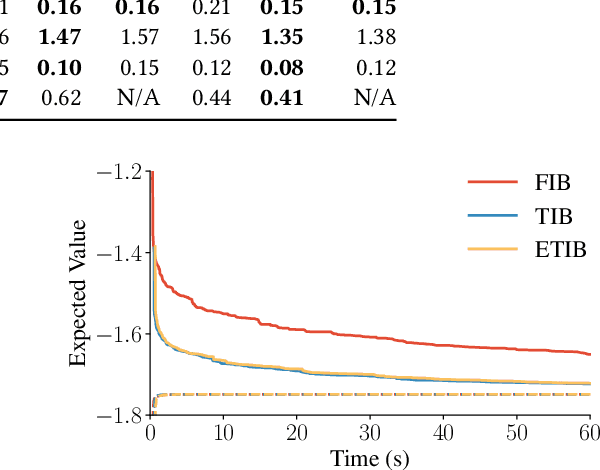
Abstract:Solving partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs) typically requires reasoning about the values of exponentially many state beliefs. Towards practical performance, state-of-the-art solvers use value bounds to guide this reasoning. However, sound upper value bounds are often computationally expensive to compute, and there is a tradeoff between the tightness of such bounds and their computational cost. This paper introduces new and provably tighter upper value bounds than the commonly used fast informed bound. Our empirical evaluation shows that, despite their additional computational overhead, the new upper bounds accelerate state-of-the-art POMDP solvers on a wide range of benchmarks.
Pessimistic Iterative Planning for Robust POMDPs
Aug 16, 2024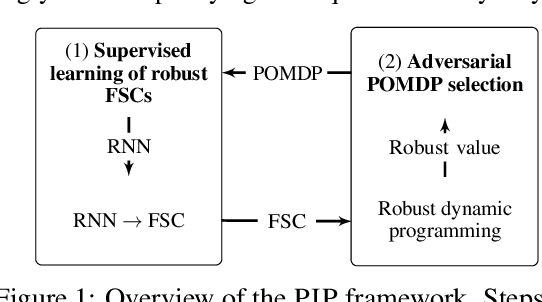
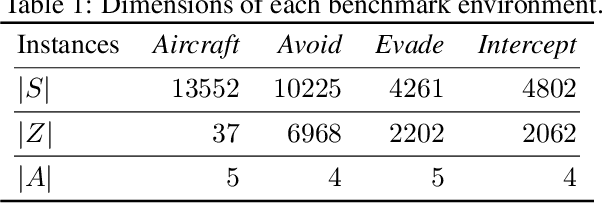
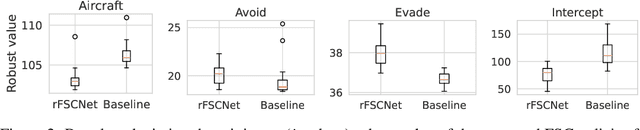
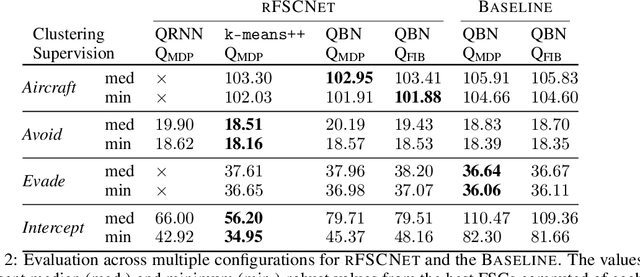
Abstract:Robust partially observable Markov decision processes (robust POMDPs) extend classical POMDPs to handle additional uncertainty on the transition and observation probabilities via so-called uncertainty sets. Policies for robust POMDPs must not only be memory-based to account for partial observability but also robust against model uncertainty to account for the worst-case instances from the uncertainty sets. We propose the pessimistic iterative planning (PIP) framework, which finds robust memory-based policies for robust POMDPs. PIP alternates between two main steps: (1) selecting an adversarial (non-robust) POMDP via worst-case probability instances from the uncertainty sets; and (2) computing a finite-state controller (FSC) for this adversarial POMDP. We evaluate the performance of this FSC on the original robust POMDP and use this evaluation in step (1) to select the next adversarial POMDP. Within PIP, we propose the rFSCNet algorithm. In each iteration, rFSCNet finds an FSC through a recurrent neural network trained using supervision policies optimized for the adversarial POMDP. The empirical evaluation in four benchmark environments showcases improved robustness against a baseline method in an ablation study and competitive performance compared to a state-of-the-art robust POMDP solver.
Maintenance Strategies for Sewer Pipes with Multi-State Degradation and Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jul 17, 2024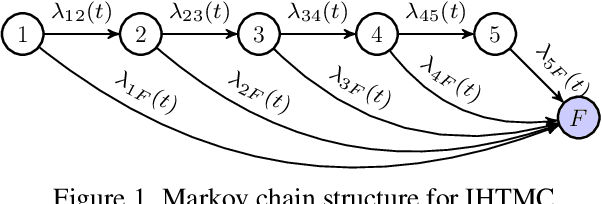

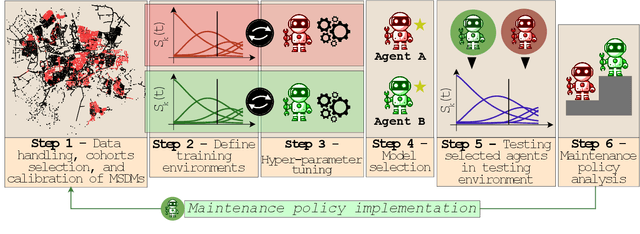

Abstract:Large-scale infrastructure systems are crucial for societal welfare, and their effective management requires strategic forecasting and intervention methods that account for various complexities. Our study addresses two challenges within the Prognostics and Health Management (PHM) framework applied to sewer assets: modeling pipe degradation across severity levels and developing effective maintenance policies. We employ Multi-State Degradation Models (MSDM) to represent the stochastic degradation process in sewer pipes and use Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to devise maintenance strategies. A case study of a Dutch sewer network exemplifies our methodology. Our findings demonstrate the model's effectiveness in generating intelligent, cost-saving maintenance strategies that surpass heuristics. It adapts its management strategy based on the pipe's age, opting for a passive approach for newer pipes and transitioning to active strategies for older ones to prevent failures and reduce costs. This research highlights DRL's potential in optimizing maintenance policies. Future research will aim improve the model by incorporating partial observability, exploring various reinforcement learning algorithms, and extending this methodology to comprehensive infrastructure management.
Factored Online Planning in Many-Agent POMDPs
Dec 22, 2023



Abstract:In centralized multi-agent systems, often modeled as multi-agent partially observable Markov decision processes (MPOMDPs), the action and observation spaces grow exponentially with the number of agents, making the value and belief estimation of single-agent online planning ineffective. Prior work partially tackles value estimation by exploiting the inherent structure of multi-agent settings via so-called coordination graphs. Additionally, belief estimation has been improved by incorporating the likelihood of observations into the approximation. However, the challenges of value estimation and belief estimation have only been tackled individually, which prevents existing methods from scaling to many agents. Therefore, we address these challenges simultaneously. First, we introduce weighted particle filtering to a sample-based online planner for MPOMDPs. Second, we present a scalable approximation of the belief. Third, we bring an approach that exploits the typical locality of agent interactions to novel online planning algorithms for MPOMDPs operating on a so-called sparse particle filter tree. Our experimental evaluation against several state-of-the-art baselines shows that our methods (1) are competitive in settings with only a few agents and (2) improve over the baselines in the presence of many agents.
Robust Active Measuring under Model Uncertainty
Dec 18, 2023



Abstract:Partial observability and uncertainty are common problems in sequential decision-making that particularly impede the use of formal models such as Markov decision processes (MDPs). However, in practice, agents may be able to employ costly sensors to measure their environment and resolve partial observability by gathering information. Moreover, imprecise transition functions can capture model uncertainty. We combine these concepts and extend MDPs to robust active-measuring MDPs (RAM-MDPs). We present an active-measure heuristic to solve RAM-MDPs efficiently and show that model uncertainty can, counterintuitively, let agents take fewer measurements. We propose a method to counteract this behavior while only incurring a bounded additional cost. We empirically compare our methods to several baselines and show their superior scalability and performance.
Reinforcement Learning by Guided Safe Exploration
Jul 26, 2023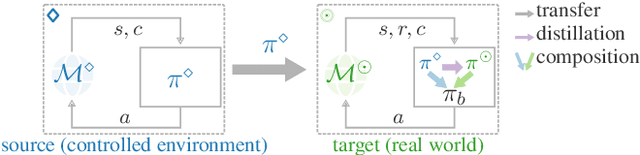
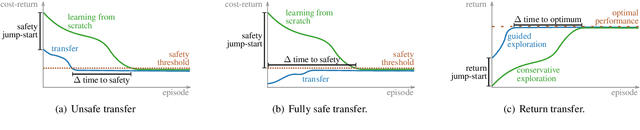
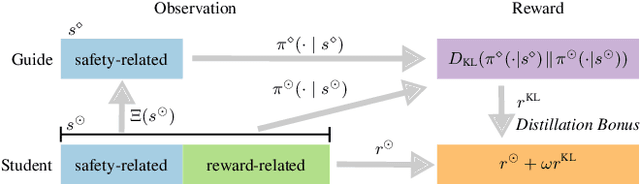
Abstract:Safety is critical to broadening the application of reinforcement learning (RL). Often, we train RL agents in a controlled environment, such as a laboratory, before deploying them in the real world. However, the real-world target task might be unknown prior to deployment. Reward-free RL trains an agent without the reward to adapt quickly once the reward is revealed. We consider the constrained reward-free setting, where an agent (the guide) learns to explore safely without the reward signal. This agent is trained in a controlled environment, which allows unsafe interactions and still provides the safety signal. After the target task is revealed, safety violations are not allowed anymore. Thus, the guide is leveraged to compose a safe behaviour policy. Drawing from transfer learning, we also regularize a target policy (the student) towards the guide while the student is unreliable and gradually eliminate the influence of the guide as training progresses. The empirical analysis shows that this method can achieve safe transfer learning and helps the student solve the target task faster.
More for Less: Safe Policy Improvement With Stronger Performance Guarantees
May 13, 2023



Abstract:In an offline reinforcement learning setting, the safe policy improvement (SPI) problem aims to improve the performance of a behavior policy according to which sample data has been generated. State-of-the-art approaches to SPI require a high number of samples to provide practical probabilistic guarantees on the improved policy's performance. We present a novel approach to the SPI problem that provides the means to require less data for such guarantees. Specifically, to prove the correctness of these guarantees, we devise implicit transformations on the data set and the underlying environment model that serve as theoretical foundations to derive tighter improvement bounds for SPI. Our empirical evaluation, using the well-established SPI with baseline bootstrapping (SPIBB) algorithm, on standard benchmarks shows that our method indeed significantly reduces the sample complexity of the SPIBB algorithm.
Act-Then-Measure: Reinforcement Learning for Partially Observable Environments with Active Measuring
Mar 14, 2023



Abstract:We study Markov decision processes (MDPs), where agents have direct control over when and how they gather information, as formalized by action-contingent noiselessly observable MDPs (ACNO-MPDs). In these models, actions consist of two components: a control action that affects the environment, and a measurement action that affects what the agent can observe. To solve ACNO-MDPs, we introduce the act-then-measure (ATM) heuristic, which assumes that we can ignore future state uncertainty when choosing control actions. We show how following this heuristic may lead to shorter policy computation times and prove a bound on the performance loss incurred by the heuristic. To decide whether or not to take a measurement action, we introduce the concept of measuring value. We develop a reinforcement learning algorithm based on the ATM heuristic, using a Dyna-Q variant adapted for partially observable domains, and showcase its superior performance compared to prior methods on a number of partially-observable environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge